vfs:结构体对象
VFS结构体
super_block
存储一个已安装的文件系统的控制信息,代表一个已安装的文件系统;每次一个实际的文件系统被安装时, 内核会从磁盘的特定位置读取一些控制信息来填充内存中的超级块对象。一个安装实例和一个超级块对象一一对应。 超级块通过其结构中的一个域s_type记录它所属的文件系统类型。
struct super_block { //超级块数据结构
struct list_head s_list; /*指向超级块链表的指针*/
……
struct file_system_type *s_type; /*文件系统类型*/
struct super_operations *s_op; /*超级块方法*/
……
struct list_head s_instances; /*该类型文件系统*/
……
};
struct super_operations { //超级块方法
……
//该函数在给定的超级块下创建并初始化一个新的索引节点对象
struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb);
……
//该函数从磁盘上读取索引节点,并动态填充内存中对应的索引节点对象的剩余部分
void (*read_inode) (struct inode *);
……
};
inode
索引节点对象存储了文件的相关信息,代表了存储设备上的一个实际的物理文件。当一个 文件首次被访问时,内核会在内存中组装相应的索引节点对象,以便向内核提供对一个文件进行操 作时所必需的全部信息;这些信息一部分存储在磁盘特定位置,另外一部分是在加载时动态填充的。
struct inode {//索引节点结构
……
struct inode_operations *i_op; /*索引节点操作表*/
struct file_operations *i_fop; /*该索引节点对应文件的文件操作集*/
struct super_block *i_sb; /*相关的超级块*/
……
};
struct inode_operations { //索引节点方法
……
//该函数为dentry对象所对应的文件创建一个新的索引节点,主要是由open()系统调用来调用
int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int, struct nameidata *);
//在特定目录中寻找dentry对象所对应的索引节点
struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, struct nameidata *);
……
};
dentry
引入目录项的概念主要是出于方便查找文件的目的。一个路径的各个组成部分,不管是目录还是 普通的文件,都是一个目录项对象。如,在路径/home/source/test.c中,目录 /, home, source和文件 test.c都对应一个目录项对象。不同于前面的两个对象,目录项对象没有对应的磁盘数据结构,VFS在遍 历路径名的过程中现场将它们逐个地解析成目录项对象。
struct dentry {//目录项结构
……
struct inode *d_inode; /*相关的索引节点*/
struct dentry *d_parent; /*父目录的目录项对象*/
struct qstr d_name; /*目录项的名字*/
……
struct list_head d_subdirs; /*子目录*/
……
struct dentry_operations *d_op; /*目录项操作表*/
struct super_block *d_sb; /*文件超级块*/
……
};
struct dentry_operations {
int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int); //判断目录项是否有效;
int (*d_weak_revalidate)(struct dentry *, unsigned int);
int (*d_hash)(const struct dentry *, struct qstr *); //为目录项生成散列值;
int (*d_compare)(const struct dentry *, const struct dentry *,
unsigned int, const char *, const struct qstr *);
int (*d_delete)(const struct dentry *);
void (*d_release)(struct dentry *);
void (*d_prune)(struct dentry *);
void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *);
char *(*d_dname)(struct dentry *, char *, int);
struct vfsmount *(*d_automount)(struct path *);
int (*d_manage)(struct dentry *, bool);
} ____cacheline_aligned;
file
文件对象是已打开的文件在内存中的表示,主要用于建立进程和磁盘上的文件的对应关系。它由sys_open() 现场创建,由sys_close()销毁。文件对象和物理文件的关系有点像进程和程序的关系一样。当我们站在用户空间来看 待VFS,我们像是只需与文件对象打交道,而无须关心超级块,索引节点或目录项。因为多个进程可以同时打开和操作 同一个文件,所以同一个文件也可能存在多个对应的文件对象。文件对象仅仅在进程观点上代表已经打开的文件,它 反过来指向目录项对象(反过来指向索引节点)。一个文件对应的文件对象可能不是惟一的,但是其对应的索引节点和 目录项对象无疑是惟一的。
struct file {
……
struct list_head f_list; /*文件对象链表*/
struct dentry *f_dentry; /*相关目录项对象*/
struct vfsmount *f_vfsmnt; /*相关的安装文件系统*/
struct file_operations *f_op; /*文件操作表*/
……
};
struct file_operations {
……
//文件读操作
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
……
//文件写操作
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
……
int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);
……
//文件打开操作
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
……
};
进程与超级块、文件、索引结点、目录项的关系
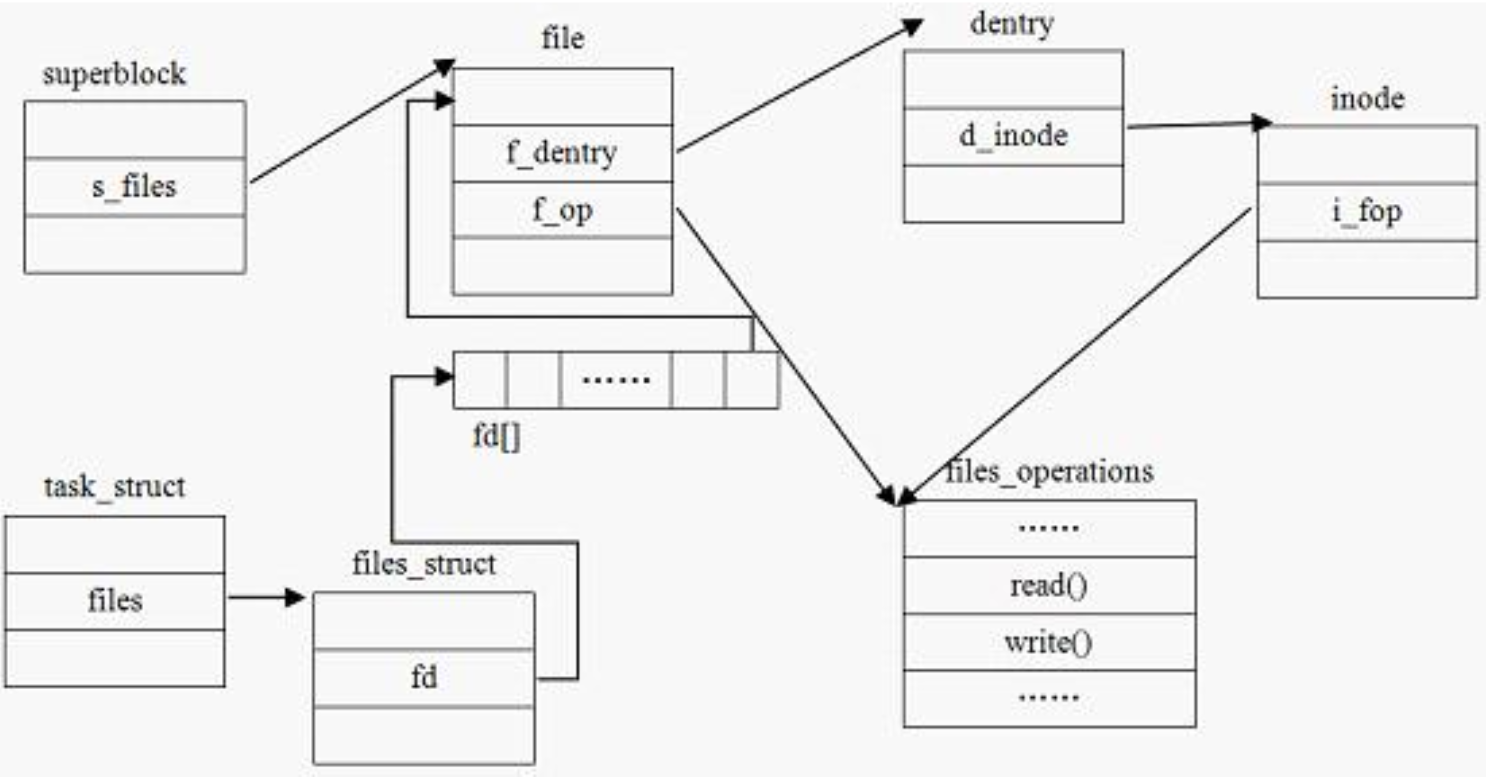
nameidata路径查找辅助结构
struct path {
struct vfsmount *mnt;
struct dentry *dentry;
};
/*
* "quick string" -- eases parameter passing, but more importantly
* saves "metadata" about the string (ie length and the hash).
*
* hash comes first so it snuggles against d_parent in the
* dentry.
*/
struct qstr {
union {
struct {
HASH_LEN_DECLARE;
};
u64 hash_len;
};
const unsigned char *name;
};
struct nameidata {
struct path path;
struct qstr last;
struct path root;
struct inode *inode; /* path.dentry.d_inode */
unsigned int flags;
unsigned seq;
int last_type;
unsigned depth;
char *saved_names[MAX_NESTED_LINKS + 1];
};
open.c
kernel-3-10
@do_sys_open
@get_unused_fd_flags
@do_filp_open
1.开始填充nameidata
2.开始填充file
@path_openat
1. file = get_empty_filp(); //开始填充file
2. file->f_flags = op->open_flag; //开始填充file
3. path_init(dfd, pathname->name, flags | LOOKUP_PARENT, nd, &base);
//开始填充初始化nameidata,并且从根查找
3.1 nd->last_type = LAST_ROOT;
3.2 nd->flags = flags | LOOKUP_JUMPED;
3.3 nd->depth = 0;
3.4 nd->path = nd->root;
3.5 nd->inode = inode;
4. link_path_walk(pathname->name, nd);
5. do_last(nd, &path, file, op, &opened, pathname);
// 某些条件下会进入:
5.1 fput(file): //释放file
5.2 dput(path->dentry); // 释放dentry
@get_unused_fd: 得到一个可用的文件描述符;通过该函数,可知文件描述符实质是进程打开文件列表中对应某个文件对象的索引值;
@do_filp_open: do_filp_open()打开文件,返回一个file对象,代表由该进程打开的一个文件;进程通过这样的一个数据结构对物理文件进行读写操作。
@path_openat:返回一个file对象,@do_filp_open 直接把活扔给@path_openat. filp = path_openat(dfd, pathname, &nd, op, flags | LOOKUP_RCU)
vfs:结构体对象的更多相关文章
- C++结构体对象数组的二进制方式读写
以一个学生信息的结构体数组为例. #include<iostream>#include<string>#include<fstream>using namespac ...
- golang 修改数组中结构体对象的值的坑
对对象数组逐个修改元素属性时候没有成功,代码如下: for _, configure := range configures { configure.Price = specPriceMap[conf ...
- tableview setData 设置数据(结构体对象)
定义设置的对象类型 Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(LISTITEMDATA *) 设置数据类型 LISTITEMDATA *ptask = &(const_cast<LISTIT ...
- Objective-C中将结构体与联合体封装为NSValue对象
在Clang 3.7之前,Objective-C已经可以使用类似@100.@YES.@10.5f等字面量表示一个NSNumber对象:用类似@"xxx"的字面量表示一个NSStri ...
- C#中的结构体和对象区别
经常听到有朋友在讨论C#中的结构与类有什么区别.正好这几日闲来无事,自己总结一下,希望大家指点. 1. 首先是语法定义上的区别啦,这个就不用多说了.定义类使用关键字class 定义结构使用关键字str ...
- C#中结构体和类的区别
结构体和类同样能够定义字段,方法和构造函数,都能实例化对象,这样看来结构体和类的功能好像是一样的了,但是他们在数据的存储上是不一样的 C#结构体和类的区别问题:这两种数据类型的本质区别主要是各自指向的 ...
- C的结构体使用
C的结构体演示 #include <stdio.h> struct A //建立结构体A { char *name; int s1; struct A *next; }; void mai ...
- C#中的结构体与类的区别
经常听到有朋友在讨论C#中的结构与类有什么区别.正好这几日闲来无事,自己总结一下,希望大家指点. 1. 首先是语法定义上的区别啦,这个就不用多说了.定义类使用关键字class 定义结构使用关键字str ...
- C#基础--struct(结构体)
结构体和类有点类似 我们定义一个类的时候 是class 类名 定义结构体的时候是 struct 结构体名 结构体的写法 struct Point { // public int ...
随机推荐
- CF #324 DIV2 E题
这题很简单,把目标位置排序,把目标位置在当前位置前面的往前交换,每次都是贪心选择第一个满足这样要求的数字. #include <iostream> #include <cstdio& ...
- clear out all variables without closing terminal
clear out all variables without closing terminal https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/172655/cle ...
- CSS之实现二级菜单动态出现
一直觉得二级菜单的出现效果仅仅有js才干控制.今天研究了一下阿里巴巴站点的首页,才发现,原来二级菜单的动态显示也能够使用CSS来控制,原来对CSS是静态的东西一直是误解它了,CSS也能够实现动态的效果 ...
- Python爬虫抓取csdn博客
昨天晚上为了下载保存某位csdn大牛的所有博文,写了一个爬虫来自己主动抓取文章并保存到txt文本,当然也能够 保存到html网页中. 这样就能够不用Ctrl+C 和Ctrl+V了,很方便.抓取别的站点 ...
- POJ - 3281 Dining(拆点+最大网络流)
Dining Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 18230 Accepted: 8132 Descripti ...
- BNUOJ ->Borrow Classroom(LCA)
B. Borrow Classroom Time Limit: 5000ms Memory Limit: 262144KB 每年的BNU校赛都会有两次赛前培训,为此就需要去借教室,由于SK同学忙于出题 ...
- git使用简易指南(转)
创建新仓库 创建新文件夹,打开,然后执行 git init以创建新的 git 仓库. 检出仓库 执行如下命令以创建一个本地仓库的克隆版本:git clone /path/to/repository 如 ...
- P1966 火柴排队(逆序对)
P1966 火柴排队 题目描述 涵涵有两盒火柴,每盒装有 n 根火柴,每根火柴都有一个高度. 现在将每盒中的火柴各自排成一列, 同一列火柴的高度互不相同, 两列火柴之间的距离定义为: ∑(ai-bi) ...
- B - Substrings Sort
Problem description You are given nn strings. Each string consists of lowercase English letters. Rea ...
- Quartz 表达式的学习
只记录用到过的,不全面 Quartz版本:quartz-all-1.6.0.jar 先看图 其他示例: 0 5,6,13 * * ? 意义:每日5:00,6:00,13:00 被触发 0 10,30 ...
