IO多路复用之select总结(转载)
1、基本概念
IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程。IO多路复用适用如下场合:
(1)当客户处理多个描述字时(一般是交互式输入和网络套接口),必须使用I/O复用。
(2)当一个客户同时处理多个套接口时,而这种情况是可能的,但很少出现。
(3)如果一个TCP服务器既要处理监听套接口,又要处理已连接套接口,一般也要用到I/O复用。
(4)如果一个服务器即要处理TCP,又要处理UDP,一般要使用I/O复用。
(5)如果一个服务器要处理多个服务或多个协议,一般要使用I/O复用。
与多进程和多线程技术相比,I/O多路复用技术的最大优势是系统开销小,系统不必创建进程/线程,也不必维护这些进程/线程,从而大大减小了系统的开销。
2、select函数
该函数准许进程指示内核等待多个事件中的任何一个发送,并只在有一个或多个事件发生或经历一段指定的时间后才唤醒。函数原型如下:
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h> int select(int maxfdp1,fd_set *readset,fd_set *writeset,fd_set *exceptset,const struct timeval *timeout)
返回值:就绪描述符的数目,超时返回0,出错返回-1
函数参数介绍如下:
(1)第一个参数maxfdp1指定待测试的描述字个数,它的值是待测试的最大描述字加1(因此把该参数命名为maxfdp1),描述字0、1、2...maxfdp1-1均将被测试。
因为文件描述符是从0开始的。
(2)中间的三个参数readset、writeset和exceptset指定我们要让内核测试读、写和异常条件的描述字。如果对某一个的条件不感兴趣,就可以把它设为空指针。struct fd_set可以理解为一个集合,这个集合中存放的是文件描述符,可通过以下四个宏进行设置:
void FD_ZERO(fd_set *fdset); //清空集合
void FD_SET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符加入集合之中
void FD_CLR(int fd, fd_set *fdset); //将一个给定的文件描述符从集合中删除
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); // 检查集合中指定的文件描述符是否可以读写
(3)timeout告知内核等待所指定描述字中的任何一个就绪可花多少时间。其timeval结构用于指定这段时间的秒数和微秒数。
struct timeval{
long tv_sec; //seconds
long tv_usec; //microseconds
};
这个参数有三种可能:
(1)永远等待下去:仅在有一个描述字准备好I/O时才返回。为此,把该参数设置为空指针NULL。
(2)等待一段固定时间:在有一个描述字准备好I/O时返回,但是不超过由该参数所指向的timeval结构中指定的秒数和微秒数。
(3)根本不等待:检查描述字后立即返回,这称为轮询。为此,该参数必须指向一个timeval结构,而且其中的定时器值必须为0。
原理图:

3、测试程序
写一个TCP回射程序,程序的功能是:客户端向服务器发送信息,服务器接收并原样发送给客户端,客户端显示出接收到的信息。
服务端程序如下:

1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <errno.h>
5 #include <netinet/in.h>
6 #include <sys/socket.h>
7 #include <sys/select.h>
8 #include <sys/types.h>
9 #include <netinet/in.h>
10 #include <arpa/inet.h>
11 #include <unistd.h>
12 #include <assert.h>
13
14 #define IPADDR "127.0.0.1"
15 #define PORT 8787
16 #define MAXLINE 1024
17 #define LISTENQ 5
18 #define SIZE 10
19
20 typedef struct server_context_st
21 {
22 int cli_cnt; /*客户端个数*/
23 int clifds[SIZE]; /*客户端的个数*/
24 fd_set allfds; /*句柄集合*/
25 int maxfd; /*句柄最大值*/
26 } server_context_st;
27 static server_context_st *s_srv_ctx = NULL;
28 /*===========================================================================
29 * ==========================================================================*/
30 static int create_server_proc(const char* ip,int port)
31 {
32 int fd;
33 struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
34 fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM,0);
35 if (fd == -1) {
36 fprintf(stderr, "create socket fail,erron:%d,reason:%s\n",
37 errno, strerror(errno));
38 return -1;
39 }
40
41 /*一个端口释放后会等待两分钟之后才能再被使用,SO_REUSEADDR是让端口释放后立即就可以被再次使用。*/
42 int reuse = 1;
43 if (setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &reuse, sizeof(reuse)) == -1) {
44 return -1;
45 }
46
47 bzero(&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
48 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
49 inet_pton(AF_INET,ip,&servaddr.sin_addr);
50 servaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
51
52 if (bind(fd,(struct sockaddr*)&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr)) == -1) {
53 perror("bind error: ");
54 return -1;
55 }
56
57 listen(fd,LISTENQ);
58
59 return fd;
60 }
61
62 static int accept_client_proc(int srvfd)
63 {
64 struct sockaddr_in cliaddr;
65 socklen_t cliaddrlen;
66 cliaddrlen = sizeof(cliaddr);
67 int clifd = -1;
68
69 printf("accpet clint proc is called.\n");
70
71 ACCEPT:
72 clifd = accept(srvfd,(struct sockaddr*)&cliaddr,&cliaddrlen);
73
74 if (clifd == -1) {
75 if (errno == EINTR) {
76 goto ACCEPT;
77 } else {
78 fprintf(stderr, "accept fail,error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
79 return -1;
80 }
81 }
82
83 fprintf(stdout, "accept a new client: %s:%d\n",
84 inet_ntoa(cliaddr.sin_addr),cliaddr.sin_port);
85
86 //将新的连接描述符添加到数组中
87 int i = 0;
88 for (i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
89 if (s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] < 0) {
90 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = clifd;
91 s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt++;
92 break;
93 }
94 }
95
96 if (i == SIZE) {
97 fprintf(stderr,"too many clients.\n");
98 return -1;
99 }
100
101 }
102
103 static int handle_client_msg(int fd, char *buf)
104 {
105 assert(buf);
106 printf("recv buf is :%s\n", buf);
107 write(fd, buf, strlen(buf) +1);
108 return 0;
109 }
110
111 static void recv_client_msg(fd_set *readfds)
112 {
113 int i = 0, n = 0;
114 int clifd;
115 char buf[MAXLINE] = {0};
116 for (i = 0;i <= s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt;i++) {
117 clifd = s_srv_ctx->clifds[i];
118 if (clifd < 0) {
119 continue;
120 }
121 /*判断客户端套接字是否有数据*/
122 if (FD_ISSET(clifd, readfds)) {
123 //接收客户端发送的信息
124 n = read(clifd, buf, MAXLINE);
125 if (n <= 0) {
126 /*n==0表示读取完成,客户都关闭套接字*/
127 FD_CLR(clifd, &s_srv_ctx->allfds);
128 close(clifd);
129 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = -1;
130 continue;
131 }
132 handle_client_msg(clifd, buf);
133 }
134 }
135 }
136 static void handle_client_proc(int srvfd)
137 {
138 int clifd = -1;
139 int retval = 0;
140 fd_set *readfds = &s_srv_ctx->allfds;
141 struct timeval tv;
142 int i = 0;
143
144 while (1) {
145 /*每次调用select前都要重新设置文件描述符和时间,因为事件发生后,文件描述符和时间都被内核修改啦*/
146 FD_ZERO(readfds);
147 /*添加监听套接字*/
148 FD_SET(srvfd, readfds);
149 s_srv_ctx->maxfd = srvfd;
150
151 tv.tv_sec = 30;
152 tv.tv_usec = 0;
153 /*添加客户端套接字*/
154 for (i = 0; i < s_srv_ctx->cli_cnt; i++) {
155 clifd = s_srv_ctx->clifds[i];
156 /*去除无效的客户端句柄*/
157 if (clifd != -1) {
158 FD_SET(clifd, readfds);
159 }
160 s_srv_ctx->maxfd = (clifd > s_srv_ctx->maxfd ? clifd : s_srv_ctx->maxfd);
161 }
162
163 /*开始轮询接收处理服务端和客户端套接字*/
164 retval = select(s_srv_ctx->maxfd + 1, readfds, NULL, NULL, &tv);
165 if (retval == -1) {
166 fprintf(stderr, "select error:%s.\n", strerror(errno));
167 return;
168 }
169 if (retval == 0) {
170 fprintf(stdout, "select is timeout.\n");
171 continue;
172 }
173 if (FD_ISSET(srvfd, readfds)) {
174 /*监听客户端请求*/
175 accept_client_proc(srvfd);
176 } else {
177 /*接受处理客户端消息*/
178 recv_client_msg(readfds);
179 }
180 }
181 }
182
183 static void server_uninit()
184 {
185 if (s_srv_ctx) {
186 free(s_srv_ctx);
187 s_srv_ctx = NULL;
188 }
189 }
190
191 static int server_init()
192 {
193 s_srv_ctx = (server_context_st *)malloc(sizeof(server_context_st));
194 if (s_srv_ctx == NULL) {
195 return -1;
196 }
197
198 memset(s_srv_ctx, 0, sizeof(server_context_st));
199
200 int i = 0;
201 for (;i < SIZE; i++) {
202 s_srv_ctx->clifds[i] = -1;
203 }
204
205 return 0;
206 }
207
208 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
209 {
210 int srvfd;
211 /*初始化服务端context*/
212 if (server_init() < 0) {
213 return -1;
214 }
215 /*创建服务,开始监听客户端请求*/
216 srvfd = create_server_proc(IPADDR, PORT);
217 if (srvfd < 0) {
218 fprintf(stderr, "socket create or bind fail.\n");
219 goto err;
220 }
221 /*开始接收并处理客户端请求*/
222 handle_client_proc(srvfd);
223 server_uninit();
224 return 0;
225 err:
226 server_uninit();
227 return -1;
228 }

客户端程序如下:

1 #include <netinet/in.h>
2 #include <sys/socket.h>
3 #include <stdio.h>
4 #include <string.h>
5 #include <stdlib.h>
6 #include <sys/select.h>
7 #include <time.h>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <sys/types.h>
10 #include <errno.h>
11
12 #define MAXLINE 1024
13 #define IPADDRESS "127.0.0.1"
14 #define SERV_PORT 8787
15
16 #define max(a,b) (a > b) ? a : b
17
18 static void handle_recv_msg(int sockfd, char *buf)
19 {
20 printf("client recv msg is:%s\n", buf);
21 sleep(5);
22 write(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf) +1);
23 }
24
25 static void handle_connection(int sockfd)
26 {
27 char sendline[MAXLINE],recvline[MAXLINE];
28 int maxfdp,stdineof;
29 fd_set readfds;
30 int n;
31 struct timeval tv;
32 int retval = 0;
33
34 while (1) {
35
36 FD_ZERO(&readfds);
37 FD_SET(sockfd,&readfds);
38 maxfdp = sockfd;
39
40 tv.tv_sec = 5;
41 tv.tv_usec = 0;
42
43 retval = select(maxfdp+1,&readfds,NULL,NULL,&tv);
44
45 if (retval == -1) {
46 return ;
47 }
48
49 if (retval == 0) {
50 printf("client timeout.\n");
51 continue;
52 }
53
54 if (FD_ISSET(sockfd, &readfds)) {
55 n = read(sockfd,recvline,MAXLINE);
56 if (n <= 0) {
57 fprintf(stderr,"client: server is closed.\n");
58 close(sockfd);
59 FD_CLR(sockfd,&readfds);
60 return;
61 }
62
63 handle_recv_msg(sockfd, recvline);
64 }
65 }
66 }
67
68 int main(int argc,char *argv[])
69 {
70 int sockfd;
71 struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
72
73 sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
74
75 bzero(&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
76 servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
77 servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
78 inet_pton(AF_INET,IPADDRESS,&servaddr.sin_addr);
79
80 int retval = 0;
81 retval = connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&servaddr,sizeof(servaddr));
82 if (retval < 0) {
83 fprintf(stderr, "connect fail,error:%s\n", strerror(errno));
84 return -1;
85 }
86
87 printf("client send to server .\n");
88 write(sockfd, "hello server", 32);
89
90 handle_connection(sockfd);
91
92 return 0;
93 }

4、程序结果
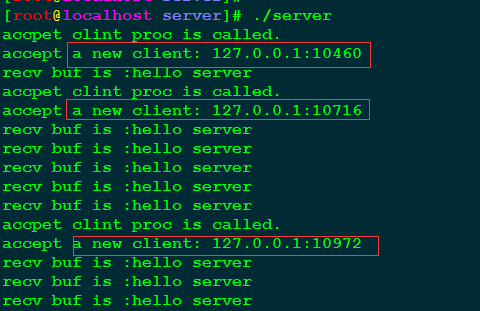
启动服务程序,执行三个个客户程序进行测试,结果如下图所示:
IO多路复用之select总结(转载)的更多相关文章
- IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll
本文转载自IO多路复用之select.poll.epoll 导语 IO多路复用:通过一种机制,一个进程可以监视多个描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(一般是读就绪或者写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作. ...
- IO多路复用之select
IO多路复用之select总结 1.基本概念 IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,它就通知该进程.IO多路复用适用如下场合: (1)当客户处理多个描述字时(一般是交 ...
- 网络通信 --> IO多路复用之select、poll、epoll详解
IO多路复用之select.poll.epoll详解 目前支持I/O多路复用的系统调用有 select,pselect,poll,epoll,I/O多路复用就是通过一种机制,一个进程可以监视 ...
- python网络编程——IO多路复用之select
1 IO多路复用的概念 原生socket客户端在与服务端建立连接时,即服务端调用accept方法时是阻塞的,同时服务端和客户端在收发数据(调用recv.send.sendall)时也是阻塞的.原生so ...
- 【python】-- IO多路复用(select、poll、epoll)介绍及实现
IO多路复用(select.poll.epoll)介绍及select.epoll的实现 IO多路复用中包括 select.pool.epoll,这些都属于同步,还不属于异步 一.IO多路复用介绍 1. ...
- Python——IO多路复用之select模块epoll方法
Python——IO多路复用之select模块epoll方法 使用epoll方法实现IO多路复用,使用方法基本与poll方法一致,epoll效率要高于select和poll. .├── epoll_c ...
- Python——IO多路复用之select模块poll方法
Python——IO多路复用之select模块poll方法 使用poll方法实现IO多路复用 .├── poll_client.py├── poll_server.py└── settings.py ...
- Python——IO多路复用之select模块select方法
Python——IO多路复用之select模块select方法 使用select模块的select方法实现Python——IO多路复用 实现同时将终端输入的文本以及客户端传输的文本写入文本文件中: w ...
- IO多路复用(select、poll、epoll)介绍及select、epoll的实现
IO多路复用(select.poll.epoll)介绍及select.epoll的实现 IO多路复用中包括 select.pool.epoll,这些都属于同步,还不属于异步 一.IO多路复用介绍 1. ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷 P7324 - [WC2021] 表达式求值(状压+dp)
题面传送门 现场人傻系列-- 首先建出 \(E\) 的表达式树,具体来说表达式的每一个叶子节点表示一个数组 \(A_i\),每一个非叶子节点都表示一次运算,它的值表示左右儿子进行该运算后得到的结果.这 ...
- 洛谷 P4709 - 信息传递(置换+dp)
题面传送门 一道挺有意思的题罢-- 首先看到这种与置换乘法相关的题,首先把这些置换拆成一个个置换环,假设输入的置换有 \(m\) 个置换环,大小分别为 \(s_1,s_2,\cdots,s_m\),显 ...
- NOIP2021 游记
不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分不要挂分释迦牟尼脚绽莲花菩提达摩你真伟大天上天下唯我独尊如来佛祖太上老君耶稣耶稣 ...
- 力扣 - 剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值
题目 剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值 思路1 因为是要求最大价值,而且只能移动下方或者右方,因此,每个位置的最大值就是本身的值加上上边 / 左边 中的最大值,然后每次遍历都可以复用上一次的值 ...
- python-django-数据查询条件
查询用户的状态是2或者是4的情况 空值和空字符串是不一样的东西!!! 需要注意的是: 项目setting.py里面的时区采用的是美国的时区,我们不要使用这个时区 使用这个时区的,我们输入的日期会进行转 ...
- python-django-模板标签
注意:这个控制语句和python的差不多,但是记住必须有endfor 和endif 结尾 模板文件的django格式的注释是不会出现再网页渲染的源代码当中的 使用列子: <!DOCTYPE ht ...
- WebRTC视频分辨率设置
前面我们能够打开摄像头.getUserMedia()时会传入参数,在参数里我们可以指定宽高信息.通过宽高参数控制输出的视频分辨率. html 在页面上摆放一些元素,下面是主要部分 <div id ...
- 日常Java 2021/9/28
字符串反转 package m; public class m { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义一个字符串 String str = &q ...
- Windows系统安装MySQL详细教程和安装过程中问题汇总(命令安装),更新时间2021-12-8
安装包下载 下载地址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/ 点击下载之后,可以选择注册Oracle账号,也可以跳过直接下载. 下载完成后,选择一个磁盘内放置并解 ...
- acid, acknowledge, acquaint
acid sulphuric|hydrochloric|nitric|carbolic|citric|lactic|nucleic|amino acid: 硫|盐|硝|碳|柠檬|乳|核|氨基酸 王水是 ...
