Spring官网阅读(十四)Spring中的BeanWrapper及类型转换
文章目录
BeanWrapper是Spring中一个很重要的接口,Spring在通过配置信息创建对象时,第一步首先就是创建一个BeanWrapper。这篇文章我们就分析下这个接口,本文内容主要对应官网中的
3.3及3.4小结
接口定义
// Spring低级JavaBeans基础设施的中央接口。通常来说并不直接使用BeanWrapper,而是借助BeanFactory或者DataBinder来一起使用,BeanWrapper对Spring中的Bean做了包装,为的是更加方便的操作Bean中的属性
public interface BeanWrapper extends ConfigurablePropertyAccessor {
void setAutoGrowCollectionLimit(int autoGrowCollectionLimit);
int getAutoGrowCollectionLimit();
// 获取包装的Bean
Object getWrappedInstance();
// 获取包装的Bean的class
Class<?> getWrappedClass();
// 获取所有属性的属性描述符
PropertyDescriptor[] getPropertyDescriptors();
// 获取指定属性的属性描述符
PropertyDescriptor getPropertyDescriptor(String propertyName) throws InvalidPropertyException;
}
这里需要解释一个概念,什么是属性描述符?
PropertyDescriptor:属性描述符,能够描述javaBean中的属性,通过属性描述符我们能知道这个属性的类型,获取到操纵属性的方法(getter/setter)
继承关系
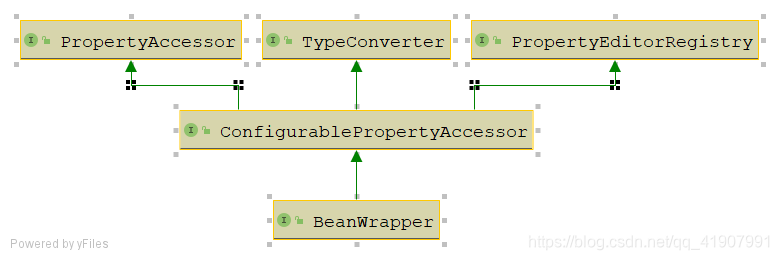
BeanWrapper的子类只有一个:BeanWrapperImpl,它继承了ConfigurablePropertyAccessor,这个接口的主要功能是进行属性访问,同时它又有三个父接口,接下来我们一一分析他们的功能。
接口功能
1、PropertyEditorRegistry(属性编辑器注册器)
接口定义
// 这个接口的功能很简单,就是用来注入属性编辑器(PropertyEditor),那么什么是PropertyEditor呢?
public interface PropertyEditorRegistry {
void registerCustomEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor);
void registerCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String propertyPath, PropertyEditor propertyEditor);
@Nullable
PropertyEditor findCustomEditor(@Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable String propertyPath);
}
PropertyEditor
概念
PropertyEditor是JavaBean规范定义的接口,这是
java.beans中一个接口,其设计的意图是图形化编程上,方便对象与String之间的转换工作,而Spring将其扩展,方便各种对象与String之间的转换工作。
Spring中对PropertyEditor使用的实例
- 我们在通过XML的方式对Spring中的Bean进行配置时,不管Bean中的属性是何种类型,都是直接通过字面值来设置Bean中的属性。那么是什么在这其中做转换呢?这里用到的就是PropertyEditor
- SpringMVC在解析请求参数时,也是使用的PropertyEditor
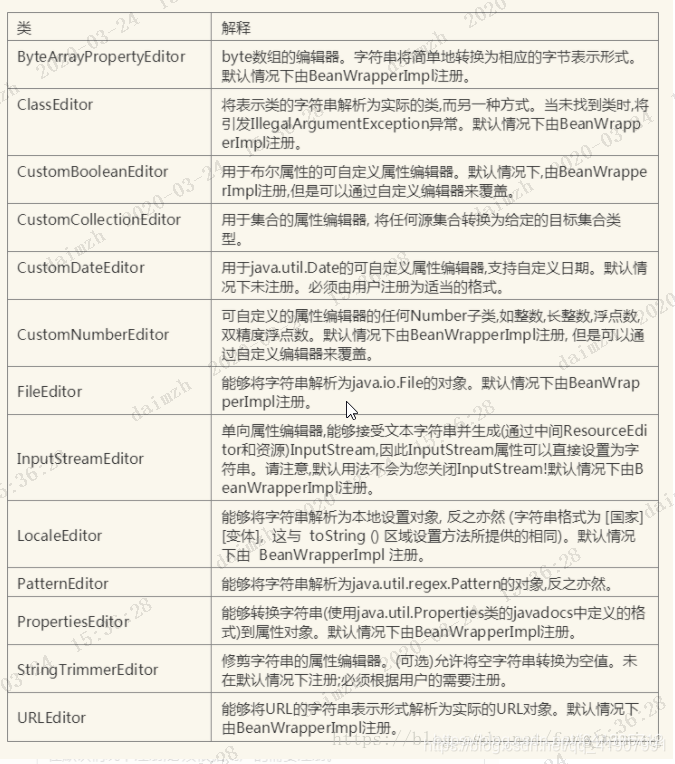
Spring内置的PropertyEditor
2、PropertyAccessor(属性访问器)
接口定义
public interface PropertyAccessor {
// 嵌套属性的分隔符,比如"foo.bar"将会调用getFoo().getBar()两个方法
String NESTED_PROPERTY_SEPARATOR = ".";
char NESTED_PROPERTY_SEPARATOR_CHAR = '.';
// 代表角标index的符号 如person.addresses[0] 这样就可以把值放进集合/数组/Map里了
String PROPERTY_KEY_PREFIX = "[";
char PROPERTY_KEY_PREFIX_CHAR = '[';
String PROPERTY_KEY_SUFFIX = "]";
char PROPERTY_KEY_SUFFIX_CHAR = ']';
// 该属性是否可读/可写,不存在则返回false
boolean isReadableProperty(String propertyName);
boolean isWritableProperty(String propertyName);
// 获取/设置属性的方法,基本见名知意
@Nullable
Class<?> getPropertyType(String propertyName) throws BeansException;
@Nullable
TypeDescriptor getPropertyTypeDescriptor(String propertyName) throws BeansException;
@Nullable
Object getPropertyValue(String propertyName) throws BeansException;
void setPropertyValue(String propertyName, @Nullable Object value) throws BeansException;
void setPropertyValue(PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException;
void setPropertyValues(Map<?, ?> map) throws BeansException;
void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs) throws BeansException;
void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown)
throws BeansException;
void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException;
}
这里需要解释一个概念,什么是PropertyValue?
当设置属性值时,少不了两样东西:
- 属性访问表达式:如
listMap[0][0]- 属性值:
ProperyValue对象就是用来封装这些信息的。如果某个值要给赋值给bean属性,Spring都会把这个值包装成ProperyValue对象。
3、TypeConverter(类型转换器)
接口定义
// 定义了进行类型转换时的一些规范,就像名字定义的那样,主要用来做类型转换
public interface TypeConverter {
// 将指定的值转换成指定的类型
@Nullable
<T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws TypeMismatchException;
// 相对于上面这个方法下面这个三种方法能处理转换过程中的泛型
@Nullable
<T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable MethodParameter methodParam) throws TypeMismatchException;
@Nullable
<T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Field field)
throws TypeMismatchException;
default <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable Object value, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws TypeMismatchException {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("TypeDescriptor resolution not supported");
}
}
4、ConfigurablePropertyAccessor
public interface ConfigurablePropertyAccessor extends PropertyAccessor, PropertyEditorRegistry, TypeConverter {
// ConversionService:进行转换的业务类,转换系统的入口
void setConversionService(@Nullable ConversionService conversionService);
@Nullable
ConversionService getConversionService();
// 进行属性编辑是是否返回旧的值
void setExtractOldValueForEditor(boolean extractOldValueForEditor);
boolean isExtractOldValueForEditor();
// 当设置(dog.name)这种嵌套属性的情况下,如果dog属性为null是否会报错
// 为true的话不会,为false会抛出NullValueInNestedPathException
void setAutoGrowNestedPaths(boolean autoGrowNestedPaths);
boolean isAutoGrowNestedPaths();
}
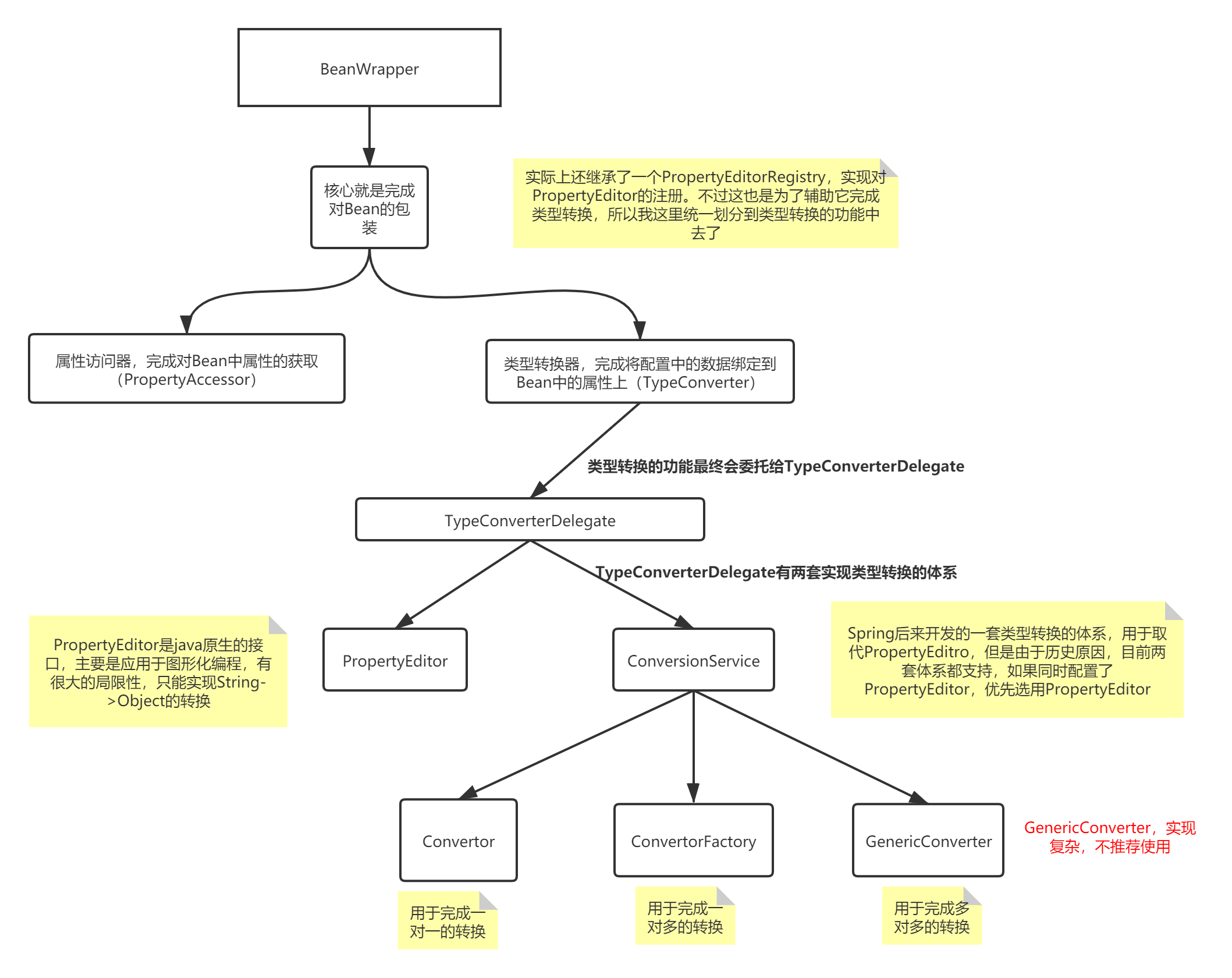
从上面可以看到,BeanWrapper接口自身对Bean进行了一层包装。另外它的几个通过间接继承了几个接口,所以它还能对Bean中的属性进行操作。PropertyAccessor赋予了BeanWrapper对属性进行访问及设置的能力,在对Bean中属性进行设置时,不可避免的需要对类型进行转换,而恰好PropertyEditorRegistry,TypeConverter就提供了类型转换的统一约束。
在了解了接口之后,我们接下来看看它的唯一实现类BeanWrapperImpl
唯一子类(BeanWrapperImpl)
继承关系
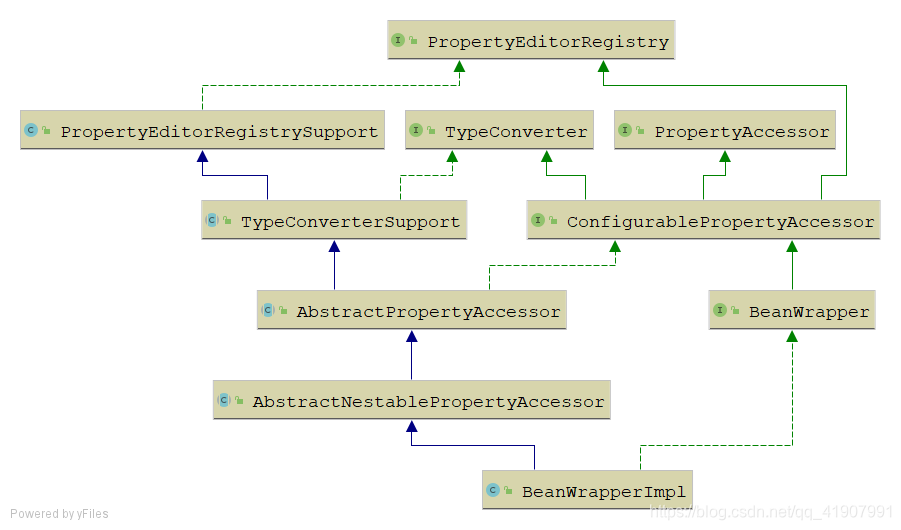
结合我们之前对接口的分析以及上面这张UML图,我们可以知道BeanWrapperImpl主要实现了一下几个功能
- 对Bean进行包装
- 对Bean的属性进行访问以及设置
- 在操作属性的过程中,必然涉及到类型转换,所以还有类型转换的功能
Java中的内置机制
在详细了解BeanWrapperImpl前,必须要了解java中的一个机制:内省
核心概念
首先可以先了解下JavaBean的概念:一种特殊的类,主要用于传递数据信息。这种类中的方法主要用于访问私有的字段,且方法名符合某种命名规则。如果在两个模块之间传递信息,可以将信息封装进JavaBean中,这种对象称为“值对象”(Value Object),或“VO”。
因此JavaBean都有如下几个特征:
- 属性都是私有的;
- 有无参的public构造方法;
- 对私有属性根据需要提供公有的getXxx方法以及setXxx方法;
- getters必须有返回值没有方法参数;setter值没有返回值,有方法参数;
符合这些特征的类,被称为JavaBean;JDK中提供了一套API用来访问某个属性的getter/setter方法,这些API存放在java.beans中,这就是内省(Introspector)。
内省和反射的区别:
反射:Java反射机制是在运行中,对任意一个类,能够获取得到这个类的所有属性和方法;它针对的是任意类
内省(Introspector):是Java语言对JavaBean类属性、事件的处理方法
- 反射可以操作各种类的属性,而内省只是通过反射来操作JavaBean的属性
- 内省设置属性值肯定会调用setter方法,反射可以不用(反射可直接操作属性Field)
- 反射就像照镜子,然后能看到.class的所有,是客观的事实。内省更像主观的判断:比如看到getName(),内省就会认为这个类中有name字段,但事实上并不一定会有name;通过内省可以获取bean的getter/setter
使用示例
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(People.class);
PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
System.out.print(propertyDescriptor.getName()+" ");
}
}
// 程序输出:age class name
// 为什么会输出class呢?前文中有提到,“看到getName(),内省就会认为这个类中有name字段,但事实上并不一定会有name”,我们知道每个对象都会有getClass方法,所以使用内省时,默认就认为它具有class这个字段
}
class People{
String name;
int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
源码分析
// 这个类我只保留一些关键的代码,其余的琐碎代码都不看了
public class BeanWrapperImpl extends AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor implements BeanWrapper {
// 缓存内省的结果,BeanWrapperImpl就是通过这个对象来完成对包装的Bean的属性的控制
@Nullable
private CachedIntrospectionResults cachedIntrospectionResults;
......
public void setBeanInstance(Object object) {
this.wrappedObject = object;
this.rootObject = object;
// 实际进行类型转换的对象:typeConverterDelegate
this.typeConverterDelegate = new TypeConverterDelegate(this, this.wrappedObject);
setIntrospectionClass(object.getClass());
}
......
// 最终调用的就是CachedIntrospectionResults的forClass方法进行内省并缓存,底层调用的就是java的内省机制
private CachedIntrospectionResults getCachedIntrospectionResults() {
if (this.cachedIntrospectionResults == null) {
this.cachedIntrospectionResults = CachedIntrospectionResults.forClass(getWrappedClass());
}
return this.cachedIntrospectionResults;
}
.......
// 最终进行类型转换的方法
private Object convertIfNecessary(@Nullable String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue,
@Nullable Object newValue, @Nullable Class<?> requiredType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor td)
throws TypeMismatchException {
Assert.state(this.typeConverterDelegate != null, "No TypeConverterDelegate");
try {
// 可以看到,最后就是调用typeConverterDelegate来进行类型转换
return this.typeConverterDelegate.convertIfNecessary(propertyName, oldValue, newValue, requiredType, td);
}
......
}
}
父类作用分析
对于接口,我们已经分析过了,这里就不再赘述了,我们重点看下BeanWrapperImpl继承的几个父类
PropertyEditorRegistrySupport
这个类最大的作用在于管理PropertyEditor,添加了很多的默认的PropertyEditor。在PropertyEditorRegistry的基础上做了进一步的扩展,提供的还是属性编辑器注册的功能。
TypeConverterSupport
public abstract class TypeConverterSupport extends PropertyEditorRegistrySupport implements TypeConverter {
@Nullable
TypeConverterDelegate typeConverterDelegate;
......
}
这个接口实现了TypeConverter,所以它具有类型转换的能力,而它这种能力的实现,依赖于它所持有的一个TypeConverterDelegate。
AbstractPropertyAccessor
public abstract class AbstractPropertyAccessor extends TypeConverterSupport implements ConfigurablePropertyAccessor {
// 省略部分代码......
@Override
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, boolean ignoreUnknown, boolean ignoreInvalid)
throws BeansException {
List<PropertyAccessException> propertyAccessExceptions = null;
List<PropertyValue> propertyValues = (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues ?
((MutablePropertyValues) pvs).getPropertyValueList() : Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()));
for (PropertyValue pv : propertyValues) {
try {
setPropertyValue(pv);
}
// ....
}
}
@Override
@Nullable
public abstract Object getPropertyValue(String propertyName) throws BeansException;
@Override
public abstract void setPropertyValue(String propertyName, @Nullable Object value) throws BeansException;
}
核心的代码其实就是这些,这个类继承了TypeConverterSupport,所以它具备了类型转换的能力。同时它也是一个属性访问器,但是它只是实现了批量设置属性的方法,真正的setPropertyValue还是留待子类实现。可以看到,到这个类为止,还没有将属性的设置跟类型转换的能力结合起来。
AbstractNestablePropertyAccessor
这个类开始真正的将属性访问跟类型转换结合到一起,它真正的实现了setPropertyValue,并在设置属性的时候会进行类型的转换,具体代码就不看了,非常繁杂,但是整体不难。
上面我们多次提到了类型转换,但是还没有真正看到类型转换的逻辑,因为上面类最终将类型转换的逻辑委托给了TypeConverterDelegate。接下来我们看看,类型转换到底是怎么完成。
类型转换
TypeConverterDelegate
这个类我们只看一个核心方法,如下:
class TypeConverterDelegate {
private final PropertyEditorRegistrySupport propertyEditorRegistry;
@Nullable
private final Object targetObject;
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(@Nullable String propertyName, @Nullable Object oldValue, @Nullable Object newValue,
@Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// 查看是否为当前这个类型配置了定制的PropertyEditor
PropertyEditor editor = this.propertyEditorRegistry.findCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyName);
ConversionFailedException conversionAttemptEx = null;
// 获取当前容器中的类型转换业务类
ConversionService conversionService = this.propertyEditorRegistry.getConversionService();
// 在这里可以看出,Spring底层在进行类型转换时有两套机制
// 1.首选的是采用PropertyEditor
// 2.在没有配置PropertyEditor的情况下,会采用conversionService
if (editor == null && conversionService != null && newValue != null && typeDescriptor != null) {
TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue);
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) {
try {
// 通过conversionService进行类型转换
return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor);
}
catch (ConversionFailedException ex) {
// fallback to default conversion logic below
conversionAttemptEx = ex;
}
}
}
Object convertedValue = newValue;
// 配置了定制的属性编辑器,采用PropertyEditor进行属性转换
if (editor != null || (requiredType != null && !ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(requiredType, convertedValue))) {
if (typeDescriptor != null && requiredType != null && Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType) &&
convertedValue instanceof String) {
TypeDescriptor elementTypeDesc = typeDescriptor.getElementTypeDescriptor();
if (elementTypeDesc != null) {
Class<?> elementType = elementTypeDesc.getType();
if (Class.class == elementType || Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(elementType)) {
convertedValue = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) convertedValue);
}
}
}
if (editor == null) {
// 没有配置定制的属性编辑器,采用默认的属性编辑器
editor = findDefaultEditor(requiredType);
}
// 采用属性编辑器进行转换,需要注意的是,默认情况下PropertyEditor只会对String类型的值进行类型转换
convertedValue = doConvertValue(oldValue, convertedValue, requiredType, editor);
}
// .....
return (T) convertedValue;
}
}
从上面的代码中我们可以知道,Spring在实现类型转换时,有两套机制,第一套机制依赖于PropertyEditor,第二套机制依赖于ConversionService。关于属性编辑器PropertyEditor我们之前已经介绍过了,主要进行的是String到Object的转换,正因为如此,属性编辑器进行类型转换有很大的局限性,所以Spring又推出了一套ConversionService的体系。
ConversionService体系
1、Converter
接口定义
package org.springframework.core.convert.converter;
// 将一个S类型的数据转换成T类型
public interface Converter<S, T> {
T convert(S source);
}
这个接口只能进行一对一的转换,S->T
2、ConverterFactory
接口定义
public interface ConverterFactory<S, R> {
<T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType);
}
利用这个转换工厂,我们可以进行一对多的转换,以Spring内置的一个转换器为例:
final class StringToEnumConverterFactory implements ConverterFactory<String, Enum> {
@Override
public <T extends Enum> Converter<String, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType) {
return new StringToEnum(ConversionUtils.getEnumType(targetType));
}
private class StringToEnum<T extends Enum> implements Converter<String, T> {
private final Class<T> enumType;
public StringToEnum(Class<T> enumType) {
this.enumType = enumType;
}
@Override
public T convert(String source) {
if (source.isEmpty()) {
// It's an empty enum identifier: reset the enum value to null.
return null;
}
return (T) Enum.valueOf(this.enumType, source.trim());
}
}
}
通过传入不同的枚举类型,我们可以从这个工厂中获取到不同的转换器,并把对应的String类型的参数转换成对应的枚举类型数据。
可以看到,通过ConverterFactory,我们能实现一对多的类型转换S->(T extends R)
3、GenericConverter
接口定义
public interface GenericConverter {
// 获取能够转换的ConvertiblePair的集合,这个对象就是一组可以进行转换的类型
@Nullable
Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes();
// 根据源数据类型转换成目标类型数据
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
final class ConvertiblePair {
// 源数据类型
private final Class<?> sourceType;
// 目标数据类型
private final Class<?> targetType;
// .....省略部分代码
}
}
相比于前面的Converter以及ConverterFactory,这个接口就更加牛逼了,使用它能完成多对多的转换。因为它内部保存了一个能够进行转换的ConvertiblePair的集合,每个ConvertiblePair代表一组能进行转换的数据类型。同时,这个接口相比我们前面介绍的两个接口,更加的复杂,所以一般情况也不推荐使用这个接口,没有非常必要的话,最好是使用上面两种
一般GenericConverter会与ConditionalGenericConverter配合使用,其接口定义如下:
public interface ConditionalConverter {
// 判断是否需要对目标类型转换到原类型,返回true的话代表要执行转换,否则不执行转换
boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}
// 结合了上面两个接口
public interface ConditionalGenericConverter extends GenericConverter, ConditionalConverter {
}
我们来看下Spring内部的一个实际使用的例子:
final class StringToCollectionConverter implements ConditionalGenericConverter {
private final ConversionService conversionService;
@Override
public Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class, Collection.class));
}
@Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return (targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor() == null ||
// 根据conversionService来判断是否需要执行转换
this.conversionService.canConvert(sourceType, targetType.getElementTypeDescriptor()));
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object convert(@Nullable Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
// 这里会借助conversionService来执行转换
}
}
可以看到,最终的实现还是借助了ConversionService,那么ConversionService到底是啥呢?
4、ConversionService
接口定义
public interface ConversionService {
// 判断是否能进行类型转换
boolean canConvert(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
boolean canConvert(@Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
// 进行类型转换
@Nullable
<T> T convert(@Nullable Object source, Class<T> targetType);
@Nullable
Object convert(@Nullable Object source, @Nullable TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}
UML类图
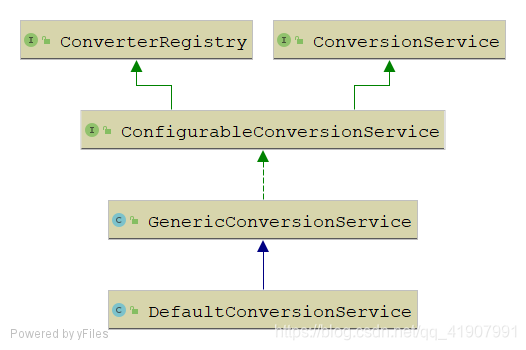
一般来说,实现了ConversionService跟ConverterRegistry会结合使用,对于这种xxxRegistry我相信大家猜都能猜出来它是干什么的了,代码如下:
ConverterRegistry
// 就是在添加Converter或者ConverterFactory
public interface ConverterRegistry {
void addConverter(Converter<?, ?> converter);
<S, T> void addConverter(Class<S> sourceType, Class<T> targetType, Converter<? super S, ? extends T> converter);
void addConverter(GenericConverter converter);
void addConverterFactory(ConverterFactory<?, ?> factory);
void removeConvertible(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType);
}
ConfigurableConversionService
// 单纯的整合了ConversionService以及ConverterRegistry的功能
public interface ConfigurableConversionService extends ConversionService, ConverterRegistry {
}
GenericConversionService
这个类已经是一个具体的实现类,可以直接使用,但是我们一般不会直接使用它,而是使用它的子类DefaultConversionService,因为子类提供了很多默认的转换器。
DefaultConversionService
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService {
@Nullable
private static volatile DefaultConversionService sharedInstance;
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
public static ConversionService getSharedInstance() {
DefaultConversionService cs = sharedInstance;
if (cs == null) {
synchronized (DefaultConversionService.class) {
cs = sharedInstance;
if (cs == null) {
cs = new DefaultConversionService();
sharedInstance = cs;
}
}
}
return cs;
}
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
......
}
public static void addCollectionConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
......
}
private static void addScalarConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new NumberToNumberConverterFactory());
......
}
}
相比其父类GenericConversionService,这个子类默认添加了很多的转换器,这样可以极大的方便我们进行开发,所以一般情况下我们都会使用这个类。
如何配置ConversionService
讲了这么多,那么如何往容器中配置一个ConversionService呢?我们需要借助Spring提供的一个ConversionServiceFactoryBean。其代码如下:
public class ConversionServiceFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<ConversionService>, InitializingBean {
@Nullable
private Set<?> converters;
@Nullable
private GenericConversionService conversionService;
public void setConverters(Set<?> converters) {
this.converters = converters;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.conversionService = createConversionService();
ConversionServiceFactory.registerConverters(this.converters, this.conversionService);
}
protected GenericConversionService createConversionService() {
return new DefaultConversionService();
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ConversionService getObject() {
return this.conversionService;
}
@Override
public Class<? extends ConversionService> getObjectType() {
return GenericConversionService.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
这个类的实现逻辑很简单,ConversionServiceFactoryBean创建完成后,在进行初始化时调用afterPropertiesSet方法,创建一个DefaultConversionService,然后将提供的converters全部注册到这个DefaultConversionService中。所以我们进行如下的配置就行了
<bean id="conversionService"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
# 提供自己的converter,可以覆盖默认的配置
<bean class="example.MyCustomConverter"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
总结
这篇文章中,我们学习了BeanWrapper,知道一个BeanWrapper其实就是一个Bean的包装器,它对Bean包装的目的是为了能操纵Bean中的属性,所以它同时需要具备获取以及设置Bean中的属性能力,所以它也必须是一个属性访问器(PropertyAccessor),另外为了将各种不同类型的配置数据绑定到Bean的属性上,那么它还得具备属性转换的能力,因为它还得是一个类型转换器(TypeConverter)。
通过上面的分析,我们知道Spring中将类型转换的功能都委托给了一个TypeConverterDelegate,这个委托类在进行类型转换时会有两套方案:
- PropertyEditor,这是Spring最初提供的方案,扩展了java中的PropertyEditor(java原先提供这个接口的目的更多是为了进行图形化编程)
- ConversionService,Spring后来提供的一个进行类型转换的体系,用来取代PropertyEditor,因为PropertyEditor有很大的局限性,只能进行String->Object的转换。
画图如下:
Spring官网阅读(十四)Spring中的BeanWrapper及类型转换的更多相关文章
- Spring官网阅读(四)BeanDefinition(上)
前面几篇文章已经学习了官网中的1.2,1.3,1.4三小结,主要是容器,Bean的实例化及Bean之间的依赖关系等.这篇文章,我们继续官网的学习,主要是BeanDefinition的相关知识,这是Sp ...
- Spring官网阅读(十六)Spring中的数据绑定
文章目录 DataBinder UML类图 使用示例 源码分析 bind方法 doBind方法 applyPropertyValues方法 获取一个属性访问器 通过属性访问器直接set属性值 1.se ...
- Spring官网阅读 | 总结篇
接近用了4个多月的时间,完成了整个<Spring官网阅读>系列的文章,本文主要对本系列所有的文章做一个总结,同时也将所有的目录汇总成一篇文章方便各位读者来阅读. 下面这张图是我整个的写作大 ...
- Spring官网阅读(十八)Spring中的AOP
文章目录 什么是AOP AOP中的核心概念 切面 连接点 通知 切点 引入 目标对象 代理对象 织入 Spring中如何使用AOP 1.开启AOP 2.申明切面 3.申明切点 切点表达式 excecu ...
- Spring官网阅读(十七)Spring中的数据校验
文章目录 Java中的数据校验 Bean Validation(JSR 380) 使用示例 Spring对Bean Validation的支持 Spring中的Validator 接口定义 UML类图 ...
- Spring官网阅读(三)自动注入
上篇文章我们已经学习了1.4小结中关于依赖注入跟方法注入的内容.这篇文章我们继续学习这结中的其他内容,顺便解决下我们上篇文章留下来的一个问题-----注入模型. 文章目录 前言: 自动注入: 自动注入 ...
- Spring官网阅读(十一)ApplicationContext详细介绍(上)
文章目录 ApplicationContext 1.ApplicationContext的继承关系 2.ApplicationContext的功能 Spring中的国际化(MessageSource) ...
- Spring官网阅读(一)容器及实例化
从今天开始,我们一起过一遍Spring的官网,一边读,一边结合在路神课堂上学习的知识,讲一讲自己的理解.不管是之前关于动态代理的文章,还是读Spring的官网,都是为了之后对Spring的源码做更全面 ...
- Spring官网阅读(二)(依赖注入及方法注入)
上篇文章我们学习了官网中的1.2,1.3两小节,主要是涉及了容器,以及Spring实例化对象的一些知识.这篇文章我们继续学习Spring官网,主要是针对1.4小节,主要涉及到Spring的依赖注入.虽 ...
随机推荐
- 数据结构和算法(Golang实现)(26)查找算法-哈希表
哈希表:散列查找 一.线性查找 我们要通过一个键key来查找相应的值value.有一种最简单的方式,就是将键值对存放在链表里,然后遍历链表来查找是否存在key,存在则更新键对应的值,不存在则将键值对链 ...
- F 最大公约数和最小公倍数问题
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/948/F来源:牛客网 输入2个正整数x0,y0(2<=x0<100000,2<=y0<=1000 ...
- 关于C++线程池的实现的思考
今天突然对前些日子一直很疑惑的c++线程池有了新的想法.其实所谓的线程池无非就是两个技术点,一个,多线程,指工作线程和主线程分离,或者说数据接收和处理分两个线程,一般就是讲需要运行的函数放到子线程执行 ...
- 基于canvas的画板
最近重新在看Html5&CSS3的知识,看到canvas的时候,想到了以前在学校学计算机图形学时做过的画图实验,于是想,可以基于html5和css3来做一款画板,经过1天的努力,完成了画板的一 ...
- CVE-2019-0193 Apache solr velocity模块漏洞
Solr简单介绍 Solr是建立在Apache Lucene ™之上的一个流行.快速.开放源代码的企业搜索平台. Solr具有高度的可靠性,可伸缩性和容错能力,可提供分布式索引,复制和负载平衡查询,自 ...
- Pytorch手写线性回归
pytorch手写线性回归 import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnim ...
- An example shows several CIM-XML extension headers
The example below shows several CIM-XML extension headers for a GetClass operation on the root/cimv2 ...
- Openstack Swift 如何查找 slave node 挂载的 VD 的 IP
1. 在 /etc/swift/container-server.conf 或者 object-server.conf 中的 devices= 一行 可以找到 /srv/node. 在 /srv/no ...
- c++库 c语言接口
//code in add.cxx #include "add.h" int sample::method() { cout<<"method is call ...
- 查看 Nginx 的日志目录
即便是 docker 容器,对应的目录也是一样的 > /var/log/nginx/xxx.log
