JAVAWEB学习总结 SERVLET开发(二)
一、ServletConfig对象
1.1、配置servlet初始化参数
在servlet的配置文件中web.xml中,可以使用一个或多个<init-param>标签为servlet配置一些初始化参数。
例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo6</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>my.servlet.demo.ServletDemo6</servlet-class>
<!--配置ServletConfigDemo1的初始化参数 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>name</param-name>
<param-value>my</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>password</param-name>
<param-value>123</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>charset</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo6</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ServletDemo6</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
1.2、通过ServletConfig获取servlet初始化参数
当servlet配置了初始化参数后,web容器在创建servlet实例对象时,会自动将这些初始化参数封装到ServletConfig对象中,并在调用servlet的init方法时,将ServletConfig对象传递给servlet。进而我们通过ServletConfig对象就可以得到当前servlet的初始化参数信息。
例如:
package my.servlet.demo;
//导入必需的 java 库
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Enumeration; import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*; // 扩展 HttpServlet 类
public class ServletDemo1 extends HttpServlet { /**
* 定义ServletConfig对象来接收配置的初始化参数
*/ private ServletConfig config;
/**
* 当servlet配置了初始化参数后,web容器在创建servlet实例对象时,
* 会自动将这些初始化参数封装到ServletConfig对象中,并在调用servlet的init方法时,
* 将ServletConfig对象传递给servlet。进而,程序员通过ServletConfig对象就可以
* 得到当前servlet的初始化参数信息。
*/ public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException
{
// 执行必需的初始化
this.config=config;
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
//获取在web.xml中配置的初始化参数
String paramVal=this.config.getInitParameter("name");//获取指定的初始化参数
response.getWriter().print(paramVal);
response.getWriter().print("<hr/>");
//获取所有的初始化参数
Enumeration<String> e =config.getInitParameterNames();
while(e.hasMoreElements())
{
String name =e.nextElement();
String value=config.getInitParameter(name);
response.getWriter().print(name+"="+value+"<br/>");
}
} public void destroy()
{
// 什么也不做
}
}
运行结果如下:

二、ServletContext对象
WEB容器在启动时,它会为每个WEB应用程序都创建一个对应的ServletContxt对象,它代表当前web应用。
ServletConfig对象中维护了ServletContext对象的引用,开发人员在编写servlet时,可以通过ServletConfig.getServletContext方法获得ServletContext对象。
由于一个WEB应用中的所有Servlet共享同一个ServletContext对象,因此Servlet对象之间可以通过ServletContext对象来实现通讯。ServletContext对象通常也被称为context域对象。
2.1、多个servlet通过ServletContext对象实现数据共享
例子:ServletDemo1和ServletDemo2通过ServletContext对象实现数据共享
package my.servlet.demo;
//导入必需的 java 库
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Enumeration; import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*; // 扩展 HttpServlet 类
public class ServletDemo1 extends HttpServlet { private ServletConfig config; public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException
{
// 执行必需的初始化
this.config=config;
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String data="itnnn";
ServletContext context=config.getServletContext();
context.setAttribute("data", data);
} public void destroy()
{
// 什么也不做
}
}
package my.servlet.demo; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /**
* Servlet implementation class ServletDemo2
*/
@WebServlet("/ServletDemo2")
public class ServletDemo2 extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ServletContext context =this.getServletContext();
String data=(String) context.getAttribute("data");
response.getWriter().print("data="+data);
} /**
* @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
} }
先运行ServletDemo1,将数据data存储到ServletContext对象中,然后运行ServletDemo2就可以从ServletContext对象中取出数据了,这样就实现了数据共享,运行结果如下图所示:
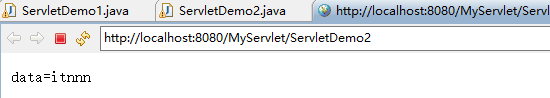
2.2、获取WEB应用的初始化参数
在web.xml文件中使用<context-param>标签配置WEB应用的初始化参数,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<display-name></display-name>
<!-- 配置WEB应用的初始化参数 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>url</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</param-value>
</context-param> <welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
package my.servlet.demo; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @WebServlet("/ServletDemo3")
public class ServletDemo3 extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context=this.getServletContext();
//获取整个web站点的初始化参数
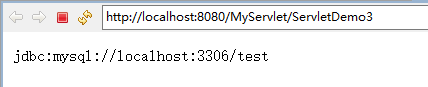
String contextInitParam =context.getInitParameter("url");
response.getWriter().print(contextInitParam );
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
} }
运行结果:
2.3、用ServletContext实现请求转发
ServletDemo4.java
package my.servlet.demo; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletDemo4 extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String data="<h1><font color='red'>abc</font></h1>";
response.getOutputStream().write(data.getBytes());
ServletContext context=this.getServletContext();
RequestDispatcher rd =context.getRequestDispatcher("/ServletDemo5");
rd.forward(request, response);
} protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
} }
ServletDemo5.java
package my.servlet.demo; import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class ServletDemo5 extends HttpServlet { protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
response.getOutputStream().write("servletDemo5".getBytes());
} protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
} }
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<servlet>
<description>This is the description of my J2EEcomponent</description>
<display-name>This is the display of my J2EEcomponent</display-name>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo4</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>my.servlet.demo.ServletDemo4</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<description>This is the description of my J2EEcomponent</description>
<display-name>This is the display of my J2EEcomponent</display-name>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo5</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>my.servlet.demo.ServletDemo5</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo4</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ServletDemo4</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo5</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/ServletDemo5</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
运行结果:
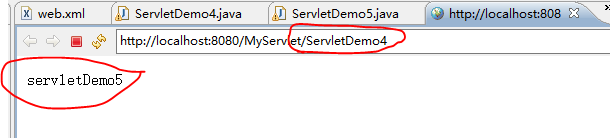
访问的是ServletDemo4,浏览器显示的却是ServletDemo5的内容,这就是使用ServletContext实现了请求转发。
2.4、利用ServletContext对象读取资源文件
2.5、在客户端缓存servlet输出
JAVAWEB学习总结 SERVLET开发(二)的更多相关文章
- javaweb学习之Servlet开发(二)
javaweb学习总结(六)--Servlet开发(二) 一.ServletConfig讲解 1.1.配置Servlet初始化参数 在Servlet的配置文件web.xml中,可以使用一个或多个< ...
- JavaWeb学习之Servlet(二)----Servlet的生命周期、继承结构、修改Servlet模板
[声明] 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→ 文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4140466.html 一.http协议回顾: 在上一篇文章中:JavaW ...
- (转)JavaWeb学习之Servlet(二)----Servlet的生命周期、继承结构、修改Servlet模板
[声明] 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→ 文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4140466.html 一.http协议回顾: 在上一篇文章中:JavaW ...
- javaweb学习总结 servlet开发(一)
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/xdp-gacl/p/3760336.html 这里主要是将其加入自己的理解过一遍. 这里的代码全在eclipse java ee中执行的. 一.s ...
- JavaWeb学习——了解Servlet
JavaWeb学习——了解Servlet 摘要:本文主要学习了什么是Servlet,以及如何使用Servlet进行开发. 基础知识 背景 随着互联网技术的发展,基于HTTP和HTML的web应用急速增 ...
- javaweb学习总结(六)——Servlet开发(二)
一.ServletConfig讲解 1.1.配置Servlet初始化参数 在Servlet的配置文件web.xml中,可以使用一个或多个<init-param>标签为servlet配置一些 ...
- javaweb学习总结(六)——Servlet开发(二)(转)
转载自 http://www.cnblogs.com/xdp-gacl/p/3763559.html 一.ServletConfig讲解 1.1.配置Servlet初始化参数 在Servlet的配置文 ...
- java web学习总结(六) -------------------servlet开发(二)
一.ServletConfig讲解 1.1.配置Servlet初始化参数 在Servlet的配置文件web.xml中,可以使用一个或多个<init-param>标签为servlet配置一些 ...
- JavaWeb学习 (六)————Servlet(二)
一.ServletConfig讲解 1.1.配置Servlet初始化参数 在Servlet的配置文件web.xml中,可以使用一个或多个<init-param>标签为servlet配置一些 ...
随机推荐
- Unity3D 中的协程
若干文章: 1.Coroutine,你究竟干了什么? 2.Radical Coroutines 3.Extended Unity Coroutines
- 版本控制简介,git使用----使用GitHub托管代码
关于版本控制: 很久以前,人们苦于对写过的代码进行版本的管理,经常过了一段时间想恢复原来写过的代码却又忘了不知道丢到哪儿去了,有的人用加上时间后缀来命名文件的方法,便于后期维护,但是这样做的麻烦也很大 ...
- ajax 异步插入图片到数据库(多图上传)
额 大概就这么个样子...截个图 点浏览 选择几张图片 选择完了 确定一下 然后插入数据库 同时在页面中显示插入的图片,代码 也没啥.看下 index.php <html><hea ...
- 【数据类型】Dictionary 与 ConcurrentDictionary 待续
Dictionary<TKey, TValue> 泛型类提供了从一组键到一组值的映射.通过键来检索值的速度是非常快的,接近于 O(1),这是因为 Dictionary<TKey, T ...
- easy ui datagrid 让某行复选框不能选中
//百度查找出来的 onLoadSuccess: function(data){//加载完毕后获取所有的checkbox遍历 if (data.rows.length > ...
- ios基础篇(二十八)—— UITableView的上拉加载
本文主要展示一个demo实现UITableView的上拉加载数据: 先看看效果图: 接着上拉,加载更多数据: 主要实现的效果是在我们上拉结束拖拽之后,开始加载数据,数据加载的过程中有滚动轮提示用户正在 ...
- !important使用
IE 6.0一直都不支持这个语法,而其他的浏览器都支持.因此我们就可以利用这一点来分别 给IE和其他浏览器不同的样式定义,例如,我们定义这样一个样式: colortest {border:20px s ...
- How to Develop blade and soul Skills
How to Develop Skills Each skill can be improved for variation effects. Some will boost more strengt ...
- Bootstrap <基础五>表格
Bootstrap 提供了一个清晰的创建表格的布局.下表列出了 Bootstrap 支持的一些表格元素: 标签 描述 <table> 为表格添加基础样式. <thead> 表格 ...
- Copy page via powershell and not save as template 分类: Sharepoint 2015-07-16 16:39 4人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
By save as template informaton of the page get lost, e.g. permissions. To avoid this, use powershell ...
