STL标准库-容器-map和multimap
技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
map与multimap为关联容器,结构如下
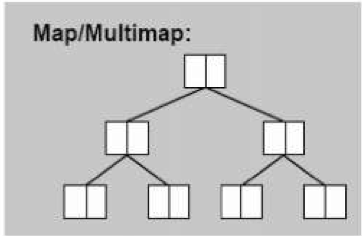
map底层实现依然是rb_tree 他的data可以改,但是key不能改,因此map仍然具有自动排序的功能
我们无法使用迭代器改变元素的key(const key),但是可以改变元素的data.
map的key必须独一无二,multimap的key可以重复
map的定义函数
- template <typename _Key, typename _Tp, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>,
- typename _Alloc = std::allocator<std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> > >
- class map
- {
- public:
- typedef _Key key_type;
- typedef _Tp mapped_type;
- typedef std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> value_type;
- typedef _Compare key_compare;
- typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
- ...
- }
参数1 class key 键值key
参数2 class T data
参数3 class compare 排序key的函数 默认为less() 升序
参数4 alloc 分配器
map的基本使用
一 定义
- //构造函数
- map<int, int> c;
- c[] = ;
- c[] = ;
- c[] = ;
- c[] = ;
- c[] = ;
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //operator =
- map<int, int> c1;
- c1 = c;
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
二 迭代器操作 map的迭代器就是红黑树的迭代器
- //迭代器操作
- /*
- map<int, int> c;
- c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
- */
- //begin()
- map<int, int>::iterator iter;
- iter = c.begin();
- cout<< "begin(): "<<"["<< iter->first <<"] = " << iter->second <<endl;
- //end()
- iter = c.end();
- iter--;
- cout<<"end(): " <<"["<< iter->first <<"] = " << iter->second <<endl;
- //rbegin()反向头迭代器
- map<int, int>::reverse_iterator riter;
- riter = c.rbegin();
- cout << "rbegin(): "<<"["<< riter->first <<"] = " << riter->second <<endl;
- //rend()反向头迭代器
- riter = c.rend();
- riter--;
- cout << "rend(): "<<"["<< riter->first <<"] = " << riter->second <<endl;
- //cbegin() const 迭代器 正向 头迭代器
- map<int, int>::const_iterator citer;
- citer = c.cbegin();
- cout << "cbegin(): "<<"["<< citer->first <<"] = " << citer->second <<endl;
- //cend() const 迭代器 反向 尾迭代器
- citer = c.cend();
- citer--;
- cout<< "cend(): "<<"["<< citer->first <<"] = " << citer->second <<endl;
三 容量
- //容量
- /*
- map<int, int> c;
- c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
- */
- //是否为kong
- cout << "empty: " << c.empty() <<endl;
- //元素个数
- cout << "size: " << c.size() <<endl;
- //最大容量
- cout << "max_size: " << c.max_size() <<endl;
四 基本操作
- //基本操作
- /*
- map<int, int> c;
- c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
- */
- //operator[] 这个和其他容器的operator有些不同,如果[index] 的index(key) 在map中存在则直接返回该key对应的data ,如果不存在则想该位置插入默认值
- cout << "operator[]: " << c[] << endl;
- cout << "operator[]: " << c[] << endl; //这时你会发现 map自动插入一个c[10]
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //at() 取data
- cout<< "at(): " << c.at() << endl;
- //插入insert() map 不允许key重复 插入重复key 不会报错但插入不成功
- c.insert(pair<int, int>(, ));
- cout <<"insetr(): ";
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- map<int, int> c_insert;
- map<int, int>::iterator insert_iter = c_insert.begin();
- c_insert.insert(insert_iter,pair<int, int>(, ));
- cout <<"insetr(): ";
- for(auto i : c_insert)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //删除
- map<int,int>::iterator erase_iter = c.begin();
- c.erase(erase_iter);
- cout <<"erase(): ";
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //指定下表删除
- c.erase();
- cout <<"erase(): ";
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //指定元素删除
- erase_iter = c.find();
- if(erase_iter != c.end())
- {
- cout<<"found index: "<< erase_iter->first <<endl;
- c.erase(erase_iter);
- }
- else{
- cout<< "Not found" <<endl;
- }
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //交换swap
- map<int, int> c_swap1;
- c_swap1.insert({pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,)});
- map<int, int> c_swap2;
- cout<<"swap() before: "<<endl;
- cout<<"c_swap1: ";
- for(auto i : c_swap1)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- cout<<"c_swap2: ";
- for(auto i : c_swap2)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- cout<<"swap() after: ";
- c_swap2.swap(c_swap1);
- cout<<"c_swap1: ";
- for(auto i : c_swap1)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- cout<<"c_swap2: ";
- for(auto i : c_swap2)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //清除clear
- c_insert.clear();
- cout <<"clear(): ";
- for(auto i : c_insert)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //elements() 插入 如果存在什么也不做 如果不存在插入
- map<int, int>::iterator element_iter = c_swap2.begin();
- auto xxx = c_swap2.emplace(pair<int, int>(,));
- if(xxx.second)
- {
- cout << "不存在" <<endl;
- }
- else
- {
- cout<< "存在" <<endl;
- }
- cout <<"elements(): ";
- for(auto i : c_swap2)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //emplace_hint() 插入
- element_iter = c.emplace_hint(element_iter, pair<int, int>(,));
- cout <<"emplace_hint(): ";
- if(element_iter != c_swap2.end())
- {
- cout<< "存在" <<endl;
- }
- else{
- cout << "不存在" <<endl;
- }
五 操作函数
- //函数
- /*
- map<int, int> c;
- c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
- */
- //key_comp 返回key排序的函数 返回仿函数
- cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(,) <<endl; //会返回1 因为1<2
- cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(,) <<endl; //会返回0 因为2>1
- cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(,) <<endl; //会返回0 因为1=1
- //value_comp 返回取value和key数据包中的 取key函数 返回仿函数
- pair<int,int> value_comp_pair = *c.begin();
- iter = c.begin();
- cout << c.value_comp()(*iter++,value_comp_pair) << endl;
六 算法
- //算法
- /*
- map<int, int> c;
- c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)});
- */
- //find() 指定key 返回对应pair
- cout <<"find(1): " << c.find()->second << endl;;
- //count() key出现的次数
- cout <<"count(1): " << c.count()<< endl;;
- c.erase();
- //lower_bound 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
- auto lower_boundObj = c.lower_bound();
- if(lower_boundObj->first)
- cout<<lower_boundObj->first<<endl;
- else
- cout<< "Not found lower_boundObj" << endl;
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //upper_bound 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
- auto upper_boundObj = c.upper_bound();
- if(upper_boundObj->first)
- cout<<upper_boundObj->first<<endl;
- else
- cout<< "Not found upper_bound" << endl;
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- //equal_range()返回该元素所在区间(闭区间),返回值是一个pair<iterator, iterator>类型,first代表所在区间的起点迭代器,second表示所在区间的终点迭代器
- auto equal_rangeObj = c.equal_range();
- if(equal_rangeObj.first->first)
- {
- cout<<equal_rangeObj.first->first<<endl;
- }
- else
- cout<< "NOT equal_rangeObj.first" << endl;
- if(equal_rangeObj.second->second)
- {
- cout<<equal_rangeObj.second->first<<endl;
- }
- else
- cout<< "NOT second" << endl;
七 自定义比较函数 map 默认为升序 改为降序
- class my_compare_
- {
- public:
- bool operator()(int a, int b)
- {
- return a > b;
- }
- };
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- map<int, int, my_compare_> c;
- c.insert({pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,),pair<int, int>(,)});
- for(auto i : c)
- {
- cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- return ;
- }
STL标准库-容器-map和multimap的更多相关文章
- STL标准库-容器-set与map
STL标准库-容器-set与multiset C++的set https://www.cnblogs.com/LearningTheLoad/p/7456024.html STL标准库-容器-map和 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与multiset
技术在于交流.沟通,转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. set与multiset关联容器 结构如下 set是一种关联容器,key即value,value即key.它是自动排序,排序特点依据key se ...
- STL标准库-容器-deque
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. deque双向开口可进可出的容器 我们知道连续内存的容器不能随意扩充,因为这样容易扩充别人那去 deque却可以,它创造了内存 ...
- STL标准库-容器-vector
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. 向量容器vector是一个动态数组,内存连续,它是动态分配内存,且每次扩张的原来的二倍. 他的结构如下 一 定义 vector ...
- STL学习笔记— —容器map和multimap
简单介绍 在头文件<map> 中定义 namespace std { template <typename Key, typename T, typename Compare = l ...
- STL标准库-容器-list
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. list 表示非连续的内存区域,并通过一对指向首尾元素的指针双向链接起来,从而允许向前和向后两个方向进行遍历.在list 的任 ...
- STL标准库-容器-rb_tree
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性 红黑树,关联式容器底层实现(map set),在使用中基本运用不到,但是还是想了解一下他的运作方式 Red_Black tree ...
- 关于C++ STL标准库中map 的多元素应用
map的特性是,所有的元素会根据键值自动排序.map的所有元素都是pair,同时拥有实值(value)和键值(key).pair的第一个元素被视为键值,第二个被视为实质piar 的定义 templat ...
- STL标准库-容器适配器
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性 上一节介绍了仿函数适配器,这节主要介绍容器适配器和迭代器适配器的概念,其实容器适配器和迭代器其适配器就是封装了一些其他class ...
随机推荐
- python 面向对象 类 __doc__
用来打印类的描述信息 class A1(object): '''类的描述信息''' print(A1.__doc__) # 类的描述信息
- python 定义类 学习2
构造函数的变量 也叫做 实例变量 class role(): # 传参数 def __init__(self,name,role,weapon,life_value=100,moneny=15000) ...
- leetcode——Search for a Range 排序数组中寻找目标下标范围(AC)
Given a sorted array of integers, find the starting and ending position of a given target value. You ...
- (转)二十三种设计模式及其python实现
本文源码寄方于github:https://github.com/w392807287/Design_pattern_of_python 参考文献: <大话设计模式>——吴强 <Py ...
- t检验&z检验学习[转载]
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37777649/article/details/74937242 1.什么是T检验? T检验是假设检验的一种,又叫student t检验(St ...
- AngularJS SQL
服务端代码 以下列出了列出了几种服务端代码类型: 使用 PHP 和 MySQL.返回 JSON. 使用 PHP 和 MS Access.返回 JSON. 使用 ASP.NET, VB, 及 MS Ac ...
- HTML5游戏开发系列教程10(译)
原文地址:http://www.script-tutorials.com/html5-game-development-lesson-10/ 最后我们将继续使用canvas来进行HTML5游戏开发系列 ...
- 推荐一个js脚本的字体拟合模型
推荐一个js脚本的字体拟合模型 http://r3mi.github.io/poly2tri.js/ 推荐一个js脚本的字体拟合模型 http://r3mi.github.io/poly2tri. ...
- iview使用vue-i18n实现国际化
iview官网中和网上的例子中使用的都是webpack方式,需要import js文件,但是由于项目架构比较简单,没有使用webpack,纯html和js进行交互.所以这里就直接使用js文件引用方式. ...
- Linux内核分析08
进程的切换和系统的一般执行过程 一,进程切换的关键代码switch_to分析 进程调度的时机 中断处理过程(包括时钟中断.I/O中断.系统调用和异常)中,直接调用schedule(),或者返回用户态时 ...
