State of Serverless
Some quick thoughts from Serverlessconf, Austin in April 2017
I wanted to take a bit of time to write up what I thought were some of the main themes I noticed at Serverlessconf Austin. I learned a lot and met some great people, so thanks a ton to A Cloud Guru for putting on the conference. In addition, I got a ton of new t-shirts, ate a few gourmet donuts, and enjoyed Austin by visiting some friends and family. Anyway, here are some notes/thoughts.
What is Serverless?
Everyone at Serverlessconf was still defining what Serverless is. The consensus seems to be:
- Serverless is more than Functions As A Service (FaaS). It includes also other services such as database, authentication, API gateway, orchestration, or more domain specific services, for instance video transcoding as a service or cognitive services, where you are not managing any of the infrastructure related to the service.
- Serverless means (close to) 100% utilisation. This is in contrast to PaaS, where applications either operate at a given scale, or scale more slowly and there will be scaling overhead (unused instances sitting around waiting for requests). In contrast, when serverless services are unused, they cost nothing, but can (almost) instantly scale to millions of users if necessary, and the cost is directly related to the usage.
Event Driven instead of Data Driven
Another big theme that came out was that serverless applications enable architectures that are designed around events rather than around data. Subscribing applications to an event queue is a nice way to manage service communication, since you can easily add new services onto an existing queue to modify or add functionality, as opposed to baking data flow directly into applications, which introduces strong coupling.
Rob Gruhl presented some interesting work from Nordstrom where they are using a central unified event log to manage data flowing through their retail systems. Applications can produce and consume events from the stream. Any application which needs a performant view of current state builds its own state database (a view database) by subscribing to the event stream. Then it can service requests based on its needs. Likewise, these applications can produce events for other services to consume. This completely removes the need for a core database system which maintains some centralised state, improving scalability and decoupling between microservices.
Their demo application, Hello Retail, provides a way for photographers to take photos of new products. When a new product is added, the system selects a photographer from its list of known photographers and sends them an SMS requesting a new photo. When they send a message back (via SMS), the system processes the photo, adds it to a photo bucket, and registers it as a photo for the product.
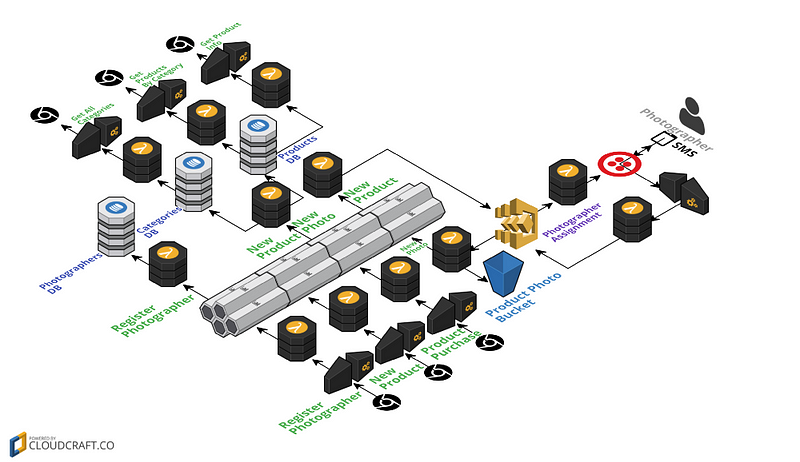
Hello Retail Architecture by Nordstrom (from https://read.acloud.guru/announcing-the-winners-of-the-inaugural-serverlessconf-architecture-competition-1dce2db6da3)
See their Hello Retail project on github for more details.
Srini Uppalapati from Capital One opened up about Capital One’s core banking systems which they are both transitioning to the Cloud and heavily leveraging serverless offerings. They are migrating their core transactions system in two steps:
- Remove read load from their mainframe systems by adding shims to their mainframe to stream events to databases in the cloud which are then consumed by user facing applications and data scientists.
- Remove the write side from consumer applications, moving core business logic to the cloud.
They are code complete on step 1. Srini shared their architecture which involves using AWS Lambda for processing batches of old data and real-time events coming from their mainframes and pumping the data into S3 for archiving, DynamoDB for consumer applications, and Redshift for analysis.
It is extremely interesting how both at architectural and application levels, using first class events is a powerful way of decoupling logic from state: one way data flow makes things simpler to reason about. At the application level we have ELM architecture and React/Redux as core examples, and now in the cloud we can use cloud functions combined with a core event stream to create functional cloud applications that operate at scale.
Enterprises are buying in quickly
As mentioned above, Nordstrom and CapitalOne are doing key work in proving out Serverless in the enterprise space. I was surprised how many other big enterprises were mentioned at Serverlessconf, and how they are quickly buying in to serverless technology.
I think one element that has led them to jump onboard is that many of them are already in the journey of moving to the cloud, and since their cloud provider has serverless offerings, they can drastically reduce their costs by going serverless. For instance, Srini from Capital One shared that they had made significant cost savings for moving to serverless in the cloud. Apparently their transactions hub costs ~$95k per year to run (which is insanely low given their customer base: ~45 million accounts).
To serve this enterprise appetite, all the cloud providers are also buying in heavily to serverless offerings in addition to AWS. The other cloud providers (Google, Microsoft, and IBM) demo’d their FaaS and serverless orchestration offerings.
Modern Agile enabled by Serverless Computing
Mike Roberts gave an awesome talk about how serverless lets app developers think more about their customers and less about technical problems. Modern Agile (Make People Awesome, Deliver Value Continuously, Make Safety a Prerequisite, Experiment and Learn Rapidly) is easier with serverless, since developers no longer have to solve problems that have been solved a million times before, by many other developers (how to do authentication, how to scale, etc…) and allows them to focus on delivering customer value. Time to go to production can now be measured in hours, not days or weeks. Since
“Most of our ideas suck” — Jeff Patton
we should try as many ideas as possible. Thanks to serverless, trying things is cheap!
In this vein, there were quite a few serverless success stories, not the least of which being Marcia Villalba talking about moving Toons.tv to serverless. They garnered significant cost savings by rethinking their architecture for the cloud. They did all that with a small team of engineers who were unfamiliar with serverless technology in a matter of months. She attributed a lot of their success to weekly workshops to get everyone on the same page about this new technology and proof of concepts for testing out new stuff.
Tools are still catching up
There was a general consensus that the tooling is lagging behind the cloud provider offerings. Florian Motlik complained extensively about how the AWS cli is immature. Other cloud providers have similar issues, in that they have invested heavily in the serverless runtimes but have neglected the tooling in the areas of deployment, monitoring and local testing.
This means basically any interaction you have with the cloud providers will be through third party tools, e.g. no one does serverless deployments with the AWS cli, mostly they are using frameworks that abstract the rawness of cloud provider interfaces into a simple application level framework for deployment (see, the serverless framework, claudiaJS, and zappa for starters).
AWS have released the Serverless Application Model (SAM) to try to address this. SAM is an abstraction layer on top of CloudFormation which makes creating Serverless Applications significantly simpler, however, the AWS cli is still immature (in my opinion).
Monitoring and debugging were also two areas that people felt are lacking in serverless applications, specifically when dealing with event based architectures (“My functions aren’t firing and I can’t tell why!”, and “Why can’t I live debug a running serverless function??”).
I’m not complaining about the lack of interactive debugging, since it is probably an anti-pattern, but if you are, Microsoft now has live debugging for Azure cloud functions via Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code (although the demo made it look a bit flakey). If you want to avoid interactive debugging, write unit tests.
Also, all the cloud providers are working hard on monitoring. Amazon X-Ray looks like a really solid monitoring option which integrates with the AWS SDK to provide live graphs and analytics of your integration points — a living architecture diagram. This pretty much comes for free if you use the AWS SDK for your service calls.
Another discussion point was that teams are still searching for the best patterns for developing serverless applications. Traditionally, it is easy to understand the domain of a particular application, because it is contained within a single server instance. You can spin up a local instance, stub any dependencies, and do some local exploratory testing as you are developing. However, with serverless development, often you are tightly coupled to the cloud provider (especially as services get smaller), and it is necessary to actually deploy your application (which might involve multiple cloud components) in order to test whether it is working end to end, even during development. There is a lot of demand for being able to do local exploratory testing, but as yet there aren’t any good patterns for how to isolate the piece of your application under test — it is common to end up with some frankenstein test application where pieces are running both locally and on the cloud. Some options in this area are the Atlassian AWS Local Stack which provides a fully functioning AWS stack on your local machine. Still, knowing why to use this versus just deploying to a development environment is still something under debate.
Serverless Orchestration
One of the issues with serverless computing that has been raised is the difficulty of orchestrating large numbers of lambda functions to create data pipelines in the cloud. Using event streams is one way of connecting lambda functions together, however there is often the need for more advanced functionality such as wait conditions or parallelisation.
Both AWS and Azure demo’d their serverless orchestration offerings: AWS Step Functions and Azure Logic Apps. Both of them look intriguing.
Azure Logic Apps has over 250 built in connectors to other Azure products as well as third party products. While I am suspicious of fancy user interfaces, in this case it is backed by a json scripting DSL, and they gave a great demo, linking live tweets to a sentiment analysis service within Microsoft and then producing a live feed of twitter sentiment around a certain topic… all in the space of a 45 minute demo (with some copy and pasted code).
While I am unsure how these workflow orchestration services will be used in a reliable way (how do you test them and deploy them?), I think they will become a part of the serverless landscape.
I am interested to see how these workflow services evolve into fully functioning platforms. Why must we script in a json DSL when we could have a better language (think Javascript or Swift) compile down to an ‘AWS Cloud Machine Language’, which is then run directly on some abstracted compute layer. AWS would then manage all the underlying servers and state without any restrictions around maximum run times or memory, where you pay exactly for the usage you need
State of Serverless的更多相关文章
- AWS Step Function Serverless Applications
Installing VS Components To follow along with this article, you must have an AWS account and install ...
- A Comparison of Serverless Frameworks for Kubernetes: OpenFaas, OpenWhisk, Fission, Kubeless and more
The term Serverless has become synonymous with AWS Lambda. Decoupling from AWS has two benefits; it ...
- 用 Serverless 快速搭建个人相册网站
日常生活中我们经常会拍摄一些视频.照片等,这些文件会占用比较多的存储空间.本文将介绍一种方法:利用 ThumbsUp 工具,结合 Serverless Framework 的 component 快速 ...
- Hexo + Serverless Framework,简单三步搭建你的个人博客
很多人都想拥有自己的个人博客,还得看起来漂亮.酷酷的.尤其对开发者来说,不仅可以分享技术(装)心得(逼),面试的时候还能成为加分.这里介绍两款好用的神器,不用忙前(前端)忙后(后端),简单3min即可 ...
- 基于 Serverless +企业微信打造 nCoV 疫情监控小助手
最近的一些疫情信息很让人揪心,为了方便大家掌握疫情信息,在空闲之余做了一个关于 nCoV 的疫情监控小助手.主要的功能是通过企业微信的 WebHook 来推送疫情信息.这里将使用 Serverless ...
- 通过 Serverless 加速 Blazor WebAssembly
Blazor ❤ Serverless 我正在开发 Ant Design 的 Blazor 版本,预览页面部署在 Github Pages 上,但是加载速度很不理想,往往需要 1 分钟多钟才完成. 项 ...
- Serverless + Egg.js 后台管理系统实战
本文将介绍如何基于 Egg.js 和 Serverless 实现一个后台管理系统 作为一名前端开发者,在选择 Nodejs 后端服务框架时,第一时间会想到 Egg.js,不得不说 Egg.js 是一个 ...
- 如何开发自己的第一个 Serverless Component
前言 上一篇 基于 Serverless Component 的全栈解决方案 介绍 Serverless Component 是什么和如何使用 Serverless Component 开发一个全栈应 ...
- 体验京东云 Serverless+AI 人脸属性识别
云原生计算基金会CNCF(Cloud Native Computing Foundation, CNCF)Serverless Whitepaper v1.0对无服务器计算作了如下定义: Server ...
随机推荐
- python控制selenium点击登录按钮时报错 unknown error: Element is not clickable at point
利用python控制selenium进行一个网页的登录时报错: C:\Users\Desktop\selenium\chrome>python chrome.py selenium.common ...
- django model 条件过滤 queryset.filter(**condtions) 用法
1.下述代码查询model对应数据库中日期等于2018-05-22的数据: queryset = model.objects.all() condtions: {'date': '2018-05-22 ...
- python、Java、大数据和Android的薪资如何?
莫名其妙,从去年年底开始,Python这个东西在中国,突然一下子就火起来了,直至现在,他的热度更是超越了java,成为软件工程师最为关注的话题.Python之所以能火起来,很大一方面是因为大数据.人工 ...
- Android-Window(一)——初识Window
Android-Window(一)--初识Window 学习自 <Android开发艺术探索> https://blog.csdn.net/qian520ao/article/detail ...
- Python基础笔记(二)
1. List和Tuple List和Tuple是Python的内置的数据类型,区别在于可变和不可变,List用[]表示,Tuple用()表示,它们之间可以相互转换: # List to Tuple ...
- 内存缓存 ehcache
内存缓存需要对内存缓存每个参数的配置意义搞明白,才能很好地去使用,例如失效时间.存活时间. 是否存储在磁盘.是否永久有效,参数要了解清楚后进行使用,不要在不清楚时盲目使用,会导致意想不到 的问题发生. ...
- 面向对象设计原则 单一职责原则(Single responsibility principle)
单一职责原则(SRP:Single responsibility principle) 又称单一功能原则,面向对象的基本原则之一.它规定 一个类应该只有一个发生变化的原因. 该原则由罗伯特·C·马丁( ...
- HDU.5181.numbers(DP)
题目链接 参考. \(Description\) 将\(1,2,\cdots,n(n\leq 300)\)依次入栈/出栈,并满足\(m(m\leq 90000)\)个形如\(x\)要在\(y\)之前出 ...
- Android任务和返回栈完全解析(转)
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/guolin_blog/article/details/41087993 本篇文章主要内容来自于Android Doc,我翻译之后又做了些加工 ...
- ios手机填坑总结
1. 日期格式 ios系统.safari只能识别"2018/10/15 00:00:00",不能识别"2018-10-15 00:00:00",所以需要转换格式 ...
