Iterator、Iterable接口的使用及详解
Java集合类库将集合的接口与实现分离。同样的接口,可以有不同的实现。
Java集合类的基本接口是Collection接口。而Collection接口必须继承java.lang.Iterable接口。
以下图表示集合框架的接口,java.lang以及java.util两个包里的。其他部分可以从左向右看,比如Collection的Subinterfaces有List,Set以及Queue等。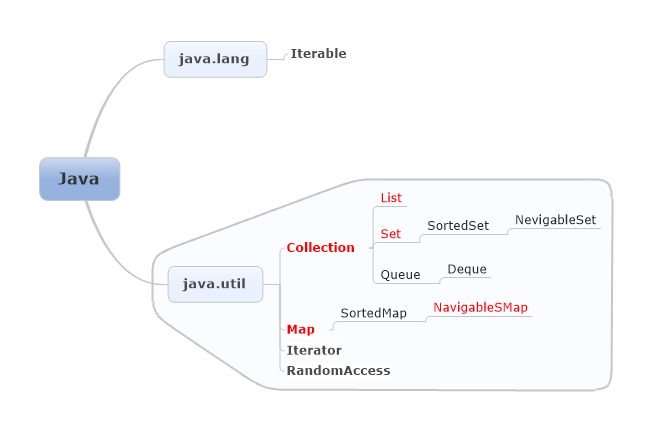
package java.util; /**
* An iterator over a collection. Iterator takes the place of Enumeration in
* the Java collections framework. Iterators differ from enumerations in two
* ways: <ul>
* <li> Iterators allow the caller to remove elements from the
* underlying collection during the iteration with well-defined
* semantics.
* <li> Method names have been improved.
* </ul><p>
*
* This interface is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @version %I%, %G%
* @see Collection
* @see ListIterator
* @see Enumeration
* @since 1.2
*/
public interface Iterator<E> {
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if the iteration has more elements. (In other
* words, returns <tt>true</tt> if <tt>next</tt> would return an element
* rather than throwing an exception.)
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the iterator has more elements.
*/
boolean hasNext(); /**
* Returns the next element (每一次迭代,the next element就是index为0的元素)in the iteration.
*
* @return the next element in the iteration.
* @exception NoSuchElementException iteration has no more elements.
*/
E next(); /**
*
* Removes from the underlying collection the last element returned by the
* iterator (optional operation). This method can be called only once per
* call to <tt>next</tt>. The behavior of an iterator is unspecified if
* the underlying collection is modified while the iteration is in
* progress in any way other than by calling this method.
*
* @exception UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>remove</tt>
* operation is not supported by this Iterator. * @exception IllegalStateException if the <tt>next</tt> method has not
* yet been called, or the <tt>remove</tt> method has already
* been called after the last call to the <tt>next</tt>
* method.
*/
void remove();
}
以下例子是利用了Iterator接口的着三个方法,实现遍历ArrayList<String>类型。
一开始迭代器在所有元素的左边,调用next()之后,迭代器移到第一个和第二个元素之间,next()方法返回迭代器刚刚经过的元素。
hasNext()若返回True,则表明接下来还有元素,迭代器不在尾部。
remove()方法必须和next方法一起使用,功能是去除刚刚next方法返回的元素。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator; public class ForEachDemo {
public static void main(String... arg) {
Collection<String> a = new ArrayList<String>();
a.add("Bob");
a.add("Alice");
a.add("Lisy"); Iterator<String> iterator = a.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String ele = iterator.next();
System.out.println(ele);//Bob Alice Lisy
}
System.out.println(a);//[Bob, Alice, Lisy]
iterator = a.iterator();
iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
System.out.println(a);//[Alice, Lisy]
}
}
package java.lang; import java.util.Iterator; /** Implementing this interface allows an object to be the target of
* the "foreach" statement.
* @since 1.5
*/
public interface Iterable<T> { /**
* Returns an iterator over a set of elements of type T.
*
* @return an Iterator.
*/
Iterator<T> iterator();
}
for-each循环可以与任何实现了Iterable接口的对象一起工作。
而java.util.Collection接口继承java.lang.Iterable,故标准类库中的任何集合都可以使用for-each循环。
Collection接口
此接口的方法
public interface Collection<E>{......}
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
boolean |
add(E e)
Ensures that this collection contains the specified element (optional operation).
|
boolean |
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation).
|
void |
clear()
Removes all of the elements from this collection (optional operation).
|
boolean |
contains(Object o)
Returns true if this collection contains the specified element.
|
boolean |
containsAll(Collection<?> c)
Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection.
|
boolean |
equals(Object o)
Compares the specified object with this collection for equality.
|
int |
hashCode()
Returns the hash code value for this collection.
|
boolean |
isEmpty()
Returns true if this collection contains no elements.
|
Iterator<E> |
iterator()
Returns an iterator over the elements in this collection.
|
boolean |
remove(Object o)
Removes a single instance of the specified element from this collection, if it is present (optional operation).
|
boolean |
removeAll(Collection<?> c)
Removes all of this collection's elements that are also contained in the specified collection (optional operation).
|
boolean |
retainAll(Collection<?> c)
Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation).
|
int |
size()
Returns the number of elements in this collection.
|
Object[] |
toArray()
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection.
|
<T> T[] |
toArray(T[] a)
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array.
|
因为其中有一个返回值为Iterator<E>类型的iterator()方法,所以,java.util.Collection接口必须继承java.lang.Iterable接口
实现Collection接口的每一个类都要实现以上众多方法,但开发者自己实现很麻烦。所以java提供了AbstractCollection类来编写具体的类。
java.util
Interface Collection<E>
- All Superinterfaces:
- Iterable<E>
- All Known Subinterfaces:
- BeanContext, BeanContextServices,
BlockingDeque<E>,
BlockingQueue<E>,
Deque<E>, List<E>, NavigableSet<E>, Queue<E>, Set<E>,
SortedSet<E>
- All Known Implementing Classes:
- AbstractCollection, AbstractList, AbstractQueue, AbstractSequentialList,
AbstractSet, ArrayBlockingQueue,
ArrayDeque, ArrayList,
AttributeList, BeanContextServicesSupport,
BeanContextSupport,
ConcurrentLinkedQueue,
ConcurrentSkipListSet,
CopyOnWriteArrayList,
CopyOnWriteArraySet,
DelayQueue, EnumSet, HashSet, JobStateReasons,
LinkedBlockingDeque,
LinkedBlockingQueue,
LinkedHashSet, LinkedList, PriorityBlockingQueue,
PriorityQueue, RoleList, RoleUnresolvedList,
Stack, SynchronousQueue, TreeSet, Vector
Collection接口有三个常用的子接口,分别是List,Set,Queue。
http://blog.csdn.net/xujinsmile/article/details/8543544
看一下JDK中的集合类,比如List一族或者Set一族,
都是继承了Iterable接口,但并不直接继承Iterator接口。
仔细想一下这么做是有道理的。因为Iterator接口的核心方法next()或者hasNext()
是依赖于迭代器的当前迭代位置的。
如果Collection直接继承Iterator接口,势必导致集合对象中包含当前迭代位置的数据(指针)。
当集合在不同方法间被传递时,由于当前迭代位置不可预置,那么next()方法的结果会变成不可预知。
除非再为Iterator接口添加一个reset()方法,用来重置当前迭代位置。
但即时这样,Collection也只能同时存在一个当前迭代位置。
而Iterable则不然,每次调用都会返回一个从头开始计数的迭代器。
多个迭代器是互不干扰的。
http://www.cnblogs.com/highriver/archive/2011/07/27/2077913.html
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ForEachAPIDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Students students = new Students(10);
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.getSid() + ":" + student.getName());
}
}
}
// 支持for each迭代循环的学生集合类
class Students implements Iterable<Student> {
// 存储所有学生类的数组
private Student[] students;
// 该构造函数可以生成指定大小的学生类变量数组,并初始化该学生类变量数组
public Students(int size) {
students = new Student[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
students[i] = new Student(String.valueOf(i), "学生" + String.valueOf(i));
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<Student> iterator() {
return new StudentIterator();
}
// 实现Iterator接口的私有内部类,外界无法直接访问
private class StudentIterator implements Iterator<Student> {
// 当前迭代元素的下标
private int index = 0;
// 判断是否还有下一个元素,如果迭代到最后一个元素就返回false
public boolean hasNext() {
return index != students.length;
}
@Override
public Student next() {
return students[index++];
}
// 这里不支持,抛出不支持操作异常
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
}
class Student {
private String sid;
private String name;
public Student(String sid, String name) {
setSid(sid);
setName(name);
}
public String getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(String sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sid='" + sid + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
What hurts more? The pain of hard work or the pain of regret?
Iterator、Iterable接口的使用及详解的更多相关文章
- 【python3+request】python3+requests接口自动化测试框架实例详解教程
转自:https://my.oschina.net/u/3041656/blog/820023 [python3+request]python3+requests接口自动化测试框架实例详解教程 前段时 ...
- OpenCV学习C++接口 Mat像素遍历详解
OpenCV学习C++接口 Mat像素遍历详解
- 微信JS接口汇总及使用详解
这篇文章主要介绍了微信JS接口汇总及使用详解,十分的全面.详尽,包含分享到朋友圈,分享给朋友,分享到QQ,拍照或从手机相册中选图,识别音频并返回识别结果,使用微信内置地图查看位置等接口,有需要的小伙伴 ...
- “全栈2019”Java第六十五章:接口与默认方法详解
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java第 ...
- python+requests接口自动化测试框架实例详解
python+requests接口自动化测试框架实例详解 转自https://my.oschina.net/u/3041656/blog/820023 摘要: python + requests实 ...
- STM32接口FSMC/FMC难点详解
STM32接口FSMC/FMC难点详解 转载 http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_808bca130102x94k.html STM32F767的FMC将外部存储器划分为 ...
- Jmeter接口之响应断言详解
响应断言 : 对服务器的响应进行断言校验 Apply to 应用范围: main sample and sub sample, main sample only , sub-sample only , ...
- 接口测试之HTTP协议详解
引言 HTTP是一个属于应用层的面向对象的协议,由于其简捷.快速的方式,适用于分布式超媒体信息系统.它于1990年提出,经过几年的使用与发展,得到不断地完善和扩展.目前在WWW中使用的是HTTP/1. ...
- python+requests接口自动化测试框架实例详解教程
1.首先,我们先来理一下思路. 正常的接口测试流程是什么? 脑海里的反应是不是这样的: 确定测试接口的工具 —> 配置需要的接口参数 —> 进行测试 —> 检查测试结果(有的需要数据 ...
随机推荐
- 【DRP】删除递归树的操作
正如图呈现的树结构.本文从任意节点删除树形结构.提供解决方案 图中,不包括其他结点的是叶子结点.包括其他结点的是父结点,即不是叶子结点. 一 本文的知识点: (1)递归调用: 由于待删除的结点的层次是 ...
- .Net C# Windows Service于server无法启动,错误 193:0xc1
1.情况说明:的近期发展windows维修,当地win7系统正常.把server安装会失败. 图中的引导失败的例子.: 解决方法:执行->输入:eventvwr.msc 打开你的事件查看器 ...
- atitit查询表改动表字段没反应--解锁锁定的表
atitit查询表改动表字段没反应--解锁锁定的表 查询表改动表字段没反应 要是使用gui 没反应,最好使用cmd 方式,不卉不个gui 锁上.. ALTER TABLE t_mb_awardweix ...
- PDF数据防扩散系统方案
在企业信息化过程中.大量的企业重要图纸和资料都是以电子文件的方式存在.为了避免内部关键数据的外泄,採取了多种方式:设计部门的门禁管制.防火墙.禁止计算机的USB接口等等. 可是泄密问题还是时有发生,原 ...
- 安装配置gerrit
Centos 安装配置gerrit 关闭selinux,不然nginx的反向代理会报错connect() to 127.0.0.1:8080 failed (13: Permission denied ...
- 多线程——达到Runnable介面
部分博客(多线程--继承Thread类)介绍了java多线程的第一种实现方法--继承Thread类.这篇博客介绍另外一种方法--实现Runnable接口,并实现run方法. 还用上篇博客的样例.如今用 ...
- php我们需要把握面试题目金鸡基础
1.session与cookie差分? 答:session:储存用户訪问的全局唯一变量,存储在server上的php指定的文件夹中的(session_dir)的位置进行的存放 cookie:用来存储连 ...
- android插件化-apkplug框架启动-02
本文章基于apkplug v1.6.7 版本号编写,最新方式以官网最新消息为准 一 apkplug框架所须要的库文件(宿主) 可从http://git.oschina.net/plug/apkplug ...
- 【UFLDL】多层神经网络
请参见原始英文教程地址:http://ufldl.stanford.edu/tutorial/supervised/MultiLayerNeuralNetworks 本文是在学习该教程时记得笔记,供參 ...
- UDP议定书图像高速传输无损失程序
下面的程序实现UDP没有图像数据的高速传输协议损耗,测试数据egtest01图片库,实现PC和图像的传输嵌入式结束.变速箱+读写速度可以达到10+M/S.考 server端程序 #include &l ...
