SpringBoot - 自定义starter
一、什么是SpringBoot starter机制
SpringBoot中的starter是一种非常重要的机制(自动化配置),能够抛弃以前繁杂的配置,将其统一集成进starter,应用者只需要在maven中引入starter依赖,SpringBoot就能自动扫描到要加载的信息并启动相应的默认配置。
starter让我们摆脱了各种依赖库的处理,需要配置各种信息的困扰。SpringBoot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。SpringBoot提供了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。
所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定成俗的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念。
二、为什么要自定义starter
在我们的日常开发工作中,经常会有一些独立于业务之外的配置模块,我们经常将其放到一个特定的包下,然后如果另一个工程需要复用这块功能的时候,需要将代码硬拷贝到另一个工程,重新集成一遍,麻烦至极。
如果我们将这些可独立于业务代码之外的功配置模块封装成一个个starter,复用的时候只需要将其在pom中引用依赖即可,SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配,简直不要太爽
三、什么时候需要创建自定义starter
在我们的日常开发工作中,可能会需要开发一个通用模块,以供其它工程复用。SpringBoot就为我们提供这样的功能机制,我们可以把我们的通用模块封装成一个个starter,这样其它工程复用的时候只需要在pom中引用依赖即可,由SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配。
常见场景:
1.通用模块-短信发送模块
2.基于AOP技术实现日志切面
3.分布式雪花ID,Long--string,解决精度问题jackson2/fastjson
4.微服务项目的数据库连接池配置
5.微服务项目的每个模块都要访问redis数据库,每个模块都要配置redisTemplate,也可以通过starter解决
四、自动加载核心注解说明
starter 组件开发,核心是自动注解类的注解顺序,即根据条件进行注解
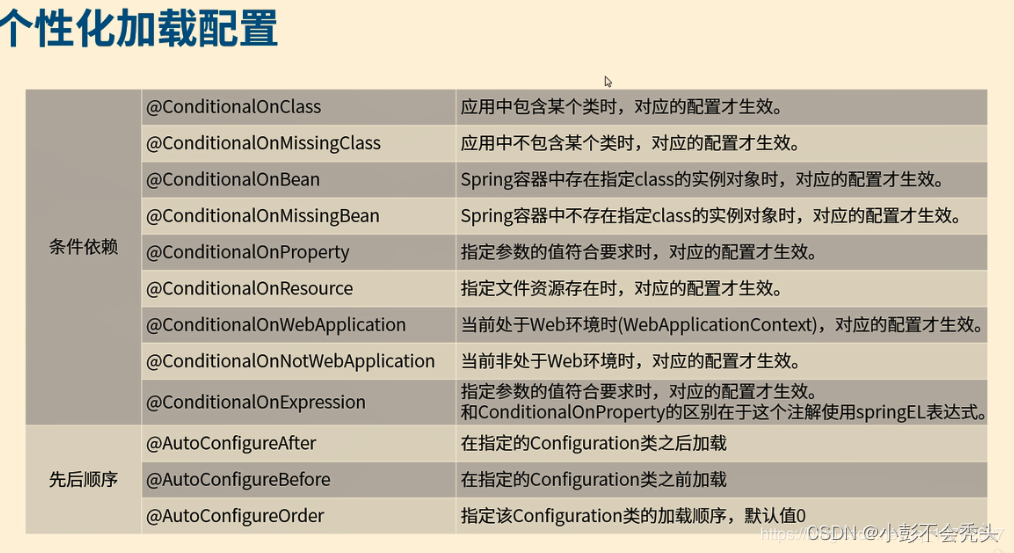
关于自动加载核心注解,详情可见:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_19782697/article/details/100727302
五、自定义starter的开发流程
那么前面对自定义 starter 机制简单介绍了一下,接下来就进入正题!
自定义starter的开发流程:
1.创建Starter项目(spring-initl 2.1.14)
2.定义Starter需要的配置类(Properties)
3.编写Starter项目的业务功能
4.编写自动配置类
5.编写spring.factories文件加载自动配置类
6.打包安装
7.其它项目引用
案例一:为短信发送功能创建一个starter
1.创建Starter项目
starter项目和SpringBoot工程结构没有什么区别,下面就把一些特殊的要求罗列一下
1.1.命名规范
SpringBoot官方命名方式
格式:spring-boot-starter-{模块名}
举例:spring-boot-starter-web
自定义命名方式
格式:{模块名}-spring-boot-starter
举例:mystarter-spring-boot-starter
1.2.必须引入的依赖
<!--表示两个项目之间依赖不传递;不设置optional或者optional是false,表示传递依赖-->
<!--例如:project1依赖a.jar(optional=true),project2依赖project1,则project2不依赖a.jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency
如果我们刚刚创建项目时选择了Spring Configuration Processor,在pom.xml文件中就会有上面的依赖
2.编写相关属性类
(XxxProperties):SmsProperties.java
--@ConfigurationProperties注解基本用法
前缀定义了哪些外部属性将绑定到类的字段上
根据 Spring Boot 宽松的绑定规则,类的属性名称必须与外部属性的名称匹配
我们可以简单地用一个值初始化一个字段来定义一个默认值
类本身可以是包私有的
类的字段必须有公共 setter 方法
注意:SmsProperties代码写完后会报如下错误,这是正常的,因为
还有配置类AutoConfig和一个注解@EnableConfigurationProperties没有加
(Not registered via @EnableConfigurationProperties or marked as Spring component)
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import java.io.Serializable;
@ConfigurationProperties("zzcloud.sms")
public class SmsProperties implements Serializable {
private String accessKeyId;
//访问ID、即帐号
private String accessKeySecret;
//访问凭证,即密码
public String getAccessKeyId() {
return accessKeyId;
}
public void setAccessKeyId(String accessKeyId) {
this.accessKeyId = accessKeyId;
}
public String getAccessKeySecret() {
return accessKeySecret;
}
public void setAccessKeySecret(String accessKeySecret) {
this.accessKeySecret = accessKeySecret;
}
}
3.编写Starter项目的业务功能
ISmsService和SmsServiceImpl相关代码如下:
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms;
public interface ISmsService {
/**
* 发送短信
*
* @param phone 要发送的手机号
* @param signName 短信签名-在短信控制台中找
* @param templateCode 短信模板-在短信控制台中找
* @param data 要发送的内容
*/
void send(String phone, String signName, String templateCode, String data);
}
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.ISmsService;
public class SmsServiceImpl implements ISmsService {
private String accessKeyId;
//访问ID、即帐号
private String accessKeySecret;
//访问凭证,即密码
public SmsServiceImpl(String accessKeyId, String accessKeySecret) {
this.accessKeyId = accessKeyId;
this.accessKeySecret = accessKeySecret;
}
@Override
public void send(String phone, String signName, String templateCode, String data) {
System.out.println("接入短信系统,accessKeyId=" + accessKeyId + ",accessKeySecret=" + accessKeySecret);
System.out.println("短信发送,phone=" + phone + ",signName=" + signName + ",templateCode=" + templateCode + ",data=" + data);
}
}
4.编写自动配置类AutoConfig
4.1. @Configuration:
定义一个配置类
4.2. @EnableConfigurationProperties:
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解的作用是@ConfigurationProperties注解生效。
如果只配置@ConfigurationProperties注解,在IOC容器中是获取不到properties配置文 件转化的bean的
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.config;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.SmsProperties;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.SmsServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Configuration //表示这个类为配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties({
SmsProperties.class
}
)
public class SmsAutoConfig {
@Resource
private SmsProperties smsProperties;
@Bean
public SmsServiceImpl smsServiceImpl(){
return new SmsServiceImpl(smsProperties.getAccessKeyId(),smsProperties.getAccessKeySecret());
}
}
5.编写spring.factories文件加载自动配置类
5.1.在resources下新建META-INF文件夹,然后创建spring.factories文件
5.2.在该文件中加入如下配置,该配置指定上步骤中定义的配置类为自动装配的配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.config.SmsAutoConfig
注1:其中AutoConfig是starter配置文件的类限定名,多个之间逗号分割,还可以\进行转义即相当于去掉后面换行和空格符号,如下所示
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.autoconfigure.MybatisPlusLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration,\
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.autoconfigure.MybatisPlusAutoConfiguration
6.打包安装
打包时需要注意一下,SpringBoot项目打包的JAR是可执行JAR,它的类放在BOOT-INF目录下,如果直接作为其他项目的依赖,会找不到类。可以通过修改pom文件来解决,代码如下:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<classifier>exec</classifier>
</configuration>
</plugin>
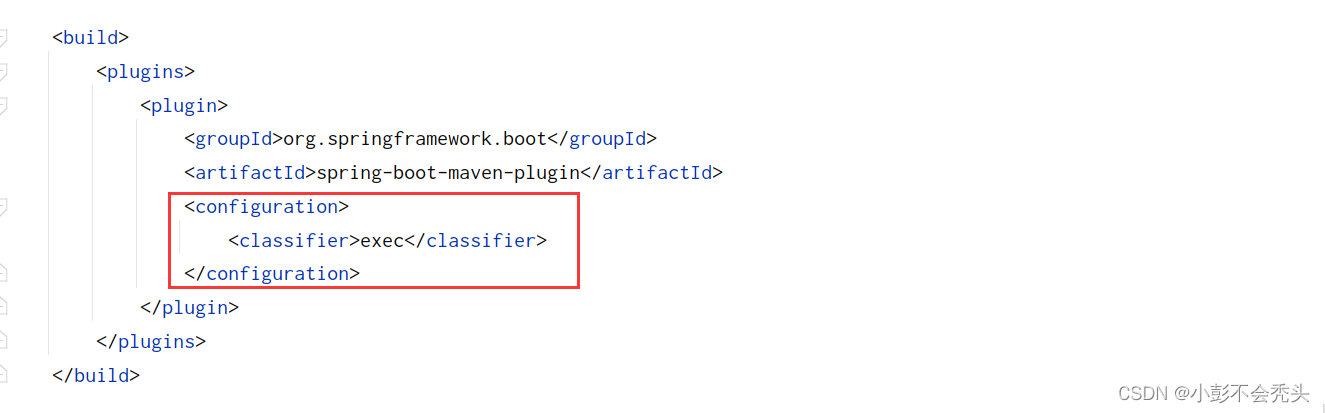
打包前,先查看我们maven仓库的位置,并设置到自己本地仓库位置中去,再打包。过程如下:
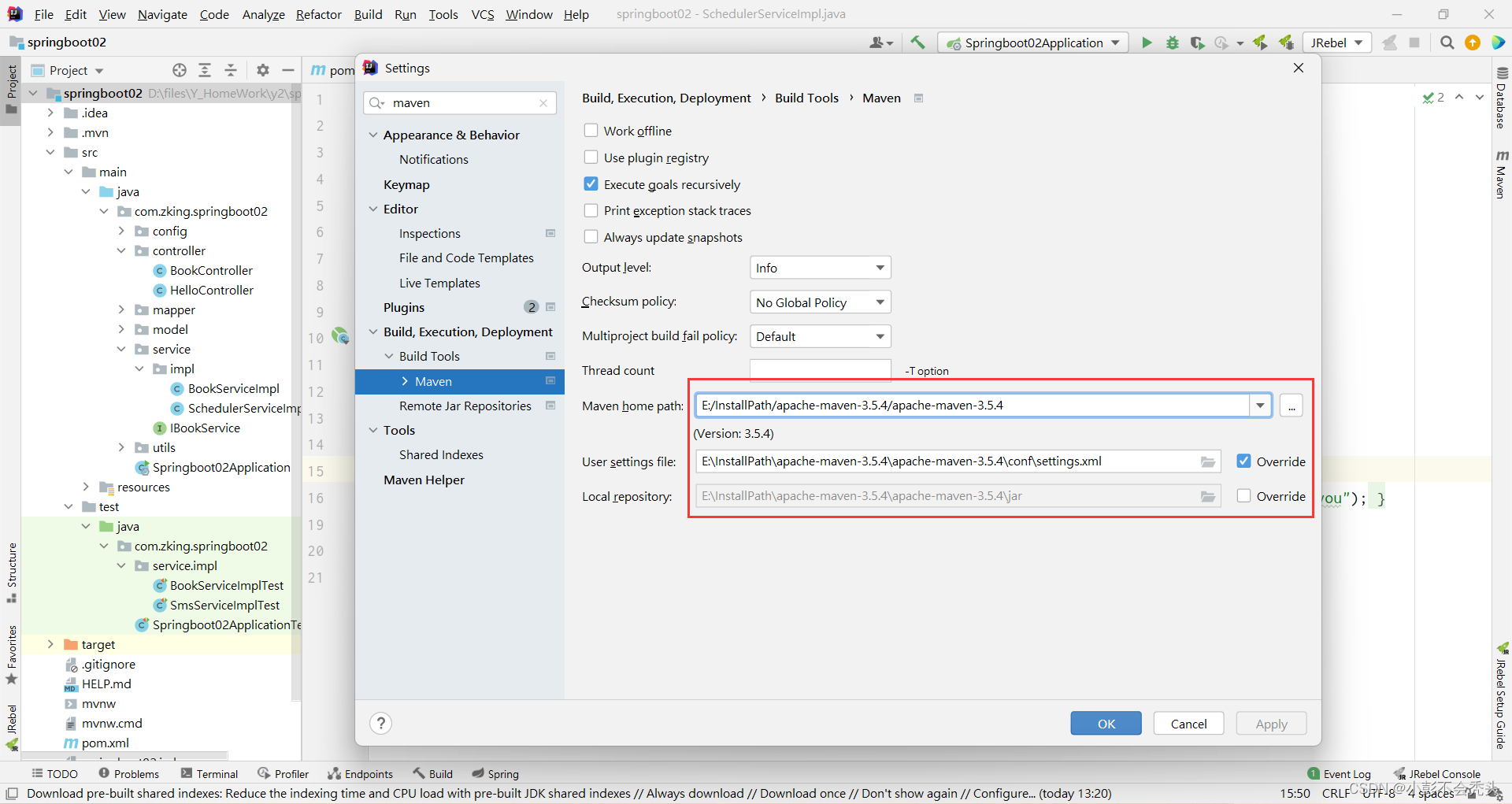
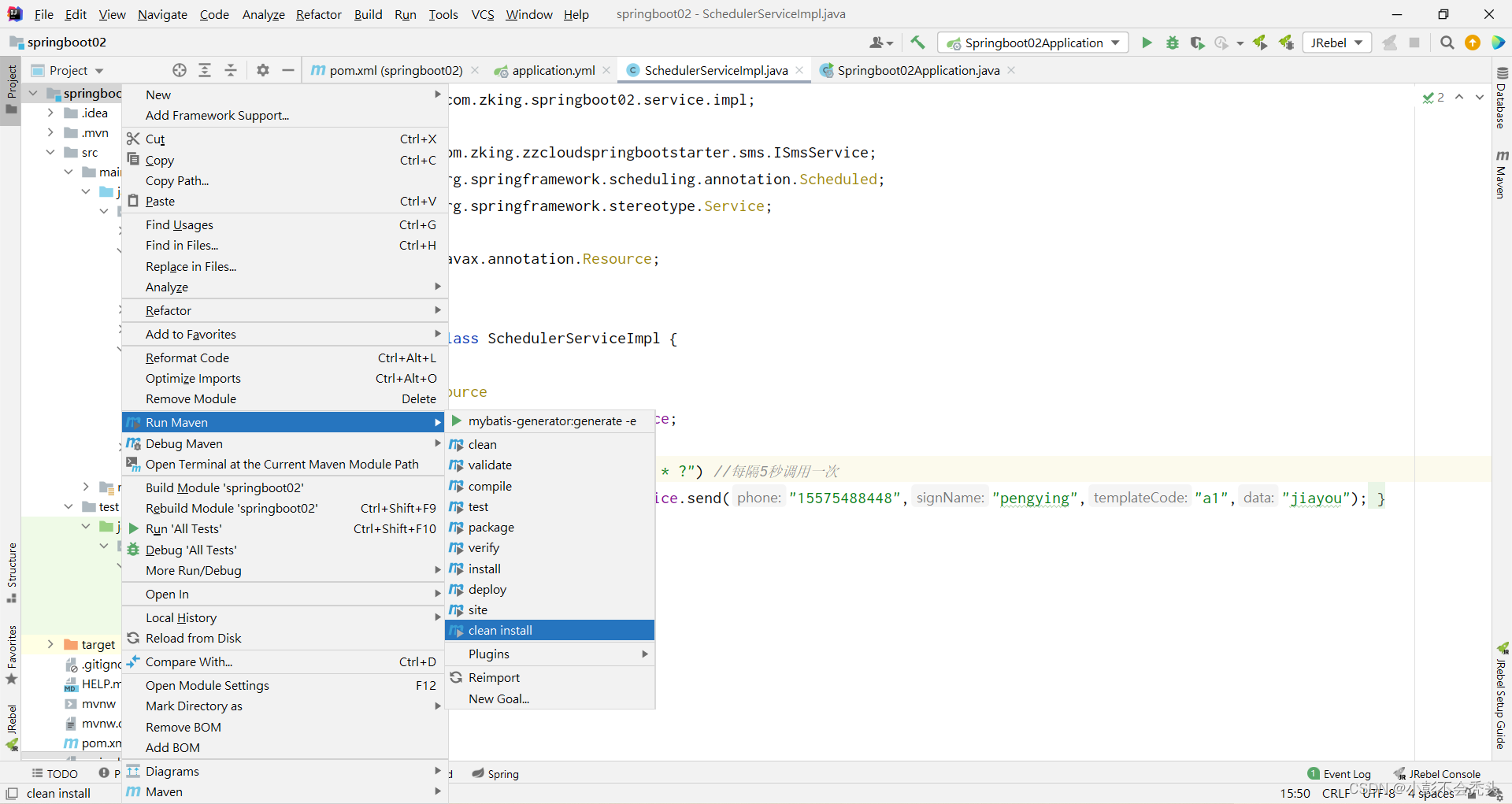
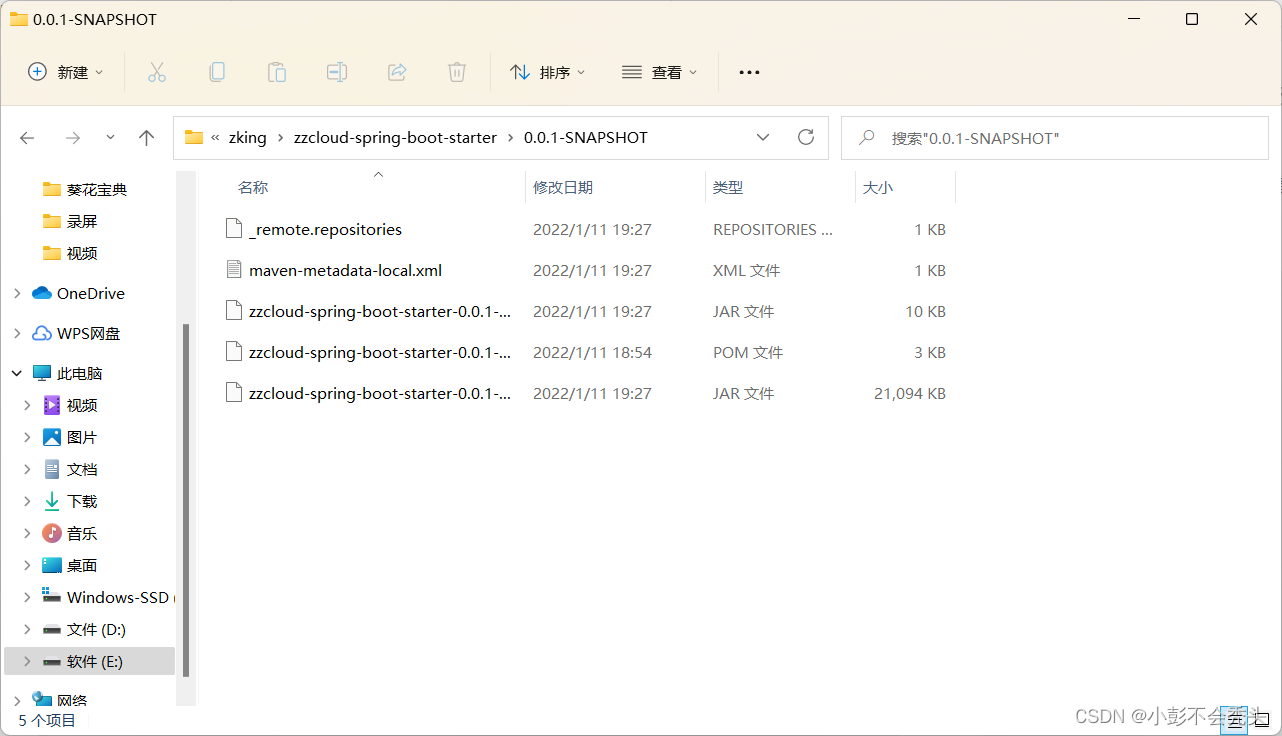
成功后,我们可以发现我们本地仓库就会有刚刚我们打包完的项目:
到这里为止,我们的整个自定义starter的准备工作就做完了,如下是我的整个自定义starter文件的结构: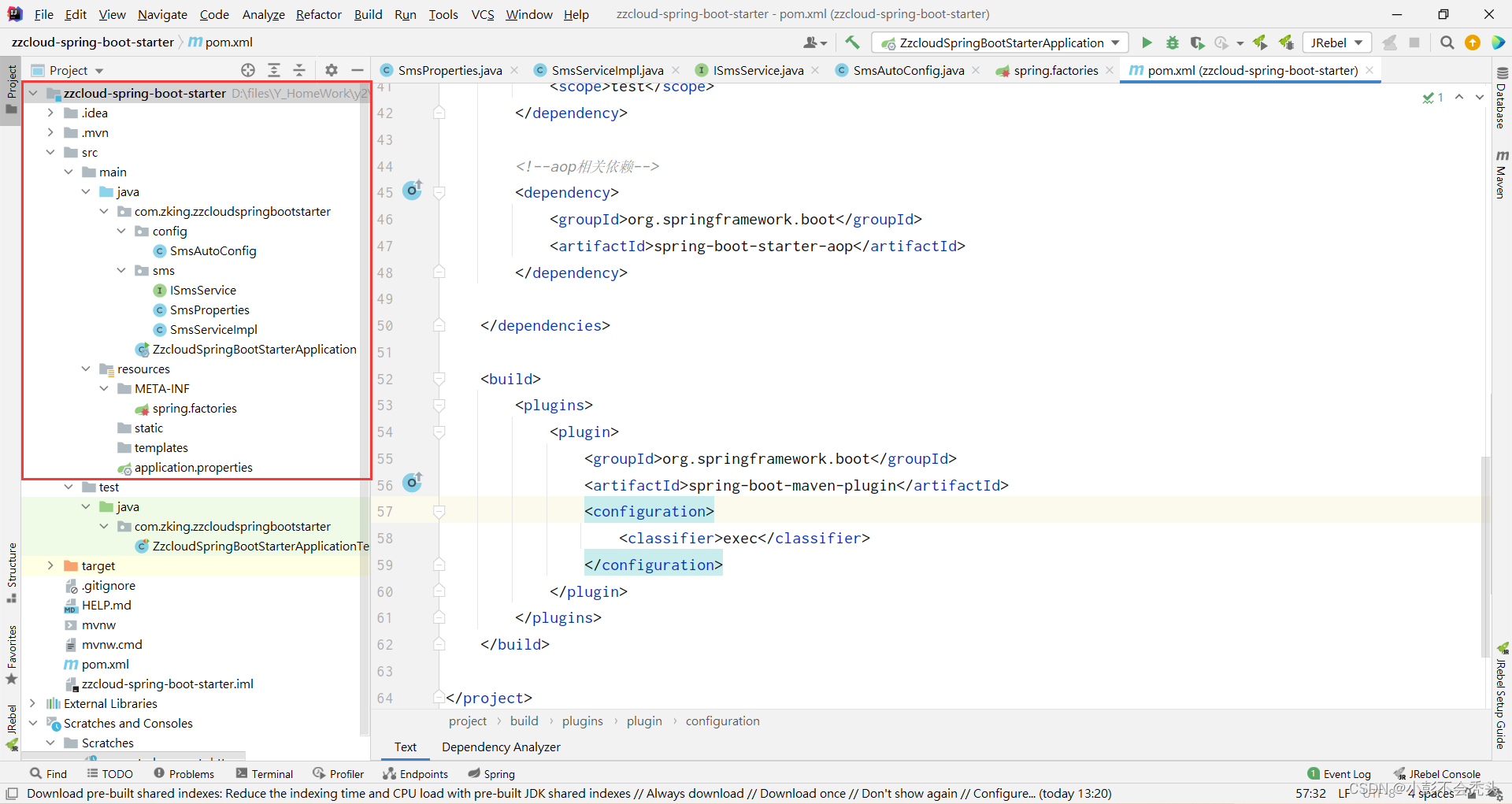
7.在其他项目中的应用
7.1.首先在其他项目的pom.xml中引入相关依赖:

7.2.在application.yml文件中添加配置

为了展示效果,我们写一个测试类,看能否看到我们想要的效果,测试代码如下:
package com.zking.springboot02.service.impl;
import com.zking.springboot02.Springboot02Application;
import com.zking.springboot02.model.Book;
import com.zking.springboot02.service.IBookService;
import com.zking.springboot02.utils.PageBean;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.ISmsService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest(classes = Springboot02Application.class)
class SmsServiceImplTest {
@Resource
private ISmsService smsService;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
}
@Test
void testRedis() {
smsService.send("15575488448","pengying","1","小彭不会秃头加油干!");
}
}
控制台效果如下:
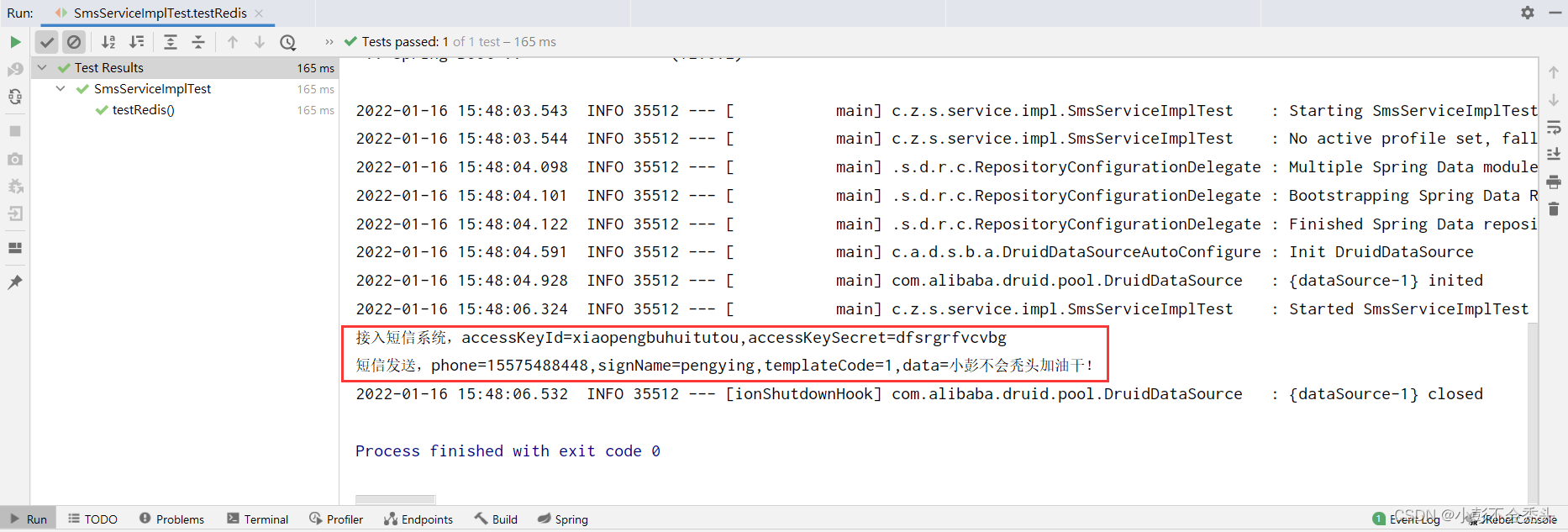
如果控制台有如上效果,说明我们整个自定义starter的过程就成功了!
案例二:AOP方式统一服务日志
原先实现统一日志都是放到每个工程中以AOP方式实现,现在有了starter方式,就可以将公司的日志规范集中到这里来统一管理。
这里我们使用之前创建好的项目进行案例二的编写,步骤与上同理:
1.导入aop相关依赖
<!--aop相关依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.编写相关属性类
(XxxProperties):WebLogProperties.java
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import java.io.Serializable;
@ConfigurationProperties("zzcloud.weblog")
public class WebLogProperties implements Serializable {
public Boolean enabled;
//Boolean封装类,默认为null
public Boolean getEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(Boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
}
3.编写Starter项目的业务功能
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.weblog;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class WebLogAspect {
//@Pointcut("execution(public * com.zking..controller.*.*(..))")
@Pointcut("execution(* *..*Controller.*(..))")
public void webLog(){}
@Before("webLog()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 接收到请求,记录请求内容
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 记录下请求内容
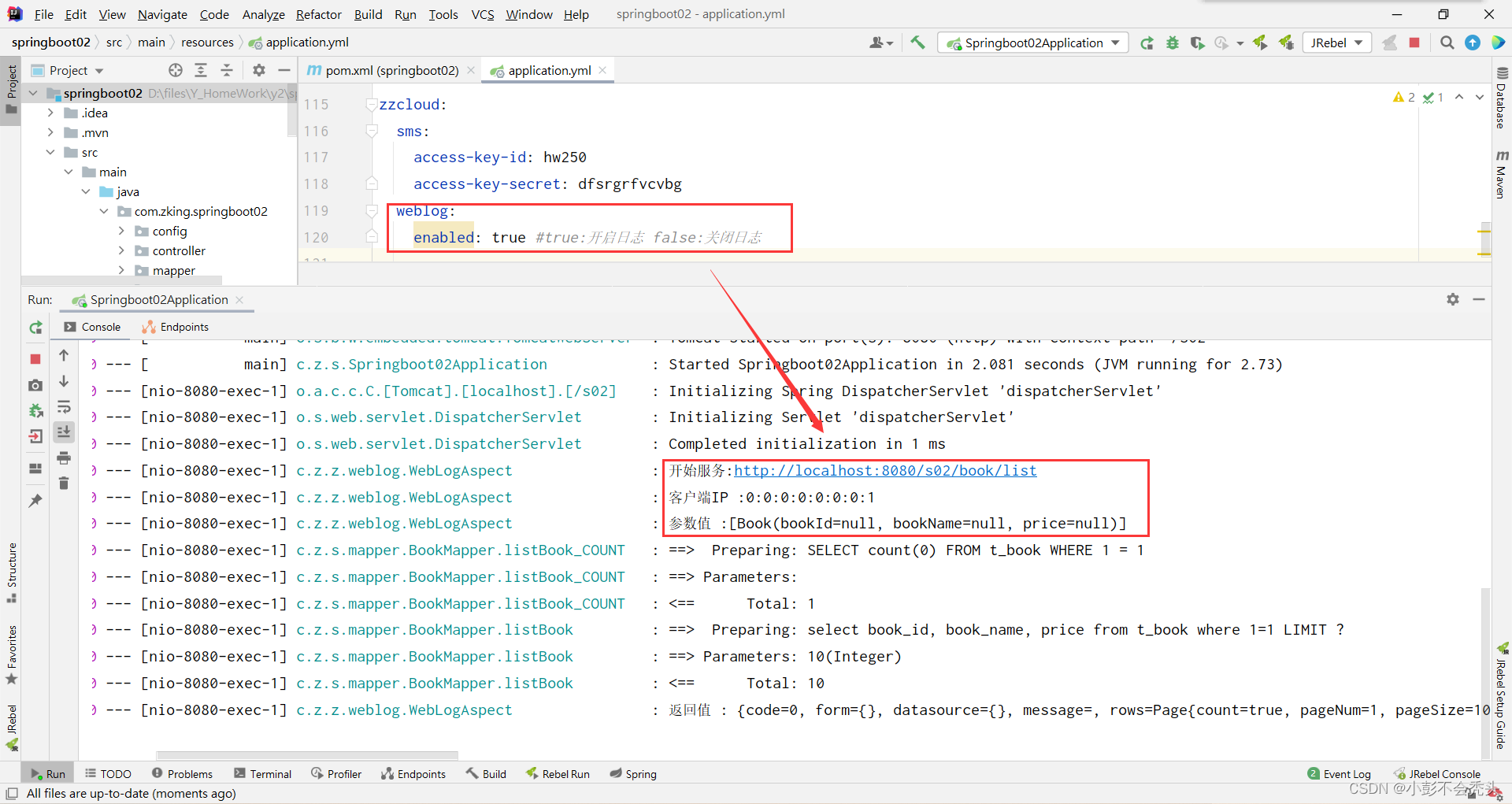
log.info("开始服务:{}", request.getRequestURL().toString());
log.info("客户端IP :{}" , request.getRemoteAddr());
log.info("参数值 :{}", Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
@AfterReturning(returning = "ret", pointcut = "webLog()")
public void doAfterReturning(Object ret) throws Throwable {
// 处理完请求,返回内容
log.info("返回值 : {}" , ret);
}
}
4.编写自动配置类AutoConfig
4.1.@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "zzcloud.weblog",value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true):
matchIfMissing属性:默认情况下matchIfMissing为false,也就是说如果未进行属性配置,则自动配置不生效。如果matchIfMissing为true,则表示如果没有对应的属性配置,则自动配置默认生效
4.2.@ConditionalOnMissingBean:
在@bean定义上,它的作用就是在容器加载它作用的bean时,检查容器中是否存在目标类型(ConditionalOnMissingBean注解的value值)的bean了,如果存在这跳过原始bean的BeanDefinition加载动作。
package com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.config;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.SmsProperties;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.SmsServiceImpl;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.sms.WebLogProperties;
import com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.weblog.WebLogAspect;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Configuration //表示这个类为配置类
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebLogProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "zzcloud.weblog",value = "enabled",matchIfMissing = true)
public class WebLogAutoConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public WebLogAspect webLogAspect(){
return new WebLogAspect();
}
}
5.编写spring.factories文件加载自动配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.config.SmsAutoConfig,\
com.zking.zzcloudspringbootstarter.config.WebLogAutoConfig
6.打包,操作同上
7.在其他项目中引用
7.1.导入依赖
由于这里我们使用的是之前的那个项目,这里就不需要重复导入依赖了
7.2.在application.yml文件中添加配置

测试如下:这里我用该项目里的方法进行测试

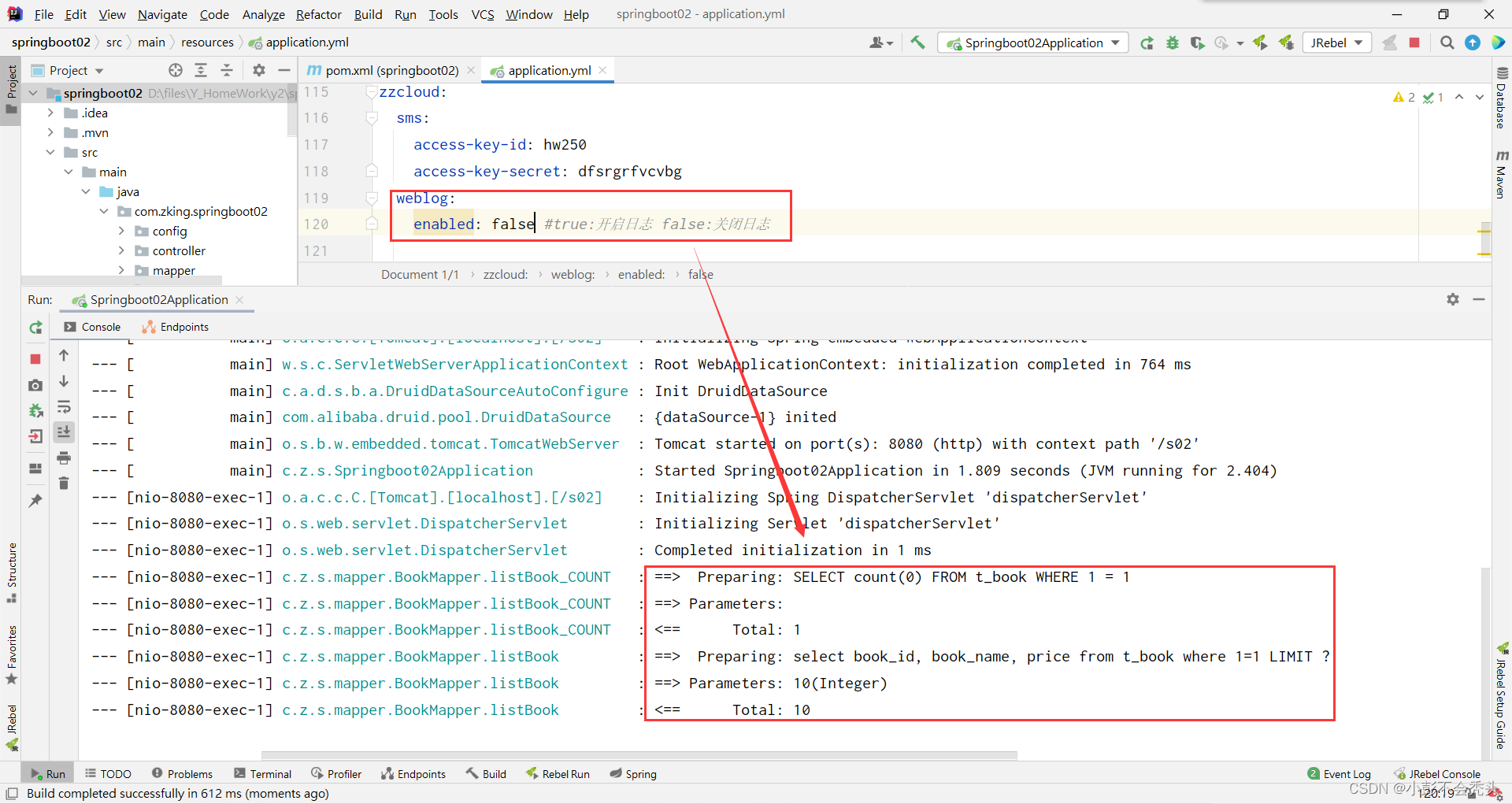
如果我不使用日志,效果如下:
反之如果我使用日志,就会拿到我请求的路径、我的客户端以及我的参数值,效果如下:
 如果由以上效果,说明我的案例二:AOP方式统一服务日志就成功了!
如果由以上效果,说明我的案例二:AOP方式统一服务日志就成功了!
SpringBoot - 自定义starter的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot --- 自定义 Starter
SpringBoot --- 自定义 Starter 创建 1.需要创建一个新的空工程 2.新的工程需要引入两个模块 一个Maven 模块 作为启动器 一个SpringBoot 模块 作为自动配置模块 ...
- SpringBoot自定义starter及自动配置
SpringBoot的核心就是自动配置,而支持自动配置的是一个个starter项目.除了官方已有的starter,用户自己也可以根据规则自定义自己的starter项目. 自定义starter条件 自动 ...
- SpringBoot自定义Starter实现
自定义Starter: Starter会把所有用到的依赖都给包含进来,避免了开发者自己去引入依赖所带来的麻烦.Starter 提供了一种开箱即用的理念,其中核心就是springboot的自动配置原理相 ...
- springboot 自定义starter之AutoConfiguration【原】
八.自定义starter AutoConfiguration: 1.这个场景需要使用到的依赖是什么? 没有特别依赖的配置 2.如何编写自动配置 @Configuration //指定这个类是一个配置类 ...
- SpringBoot自定义starter开发分布式任务调度实践
概述 需求 在前面的博客<Java定时器演进过程和生产级分布式任务调度ElasticJob代码实战>中,我们已经熟悉ElasticJob分布式任务的应用,其核心实现为elasticjob- ...
- SpringBoot系列三:SpringBoot自定义Starter
在前面两章 SpringBoot入门 .SpringBoot自动配置原理 的学习后,我们对如何创建一个 SpringBoot 项目.SpringBoot 的运行原理以及自动配置等都有了一定的了解.如果 ...
- springboot自定义starter
1,创建一个空工程 2,new一个Modules ---------------- maven (启动器) : springboottest-spring-boot-starter 3,new一个M ...
- Springboot自定义starter打印sql及其执行时间
前面写到了通过实现mybatis提供的org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor接口实现了打印SQL执行时间,并格式化SQL及其参数,如果我们使用的是ssm还得再配置文件 ...
- Spring-Boot自定义Starter实践
此文已由作者王慎为授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. disconf-spring-boot-starter 使用方法: 引入maven依赖: <depen ...
- SpringBoot之旅第六篇-启动原理及自定义starter
一.引言 SpringBoot的一大优势就是Starter,由于SpringBoot有很多开箱即用的Starter依赖,使得我们开发变得简单,我们不需要过多的关注框架的配置. 在日常开发中,我们也会自 ...
随机推荐
- vue全家桶进阶之路23:Element UI
Element UI 是一套基于 Vue.js 的组件库,它提供了一系列常用的 UI 组件,包括表单.弹窗.布局.导航等等.Element UI 的设计风格简洁.易用.美观,且易于定制. Elemen ...
- C# 中的“智能枚举”:如何在枚举中增加行为
目录 枚举的基本用法回顾 枚举常见的设计模式运用 介绍 智能枚举 代码示例 业务应用 小结 枚举的基本用法回顾 以下是一个常见的 C# 枚举(enum)的示例: enum Weekday { Mond ...
- LOTO示波器如何测试阻抗的频响曲线
LOTO示波器如何测试阻抗的频响曲线 模块的输入输出端口,在电路分析上,一般简单表征为电阻来进行计算和分析.但多数情况下,这些端口并不是纯电阻的特性,更精确一些,它可能是电阻电容以及电感的组合,表现为 ...
- elment UI + EasyExcel 实现 导入
前端组件 <hd-flex> <el-dialog v-model="isUploadDialog" width="50%" lock-scr ...
- spring-boot集成mybatis真的很简单吗?
在日常的后端开发中,使用mybatis作为DAO层的持久框架已经是惯例.但很多时候都是在别人搭好的框架中进行开发,对怎么搭建环境是一知半解,今天就来实践下. 一.集成分哪些步骤 来看下集成mybati ...
- 解决github无法打开问题
在国内访问国外服务器(如github)会有卡顿.无法加载等问题,提供两种解决方案: 1.查看github的IP地址并修改Hosts windows键+R,打开cmd(或windows键+X,打开Win ...
- TVM 源码阅读PASS — VectorizeLoop
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanger-sjtu/p/17501119.html VectorizeLoop这个PASS就是对标记为ForKind::kVectoriz ...
- MySQL 存储引擎 InnoDB 内存结构之缓冲池
缓冲池是主存储器中的一个区域,在访问 table 和索引数据时InnoDB会对其进行缓存.缓冲池允许直接从内存中访问频繁使用的数据,从而加快处理速度.在专用服务器上,通常将高达 80% 的物理内存分配 ...
- java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException
org.mybatis.spring.MyBatisSystemException: nested exception is org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.Persiste ...
- BeanDefinitionStoreException: Failed to read candidate component class
ssm 整合时出现问题 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Failed to read candidate ...
