【python之路43】tornado的用法(一)
一、tonado的代码
1、返回字符串
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
self.write("Hello, world")
def post(self):
self.write("Hello, world") #路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
]) if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
tornado的基本代码
2、render返回html文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html') #直接返回本录下的s1.html
def post(self):
self.write("Hello, world") #路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
]) if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
render直接返回html文件
3、html模板配置
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html') #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self):
self.write("Hello, world") #配置全局文件路径为:template
settings = {
'template_path':'template',
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
html全局路径模板配置
4、html中的静态路径配置
对html中引用的css和js文件的静态路径,需要在settings中配置,否则是无法找到文件的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="static/common.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello world!</h1>
<script src="static/oldboy.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html') #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self):
self.write("Hello, world") settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py
5、静态路径的前缀
实际存放路径见上面4的图片,只要定义了前缀,不管静态文件路径是什么,html中都需要用定义的前缀
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="sss/common.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>hello world!</h1>
<script src="sss/oldboy.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html') #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self):
self.write("Hello, world") settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
'static_url_prefix':'/sss/', #静态路径的前缀,html实际是存放在static中,但html中引用是用sss
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py
6、post方法中self.get_argument接收对应的参数的值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="sss/common.css" />
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="/index">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
<script src="sss/oldboy.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html') #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
re = self.get_argument('user') #获取html传过来的user对应的参数值
print(re)
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html') #返回html settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
'static_url_prefix':'/sss/', #静态路径的前缀,html实际是存放在static中,但html中引用是用sss
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py
7、模板语言
两个知识点:
1)循环,item表示变量,用两个大括号表示
<ul>
{% for item in xx %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
</ul>
2)render可以加第2个参数,xx必须与html中模板语言中的xx一致,INPUT_LIST表示py中的列表
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST)
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST,yy = aa) #yy表示html中的变量yy,aa表示py中的变量
re = self.get_argument('user',None) #表示如果参数user不存在则re==None
下面例子,在页面文本框中增加内容立即显示在页面上:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="sss/common.css" />
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="/index">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form> <ul>
{% for item in xx %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
</ul>
<script src="sss/oldboy.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web INPUT_LIST = []
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST) #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
re = self.get_argument('user',None) #获取html传过来的user对应的参数值
if re:
INPUT_LIST.append(re)
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST) #返回html settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
'static_url_prefix':'/sss/', #静态路径的前缀,html实际是存放在static中,但html中引用是用sss
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py

<ul>
{% for item in xx %}
{% if item == "alex" %}
<li style="color: red;">{{item}}</li>
{% else %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
{% end %}
</ul>
8、模板语言自定义函数
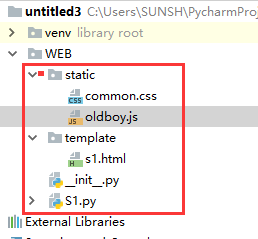
1)目录结构如下:

2)在s1.py同级目录中增加uimethod.py,并在uimethod.py中定义方法:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def func(self,arg):
return ""
uimethod.py
3)在s1.py中导入uimethod.py,import uimethod as mt,并在settings中进行配置
'ui_methods':mt,html中可以使用函数了<h1>{{func(npm)}}</h1>
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import uimethod as mt INPUT_LIST = []
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST, npm="NPM") #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
re = self.get_argument('user',None) #获取html传过来的user对应的参数值
if re:
INPUT_LIST.append(re)
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST) #返回html settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
'static_url_prefix':'/sss/', #静态路径的前缀,html实际是存放在static中,但html中引用是用sss
'ui_methods':mt, #自定义函数路径配置,表示来自mt,mt是从uimethod导入的
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="sss/common.css" />
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="/index">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form> <ul>
{% for item in xx %}
{% if item == "alex" %}
<li style="color: red;">{{item}}</li>
{% else %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
{% end %}
</ul>
<h1>{{func(npm)}}</h1> <script src="sss/oldboy.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
结果如下图:
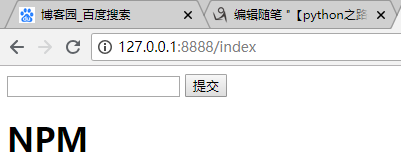
执行顺序:
A、执行s1.py,
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST, npm="NPM") #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
B、执行s1.html中的模板语言,遇到自定义函数,npm = "NPM"
<h1>{{func(npm)}}</h1>
C、根据settings配置和导入模块执行uimethod.py函数,arg = npm = "NPM"
def func(self,arg):
return arg
9、模板语言自定义类
1)目录结构如下
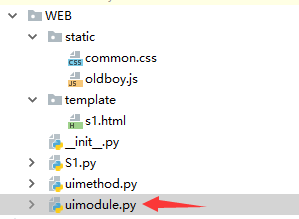
2)在s1.py同级目录中增加uimodule.py,并在uimodule.py中定义方法:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from tornado.web import UIModule
from tornado import escape class custom(UIModule):
def render(self, *args, **kwargs):
#return escape.xhtml_escape('<h1>sunshuhai</h1>')
return 'Hello world!'
uimodule.py
3)在s1.py中导入uimodule.py,import uimodule as md,并在settings中进行配置
'ui_modules':md,html中可以使用函数了<h1>{% module custom() %}</h1>
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import uimethod as mt
import uimodule as md INPUT_LIST = []
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST, npm="NPM") #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
re = self.get_argument('user',None) #获取html传过来的user对应的参数值
if re:
INPUT_LIST.append(re)
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST) #返回html settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
'static_url_prefix':'/sss/', #静态路径的前缀,html实际是存放在static中,但html中引用是用sss
'ui_methods':mt, #自定义函数路径配置,表示来自mt,mt是从uimethod导入的
'ui_modules':md, #自定义类路径配置,表示来自md,md是从uimodule导入的
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="sss/common.css" />
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="/index">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form> <ul>
{% for item in xx %}
{% if item == "alex" %}
<li style="color: red;">{{item}}</li>
{% else %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
{% end %}
</ul>
<h1>{{func(npm)}}</h1>
<h1>{% module custom() %}</h1> <script src="sss/oldboy.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
4)最终显示结果如下:
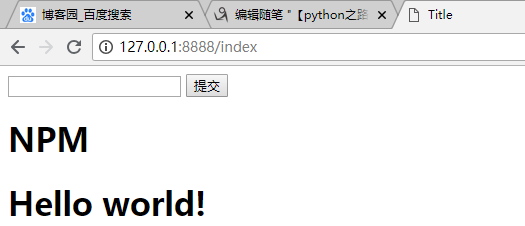
10、模板中默认的字段、函数
在模板中默认提供了一些函数、字段、类以供模板使用:
escape:tornado.escape.xhtml_escape的別名xhtml_escape:tornado.escape.xhtml_escape的別名url_escape:tornado.escape.url_escape的別名json_encode:tornado.escape.json_encode的別名squeeze:tornado.escape.squeeze的別名linkify:tornado.escape.linkify的別名datetime: Python 的datetime模组handler: 当前的RequestHandler对象request:handler.request的別名current_user:handler.current_user的別名locale:handler.locale的別名_:handler.locale.translate的別名static_url: forhandler.static_url的別名xsrf_form_html:handler.xsrf_form_html的別名
Tornado默认提供的这些功能其实本质上就是 UIMethod 和 UIModule
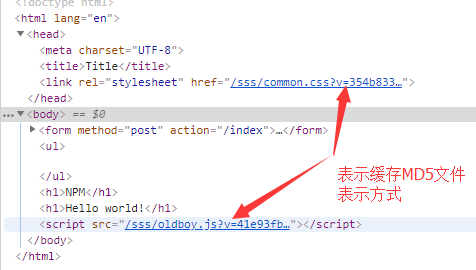
1)static_url配件html静态文件路径,具有缓存功能,静态文件更新后才重新下载
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{static_url('common.css')}}" />
<script src="{{static_url('oldboy.js')}}"></script>
代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import uimethod as mt
import uimodule as md INPUT_LIST = []
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST, npm="NPM") #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
re = self.get_argument('user',None) #获取html传过来的user对应的参数值
if re:
INPUT_LIST.append(re)
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('s1.html',xx = INPUT_LIST) #返回html settings = {
'template_path':'template', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static', #配置html中的静态文件路径为static
'static_url_prefix':'/sss/', #静态路径的前缀,html实际是存放在static中,但html中引用是用sss
'ui_methods':mt, #自定义函数路径配置,表示来自mt,mt是从uimethod导入的
'ui_modules':md, #自定义类路径配置,表示来自md,md是从uimodule导入的
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/",MainHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
s1.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{static_url('common.css')}}" />
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="/index">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form> <ul>
{% for item in xx %}
{% if item == "alex" %}
<li style="color: red;">{{item}}</li>
{% else %}
<li>{{item}}</li>
{% end %}
{% end %}
</ul>
<h1>{{func(npm)}}</h1>
<h1>{% module custom() %}</h1> <script src="{{static_url('oldboy.js')}}"></script>
</body>
</html>
s1.html
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- def func(self,arg):
return arg
uimethod.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from tornado.web import UIModule
from tornado import escape class custom(UIModule):
def render(self, *args, **kwargs):
#return escape.xhtml_escape('<h1>sunshuhai</h1>')
return 'Hello world!'
ui_module.py
#h{
color: red;
}
common.css
console.log('aaa')
oldboy.js
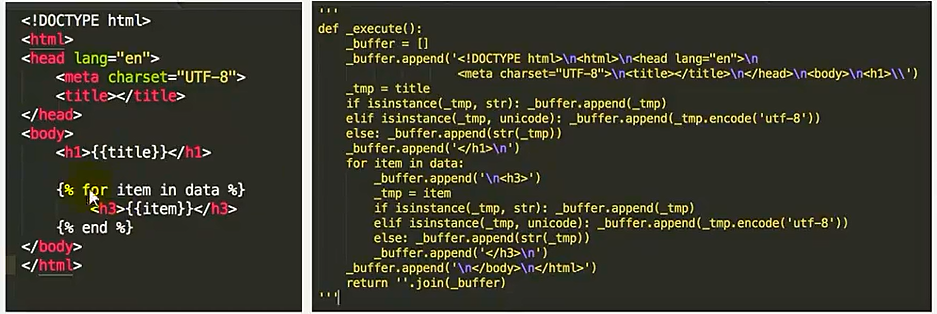
11、模板语言的实质
模板语言的实质是将html字符串分隔之后,再进行的拼接,如下图:
下面代码是执行有变量的字符串函数:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- code ="""
def helocute():
return "name %s,age %d" %(name,data[0],)
""" func = compile(code,'<string>','exec')
nameplace = {'name':'sunshuhai','data':[18,73,84]}
exec(func,nameplace) #将函数func(此时func指向helocute函数)加入到字典nameplace
result = nameplace['helocute']()
print(result) #结果:name sunshuhai,age 18
执行字符串代码
12、跳转页面
self.redirect("/login.html")
13、Cookie的用法
1)、设置Cookie
def set_cookie(self, name, value, domain=None, expires=None, path="/",expires_days=None, **kwargs):
name,value 键值对
domain 域名
expires 到期时间,time.time()+10 表示10秒后过期,time.time()表示立即过期
expires_days 表示多少天后过期
2)得到cookie
co = self.get_cookie("auth")
3)加密的cookie,配置settings,字符串为加盐字符串,可以随便设置
settings = {
'cookie_secret':'qerqrdfd12dds',
}
设置加密cookie:
self.set_secure_cookie("auth","wuzheng")
获取加密cookie:
co = self.get_secure_cookie("auth") #结果返回b'wuzheng',是字节类型
co1 = str(co,encoding='utf-8') #转化为字符串类型,co1="wuzheng"
4)实例:


#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import time class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#self.write("Hello, world")
self.render('index.html') #因为配置了全局文件路径,所以s1.html表示template/s1.html class ManagerHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self,*args,**kwargs):
#co = self.get_cookie("auth")
co = self.get_secure_cookie("auth") #返回b'wuzheng',是字节类型
co1 = str(co,encoding='utf-8') #转化为字符串类型
print(co1)
if co1 == "wuzheng":
self.render('manager.html')
else:
self.redirect("\login") class LogInHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self,*args,**kwargs):
self.render('login.html',status="")
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
username = self.get_argument("username",None)
password = self.get_argument("password",None)
if username == "sunshuhai" and password == "":
#self.set_cookie("auth","1")
#self.set_cookie("auth,","wuzheng",expires_days=7) #expires_days表示7天后cookie过期 #r = time.time() + 10
#self.set_cookie("auth,","wuzheng",expires=r) #表示10秒后过期 #self.set_cookie("auth,","wuzheng",expires=time.time()) #表示立即过期
self.set_secure_cookie("auth","wuzheng")
self.render("index.html")
else:
self.render('login.html',status = "用户名密码错误!") class LogOutHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.set_cookie("auth","") #将cookie中auth的值改掉
self.redirect("/login")
settings = {
'template_path':'views', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'cookie_secret':'qerqrdfd12dds',
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/index", MainHandler),
(r"/manager",ManagerHandler),
(r"/login",LogInHandler),
(r"/logout",LogOutHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
index.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>我的首页</h1>
</body>
</html>
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/login" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="登陆">
<span style="color:red;">{{status}}</span>
</form>
</body>
</html>
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="/logout">退出登陆</a>
<h1>银行卡余额为:-1500元</h1>
</body>
</html>
manager.html
14、Ajax用法
1)概述
Ajax主要就是用【XmlHttpRequest】对象来完成请求的操作,该对象在主流浏览器中均存在(除另类IE),其实是不刷新 页面的前提下偷偷的通过浏览器向服务器发送请求
2)XmlHttpRequest对象的主要方法
a ) void open(String method,String url,Boolen async)
用于创建请求
参数:
method 请求方式(字符串类型),如POST、GET、DELETE
url 要请求的地址(字符串类型)
async 是否异步(布尔类型),默认为true,如果设置为false那么页面会hold住,完成前不能做其他的事情,所以一般设置为默认的true
b)void send(String body)
用于发送请求
c) void setRequestHeader(String header,String value)
用于设置请求头,参数:header:请求头key(字符串类型)
参数:value:请求头的value(字符串类型)
d)、String getAllResponseHeaders()
获取所有响应头
e)void abort()
终止请求
2)XmlHttpRequest对象的主要属性
a)Nmber ReadyState
状态值(整型):
详细:
0-未初始化,尚未调用open() 方法
1-启动,调用了open()方法,未调用send()方法
2-发送,调用了send()方法,未收到相应
3-接收,已经接收到部分响应数据
4-完成,已经接收都全响应部数据
b)Function onreadystatechange
当readyState的值改变时自动触发执行其对应的函数(回调函数)
c)String responseText
服务器返回的数据(字符串类型)
d)XmlDocument responseXML
服务器返回的数据(Xml对象)
e)Number states
状态码(整数),如:200 404 。。。。
f)String statesText
状态文本(字符串),如:OK、NotFound......
3)原生Ajax的实例:

#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class LogInHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self,*args,**kwargs):
self.render('login.html')
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
dic = {"result":True,"message":""}
user = self.get_argument("username")
pwd = self.get_argument("password")
#print(user,pwd)
if user == "sunshuhai" and pwd == "":
pass
else:
dic["result"]=False
dic["message"]="登陆失败"
import json
dicStr = json.dumps(dic)
self.write(dicStr) settings = {
'template_path':'views', #配置全局文件路径为:template
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/login",LogInHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
index.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body> <input id="t1" type="text" name="username">
<input id="t2" type="password" name="password">
<input type="button" value="登陆" onclick="SubmitForm()">
<script>
xhr = null;
function SubmitForm() {
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.onreadystatechange=func;
xhr.open("POST","/login");
xhr.setRequestHeader("content-type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
//xhr.send("username=alex;password=123"); var user = document.getElementById("t1").value //获得用户名
var pwd = document.getElementById('t2').value //获得密码
xhr.send("username=" +user+ ";password=" + pwd)
}
function func() {
console.log(xhr.readyState) //每次readyState的变化该函数都会捕获到
if(xhr.readyState == 4){
console.log(xhr.responseText); //请求完毕后服务器返回的内容
var resContent = xhr.responseText;
var resJson = JSON.parse(resContent); //将获取的内容转化为js,json对象
if(resJson["result"]){
alert("登陆成功!")
}else{
alert("登陆失败!")
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
login.html
4)JQuery下的Ajax实例
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web class LogInHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self,*args,**kwargs):
self.render('login.html')
def post(self,*args,**kwargs):
dic = {"result":True,"message":""}
user = self.get_argument("username")
pwd = self.get_argument("password")
#print(user,pwd)
if user == "sunshuhai" and pwd == "":
pass
else:
dic["result"]=False
dic["message"]="登陆失败"
import json
dicStr = json.dumps(dic)
self.write(dicStr) settings = {
'template_path':'views', #配置全局文件路径为:template
'static_path':'static',
}
#路由映射
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r"/login",LogInHandler),
],**settings) #**settings是让配置生效 if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(8888)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
index.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body> <input id="t1" type="text" name="username">
<input id="t2" type="password" name="password">
<input type="button" value="登陆" onclick="SubmitForm()">
<script src= {{static_url('jquery.js')}}></script>
<script>
function SubmitForm() {
$.post('/login',{"username":$('#t1').val(),"password":$('#t2').val()},function (callback) {
console.log(callback) //callback为服务器响应的结果
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
login.html
【python之路43】tornado的用法(一)的更多相关文章
- 百万年薪python之路 -- socket()模块的用法
socket()模块的用法: import socket socket.socket(socket_family,socket_type,protocal=0) socket_family 可以是 A ...
- 【python之路45】tornado的用法 (三)
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunshuhai/articles/6253815.html 一.cookie用法补充 1.cookie的应用场景 浏览器端保存的键值对,每次访 ...
- 【python之路44】tornado的用法 (二)
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunshuhai/articles/6253815.html 一.代码目录构建 代码目录设置如下图: #!/usr/bin/env python ...
- Python之路【第二十篇】Tornado框架
Tornado Tornado是使用Python编写的一个强大的.可扩展的Web服务器.它在处理严峻的网络流量时表现得足够强健,但却在创建和编写时有着足够的轻量级,并能够被用在大量的应用和工具中. 我 ...
- 【Python之路】第十六篇--Web框架之Tornado
概述 Tornado 是 FriendFeed 使用的可扩展的非阻塞式 web 服务器及其相关工具的开源版本.这个 Web 框架看起来有些像web.py 或者 Google 的 webapp,不过为了 ...
- 【python之路42】web框架们的具体用法
Python的WEB框架 (一).Bottle Bottle是一个快速.简洁.轻量级的基于WSIG的微型Web框架,此框架只由一个 .py 文件,除了Python的标准库外,其不依赖任何其他模块. p ...
- python之路 目录
目录 python python_基础总结1 python由来 字符编码 注释 pyc文件 python变量 导入模块 获取用户输入 流程控制if while python 基础2 编码转换 pych ...
- Python之路【第十八篇】:Web框架们
Python之路[第十八篇]:Web框架们 Python的WEB框架 Bottle Bottle是一个快速.简洁.轻量级的基于WSIG的微型Web框架,此框架只由一个 .py 文件,除了Pytho ...
- Python之路【第十五篇】:Web框架
Python之路[第十五篇]:Web框架 Web框架本质 众所周知,对于所有的Web应用,本质上其实就是一个socket服务端,用户的浏览器其实就是一个socket客户端. 1 2 3 4 5 6 ...
随机推荐
- ES6和常用特性归纳
ECMAScript 6(以下简称ES6)是JavaScript语言的下一代标准,已经在2015年6月正式发布了.Mozilla公司将在这个标准的基础上,推出JavaScript 2.0. ECMAS ...
- SDOI2018Round1 && 九省联考 爆炸记
Day 0 做了一上午火车,大概中午十二点左右到了烟台核电培训中心宾馆,宾馆蛮不错的,跟我在北京参加英才论坛时住的宾馆舒适程度上差不多. 下午花式颓颓颓,吃了晚饭(体验一般)去试机,听说用Lemon评 ...
- 新一代云WAF:防御能力智能化,用户享有规则“自主权”
近日,在国际权威分析机构Frost & Sullivan发布的<2017年亚太区Web应用防火墙市场报告>中,阿里云以市场占有率45.8%的绝对优势连续两年领跑大中华区云WAF市场 ...
- 2-sat——hdu3062
对于怎么建边还是不太清楚 选了a,那么b c不选,所以连边 选了b或c,那么a必定不选 /* 每个点拆成i*2,i*2+1 队长选,那么队友不选 队长不选,那么队友必定要选 */ #include&l ...
- PDO连续query()失败问题
设置了非缓冲查询(PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_USE_BUFFERED_QUERY)以后,连续query会导致下一次结果为false $conn = "mysql:host=127.0. ...
- System.Web.Mvc.FileContentResult.cs
ylbtech-System.Web.Mvc.FileContentResult.cs 1.程序集 System.Web.Mvc, Version=5.2.3.0, Culture=neutral, ...
- C# 检测真实的文件类型函数
private bool IsAllowedExtension(HttpPostedFile hifile) { bool ret = false; System.IO.FileStream fs = ...
- mysql emoji存储问题
偶然存储一条用户记录的时候,发现mysql一直报错 mysql_real_query failed:Incorrect stringvalue: '\xF0\x9F\x98\x8E T...' for ...
- js 使用script或template标签:分离js代码template中的HTML元素
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/332252abe016 方法一. script: <div id="app"> <com-first& ...
- pandas一些基本操作(DataFram和Series)_4
import numpy as np;import pandas as pd;kill_num=pd.Series([10,12,8,5,0,2,6])#击杀数量#青铜1200-2000#白银2001 ...
