02-springboot配置
目录
6,@PropertySource、@ImportResource和@Bean注解
1,前言
主要讲的有yaml语法,配置文件,配置文件加载顺序,配置文件配置原理。
2,YAML介绍
A:什么是YAML
YAML(/ˈjæməl/,尾音类似camel骆驼)是一个可读性高,用来表达数据序列化的格式。内容是一个键值对,所以它是与数据为中心,更加适合作为配置文件。文件后缀是以yml结尾,用于springboot的配置文件中,默认的配置文件名为:application.yml。
B:YAML语法
a:基本语法
K:(空格)V:表示一个键值对,在冒号后面必须有一个空格,空格表示的是层级关系,如果多行的时候是对齐的,表示是同级关系:
server:
port: 8080注意:属性和值之间是区分大小写的;双引号不会转义字符(name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi );
单引号会转义字符(name: ‘zhangsan \n lisi’:输出;zhangsan \n lisi );字符串可以不需要引号。
b:值的写法
字面值:
:字面直接来写;
对象。Map:
k: v:在下一行来写对象的属性和值的关系;注意缩进 ,对象还是k: v的方式;
friends:
lastName: zhangsan
age: 20行内写法:
friends: {lastName: zhangsan,age: 18}集合:
pets:
‐ cat
‐ dog
‐ pig行内写法:
pets: [cat,dog,pig] 3,获取yml配置文件内容
A:编写两个实体类Person,Student,用于存放属性。
Person类:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="Person")
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
private Map<String,String> map;
private List<String> list;
private Student student;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [age="+ age + ", name=" + name + ", map=" + map + ", list=" + list + ", student=" + student
+ "]";
}
}Student类:
public class Student {
private int age;
private String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}编写yml配置文件:
server:
port: 8080
Person:
age: 18
name: xiaozhi
map:
k1: we
k2: wo
list:
-haha
-hoho
student:
age: 20
name:xiaofang这是需要将我们通知springboot该类类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定,使用的注解为:@ConfigurationProperties:该注解有个属性prefix ,值为类,配置文件中哪个类下面的所有属性进行映射。
同时还需要将给类加入到springboot组件,需要的注解为:@Component
还需要在pom文件添加一个坐标,该坐标表示的是扫描配置文件,文件校验,可以不给出,如果不给,编写yml配置文件不给出提示和校验。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐configuration‐processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependencyB:在主程序运行结果(可使用单元测试)
控制类:
@Controller
public class AppController {
@Resource
private Person person;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/show")
public String show(){
System.out.print(person);
return "你好!世界";
}
}测试结果为:
可以看到Person类的属性以及被注入了。
4,springboot的配置文件
A:springboot给出两种配置文件
•application.properties
•application.yml
配置文件默认为固定文件名,springboot可以将自动将文件扫描到容器中。之前一起讲了yml配置文件的编写方法和加载方式。项目将会说properties 文件的编写和加载方式;
B:编写properties 文件
Person.age=18
Person.name=xiaozhi
Person.map.k1=we
Person.map.k2=wuw
Person.list=we.weo.werf
Person.student.age=20
Person.student.name=xiaofang只要编写程这样就可以了,加载方式和yml的一样,结果如下图所示:
5,springboot使用@Value实现映射
之前使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="Person")这个注解实现配置文件到类属性的映射,@ConfigurationProperties注解表示的是将该类的全部属性实现映射,只要配置文件有对应的属性,就将配置文件的内容注入到类中。而@Value是单个注入,分别对类的属性进行注入。
A:使用@Value实现注入
只需要通过修改Person类就可以了,如下段代码:
@Component
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="Person")
public class Person {
@Value("${Person.age}")
private int age;
private String name;
private Map<String,String> map;
private List<String> list;
private Student student;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [age="+ age + ", name=" + name + ", map=" + map + ", list=" + list + ", student=" + student
+ "]";
}
}
测试结果:
可以发现,只是在age属性上加上@Value时,注入值只是注入这个属性的值。
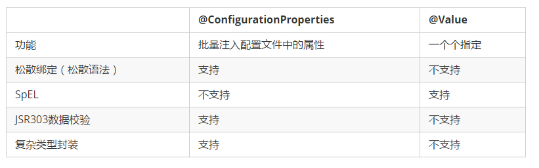
B:@Value和@ConfigurationProperties的比较
6,@PropertySource、@ImportResource和@Bean注解
A:PropertySource:读取指定的文件(只适用于Properties文件)
属性:value:String[]
写一个a.Properties文件
Person.age=20
Person.name=xiao
Person.map.k1=hahah
Person.map.k2=xixi
Person.list=we,weo,werfwowowoowowo
Person.student.age=210
Person.student.name=xiaofan在Person类上添加注解
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:a.properties"})
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="Person")
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
private Map<String,String> map;
private List<String> list;
private Student student;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [age="+ age + ", name=" + name + ", map=" + map + ", list=" + list + ", student=" + student
+ "]";
}
}
运行结果:
值得注意的是使用此注解扫描时,如果配置文件目录有一个application.properties文件,而且该文件中存在该类的配置,它会优先使用默认配置文件而不去加载自定义配置文件。
B:@ImportResource注解:用于加载spring配置文件
在学习spring的时候,spring的配置文件主要配置的是bean对象,springboot页提供了一个扫描器用于加载spring的配置文件。该注解就是扫描spring配置文件所使用的。
编写一个spring的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF‐8"?> <beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema‐instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring‐beans.xsd">
<bean id="helloService" class="com.atguigu.springboot.service.HelloService"></bean>
</beans>在主程序类中加入注解:
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})就可以将该bean对象注入到sprig容器中。
C:@Bean标签
spring不建议我们使用@ImportResource注解,主要是会导致开发的周期过长,编写spring配置文件过于麻烦。为了解决这个问题,springboot提供@Bean注解,将类注入到spring容器中。使用该注解需要指定需要配置的类,@Configuration注解就可以指定配置类。
@Configuration//指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
public class Person {
private int age;
private String name;
private Map<String,String> map;
private List<String> list;
private Student student;
@Bean//在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件
public void show(){}7,Springboot的占位符
springboot在配置文件中可以定义占位符,通过占位符设置默认值,获取该配置文件其他值,拼接一些随机数等。
A:随机数
${random.value}、${random.int}、${random.long}
${random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]}springboot自己定义了一些获取随机数或者uuid的方法,如下所示:
Person.age=$(random.int)
Person.name=xiao$(random.uuid)
Person.map.k1=hahah
Person.map.k2=xixi
Person.list=we,weo,werfwowowoowowo
Person.student.age=210
Person.student.name=xiaofanB:获取配置文件其他值:
Person.age=20
Person.name=xiao
Person.map.k1=hahah
Person.map.k2=xixi
Person.list=we,weo,werfwowowoowowo
Person.student.age=210${Person.age}
Person.student.name=xiaofan表示获取到Person.age的值拼接到Person.student.age的值的后面,如果配置文件中没有属性和值,而配置类中有该属性,通过配置配置文件中的属性,将获取不到该值:
#Person.age=20
Person.name=xiao
Person.map.k1=hahah
Person.map.k2=xixi
Person.list=we,weo,werfwowowoowowo
Person.student.age=210${Person.age}
Person.student.name=xiaofan如上面代码所示,将Person.age注释掉,将会导致出错。
C:设置默认值
Person.age=20
Person.name=xiao
Person.map.k1=hahah
Person.map.k2=xixi
Person.list=we,weo,werfwowowoowowo
Person.student.age=210${Person.hahah}
Person.student.name=xiaofan这种上面代码的情况是如果配置文件中的占位符在配置类没有属性,没有给出默认值,表示的是字符拼接。
Person.age=20
Person.name=xiao
Person.map.k1=hahah
Person.map.k2=xixi
Person.list=we,weo,werfwowowoowowo
Person.student.age=210${Person.hahah:html}
Person.student.name=xiaofan这种情况是给该属性赋值一个默认值,获取的时候是直接获取html这个值而不是直接拼接。
8,profile
springboot为我们提供了在不同环境使用不同配置文件的方式,例如配置端口号,在生产环境下使用8080端口,在测试环境下使用8081端口,开发环境使用8082端口,通过使用profile,可以让我们快速更换端口号
A:多个Profifile文件
文件命名格式:
application-dev.properties
application-dev.ymlB:properties配置文件使用profile功能
编写多个properties文件
server.port=8080application-dev.properties
server.port=8081激活profile:在默认配置文件application.properties中配置:
spring.profiles.active=dev表示的是使用dev环境,也就是端口号为8081的配置。
C:yml配置文件使用profile
这种方式比较简单,只需要编写在一个yml文件就可以了,这种方式在yml被叫做多文档块,通过"---"将一个yml文件分为多个文档块(三个横线),在最上面通过最上面的文档块进行激活:
spring:
profiles:
active: prod全部的配置文件如下所示:
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod #激活prod环境
‐‐‐
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
‐‐‐
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #指定属于哪个环境9,配置文件存放目录优先级(从高到低)
项目/config
项目目录项
classpath:config
classpath目录
10,总结
没有总结的总结
02-springboot配置的更多相关文章
- springboot配置server相关配置&整合模板引擎Freemarker、thymeleaf&thymeleaf基本用法&thymeleaf 获取项目路径 contextPath 与取session中信息
1.Springboot配置server相关配置(包括默认tomcat的相关配置) 下面的配置也都是模板,需要的时候在application.properties配置即可 ############## ...
- SpringBoot配置属性之Server
SpringBoot配置属性系列 SpringBoot配置属性之MVC SpringBoot配置属性之Server SpringBoot配置属性之DataSource SpringBoot配置属性之N ...
- SpringBoot基础系列-SpringBoot配置
原创作品,可以转载,但是请标注出处地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/V1haoge/p/9990680.html SpringBoot基础系列-SpringBoot配置 概述 属性 ...
- springboot上传文件 & 不配置虚拟路径访问服务器图片 & springboot配置日期的格式化方式 & Springboot配置日期转换器
1. Springboot上传文件 springboot的文件上传不用配置拦截器,其上传方法与SpringMVC一样 @RequestMapping("/uploadPicture&q ...
- springboot配置Druid数据源
springboot配置druid数据源 Author:SimpleWu springboot整合篇 前言 对于数据访问层,无论是Sql还是NoSql,SpringBoot默认采用整合SpringDa ...
- springboot配置详解
springboot配置详解 Author:SimpleWu properteis文件属性参考大全 springboot默认加载配置 SpringBoot使用两种全局的配置文件,全局配置文件可以对一些 ...
- SpringBoot 配置 Servlet、Filter、Listener
SpringBoot 配置 Servlet.Filter.Listener 在SpringBoot应用中,嵌入式的 Servlet 3.0+ 容器不会直接使用 ServletContainerInit ...
- SpringBoot 配置静态资源映射
SpringBoot 配置静态资源映射 (嵌入式servlet容器)先决知识 request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("/& ...
- springboot配置cxf
1.引入两个需要的jar <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId> <artifactId>cxf- ...
- SpringBoot配置(2) slf4j&logback
SpringBoot配置(2) slf4j&logback 一.SpringBoot的日志使用 全局常规设置(格式.路径.级别) SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4 ...
随机推荐
- phpstorm对laravel开发的配置
摘自:https://www.cnblogs.com/Richard-Tang/p/10218178.html phpstorm对laravel开发的配置 一.安装Laravel 1.下载comp ...
- 胃食管反流之 SAP分析( in the Ohmega software)
原文:https://note.youdao.com/s/GED6wise SAP analysis in the Ohmega software ohmega software 关于胃食管反流疾病 ...
- FFmpeg中的关键方法及结构体(二)avformat_open_input
1.avformat_open_input 该方法声明在libavformat/avformat.h:2093 int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps ...
- NOIP模拟90(多校23)
T1 回文 解题思路 原来 \(n^3\) 可以过 500 ... 先枚举一下路径长度,对于同一路径长度点数最多是 \(n\) 个,我们可以接着枚举从 \((n,m)\) 出发的路径长度相同的点. 然 ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 357
ABC357总结 AtCoder Beginner Contest 357 A - Sanitize Hands 翻译 有一瓶消毒剂,正好可以消毒 \(M\) 双手. \(N\) 名外星人陆续前来消毒 ...
- vue动态页签
效果图 前端 1 <template> 2 <!-- 总体情况 - 总览echarts --> 3 4 <div v-loading="loading" ...
- Windows 下自动预约申购 i茅台
今天分享一个自动预约抢茅子的工具! 前期准备工作: 1.需安装:.Net6 依赖 (根据操作系统选择 x64 或 x86 版本进行下载.) 安装软件 1.软件下来下来之后,解压并进入软件目录,我们双击 ...
- Vector | Graph:蚂蚁首个开源Graph RAG框架设计解读
检索增强生成(RAG:Retrieval Augmented Generation)技术旨在把信息检索与大模型结合,以缓解大模型推理"幻觉"的问题.近来关于RAG的研究如火如荼,支 ...
- 实现 Emlog 最新评论列表不显示博主的评论回复
Tips:当你看到这个提示的时候,说明当前的文章是由原emlog博客系统搬迁至此的,文章发布时间已过于久远,编排和内容不一定完整,还请谅解` 实现 Emlog 最新评论列表不显示博主的评论回复 日期: ...
- python globals()[]将字符串转化类,并通过反射执行方法
背景: 通过关键字设计ui自动化框架,将测试用例及其步骤存放到excel文件:其中步骤中包含了封装好的关键字方法,如打开浏览器.输入页面操作等,关键字保存的内容:具体类实例.方法 通过excel获取到 ...