CodeForces 1099F - Cookies - [DFS+博弈+线段树]
题目链接:https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1099/F
Mitya and Vasya are playing an interesting game. They have a rooted tree with $n$ vertices, and the vertices are indexed from $1$ to $n$. The root has index $1$. Every other vertex $i≥2$ has its parent $p_i$, and vertex $i$ is called a child of vertex $p_i$.
There are some cookies in every vertex of the tree: there are $x_i$ cookies in vertex $i$. It takes exactly $t_i$ time for Mitya to eat one cookie in vertex $i$. There is also a chip, which is initially located in the root of the tree, and it takes $l_i$ time to move the chip along the edge connecting vertex $i$ with its parent.
Mitya and Vasya take turns playing, Mitya goes first.
Mitya moves the chip from the vertex, where the chip is located, to one of its children.
Vasya can remove an edge from the vertex, where the chip is located, to one of its children. Vasya can also decide to skip his turn.
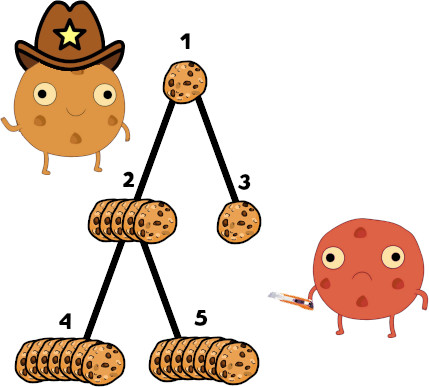
Mitya can stop the game at any his turn. Once he stops the game, he moves the chip up to the root, eating some cookies along his way. Mitya can decide how many cookies he would like to eat in every vertex on his way. The total time spent on descend, ascend and eating cookies should not exceed $T$. Please note that in the end of the game the chip is always located in the root of the tree: Mitya can not leave the chip in any other vertex, even if he has already eaten enough cookies — he must move the chip back to the root (and every move from vertex $v$ to its parent takes $l_v$ time).
Find out what is the maximum number of cookies Mitya can eat, regardless of Vasya's actions.
Input
The first line contains two integers $n$ and $T$ — the number of vertices in the tree and the time he has to accomplish his task $(2≤n≤10^5; 1≤T≤10^{18})$.
The second line contains $n$ integers $x_1, x_2, ..., x_n$ — number of cookies located in the corresponding vertex $(1≤x_i≤10^6)$. The third line contains $n$ integers $t_1, t_2, ..., t_n$ — how much time it takes Mitya to eat one cookie in vertex $i$ $(1≤t_i≤10^6)$.
Each of the following $n-1$ lines describe the tree. For every $i$ from $2$ to $n$, the corresponding line contains two integers $p_i$ and $l_i$, where $p_i$ denotes the parent of vertex $i$ and $l_i$ denotes the time it takes Mitya to move the chip along the edge from vertex $i$ to its parent $(1≤p_i<i, 0≤l_i≤10^9)$.
Output
Output a single integer — maximum number of cookies Mitya can eat.
Examples
Input
5 26
1 5 1 7 7
1 3 2 2 2
1 1
1 1
2 0
2 0
Output
11
Input
3 179
2 2 1
6 6 6
1 3
2 3
Output
4
Note
In the first example test case, Mitya can start by moving the chip to vertex 2. In this case no matter how Vasya plays, Mitya is able to eat at least 11 cookies. Below you can find the detailed description of the moves:
Mitya moves chip to vertex $2$.
Vasya removes edge to vertex $4$.
Mitya moves chip to vertex $5$.
Since vertex $5$ has no children, Vasya does not remove any edges.
Mitya stops the game and moves the chip towards the root, eating cookies along the way ($7$ in vertex $5$, $3$ in vertex $2$, $1$ in vertex $1$).
Mitya spend $1+0$ time to go down, $0+1$ to go up, $7⋅2$ to eat $7$ cookies in vertex $5$, $3⋅3$ to eat $3$ cookies in vertex $2$, $1⋅1$ to eat $1$ cookie in vertex $1$. Total time is $1+0+0+1+7⋅2+3⋅3+1⋅1=26$.
题意:
给你一棵树,每个节点上有若干饼干,并且给出每个节点上吃一块饼干需要多少时间,同时给出走过一条边所需时间。
总时限为 $T$,两个人轮流进行操作:
Mitya从当前节点选择一个子节点向下走,或者直接结束游戏并往根回动吃饼干;
Vasya割断当前节点到其某个子节点的边,或者什么都不做。
问Mitya可以吃到的最多的多少块饼干。
题解:
假如我确定某个节点作为终点,那么我就可以得到一条链,走路的时间是固定的,那么要尽量多吃饼干,显然是尽量吃耗时短的饼干。
那么我们可以很容易就可以想到搞一个类似于树上DP的思想来做,某个节点 $x$ 的 $dp[x]$ 就代表在整棵 $tree(x)$ 中选取某个节点作为终点,能吃到的最多饼干数目。
这样一来,就有 $dp[x] = \max[ calc(x), \max_{edge(x,y)}(dp[y]) ]$,其中 $calc(x)$ 就是以节点 $x$ 为终点,能吃到的做多饼干数目。
当然,由于是博弈,因此对于 $\max_{edge(x,y)}(dp[y])$,使得 $dp[y]$ 最大的那条边 $edge(x,y)$ 会被Vasya割断,因此要选择次大的 $dp[y]$。
这样一来,问题就变成了怎么求 $calc(x)$。显然,如果用朴素的做法求 $calc(x)$,是会T的,应当进行一定的优化。
考虑建立一棵线段树,以每个节点吃一块饼干所需的时间作为下标,维护饼干数目以及吃完所有饼干所需时间。这样一来可以 $O(logN)$ 得到 $calc(x)$。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=1e5+;
const int maxt=1e6+;
int n;
ll T;
struct Vtx{
int x,t;
}vtx[maxn];
struct Edge{
int v;
ll w;
};
vector<Edge> E[maxn]; #define ls (rt<<1)
#define rs (rt<<1|1)
struct Node{
int l,r;
ll num,sum;
}node[maxt<<];
void pushup(int rt)
{
node[rt].num=node[ls].num+node[rs].num;
node[rt].sum=node[ls].sum+node[rs].sum;
}
void build(int rt,int l,int r)
{
node[rt].l=l, node[rt].r=r;
if(l==r)
{
node[rt].num=node[rt].sum=;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>;
build(ls,l,mid);
build(rs,mid+,r);
pushup(rt);
}
void update(int rt,int pos,ll val)
{
if(node[rt].l==node[rt].r)
{
node[rt].num+=val;
node[rt].sum+=val*pos;
return;
}
int mid=(node[rt].l+node[rt].r)>>;
if(pos<=mid) update(ls,pos,val);
if(pos>mid) update(rs,pos,val);
pushup(rt);
}
ll query(int rt,ll val)
{
if(node[rt].l==node[rt].r) return min(node[rt].num,val/node[rt].l);
if(val<node[ls].sum) return query(ls,val);
else return node[ls].num+query(rs,val-node[ls].sum);
} ll dfs(int u,ll rest)
{
update(,vtx[u].t,vtx[u].x);
ll res=query(,rest);
ll mx1=, mx2=;
for(auto e:E[u])
{
if(*e.w>=rest) continue;
int v=e.v;
ll t=dfs(v,rest-*e.w);
if(t>mx1) mx2=mx1, mx1=t;
else if(t>mx2) mx2=t;
}
update(,vtx[u].t,-vtx[u].x);
if(u==) return max(res,mx1);
else return max(res,mx2);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%I64d",&n,&T);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&vtx[i].x);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&vtx[i].t);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int u; ll w; scanf("%d%I64d",&u,&w);
E[u].push_back((Edge){i,w});
}
build(,,1e6);
cout<<dfs(,T)<<endl;
}
CodeForces 1099F - Cookies - [DFS+博弈+线段树]的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 1192B 全dfs序 + 线段树
题意:给你一颗树,每次会修改一条边的边权,问修改之后的树的直径是多少? 思路:来源于:https://www.cnblogs.com/TinyWong/p/11260601.html 得到树的全序df ...
- Codeforces 916E(思维+dfs序+线段树+LCA)
题面 传送门 题目大意:给定初始根节点为1的树,有3种操作 1.把根节点更换为r 2.将包含u,v的节点的最小子树(即lca(u,v)的子树)所有节点的值+x 3.查询v及其子树的值之和 分析 看到批 ...
- CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树
CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树 题意 就是树上有n个点,然后每个点都有一盏灯,给出初始的状态,1表示亮,0表示不亮,然后有两种操作,第一种是get x,表示你需要输出x的子树和x本身 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 6 E dfs序+线段树
题意:给出一颗有根树的构造和一开始每个点的颜色 有两种操作 1 : 给定点的子树群体涂色 2 : 求给定点的子树中有多少种颜色 比较容易想到dfs序+线段树去做 dfs序是很久以前看的bilibili ...
- Codeforces 343D Water Tree(DFS序 + 线段树)
题目大概说给一棵树,进行以下3个操作:把某结点为根的子树中各个结点值设为1.把某结点以及其各个祖先值设为0.询问某结点的值. 对于第一个操作就是经典的DFS序+线段树了.而对于第二个操作,考虑再维护一 ...
- Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2)A,B,C,D,E(STL,dp,贪心,bfs,dfs序+线段树)
A. Alex and broken contest time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input s ...
- CodeForces 877E Danil and a Part-time Job(dfs序+线段树)
Danil decided to earn some money, so he had found a part-time job. The interview have went well, so ...
- 【BZOJ-3252】攻略 DFS序 + 线段树 + 贪心
3252: 攻略 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 339 Solved: 130[Submit][Status][Discuss] D ...
- BZOJ2434 [Noi2011]阿狸的打字机(AC自动机 + fail树 + DFS序 + 线段树)
题目这么说的: 阿狸喜欢收藏各种稀奇古怪的东西,最近他淘到一台老式的打字机.打字机上只有28个按键,分别印有26个小写英文字母和'B'.'P'两个字母.经阿狸研究发现,这个打字机是这样工作的: 输入小 ...
随机推荐
- C++11 并发指南九(综合运用: C++11 多线程下生产者消费者模型详解)
前面八章介绍了 C++11 并发编程的基础(抱歉哈,第五章-第八章还在草稿中),本文将综合运用 C++11 中的新的基础设施(主要是多线程.锁.条件变量)来阐述一个经典问题——生产者消费者模型,并给出 ...
- tsung -- 压力测试利器
Tsung 是一个压力测试工具,可以测试包括HTTP, WebDAV, PostgreSQL, MySQL, LDAP, and XMPP/Jabber等服务器.针对 HTTP 测试,Tsung 支持 ...
- Winform开发框架之通用附件管理模块 --SNF快速开发平台3.3-Spring.Net.Framework
最近项目太多都没有时间写文章了,实际项目需求一,CS端和windows平板都需要附件上传管理功能.以前做的都是BS的附件管理和上传功能.本来计划在Winform上嵌套一个浏览器直接用bs的附件上传功能 ...
- C#-MVC开发微信应用(5)--自动应答系统-自动回复机器人
前几篇已经介绍菜单和有回复信息操作,下面我们就结合snf微信端管理页面,看一下什么才是自动应答系统. 定制的服务 对于微信服务号来说,最主要的功能是提供更好的服务.用户更方便的操作,以及更快的反馈响应 ...
- Spark 核心篇-SparkEnv
本章内容: 1.功能概述 SparkEnv是Spark的执行环境对象,其中包括与众多Executor执行相关的对象.Spark 对任务的计算都依托于 Executor 的能力,所有的 Executor ...
- 从NSTimer的失效性谈起(二):关于GCD Timer和libdispatch
一.GCD Timer的创建和安放 尽管GCD Timer并不依赖于NSRunLoop,可是有没有可能在某种情况下,GCD Timer也失效了?就好比一開始我们也不知道NSTimer相应着一个runl ...
- sql in not in 案例用 exists not exists 代替
from AppStoke B WHERE B.Opencode=A.Code) in用extist代替 select distinct * from Stoke where Code not in ...
- 深入研究 Runloop 与线程保活
深入研究 Runloop 与线程保活 在讨论 runloop 相关的文章,以及分析 AFNetworking(2.x) 源码的文章中,我们经常会看到关于利用 runloop 进行线程保活的分析,但如果 ...
- Linux免密码登录设置 && 设置快捷键
看到这篇文章,你肯定是有这种需求. 假设要登录的机器为192.168.1.100,当前登录的机器为192.168.1.101. 首先在101的机器上生成密钥(如果已经生成可以跳过): $ ssh-ke ...
- 阿里云 FTP 无法读取目录问题
安全组除了添加制定 FTP端口外 需要加入再添加1024/65535端口 放行策略,ftp被动模式需要随机开一个此范围端口进行传输 添加安全组规则参考文档:https://help.aliyun.co ...
