Could not locate executable null 解决办法
HBase版本:0.94.15-cdh4.7.0
在 HBase中,大部分的操作都是在RegionServer完成的,Client端想要插入、删除、查询数据都需要先找到相应的 RegionServer。什么叫相应的RegionServer?就是管理你要操作的那个Region的RegionServer。Client本身并 不知道哪个RegionServer管理哪个Region,那么它是如何找到相应的RegionServer的?本文就是在研究源码的基础上了解这个过程。
首先来看看写过程的序列图:

客户端代码
1、put方法
HTable的put有两个方法:
public void put(final Put put) throws IOException {
doPut(put);
if (autoFlush) {
flushCommits();
}
}
public void put(final List<Put> puts) throws IOException {
for (Put put : puts) {
doPut(put);
}
if (autoFlush) {
flushCommits();
}
}
从上面代码可以看出:你既可以一次put一行记录也可以一次put多行记录,两个方法内部都会调用doPut方法,最后再来根据autoFlush(默认为true)判断是否需要flushCommits,在autoFlush为false的时候,如果当前容量超过了缓冲区大小(默认值为:2097152=2M),也会调用flushCommits方法。也就是说,在自动提交情况下,你可以手动控制通过一次put多条记录(这时候缓冲区不会满),然后将这些记录flush,以提高写操作tps。
doPut代码如下:
private void doPut(Put put) throws IOException{
validatePut(put); //验证Put有效,主要是判断kv的长度
writeBuffer.add(put); //写入缓存
currentWriteBufferSize += put.heapSize(); //计算缓存容量
if (currentWriteBufferSize > writeBufferSize) {
flushCommits(); //如果超过缓存容量,则调用flushCommits()
}
}
2、flushCommits方法如下:
public void flushCommits() throws IOException {
try {
Object[] results = new Object[writeBuffer.size()];
try {
//调用HConnection来提交Put
this.connection.processBatch(writeBuffer, tableName, pool, results);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException(e);
} finally {
// mutate list so that it is empty for complete success, or contains
// only failed records results are returned in the same order as the
// requests in list walk the list backwards, so we can remove from list
// without impacting the indexes of earlier members
for (int i = results.length - 1; i>=0; i--) {
if (results[i] instanceof Result) {
// successful Puts are removed from the list here.
writeBuffer.remove(i);
}
}
}
} finally {
if (clearBufferOnFail) {
writeBuffer.clear();
currentWriteBufferSize = 0;
} else {
// the write buffer was adjusted by processBatchOfPuts
currentWriteBufferSize = 0;
//currentWriteBufferSize又重新计算了一遍,看来一批提交不一定会全部提交完
for (Put aPut : writeBuffer) {
currentWriteBufferSize += aPut.heapSize();
}
}
}
}
其核心是调用this.connection的processBatch方法,其参数有:writeBuffer、tableName、pool、results
- writeBuffer,缓冲区,带提交的数据
- tableName,表名
- pool,ExecutorService类,可以通过HTable构造方法传入一个参数来初始化(例如:HConnectionManager的
getTable(byte[] tableName, ExecutorService pool)方法),也可以内部初始化。内部初始化时,其最大线程数由hbase.htable.threads.max设置,keepAliveTime由hbase.htable.threads.keepalivetime设置,默认为60秒 - results,保存运行结果
在默认情况下,connection由如下方式初始化:
this.connection = HConnectionManager.getConnection(conf); //HConnection的实现类为HConnectionImplementation
3、ConnectionImplementation的processBatch方法
public void processBatch(List<? extends Row> list,
final byte[] tableName,
ExecutorService pool,
Object[] results) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// This belongs in HTable!!! Not in here. St.Ack
// results must be the same size as list
if (results.length != list.size()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument results must be the same size as argument list");
}
processBatchCallback(list, tableName, pool, results, null);
}
最后是调用的processBatchCallback方法,第五个参数为空,即没有回调方法。
processBatchCallback方法内部可以失败后进行重试,重试次数为hbase.client.retries.number控制,默认为10,每一次重试直接都会休眠一下,每次休眠时间为:
pause * HConstants.RETRY_BACKOFF[ntries]+(long)(normalPause * RANDOM.nextFloat() * 0.01f);
//RETRY_BACKOFF[] = { 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 }
pause通过hbase.client.pause设置,默认值为1000,即1秒;ntries为当前重复次数
接下来,第一步,遍历List<? extends Row>,获取每一个行对应HRegion所在位置,并且按regionName对这些待put的行进行分组。
第二步,发送异步请求到服务端。
第三步,接收异步请求的结果,收集成功的和失败的,做好重试准备
第四步,对于失败的,进行重试。
达到重试次数之后,对运行结果判断是否有异常,如果有则抛出RetriesExhaustedWithDetailsException异常。
由以上四步可以看出,重点在于第一、二步。
第一步查找HRegion所在位置过程关键在private HRegionLocation locateRegion(final byte [] tableName,final byte [] row, boolean useCache)方法中,并且为递归方法,过程如下:
- 调用locateRegionInMeta方法到.META.表中查找tableName的row所对应的HRegion所在位置,先从本地缓存查找,如果没有,则进行下一步;
- 调用locateRegionInMeta方法到-ROOT-表中查找.META.所对应的HRegion所在位置,先从本地缓存查找,如果没有,则进行下一步
- 通过rootRegionTracker(即从zk上)获取RootRegionServer地址,即找到-ROOT-表所在的RegionServer地址,然后获取到.META.所在位置,最后在获取.META.表上所有HRegion,并将其加入到本地缓存。
通过示例描述如下:
获取 Table2,RowKey为RK10000的RegionServer
=> 获取.META.,RowKey为Table2,RK10000, 99999999999999 的RegionServer
=> 获取-ROOT-,RowKey为.META.,Table2,RK10000,99999999999999,99999999999999的RegionServer
=> 获取-ROOT-的RegionServer
=> 从ZooKeeper得到-ROOT-的RegionServer
=> 从-ROOT-表中查到RowKey最接近(小于) .META.,Table2,RK10000,99999999999999,99999999999999 的一条Row,并得到.META.的RegionServer
=> 从.META.表中查到RowKey最接近(小于)Table2,RK10000,99999999999999 的一条Row,并得到Table2的K10000的Row对应的HRegionLocation
说明:
- 当我们创建一个表时,不管是否预建分区,该表创建之后,在.META.上会有一条记录的。
- 在客户端第一次连接服务端时,会两次查询缓存并没有查到结果,最后在通过
-ROOT-–>.META.–>HRegion找到对应的HRegion所在位置。
第二步中,先是创建到RegionServer的连接,后是调用RegionServer上的multi方法,显然这是远程调用的过程。第二步中提交的任务通过下面代码创建:
private <R> Callable<MultiResponse> createCallable(final HRegionLocation loc,
final MultiAction<R> multi, final byte [] tableName) {
// TODO: This does not belong in here!!! St.Ack HConnections should
// not be dealing in Callables; Callables have HConnections, not other
// way around.
final HConnection connection = this;
return new Callable<MultiResponse>() {
public MultiResponse call() throws IOException {
ServerCallable<MultiResponse> callable =
new ServerCallable<MultiResponse>(connection, tableName, null) {
public MultiResponse call() throws IOException {
return server.multi(multi);
}
@Override
public void connect(boolean reload) throws IOException {
server = connection.getHRegionConnection(loc.getHostname(), loc.getPort());
}
};
return callable.withoutRetries();
}
};
}
从上面代码可以看到,通过connection.getHRegionConnection(loc.getHostname(), loc.getPort())创建一个HRegionInterface的实现类即HRegionServer,方法内使用了代理的方式创建对象。
server = HBaseRPC.waitForProxy(this.rpcEngine,
serverInterfaceClass, HRegionInterface.VERSION,
address, this.conf,
this.maxRPCAttempts, this.rpcTimeout, this.rpcTimeout);
服务端
上面客户端调用过程分析完毕,继续跟RegionServer服务端的处理。
HRegionServer的multi方法
对于客户端写操作,最终会调用HRegionServer的multi方法。
因为传递到RegionServer都是按regionName分组的,故最后的操作实际上都是调用的HRegion对象的方法。
该方法主要就是遍历multi并对actionsForRegion按rowid进行排序,然后分类别对action进行处理,Put和Delete操作会放到一起然后调用batchMutate方法批量提交:
OperationStatus[] codes =region.batchMutate(mutationsWithLocks.toArray(new Pair[]{}));
其他的:
- 对于Get,会调用get方法;
- 对于Exec,会调用execCoprocessor方法;
- 对于Increment,会调用increment方法;
- 对于Append,会调用append方法;
- 对于RowMutations,会调用mutateRow方法;
对于Put和Delete操作(保存在mutations中),在处理之前,先通过cacheFlusher检查memstore大小吃否超过限定值,如果是,则进行flush。
接下来遍历mutations,为每个Mutation添加一个锁lock,然后再调用region的batchMutate方法。
HRegion的batchMutate
batchMutate方法内部,依次一个个处理:
- 先检查是否只读
- 检查当前资源是否支持update操作,会比较memstoreSize和blockingMemStoreSize大小,然后会阻塞线程
- 调用startRegionOperation,给lock.readLock()加锁
- 调用doPreMutationHook执行协作器里的一些方法
- 计算其待添加的大小
- 计算加入memstore之后的memstore大小
- 写完之后,释放lock.readLock()锁
- 判断是否需要flush memstore,如果需要,则调用requestFlush方法,其内部实际是通过RegionServerServices中的FlushRequester(其实现类为MemStoreFlusher)来执行flush操作
MemStoreFlusher flush过程
HRegion中的requestFlush方法:
private void requestFlush() {
if (this.rsServices == null) {
return;
}
synchronized (writestate) {
if (this.writestate.isFlushRequested()) {
return;
}
writestate.flushRequested = true;
}
// Make request outside of synchronize block; HBASE-818.
this.rsServices.getFlushRequester().requestFlush(this);
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Flush requested on " + this);
}
}
上面this.rsServices.getFlushRequester()其实际上返回的是MemStoreFlusher类。

MemStoreFlusher内部有一个队列和一个Map:
//保存待flush的对象
private final BlockingQueue<FlushQueueEntry> flushQueue =
new DelayQueue<FlushQueueEntry>();
//记录队列中存在哪些Region
private final Map<HRegion, FlushRegionEntry> regionsInQueue =
new HashMap<HRegion, FlushRegionEntry>();
MemStoreFlusher构造方法:
- 初始化threadWakeFrequency,该值由hbase.server.thread.wakefrequency设置,默认为10 * 1000
- 初始化globalMemStoreLimit,该值为最大堆内存乘以hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit的值,hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit参数默认值为0.4
- 初始化globalMemStoreLimitLowMark,该值为最大堆内存乘以hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit的值,hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit参数默认值为0.35
- 初始化blockingWaitTime,该值由hbase.hstore.blockingWaitTime设置,默认为90000
MemStoreFlusher实现了Runnable接口,在RegionServer启动过程中会启动一个线程,其run方法逻辑如下:
- 只要RegionServer一直在运行,该线程就不会停止运行
- 每隔threadWakeFrequency时间从flushQueue中取出一个对象
- 如果取出的对象为空或者WakeupFlushThread,则判断:如果当前RegionServer的总大小大于globalMemStoreLimit值,则找到没有太多storefiles(只个数小于hbase.hstore.blockingStoreFiles的,该参数默认值为7)的最大的region和不管有多少storefiles的最大region,比较两个大小找出最大的一个,然后flush该region,并休眠1秒;最后在唤醒flush线程
- 先flush region上的memstore,这部分代码通过HRegion的internalFlushcache方法来完成,其内部使用了mvcc
- 判断是否该拆分,如果是则拆分 - 判断是否该压缩合并,如果是则合并
- 如果如果取出的对象为FlushRegionEntry,则flush该对象。
- 如果当前region不是meta region并且当前region的storefiles数大于
hbase.hstore.blockingStoreFiles,先判断是否要拆分,然后再判断是否需要合并小文件。这个过程会阻塞blockingWaitTime值定义的时间。 - 否则, 直接flush该region上的memstore(调用HRegion的internalFlushcache方法),然后再判断是否需要拆分和合并
- 如果当前region不是meta region并且当前region的storefiles数大于
总结
最后总结一下,HRegionServer作用如下:
- 使得被它管理的一系列HRegion能够被客户端来使用,每个HRegion对应了Table中的一个Region,HRegion中由多个HStore组成。
- 主要负责响应用户I/O请求,向HDFS文件系统中读写数据。
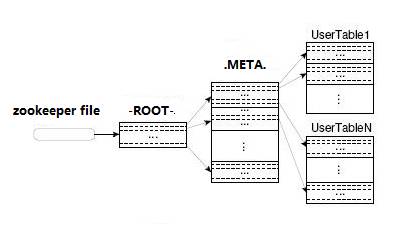
HRegion定位过程:
client -> zookeeper -> -ROOT- -> .META -> HRegion地址 -> HRegionServer-> HRegion
在这个过程中客户端先通过zk找到Root表所在的RegionServer(通过zk上的/hbase/root-region-server节点获取),然后找到Meta表对应的HRegion地址,最后在Meta表里找到目标表所在的HRegion地址,这个过程客户端并没有和HMaster进行交互。
Client端并不会每次数据操作都做这整个路由过程,因为HRegion的相关信息会缓存到本地,当有变化时,通过zk监听器能够及时感知。
数据写入过程:
- client先根据rowkey找到对应的region和regionserver
- client想regionserver提交写请求
- region找到目标region
- region检查数据是否与scheam一致
- 如果客户端没有指定版本,则获取当前系统时间作为数据版本
- 将更新写入wal log
- 将更新写入memstore
- 判断memstore是否需要flush为store文件
Could not locate executable null 解决办法的更多相关文章
- java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable null\bin\winutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries
在已经搭建好的集群环境Centos6.6+Hadoop2.7+Hbase0.98+Spark1.3.1下,在Win7系统Intellij开发工具中调试Spark读取Hbase.运行直接报错: ? 1 ...
- spark开发常见问题之一:java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable null\bin\winutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries.
最近在学习研究pyspark机器学习算法,执行代码出现以下异常: 19/06/29 10:08:26 ERROR Shell: Failed to locate the winutils binary ...
- Spark报错java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable null\bin\winutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries.
Spark 读取 JSON 文件时运行报错 java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable null\bin\winutils.exe in the ...
- windows 中使用hbase 异常:java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable null\bin\winutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries.
平时一般是在windows环境下进行开发,在windows 环境下操作hbase可能会出现异常(java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable nul ...
- Spark- ERROR Shell: Failed to locate the winutils binary in the hadoop binary path java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable null\bin\winutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries.
运行 mport org.apache.log4j.{Level, Logger} import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{S ...
- Windows下运行MapReduce程序出现Could not locate executable null\winutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries.
运行环境:windows10 64位,虚拟机:Ubuntu Kylin 14.04,Hadoop2.7.1 错误信息: java.io.IOException: Could not locate ex ...
- Android界面隐藏软键盘的探索(兼findViewById返回null解决办法)
最近写的APP,老师说我的登陆界面虽然有ScrollView滑动,但用户体验不太好,因为软键盘会挡住输入框或登录button(小米Pad,横屏,当指定只能输入数字时没找到关闭系统自带键盘的下箭头). ...
- SQLNestedException: Cannot create JDBC driver of class '' for connect URL 'null' 解决办法
当跑jndi项目时抛出:org.apache.tomcat.dbcp.dbcp.SQLNestedException: Cannot create JDBC driver of class '' fo ...
- Hbase出现ERROR: Can't get master address from ZooKeeper; znode data == null解决办法
问题描述如下: hbase(main)::> list TABLE ERROR: Can't get master address from ZooKeeper; znode data == n ...
随机推荐
- js截取所需字符串长度
//title :字符串 :interceptLength:所需的长度 function TitleThumbnail(title, interceptLength, thumbnailCharac ...
- Unity3d读取.csv文件
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/dingkun520wy/article/details/26594991 (一)文件路径 需要把csv文件放在StreamingAssets这个文 ...
- The 6th Zhejiang Provincial Collegiate Programming Contest->ProblemF:80ers' Memory
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemCode=3207 题意:给出N个关键字符串,然后给出k行,每行Ni个字符串,找出每行有 ...
- ***用php的strpos() 函数判断字符串中是否包含某字符串的方法
判断某字符串中是否包含某字符串的方法 if(strpos('www.idc-gz.com','idc-gz') !== false){ echo '包含'; }else{ echo '不包含'; } ...
- poj 3318 Matrix Multiplication 随机化算法
方法1:暴力法 矩阵乘法+优化可以卡时间过的. 方法2:随机化 随机构造向量x[1..n],则有xAB=xC;这样可以将小运算至O(n^2). 代码如下: #include<iostream&g ...
- 苹果p12文件--一个苹果证书怎么多次使用(蛋疼,这些问题只有和其他企业合作才会遇到,别人的账号不可能给你,蛋疼....)
在苹果开发者网站申请的证书,是授权mac设备的开发或者发布的证书,这意味着一个设备对应一个证书,但是99美元账号只允许生成3个发布证书,两个开发证书,这满足不了多mac设备的使用,使用p12文件可以解 ...
- 【转】深入研究java.lang.Runtime类
一.概述 Runtime类封装了运行时的环境.每个 Java 应用程序都有一个 Runtime 类实例,使应用程序能够与其运行的环境相连接. 一般不能实例化一个Runtime对象, ...
- vs2015 打不开了 提示"CSharpPackage",未能正确加载xx包
原文:vs2015 打不开了 提示"CSharpPackage" 最近发现vs2015 在新建项目和加载现有项目的时候会报错 提示 开始我以为是系统的问题导致vs 配置除了问题,重 ...
- Python之异常篇 [待更新]
简介 当你的程序中出现某些 异常的 状况的时候,异常就发生了.例如,当你想要读某个文件的时候,而那个文件不存在.或者在程序运行的时候,你不小心把它删除了.上述这些情况可以使用异常来处理. 假如你的程序 ...
- 第一章 CLR的执行模型
编译器将源代码编译为托管模块.托管木块包含: PE32或PE32+头 CLR头 元数据 IL(中间语言)代码 PE32头的文件可在32或64位的电脑上运行,PE32+的只能在64上运行.Window6 ...
