CUDA中block和thread的合理划分配置
CUDA并行编程的基本思路是把一个很大的任务划分成N个简单重复的操作,创建N个线程分别执行执行,每个网格(Grid)可以最多创建65535个线程块,每个线程块(Block)一般最多可以创建512个并行线程,在第一个CUDA程序中对核函数的调用是:
addKernel<<<1, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
这里的<<<>>>运算符内是核函数的执行参数,告诉编译器运行时如何启动核函数,用于说明内核函数中的线程数量,以及线程是如何组织的。
<<<>>>运算符完整的执行配置参数形式是<<<Dg, Db, Ns, S>>>
- 参数Dg用于定义整个grid的维度和尺寸,即一个grid有多少个block。为dim3类型。Dim3 Dg(Dg.x, Dg.y, 1)表示grid中每行有Dg.x个block,每列有Dg.y个block,第三维恒为1(目前一个核函数只有一个grid)。整个grid中共有Dg.x*Dg.y个block,其中Dg.x和Dg.y最大值为65535。
- 参数Db用于定义一个block的维度和尺寸,即一个block有多少个thread。为dim3类型。Dim3 Db(Db.x, Db.y, Db.z)表示整个block中每行有Db.x个thread,每列有Db.y个thread,高度为Db.z。Db.x和Db.y最大值为512,Db.z最大值为62。 一个block中共有Db.x*Db.y*Db.z个thread。计算能力为1.0,1.1的硬件该乘积的最大值为768,计算能力为1.2,1.3的硬件支持的最大值为1024。
- 参数Ns是一个可选参数,用于设置每个block除了静态分配的shared Memory以外,最多能动态分配的shared memory大小,单位为byte。不需要动态分配时该值为0或省略不写。
- 参数S是一个cudaStream_t类型的可选参数,初始值为零,表示该核函数处在哪个流之中。
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size);
__global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b)
{
int i = blockIdx.x;
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
int main()
{
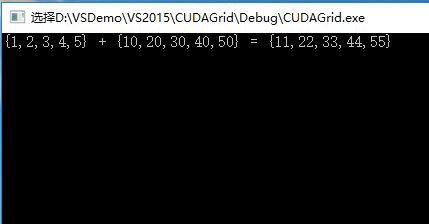
const int arraySize = 5;
const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int c[arraySize] = { 0 };
// Add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return 1;
}
printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n",
c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4]);
// cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return 1;
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
// Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size)
{
int *dev_a = 0;
int *dev_b = 0;
int *dev_c = 0;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
}
// Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
//addKernel<<<1, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
addKernel << <size, 1 >> > (dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
// Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
}
// cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
}
// Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
return cudaStatus;
}
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size);
__global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b)
{
int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x;
if (i < 15)
c[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
int main()
{
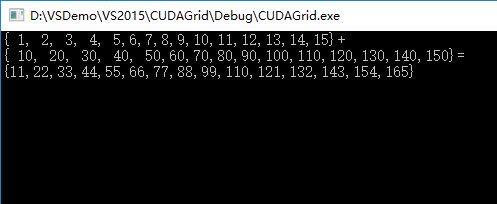
const int arraySize = 15;
const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 };
const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120,130,140,150 };
int c[arraySize] = { 0 };
// Add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return 1;
}
printf("{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15}+\n{ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50,60,70,80,90,100,110,120,130,140,150}=\n{%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n",
c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4], c[5], c[6], c[7], c[8], c[9], c[10], c[11], c[12], c[13], c[14]);
// cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and
// tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return 1;
}
getchar();
return 0;
}
// Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel.
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size)
{
int *dev_a = 0;
int *dev_b = 0;
int *dev_c = 0;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system.
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
}
// Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) .
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
// Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element.
//addKernel<<<1, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
addKernel << <(size + 5) / 6, 6 >> > (dev_c, dev_a, dev_b);
// Check for any errors launching the kernel
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
}
// cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns
// any errors encountered during the launch.
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
}
// Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory.
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Error:
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
return cudaStatus;
}
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include <highgui.hpp>
using namespace cv;
#define DIM 600 //图像长宽
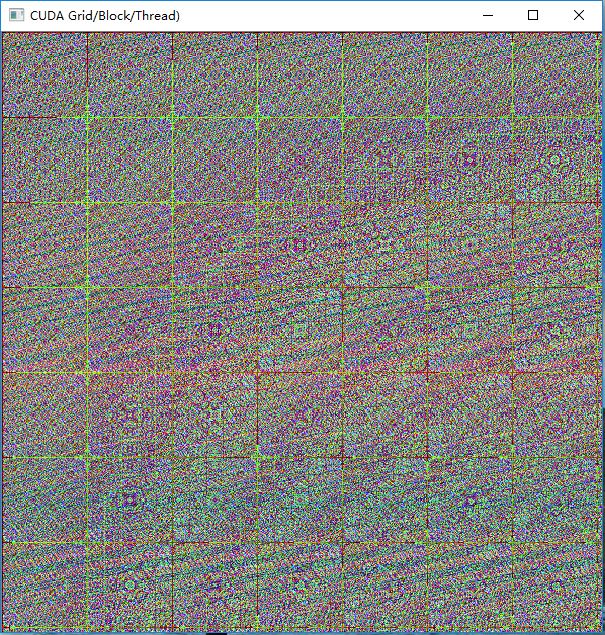
__global__ void kernel(unsigned char *ptr)
{
// map from blockIdx to pixel position
int x = blockIdx.x;
int y = blockIdx.y;
int offset = x + y * gridDim.x;
//BGR设置
ptr[offset * 3 + 0] = 999 * x*y % 255;
ptr[offset * 3 + 1] = 99 * x*x*y*y % 255;
ptr[offset * 3 + 2] = 9 * offset*offset % 255;
}
// globals needed by the update routine
struct DataBlock
{
unsigned char *dev_bitmap;
};
int main(void)
{
DataBlock data;
cudaError_t error;
Mat image = Mat(DIM, DIM, CV_8UC3, Scalar::all(0));
data.dev_bitmap = image.data;
unsigned char *dev_bitmap;
error = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_bitmap, 3 * image.cols*image.rows);
data.dev_bitmap = dev_bitmap;
dim3 grid(DIM, DIM);
//DIM*DIM个线程块
kernel <<<grid, 1 >>> (dev_bitmap);
error = cudaMemcpy(image.data, dev_bitmap,
3 * image.cols*image.rows,
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
error = cudaFree(dev_bitmap);
imshow("CUDA Grid/Block/Thread)", image);
waitKey();
}执行效果:
CUDA中block和thread的合理划分配置的更多相关文章
- CUDA中确定你显卡的thread和block数
CUDA中确定你显卡的thread和block数 在进行并行计算时, 你的显卡所支持创建的thread数与block数是有限制的, 因此, 需要自己提前确定够用, 再进行计算, 否则, 你需要改进你的 ...
- CUDA中并行规约(Parallel Reduction)的优化
转自: http://hackecho.com/2013/04/cuda-parallel-reduction/ Parallel Reduction是NVIDIA-CUDA自带的例子,也几乎是所有C ...
- cuda学习2-block与thread数量的选取
由上一节可知,在main函数中,cuda程序的并行能力是在add<<<N,1>>>( dev_a, dev_b, dev_c )函数中体现的,这里面设置的是由N个b ...
- OpenCV二维Mat数组(二级指针)在CUDA中的使用
CUDA用于并行计算非常方便,但是GPU与CPU之间的交互,比如传递参数等相对麻烦一些.在写CUDA核函数的时候形参往往会有很多个,动辄达到10-20个,如果能够在CPU中提前把数据组织好,比如使用二 ...
- CUDA中使用多维数组
今天想起一个问题,看到的绝大多数CUDA代码都是使用的一维数组,是否可以在CUDA中使用一维数组,这是一个问题,想了各种问题,各种被77的错误状态码和段错误折磨,最后发现有一个cudaMallocMa ...
- swift中block的使用
在OC中习惯用block来传值,而swift中,block被重新定义了一下,叫闭包: 使用的技巧:谁定义谁传值: 案例使用A.B控制器: 1~4步在B中执行,最后在A中执行: - B控制器: 1- ...
- Objective-C中block的底层原理
先出2个考题: 1. 上面打印的是几,captureNum2 出去作用域后是否被销毁?为什么? 同样类型的题目: 问:打印的数字为多少? 有人会回答:mutArray是captureObject方法的 ...
- iOS中block的用法 以及和函数用法的区别
ios中block的用法和函数的用法大致相同 但是block的用法的灵活性更高: 不带参数的block: void ^(MyBlock)() = ^{}; 调用的时候 MyBlock(); 带参数的 ...
- cuda中时间用法
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/jdhanhua/article/details/4843653 在CUDA中统计运算时间,大致有三种方法: <1>使用cutil.h中的函 ...
随机推荐
- QWaitCondition 的正确使用方法(通过 mutex 把有严格时序要求的代码保护起来,同时把 wakeAll() 也用同一个 mutex 保护起来)
简单用法 QWaitCondition 用于多线程的同步,一个线程调用QWaitCondition::wait() 阻塞等待,直到另一个线程调用QWaitCondition::wake() 唤醒才继续 ...
- UVA 11090 - Going in Cycle!! SPFA
http://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem&p ...
- 如何使用SVN协调代源代码,多人同步开发
转自linFen原文如何使用SVN协调代源代码,多人同步开发 1.什么是SVN SVN是一种版本管理系统,前身是CVS,是开源软件的基石.即使在沟通充分的情况下,多人维护同一份源代码的一定也会出现混乱 ...
- 安装spark1.3.1单机环境 分类: B8_SPARK 2015-04-27 14:52 1873人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
本文介绍安装spark单机环境的方法,可用于测试及开发.主要分成以下4部分: (1)环境准备 (2)安装scala (3)安装spark (4)验证安装情况 1.环境准备 (1)配套软件版本要求:Sp ...
- get_mysql_conn_info.py
#!/usr/bin/env python#-*- encoding: utf8 -*- import xlrd """此模块作用:从excel文件获取数据库连接信息,第 ...
- HDU 1800 Flying to the Mars Trie或者hash
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1800 题目大意: 又是废话连篇 给你一些由数字组成的字符串,判断去掉前导0后那个字符串出现频率最高. 一开始敲h ...
- POJ 1065 Wooden Sticks(zoj 1025) 最长单调子序列
POJ :http://poj.org/problem?id=1065 ZOJ: http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId= ...
- Eclipse 使用技巧之 ---- 查看本类调用和被调用列表
当工程复杂的情况下,用眼睛去人工查看调用情况是很费力也没必要的.我们需要用 Eclipse 来做这点. (1) 我们查看本类调用他类情况可以直接看 import . (2) 如果要查看本类 ...
- 前端js实现打印excel表格
产品原型: 图片.png 功能需求:点击导出考勤表格按钮,会自动下载成Excel格式 图片.png 图片.png jsp页面代码: <div class="tools"> ...
- 《转》couldn't connect to server 127.0.0.1:27017 at src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:145
couldn't connect to server 127.0.0.1:27017 at src/mongo/shell/mongo.js:145,有须要的朋友能够參考下. 应为昨天安装的时候没及时 ...
