《UNIX网络编程》 -- 第五章
str_cli 和 str_echo 函数
需要先弄清楚 3.9 readn、writen 和 readline 函数
str_cli
void
str_cli(FILE *fp, int sockfd)
{
char sendline[MAXLINE], recvline[MAXLINE]; while (Fgets(sendline, MAXLINE, fp) != NULL) { Writen(sockfd, sendline, strlen(sendline)); if (Readline(sockfd, recvline, MAXLINE) == 0)
err_quit("str_cli: server terminated prematurely"); Fputs(recvline, stdout);
}
}
Fgets
char * fgets ( char * str, int num, FILE * stream );
Get string from stream
Reads characters from stream and stores them as a C string into str until (num-1) characters have been read or either a newline or the end-of-file is reached, whichever happens first.A newline character makes fgets stop reading, but it is considered a valid character by the function and included in the string copied to str.
A terminating null character is automatically appended after the characters copied to str.
Notice that fgets is quite different from gets: not only fgets accepts a stream argument, but also allows to specify the maximum size of str and includes in the string any ending newline character.
Parameters
str
Pointer to an array of chars where the string read is copied.
num
Maximum number of characters to be copied into str (including the terminating null-character).
stream
Pointer to a FILE object that identifies an input stream.
stdin can be used as argument to read from the standard input.Return Value
On success, the function returns str.
If the end-of-file is encountered while attempting to read a character, the eof indicator is set (feof). If this happens before any characters could be read, the pointer returned is a null pointer (and the contents of str remain unchanged).
If a read error occurs, the error indicator (ferror) is set and a null pointer is also returned (but the contents pointed by str may have changed).
fgets 为 NULL 的情况:
1. read EOF 在有字节读取之前;
2. 发生错误;
char *
Fgets(char *ptr, int n, FILE *stream)
{
char *rptr; if ( (rptr = fgets(ptr, n, stream)) == NULL && ferror(stream))
err_sys("fgets error"); return (rptr);
}
包裹之后的 Fgets:如果发生错误,调用 err_sys,然后继续返回 rptr。
err_sys
The C library function void perror(const char *str) prints a descriptive error message to stderr. First the string str is printed, followed by a colon then a space.
void err_sys(const char* x)
{
perror(x);
exit(1);
}
为什么 Readline 返回 0 就说明对方关闭了连接呢?
read 当 EOF 时等于 0,因为 EOF 说明接下来没有数据可以读了。
In computing, end-of-file (commonly abbreviated EOF) is a condition in a computer operating system where no more data can be read from a data source.
str_echo
信号处理
Signal(SIGCHLD, sig_chld);
为什么 sig_chld 的 signo 参数没有用到?stat 又是什么?
#include "unp.h" void
sig_chld(int signo)
{
pid_t pid;
int stat; pid = wait(&stat);
printf("child %d terminated\n", pid);
return;
}
5.12 服务器进程终止


不明白:(7) 中说明了,由于客户进程之前接收了 FIN,所以 readline 返回 0。为什么在小字中,还会读取到 RST?
习题
5.1 查看机器的 MSL
对于 MacOS 系统,通过 sysctl net.inet.tcp 系统 tcp 的各种设置。对于 msl,使用
$ sysctl net.inet.tcp | grep msl
net.inet.tcp.msl: 15000
表示这台机器上的 msl 是 15000 毫秒,即 15秒。
然后,TIME_WAIT 的时间是 2*msl,即 30秒。
The duration that this endpoint remains in this state is twice the maximum segment lifetime (MSL), sometimes called 2MSL
from: 2.7 TIME_WAIT State


没弄懂。
为什么二进制会返回空字节?


5.4 杀掉服务器子进程之后,客户向服务器发送数据导致服务器TCP响应以一个RST。这个RST使得连接中断,并防止连接的服务器端经历TIME_WAIT状态。所以最后两个分节并不发送。
5.5 重启服务器进程后,新启动的服务器看不到之前某个 ESTABLISHED 状态的数据分节,所以同样返回 RST。

5.6

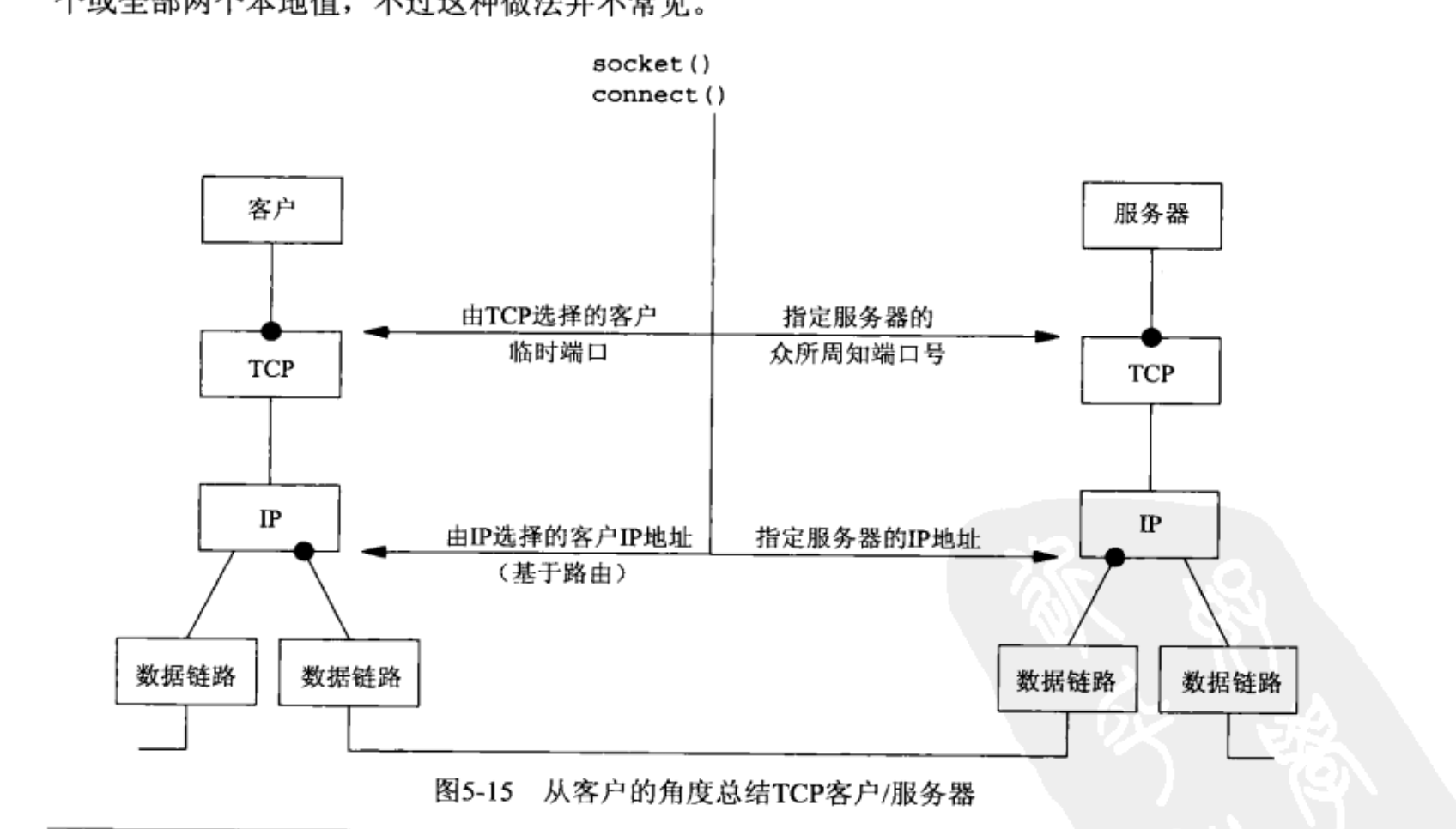
不明白 图5-15,左端数据链路与右端的不同。
5.8 数据格式不同,大端与小端。
参考答案:


总结
这章花了很多时间,
一是之前的函数没有弄懂,倒回去把之前的 readn, writen 弄懂了;
二是习题不会做,原因是么弄清概念,比如字节序大端和小端,32位和64位,函数修改之后编译;
《UNIX网络编程》 -- 第五章的更多相关文章
- Linux内核设计与实现 第五章
1. 什么是系统调用 系统调用就是用户程序和硬件设备之间的桥梁. 用户程序在需要的时候,通过系统调用来使用硬件设备. 系统调用的存在意义: 1)用户程序通过系统调用来使用硬件,而不用关心具体的硬件设备 ...
- linux及安全《Linux内核设计与实现》第一章——20135227黄晓妍
<linux内核设计与实现>第一章 第一章Linux内核简介: 1.3操作系统和内核简介 操作系统:系统包含了操作系统和所有运行在它之上的应用程序.操作系统是指整个在系统中负责完成最基本功 ...
- 《linux内核设计与实现》第一章
第一章Linux内核简介 一.unix 1.Unix的历史 Unix是现存操作系统中最强大和最优秀的系统. ——1969年由Ken Thompson和Dernis Ritchie的灵感点亮的产物. — ...
- Linux内核设计与实现 第十七章
1. 设备类型 linux中主要由3种类型的设备,分别是: 设备类型 代表设备 特点 访问方式 块设备 硬盘,光盘 随机访问设备中的内容 一般都是把设备挂载为文件系统后再访问 字符设备 键盘,打印机 ...
- linux及安全《Linux内核设计与实现》第二章——20135227黄晓妍
第二章:从内核出发 2.1获取源代码 2.1.1使用git Git:内核开发者们用来管理Linux内核源代码的控制系统. 我们使用git来下载和管理Linux源代码. 2.1.2安装内核源代码(如果使 ...
- Linux内核设计与实现 第三章
1. 进程和线程 进程和线程是程序运行时状态,是动态变化的,进程和线程的管理操作都是由内核来实现的. Linux中的进程于Windows相比是很轻量级的,而且不严格区分进程和线程,线程不过是一种特殊的 ...
- 《linux内核设计与实现》第二章
第二章 从内核出发 一.获取内核源码 1.使用Git(linux创造的系统) 使用git来获取最新提交到linux版本树的一个副本: $ git clone git://git.kernel.org/ ...
- Linux内核设计与实现 第四章
1. 什么是调度 现在的操作系统都是多任务的,为了能让更多的任务能同时在系统上更好的运行,需要一个管理程序来管理计算机上同时运行的各个任务(也就是进程). 这个管理程序就是调度程序,功能: 决定哪些进 ...
- Linux内核设计与实现第五周读书笔记
第十八章 调试 18.1准备开始 需要的只是: 一个确定的bug.大部分bug通常都不是行为可靠而且定义明确的. 一个藏匿bug的内核版本. 相关的内核代码的知识和运气. 18.2内核中的bug 内核 ...
- 【读书笔记】Linux内核设计与实现(第一章&第二章)
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1hqYAZNQ OneNote做的笔记没法儿带着格式一起导进来.所以上传到百度云,麻烦老师下载一下了. 下次不再用OneNote.
随机推荐
- mysqli 预处理语句
预处理语句用于执行多个相同的 SQL 语句,并且执行效率更高. <?php // 设置编码格式 header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8'); / ...
- lodash capitalize 首字母大写
_.capitalize([string='']) 转换字符串首字母为大写,剩下为小写. _.capitalize('FRED'); // => 'Fred'
- 读写锁pthread_rwlock_t的使用(转)
读写锁是用来解决读者写者问题的,读操作可以共享,写操作是排他的,读可以有多个在读,写只有唯一个在写,同时写的时候不允许读. 具有强读者同步和强写者同步两种形式 强读者同步:当写者没有进行写操作,读者就 ...
- iOS 自定义转场动画
代码地址如下:http://www.demodashi.com/demo/12955.html 一.总效果 本文记录分享下自定义转场动画的实现方法,具体到动画效果:新浪微博图集浏览转场效果.手势过渡动 ...
- Vue 全家桶 + Electron 开发的一个跨三端的应用
代码地址如下:http://www.demodashi.com/demo/11738.html GitHub Repo:vue-objccn Follow: halfrost · GitHub 利用 ...
- PCIE博文链接
http://blog.csdn.net/mao0514/article/category/1518607/1
- INSERT 失败,因为下列 SET 选项的设置不正确: 'ARITHABORT'
当你在SQL Server上试图更新一个索引视图引用的表时,你可能回收到如下有错误 INSERT 失败,因为下列 SET 选项的设置不正确: 'ARITHABORT' 你必须在TSQL前Set ARI ...
- Angularjs学习笔记8_directive2
指令难点在于参数 angular.module('app', []) .directive('myDirective', function() { return { restrict: String, ...
- active mq 配置
<transportConnectors> <!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to 1000 and frame s ...
- Emoji表情图标在iOS与PHP之间通信及MySQL存储
在某个 iOS 项目中,需要一个服务器来保存一些用户数据,例如用户信息.评论等,我们的服务器端使用了 PHP+MySQL 的搭配.在测试过程中我们发现,用户在 iOS 端里输入了 Emoji 表情提交 ...
