给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(4)-HashMap源码解析
public interface Map<K,V> {
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
V get(Object key);
V put(K key, V value);
V remove(Object key);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
void clear();
Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
interface Entry<K,V> {
V getValue();
V setValue(V value);
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
}
public class MyMap {
private Entry[] data = new Entry[100];
private int size;
public Object put(Object key, Object value) {
// 检查key是否存在,存在则覆盖
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (key.equals(data [i].key)) {
Object oldValue = data[i].value ;
data[i].value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
Entry e = new Entry(key, value);
data[size ] = e;
size++;
return null;
}
public Object get(Object key) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (key.equals(data [i].key)) {
return data [i].value;
}
}
return null;
}
public int size() {
return size ;
}
private class Entry {
Object key;
Object value;
public Entry(Object key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyMap map = new MyMap();
map.put( "tstd", "angelababy" );
map.put( "张三" , "李四");
map.put( "tstd", "高圆圆" );
System. out.println(map.size());
System. out.println(map.get("tstd" ));
System. out.println(map.get("张三" ));
}
}
看下结果:
2
高圆圆
李四
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
// 默认初始容量为16,必须为2的n次幂
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; // 最大容量为2的30次方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 默认加载因子为0.75f
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // Entry数组,长度必须为2的n次幂
transient Entry[] table; // 已存储元素的数量
transient int size ; // 下次扩容的临界值,size>=threshold就会扩容,threshold等于capacity*load factor
int threshold; // 加载因子
final float loadFactor ;
可以看出HashMap底层是用Entry数组存储数据,同时定义了初始容量,最大容量,加载因子等参数,至于为什么容量必须是2的幂,加载因子又是什么,下面再说,先来看一下Entry的定义。
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key ;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next; // 指向下一个节点
final int hash;
Entry( int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key ;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value ;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return (key ==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^
( value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
// 当向HashMap中添加元素的时候调用这个方法,这里没有实现是供子类回调用
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
// 当从HashMap中删除元素的时候调动这个方法 ,这里没有实现是供子类回调用
void recordRemoval(HashMap<K,V> m) {
}
}
Entry是HashMap的内部类,它继承了Map中的Entry接口,它定义了键(key),值(value),和下一个节点的引用(next),以及hash值。很明确的可以看出Entry是什么结构,它是单线链表的一个节点。也就是说HashMap的底层结构是一个数组,而数组的元素是一个单向链表。
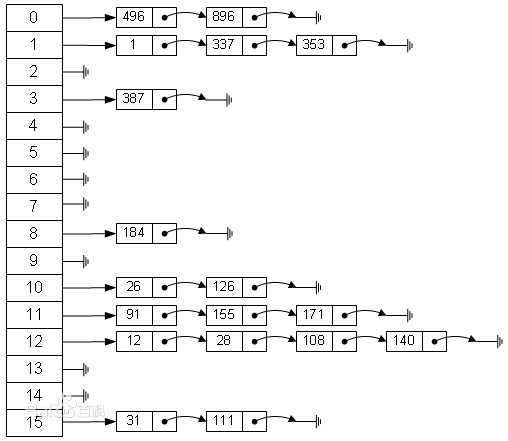
/**
* 构造一个指定初始容量和加载因子的HashMap
*/
public HashMap( int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// 初始容量和加载因子合法校验
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor); // Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
// 确保容量为2的n次幂,是capacity为大于initialCapacity的最小的2的n次幂
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1; // 赋值加载因子
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// 赋值扩容临界值
threshold = (int)(capacity * loadFactor);
// 初始化hash表
table = new Entry[capacity];
init();
} /**
* 构造一个指定初始容量的HashMap
*/
public HashMap( int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
} /**
* 构造一个使用默认初始容量(16)和默认加载因子(0.75)的HashMap
*/
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
} /**
* 构造一个指定map的HashMap,所创建HashMap使用默认加载因子(0.75)和足以容纳指定map的初始容量。
*/
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
// 确保最小初始容量为16,并保证可以容纳指定map
this(Math.max(( int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY ), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
putAllForCreate(m);
}
最后一个构造方法引入一下三个方法进行map元素添加,具体内容不多看了,逻辑和put一样但是少了数组扩容逻辑,直接跳过去看增加方法。
private void putAllForCreate(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
for(Iterator<?extendsMap.Entry<?extendsK, ?extendsV>> i = m.entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e = i.next();
putForCreate(e.getKey(), e.getValue());
}
}
/**
* This method is used instead of put by constructors and
* pseudoconstructors (clone, readObject). It does not resize the table,
* check for comodification, etc. It calls createEntry rather than
* addEntry.
*/
private void putForCreate(K key, V value) {
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length );
for (Entry<K,V> e = table [i]; e != null; e = e. next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e. key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
e. value = value;
return;
}
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, i);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 如果key为null,调用putForNullKey方法进行存储
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 使用key的hashCode计算key对应的hash值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 通过key的hash值查找在数组中的index位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length );
// 取出数组index位置的链表,遍历链表找查看是有已经存在相同的key
for (Entry<K,V> e = table [i]; e != null; e = e. next) {
Object k;
// 通过对比hash值、key判断是否已经存在相同的key
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
// 如果存在,取出当前key对应的value,供返回
V oldValue = e. value;
// 用新value替换之旧的value
e. value = value;
e.recordAccess( this);
// 返回旧value,退出方法
return oldValue;
}
}
// 如果不存在相同的key
// 修改版本+1
modCount++;
// 在数组i位置处添加一个新的链表节点
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
// 没有相同key的情况,返回null
return null;
}
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
// 取出数组第1个位置(下标等于0)的节点,如果存在则覆盖不存在则新增,和上面的put一样不多讲,
for (Entry<K,V> e = table [0]; e != null; e = e. next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e. value;
e. value = value;
e.recordAccess( this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 如果key等于null,则hash值等于0
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
增加和我们上面分析的一样,通过将key做hash取得一个散列值,将散列值对应到数组下标,然后将k-v组成链表节点存进数组中。
上面有三个方法需要重点关注,计算hash值的hash方法,计算数组索引位置的indexFor方法,添加新链表节点的addEntry方法,下面我们逐一的看一下。
/**
* Applies a supplemental hash function to a given hashCode, which
* defends against poor quality hash functions. This is critical
* because HashMap uses power -of- two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
} /**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
/**
* 增加一个k-v,hash组成的节点在数组内,同时可能会进行数组扩容。
*/
void addEntry( int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 下面两行行代码的逻辑是,创建一个新节点放到单向链表的头部,旧节点向后移
// 取出索引bucketIndex位置处的链表节点,如果节点不存在那就是null,也就是说当数组该位置处还不曾存放过节点的时候,这个地方就是null,
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 创建一个节点,并放置在数组的bucketIndex索引位置处,并让新的节点的next指向原来的节点
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
// 如果当前HashMap中的元素已经到达了临界值,则将容量扩大2倍,并将size计数+1
if (size ++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length );
}
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize( int newCapacity) {
// 当前数组
Entry[] oldTable = table;
// 当前数组容量
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length ;
// 如果当前数组已经是默认最大容量MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ,则将临界值改为Integer.MAX_VALUE 返回
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
} // 使用新的容量创建一个新的链表数组
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 将当前数组中的元素都移动到新数组中
transfer(newTable);
// 将当前数组指向新创建的数组
table = newTable;
// 重新计算临界值
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
} /**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
// 当前数组
Entry[] src = table;
// 新数组长度
int newCapacity = newTable.length ;
// 遍历当前数组的元素,重新计算每个元素所在数组位置
for (int j = 0; j < src. length; j++) {
// 取出数组中的链表第一个节点
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
// 将旧链表位置置空
src[j] = null;
// 循环链表,挨个将每个节点插入到新的数组位置中
do {
// 取出链表中的当前节点的下一个节点
Entry<K,V> next = e. next;
// 重新计算该链表在数组中的索引位置
int i = indexFor(e. hash, newCapacity);
// 将下一个节点指向newTable[i]
e. next = newTable[i];
// 将当前节点放置在newTable[i]位置
newTable[i] = e;
// 下一次循环
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
/**
* 根据key删除元素
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e. value);
} /**
* 根据key删除链表节点
*/
final Entry<K,V> removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
// 计算key的hash值
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
// 根据hash值计算key在数组的索引位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length );
// 找到该索引出的第一个节点
Entry<K,V> prev = table[i];
Entry<K,V> e = prev; // 遍历链表(从链表第一个节点开始next),找出相同的key,
while (e != null) {
Entry<K,V> next = e. next;
Object k;
// 如果hash值和key都相等,则认为相等
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e. key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
// 修改版本+1
modCount++;
// 计数器减1
size--;
// 如果第一个就是要删除的节点(第一个节点没有上一个节点,所以要分开判断)
if (prev == e)
// 则将下一个节点放到table[i]位置(要删除的节点被覆盖)
table[i] = next;
else
// 否则将上一个节点的next指向当要删除节点下一个(要删除节点被忽略,没有指向了)
prev. next = next;
e.recordRemoval( this);
// 返回删除的节点内容
return e;
}
// 保存当前节点为下次循环的上一个节点
prev = e;
// 下次循环
e = next;
} return e;
}
public V get(Object key) {
// 如果key等于null,则调通getForNullKey方法
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
// 计算key对应的hash值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 通过hash值找到key对应数组的索引位置,遍历该数组位置的链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table [indexFor (hash, table .length)];
e != null;
e = e. next) {
Object k;
// 如果hash值和key都相等,则认为相等
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
// 返回value
return e.value ;
}
return null;
}
private V getForNullKey() {
// 遍历数组第一个位置处的链表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table [0]; e != null; e = e. next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value ;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the
* specified key.
*
* @param key The key whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt> true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified
* key.
*/
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
} /**
* Returns the entry associated with the specified key in the
* HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for the key.
*/
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table [indexFor (hash, table .length)];
e != null;
e = e. next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e. key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}
containsKey的代码逻辑和get的代码逻辑90%是相同的啊,为什么没有封装下呢?
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt> true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
if (value == null)
return containsNullValue(); Entry[] tab = table;
// 遍历整个table查询是否有相同的value值
for (int i = 0; i < tab. length ; i++)
// 遍历数组的每个链表
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (value.equals(e.value ))
return true;
return false;
} /**
* Special -case code for containsValue with null argument
*/
private boolean containsNullValue() {
Entry[] tab = table;
for (int i = 0; i < tab. length ; i++)
for (Entry e = tab[i] ; e != null ; e = e.next)
if (e.value == null)
return true;
return false;
}
可以看到针对指定key的查找,由于HashMap在结构上的优化,查找相对是十分高效的,而对于指定value的查找,要遍历整个hash表,这样是非常低效费时的。。。
10.容量检查
/**
* Returns the number of key -value mappings in this map.
*
* @return the number of key- value mappings in this map
*/
public int size() {
return size ;
} /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key -value mappings.
*
* @return <tt> true</tt> if this map contains no key -value mappings
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(4)-HashMap源码解析的更多相关文章
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(7)-TreeMap源码解析
TreeMap是基于红黑树结构实现的一种Map,要分析TreeMap的实现首先就要对红黑树有所了解. 要了解什么是红黑树,就要了解它的存在主要是为了解决什么问题,对比其他数据结构比如数组,链 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(6)-HashSet源码解析&Map迭代器
今天的主角是HashSet,Set是什么东东,当然也是一种java容器了. 现在再看到Hash心底里有没有会心一笑呢,这里不再赘述hash的概念原理等一大堆东西了(不懂得需要先回去看下Has ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(5)-LinkedHashMap源码解析
前面分析了HashMap的实现,我们知道其底层数据存储是一个hash表(数组+单向链表).接下来我们看一下另一个LinkedHashMap,它是HashMap的一个子类,他在HashMap的基础上维持 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(12)-PriorityQueue源码解析
PriorityQueue是一种什么样的容器呢?看过前面的几个jdk容器分析的话,看到Queue这个单词你一定会,哦~这是一种队列.是的,PriorityQueue是一种队列,但是它又是一种什么样的队 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(2)-LinkedList源码解析
LinkedList是基于链表结构的一种List,在分析LinkedList源码前有必要对链表结构进行说明. 1.链表的概念 链表是由一系列非连续的节点组成的存储结构,简单分下类的话,链 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(1)-ArrayList源码解析
工作中经常听到别人讲“容器”,各种各样的容器,话说到底什么是容器,通俗的讲“容器就是用来装东西的器皿,比如:水桶就是用来盛水的,水桶就是一个容器.” ok,在我们写程序的时候常常要对大量的对象进行管理 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(13)-总结篇之Java集合与数据结构
是的,这篇blogs是一个总结篇,最开始的时候我提到过,对于java容器或集合的学习也可以看做是对数据结构的学习与应用.在前面我们分析了很多的java容器,也接触了好多种常用的数据结构,今天 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(11)-Queue之ArrayDeque源码解析
前面讲了Stack是一种先进后出的数据结构:栈,那么对应的Queue是一种先进先出(First In First Out)的数据结构:队列. 对比一下Stack,Queue是一种先进先出的容 ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(10)-Stack&Vector源码解析
前面我们已经接触过几种数据结构了,有数组.链表.Hash表.红黑树(二叉查询树),今天再来看另外一种数据结构:栈. 什么是栈呢,我就不找它具体的定义了,直接举个例子,栈就相当于一个很窄的木桶 ...
随机推荐
- 快速切换目录软件推荐——autojump
受到<autojump: 在命令行下快速更改目录>的鼓动,决定试用下这个软件. 但ubuntu下的源貌似有些问题, sudo apt get install autojump 后,死活提示 ...
- 12 为何使用Html5+CSS3
一:大多浏览器支持,低版本也没问题 我看点这方面的资料,是为了做手机应用网站(有三个方案,这个是备用方案),可以开发响应式网站,可以脱离开发平台进行跨平台. 在Html5网页中引入Modernizr, ...
- jquery ajax请求后台 的简单例子
jQuery.ajax(url,[settings]) 概述 通过 HTTP 请求加载远程数据. jQuery 底层 AJAX 实现.简单易用的高层实现见 $.get, $.post 等.$.ajax ...
- MyBatis中井号与美元符号的区别
#{变量名}可以进行预编译.类型匹配等操作,#{变量名}会转化为jdbc的类型. select * from tablename where id = #{id} 假设id的值为12,其中如果数据库字 ...
- iOS-default.png启动图片
我在xcode5下写的代码,我下载了iOS6的模拟器,我用iOS6和iOS7的模拟器切换运行,有的时候可以运行有的时候不可以运行,报错: 2013-11-17 16:49:04.049 sim[474 ...
- 使用WPF来创建 Metro UI程序
本文转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/TianFang/p/3184211.html 这个是我以前网上看到的一篇文章,原文地址是:Building a Metro UI with W ...
- Spring容器-ApplicationContext的单例设计
Spring容器-ApplicationContext的单例设计 每次通过new创建一个ApplicationContext容器,都会执行refresh方法,看源代码了解到这个refresh方法会 ...
- 手机调用系统的拍照和裁剪功能,假设界面有输入框EditText,在一些手机会出现点击EditText会弹出输入法,却不能输入的情况。
1. 拍照裁剪后 点击EditText会弹出输入法,却不能输入.可是点击点一EdtiText就能够输入了,所以我就写了一个看不见的EdtiText,切换焦点,这样就攻克了这个奇怪的这问题,应该是and ...
- 目录启动CXF启动报告LinkageError异常以及Java的endorsed机制
本文纯属个人见解,是对前面学习的总结,如有描述不正确的地方还请高手指正~ Exception in thread "main" java.lang.LinkageError: JA ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 2 C. Make Palindrome 贪心
C. Make Palindrome Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/600/pr ...
