POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines (判断直线位置关系)
题目链接:POJ 1269
Problem Description
We all know that a pair of distinct points on a plane defines a line and that a pair of lines on a plane will intersect in one of three ways: 1) no intersection because they are parallel, 2) intersect in a line because they are on top of one another (i.e. they are the same line), 3) intersect in a point. In this problem you will use your algebraic knowledge to create a program that determines how and where two lines intersect.
Your program will repeatedly read in four points that define two lines in the x-y plane and determine how and where the lines intersect. All numbers required by this problem will be reasonable, say between -1000 and 1000.
Input
The first line contains an integer N between 1 and 10 describing how many pairs of lines are represented. The next N lines will each contain eight integers. These integers represent the coordinates of four points on the plane in the order x1y1x2y2x3y3x4y4. Thus each of these input lines represents two lines on the plane: the line through (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) and the line through (x3,y3) and (x4,y4). The point (x1,y1) is always distinct from (x2,y2). Likewise with (x3,y3) and (x4,y4).
Output
There should be N+2 lines of output. The first line of output should read INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUT. There will then be one line of output for each pair of planar lines represented by a line of input, describing how the lines intersect: none, line, or point. If the intersection is a point then your program should output the x and y coordinates of the point, correct to two decimal places. The final line of output should read "END OF OUTPUT".
Sample Input
50 0 4 4 0 4 4 05 0 7 6 1 0 2 35 0 7 6 3 -6 4 -32 0 2 27 1 5 18 50 3 4 0 1 2 2 5
Sample Output
INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUTPOINT 2.00 2.00NONELINEPOINT 2.00 5.00POINT 1.07 2.20END OF OUTPUT
Solution
题意
\(n\) 组样例。每组样例给定两条直线,判断直线是平行,重合还是相交。若相交求交点。
题解
叉积
- 判断共线:
若 \(\boldsymbol{ab}\) 与 \(\boldsymbol{cd}\) 共线,则 \(\boldsymbol{ab} \times \boldsymbol{cd} = 0\)。
- 判断重合:
若 \(\boldsymbol{ab}\) 与 \(\boldsymbol{cd}\) 重合,则 \(\boldsymbol{bc} \times \boldsymbol{ad} = 0\)。
- 判断平行:
共线且不重合。
- 求交点:
首先要满足相交。
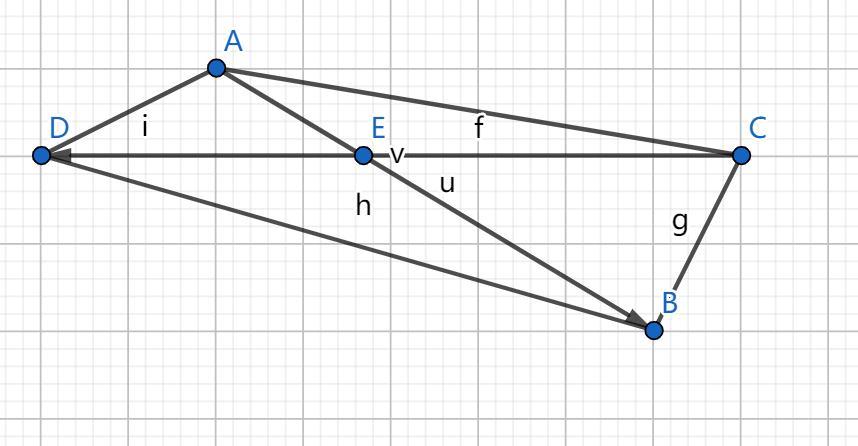
如上图,求 \(\boldsymbol{AB}\) 与 \(\boldsymbol{CD}\) 的交点 \(E\)。
\]
\]
设原点为 \(O\),则
\]
\(\boldsymbol{OE}\) 即为点 \(E\) 的坐标。
Code
#include <cstdio>#include <iostream>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>#include <vector>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;typedef double db;const db eps = 1e-10;const db pi = acos(-1.0);const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;const ll maxn = 1e5 + 10;inline int dcmp(db x) {if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;return x > 0? 1: -1;}class Point {public:double x, y;Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}void input() {scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);}bool operator<(const Point &a) const {return (!dcmp(x - a.x))? dcmp(y - a.y) < 0: x < a.x;}bool operator==(const Point &a) const {return dcmp(x - a.x) == 0 && dcmp(y - a.y) == 0;}db dis2(const Point a) {return pow(x - a.x, 2) + pow(y - a.y, 2);}db dis(const Point a) {return sqrt(dis2(a));}db dis2() {return x * x + y * y;}db dis() {return sqrt(dis2());}Point operator+(const Point a) {return Point(x + a.x, y + a.y);}Point operator-(const Point a) {return Point(x - a.x, y - a.y);}Point operator*(double p) {return Point(x * p, y * p);}Point operator/(double p) {return Point(x / p, y / p);}db dot(const Point a) {return x * a.x + y * a.y;}db cross(const Point a) {return x * a.y - y * a.x;}};typedef Point Vector;class Line {public:Point s, e;Line() {}Line(Point s, Point e) : s(s), e(e) {}void input() {scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &s.x, &s.y, &e.x, &e.y);}int toLeftTest(Point p) {if((e - s).cross(p - s) > 0) return 1;else if((e - s).cross(p - s) < 0) return -1;return 0;}// 共线bool collinear(Line l) {if(dcmp((e - s).cross(l.e - l.s)) == 0) {return 1;}return 0;}// 同线bool same(Line l) {if(dcmp((l.s - e).cross(l.e - s)) == 0) {return 1;}return 0;}// 平行bool parallel(Line l) {return collinear(l) && (!same(l));}// 直线与直线交点Point crosspoint(Line l) {double a1 = (l.e - l.s).cross(s - l.s);double a2 = (l.e - l.s).cross(e - l.s);Point ans = s + (e - s) * (-a1) / (a2 - a1);if(dcmp(ans.x) == 0) ans.x = 0;if(dcmp(ans.y) == 0) ans.y = 0;return ans;}// 直线与直线位置关系 0-重合 1-平行 2-相交int linecrossline (Line l) {if(dcmp((e - s).cross(l.e - l.s)) == 0) {if(dcmp((l.s - e).cross(l.e - s)) == 0) {return 0;}return 1;}return 2;}};Line l1, l2;int main() {int T;scanf("%d", &T);printf("INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUT\n");while(T--) {l1.input();l2.input();if(l1.linecrossline(l2) == 0) {printf("LINE\n");} else if(l1.linecrossline(l2) == 1) {printf("NONE\n");} else {Point ans = l1.crosspoint(l2);printf("POINT %.2lf %.2lf\n", ans.x, ans.y);}}printf("END OF OUTPUT\n");return 0;}
POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines (判断直线位置关系)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines(直线相交判断,求交点)
Intersecting Lines Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 8342 Accepted: 378 ...
- poj 1269 Intersecting Lines(判断两直线关系,并求交点坐标)
Intersecting Lines Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 12421 Accepted: 55 ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines(直线求交点)
Description We all know that a pair of distinct points on a plane defines a line and that a pair of ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines 判断两直线关系
用的是初中学的方法 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <al ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines(判断两直线位置关系)
题目传送门:POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines Description We all know that a pair of distinct points on a plane ...
- 判断两条直线的位置关系 POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines
两条直线可能有三种关系:1.共线 2.平行(不包括共线) 3.相交. 那给定两条直线怎么判断他们的位置关系呢.还是用到向量的叉积 例题:POJ 1269 题意:这道题是给定四个点p1, ...
- 简单几何(直线位置) POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines
题目传送门 题意:判断两条直线的位置关系,共线或平行或相交 分析:先判断平行还是共线,最后就是相交.平行用叉积判断向量,共线的话也用叉积判断点,相交求交点 /********************* ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines【判断直线相交】
题意:给两条直线,判断相交,重合或者平行 思路:判断重合可以用叉积,平行用斜率,其他情况即为相交. 求交点: 这里也用到叉积的原理.假设交点为p0(x0,y0).则有: (p1-p0)X(p2-p0) ...
- POJ 1269 - Intersecting Lines 直线与直线相交
题意: 判断直线间位置关系: 相交,平行,重合 include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; str ...
随机推荐
- 分布式调度框架TBSchedule使用方法
一.TBSchedule简介 TBSchedule是来自淘宝的分布式调度开源框架,基于Zookeeper纯Java实现,其目的是让一种批量任务或者不断变化的任务,能够被动态的分配到多个主机的JVM中的 ...
- 微信小程序,获取二维码
微信小程序,获取二维码 找到一篇很实用的博客,他已经写得很详细了,自己也懒得写,亲测有效 参考网址
- git push 报错:failed to push some refs to 'git@git.xxxx:devops/thor.git'
error: failed to push some refs to 'git@git.caicaivip.com:devops/thor.git' hint: Updates were reject ...
- (转)GitHub上想下载单个文件方法
找到该文件,单机raw,如下图: 然后会在网页打开该文件,复制URL,下载即可(如果是不可预览文件,会自动下载). 转自: GitHub上想下载单个文件方法 - Smallcaff的博客 - CSDN ...
- HBase版本进化史及大版本特性
HBase 2.0 新特性介绍 2018年4月30日HBase发布了2.0的Release版本.HBase的2.0版本承载了太多的Features,共包含4551个Issues,可以说是迄今最大的一个 ...
- MySQL数据库安装与启动(Linux)
1.用yum安装 用root权限打开命令行界面,执行以下yum指令: yum安装MySQL yum install mysql mysql-server mysql-devel -y 在最终提示Com ...
- python基础之基础数据类型1
int 整形 数字用于计算和比较 python3没有long,python2有整形和长整型 十进制二进制转换方法 bin(10进制) ==二进制 0b(二进制) int("二进制" ...
- 用dialog包制作窗口
#!/bin/bash temp=$(mktemp -t test.XXXXXX) temp2=$(mktemp -t test.XXXXXX) function diskspace { df -k ...
- BUUCTF 派大星的烦恼
这道题做的累死了,题目关键在于思路,这里将做题的完整思路记下来.题目给了一张bmp,用010打开可以看出题目关键就在于这一段D和“,保存出来 "DD"DD""& ...
- Lock中使用Condition实现等待通知
Condition类有很好的灵活性,可以实现多路通知功能,一个Lock对象中可以创建多个Condition对象实例,线程对象可以注册在指定的Condition中,进而有选择的进行线程通知,在调度线程上 ...
