springMvc的执行流程(源码分析)
1.在springMvc中负责处理请求的类为DispatcherServlet,这个类与我们传统的Servlet是一样的。我们来看看它的继承图
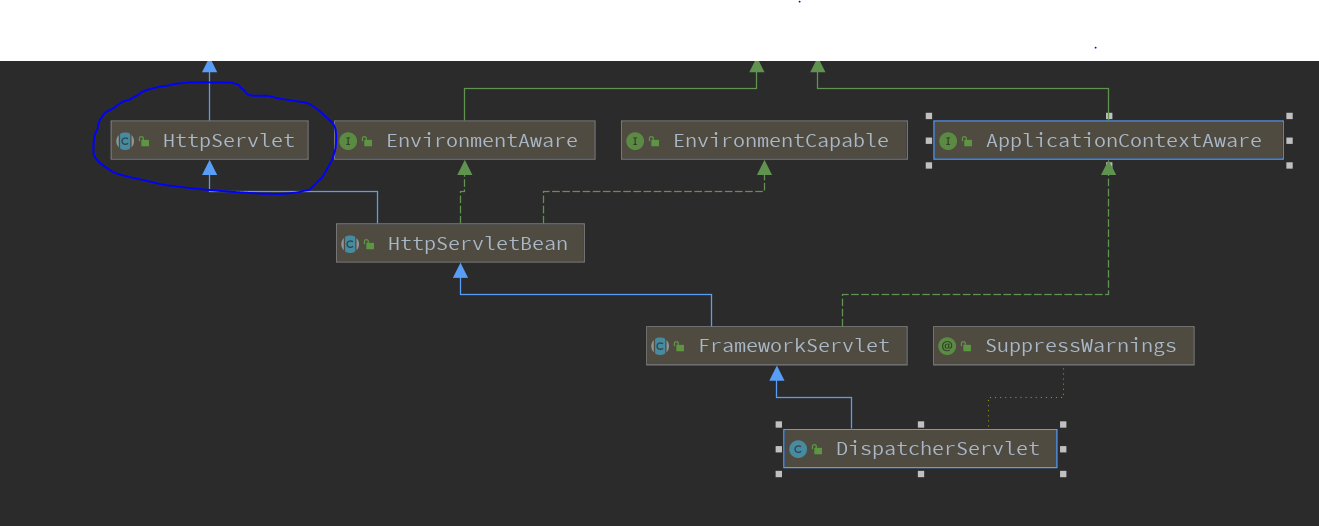
2. 我们发现DispatcherServlet也继承了HttpServlet,所以DispatcherServlet在处理请求时也会从service()方法开始。知道这一点后我们开始分析它的处理过程。
(1).我们在ApplicationFilterChain中的internalDoFilter()方法中打断点(至于为什么从这儿开始,需要去看Tomcat)
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException { // Call the next filter if there is one
if (pos < n) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter(); if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal(); Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege ("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
} // We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
} if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response); //在这里打断点,进入到我们的service方法
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.servlet"), e);
} finally {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(null);
lastServicedResponse.set(null);
}
}
}
(2)进入到FrameworkServlet中的service方法(注意在FrameworkServlet中重写了HttpServlet中的service方法)
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod()); //HttpMethod为枚举类型,成员为GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, TRACE;
if (HttpMethod.PATCH == httpMethod || httpMethod == null) { //如果请求方法为空,或者是PATCH
processRequest(request, response); //处理请求
}
else {
super.service(request, response); //交给父类进行处理,本例中我们是get请求,所以转到这里
}
}
(3)进入到父类HttpServlet中的service方法
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); //获取请求的方法 if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp); //执行get请求
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
} } else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp); } else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
// String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
(4)由于doGet方法也被我们的FrameworkServlet重写,所以这里转向FrameworkServlet类
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); //我们在这里发现最终还是会到达processRequest方法
}
(4)我们来看看FrameworkServlet中的processRequest方法
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //在本篇中只介绍大致的执行过程,这里不详细介绍。。。。
Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try {
doService(request, response); //我们关心这个方法,发现它会转向doService方法
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
} finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
} publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
(5)FrameworkServlet中的doService方法(该方法为抽象方法,有自类具体实现) 所以processRequest为模板模式的实现
protected abstract void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception;
(6)我们看上面的类图,FrameworkServlet的自类为DispatcherServlet(饶了半天终于到了我们的DispatcherServlet)
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
} // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
} // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try {
doDispatch(request, response); //我们重点关注这个方法,进行调度
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
(7)我们发现最终的调度过程都是交个DispatcherServlet中的doDispatcher()方法来完成的,重点分析这个方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); //获取HandlerExecutionChain,在HandlerExecutionChain中包含了我们的Controller以及拦截器
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return; //如果找不到执行方法则退出
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); //通过我们的Handler来找到HandlerAdpter(处理器执行器)
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { //执行拦截器的preHadnle()方法
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); //执行具体的Controller中的方法,得到一个ModelAndView对象
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); //执行拦截器的postHandler方法
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); //在这里进行师徒解析的过程
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
这样DispatcherServlet的一次请求过程就完成了(当然这里只是粗略的解析了一下执行流程,之后再去看源码不断的细化)
springMvc的执行流程(源码分析)的更多相关文章
- springmvc执行流程 源码分析
进入DispatcherServlet 执行onRefresh,然后执行初始化方法initStrategies.然后调用doService——>doDispatch. 根据继承关系执行Servl ...
- Springboot中mybatis执行逻辑源码分析
Springboot中mybatis执行逻辑源码分析 在上一篇springboot整合mybatis源码分析已经讲了我们的Mapper接口,userMapper是通过MapperProxy实现的一个动 ...
- springmvc拦截器入门及其执行顺序源码分析
springmvc拦截器是偶尔会用到的一个功能,本案例来演示一个较简单的springmvc拦截器的使用,并通过源码来分析拦截器的执行顺序的控制.具体操作步骤为:1.maven项目引入spring依赖2 ...
- Django rest framework 的认证流程(源码分析)
一.基本流程举例: urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^users/', views.HostView.as_view() ...
- (五)myBatis架构以及SQlSessionFactory,SqlSession,通过代理执行crud源码分析---待更
MyBatis架构 首先MyBatis大致上可以分为四层: 1.接口层:这个比较容易理解,就是指MyBatis暴露给我们的各种方法,配置,可以理解为你import进来的各种类.,告诉用户你可以干什么 ...
- springmvc工作原理以及源码分析(基于spring3.1.0)
springmvc是一个基于spring的web框架.本篇文章对它的工作原理以及源码进行深入分析. 一.springmvc请求处理流程 二.springmvc的工作机制 三.springmvc核心源码 ...
- springMVC容器加载源码分析
springmvc是一个基于servlet容器的轻量灵活的mvc框架,在它整个请求过程中,为了能够灵活定制各种需求,所以提供了一系列的组件完成整个请求的映射,响应等等处理.这里我们来分析下spring ...
- Spring Securtiy 认证流程(源码分析)
当用 Spring Security 框架进行认证时,你可能会遇到这样的问题: 你输入的用户名或密码不管是空还是错误,它的错误信息都是 Bad credentials. 那么如果你想根据不同的情况给出 ...
- hbase0.96 put流程 源码分析
无意间多瞄了一眼hbase0.98的代码,想复习下put流程.发现htable里面已经找不到processBatchOfPuts()奇怪了.看了半天原来变化还真大事实上0.96就没这个了,于是又搞了个 ...
随机推荐
- 2018.06.30 BZOJ4765: 普通计算姬(dfs序+分块+树状数组)
4765: 普通计算姬 Time Limit: 30 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB Description "奋战三星期,造台计算机".小G响应号召,花了三小时 ...
- hdu-1066(大数)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1066 思路:统计2的个数,如果遇到5,就抵消,最后求和加上为来得及抵消的2的个数. 参考文章:http ...
- css3美化滚动条样式
1.改变浏览器默认的滚动条样式 ::-webkit-scrollbar-track-piece { //滚动条凹槽的颜色,还可以设置边框属性 background-color:#f8f8f8; } : ...
- python编码(七)
本文中,以'哈'来解释作示例解释所有的问题,“哈”的各种编码如下: 1. UNICODE (UTF8-16),C854:2. UTF-8,E59388:3. GBK,B9FE. 一.python中的s ...
- Java文件复制删除操作合集
import java.io.*; public class FileOperate { public FileOperate() { } /** * 新建目录 * @param folderPath ...
- 3D indoor map positioning with a smartphone image
menu 1. 基于Tango的三维建模技术(SLAM)(视觉SLAM,RGBD单目深度摄像机+罗盘仪)导出或不导出->Android 三维游戏开发技术(普通Android手机) 2. 基于An ...
- Java设计模式 -- 简单工厂模式(SimpleFactory)
一.什么是简单工厂模式 简单工厂模式属于类的创建型模式,又叫做静态工厂方法模式.通过专门定义一个类来负责创建其他类的实例,被创建的实例通常都具有共同的父类. 二.模式中包含的角色及其职责 1.工厂(C ...
- jbpm(流程管理)
1.jbpm是什么 JBPM,全称是Java Business Process Management(业务流程管理),它是覆盖了业务流程管理.工作流.服务协作等领域的一个开源的.灵活的.易扩展的可执行 ...
- python与JavaScript中正则表达式如何转换
使用python爬取网站数据的时候,总会遇到各种各样的反爬虫策略,有很大一部分都和JavaScript(以下简称为JS) 有关.在破解这些JS代码的过程中,经常会遇到模拟JS正则表达式的情况,因此,今 ...
- (线段树模板)A Simple Problem with Integers --POJ--3468
链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=3468 代码: #include<stdio.h> #include<algorithm> #include< ...
