Linux性能优化-理解平均负载
1 理解CPU
CPU(Cental Processing Unit)是计算机系统的运算和控制核心,是信息处理、程序运行的最终执行单元,相当系统的“大脑”。
当 cpu 过于繁忙,就像“人脑”并发处理过多事情,会降低做事效率,严重时甚至会导致崩溃“宕机”。因此,理解 CPU 工作原理,合理控制资源,是保障系统稳定持续运行的重要手段。
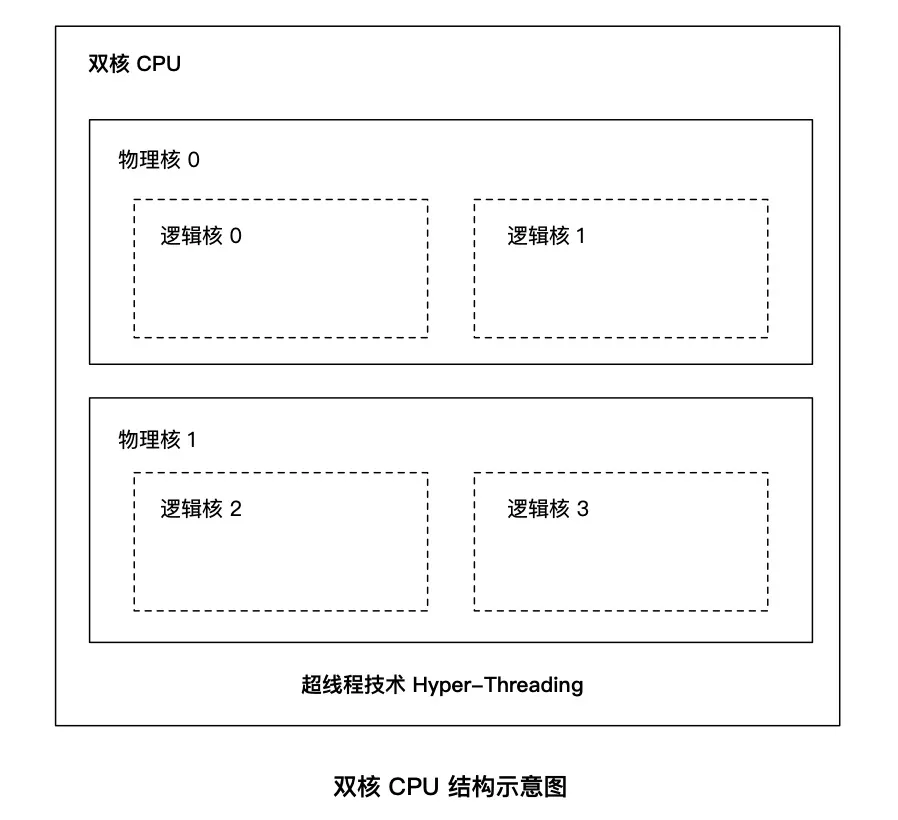
1.1 多 cpu 和多核 cpu
多个物理CPU,CPU通过总线进行通信,效率比较低:
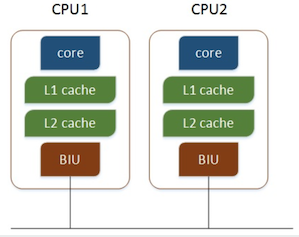
用于双路Xeon可扩展的主板:超微X11DAi-N
多核CPU,不同的核通过L2 cache进行通信,存储和外设通过总线与CPU通信:
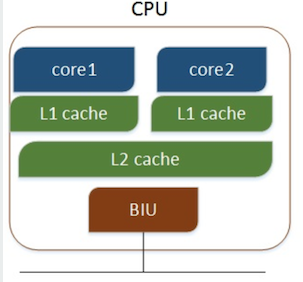
用于单路Xeon-W的主板:超微X11SRA
2 查询CPU信息
- [root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'physical id' | sort | uniq | wc -l //查看 cpu 个数
- [root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'cpu cores' | sort | uniq // 查看cpu物理核数
- cpu cores :
- [root@localhost ~]# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'siblings' | sort | uniq // 查看 cpu 逻辑核数
- siblings :
3 平均负载含义
当系统变慢的时候,我们一般使用 top 或 uptime 命令来查看系统平均负载情况。
正确定义:单位时间内,系统中处于 可运行状态(R,Running/Runnable)和不可中断睡眠状态(D,Disk Sleep) 的平均进程数。
错误定义:单位时间内的 cpu 使用率。
可运行状态的进程:正在使用 cpu 或者正在等待 cpu 的进程,即 ps aux 命令下 STAT 处于 R 状态的进程
不可中断状态的进程:处于内核态关键流程中的进程,且不可被打断,如等待硬件设备IO响应,ps命令D状态的进程。
理想状态:每个 cpu 上都有一个活跃进程,即平均负载数等于 cpu 数。
过载经验值:平均负载高于 cpu 数量 70% 的时候。
假如在一个单 cpu 系统上看到 1.73 0.60 7.98,表示在过去一分钟内系统有73%的超载,而在15分钟内,有698%的超载。
注:可运行状态进程包括正在使用cpu或等待cpu的进程;不可中断状态进程是指处于内核关键流程中的进程,并且该流程不可被打断,比如当进程向磁盘写数据时,如果被打断,就可能出现磁盘数据与进程数据不一致。
不可中断进程状态,本质上是系统对进程和硬件设备的一种保护机制。
4 平均负载案例分析
系统环境和工具
系统环境和配置:CentOS 7 64bit 4G内存 2CPU
相关工具:stress、sysstat。
stress:一个Linux系统压力测试工具。
sysstat:监控和分析系统的性能工具,包括mpstat关于cpu详细信息(单独输出或分组输出)、pidstat(进程性能分析)命令、iostat等。
安装工具:yum install -y epel-release stress sysstat
同一个Linux系统开三个终端。
场景一:CPU密集型进程
第一个终端运行stress命令模拟一个cpu使用率100%
- [root@localhost ~]# stress --cpu --timeout
- stress: info: [] dispatching hogs: cpu, io, vm, hdd
第二个终端运行uptime查看平均负载变化情况
#-d参数表示高亮显示变化的区域
- [root@localhost ~]# watch -d uptime
第三个终端云溪mpstat查看cpu使用率变化情况
#-P ALL表示监控所有cpu,5表示间隔5秒输出一组数据
- [root@localhost zhiwenwei]# mpstat -P ALL
- Linux 3.10.-957.10..el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月01日 _x86_64_ ( CPU)
- 22时33分45秒 CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle
- 22时33分50秒 all 50.95 0.00 0.30 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 48.75
- 22时33分50秒 1.80 0.00 0.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 97.60
- 22时33分50秒 100.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
结论:从终端二看到1分钟的平均负载会慢慢增加到1.00;终端三正好有一个cpu使用率为100%,但它的iowait只有0,说明平均负载的升高正是由于cpu使用率的升高。
那么到底是哪个进程导致cpu使用率为100%,可以使用top命令来来查或使用pidstat命令。
- [root@localhost zhiwenwei]# pidstat -u
- Linux 3.10.-957.10..el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月01日 _x86_64_ ( CPU)
- 22时37分09秒 UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command
- 22时37分14秒 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 xfsaild/dm-
- 22时37分14秒 1.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.40 mono
- 22时37分14秒 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 rsyslogd
- 22时37分14秒 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 watch
- 22时37分14秒 100.20 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.20 stress
- 22时37分14秒 0.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.40 pidstat
- 平均时间: UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command
- 平均时间: 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - xfsaild/dm-
- 平均时间: 1.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.40 - mono
- 平均时间: 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - rsyslogd
- 平均时间: 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - watch
- 平均时间: 100.20 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.20 - stress
- 平均时间: 0.20 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.40 - pidstat
场景二:I/O密集型进程
第一个终端运行stress命令模拟I/O压力
- [root@localhost ~]# stress -i --timeout
第二个终端运行uptime查看当前平均负载变化情况
- [root@localhost ~]# watch -d uptime
第三个终端运行mpstat查看cpu使用率变化情况
- [zhiwenwei@localhost tmp]$ mpstat -P ALL
- Linux 3.10.-957.10..el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月02日 _x86_64_ ( CPU)
- 13时44分56秒 CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle
- 13时45分01秒 all 1.41 0.00 47.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.16
- 13时45分01秒 1.61 0.00 89.52 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 8.87
- 13时45分01秒 1.21 0.00 5.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 93.36
- 平均时间: CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle
- 平均时间: all 1.41 0.00 47.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.16
- 平均时间: 1.61 0.00 89.52 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 8.87
- 平均时间: 1.21 0.00 5.43 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 93.36
结论:1分钟的平均负载会慢慢增加到1,其中两个cpu平均使用率49.40,而idle平均达到50.40。说明平均负载的升高由于idle的升高。
查看导致idle升高的进程:
- [zhiwenwei@localhost tmp]$ pidstat -u
- Linux 3.10.-957.10..el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月02日 _x86_64_ ( CPU)
- 13时50分46秒 UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command
- 13时50分51秒 0.00 8.58 0.00 1.60 8.58 kworker/u4:
- 13时50分51秒 1.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.40 mono
- 13时50分51秒 1.00 62.08 0.00 3.59 63.07 stress
- 13时50分51秒 0.00 14.77 0.00 1.60 14.77 kworker/u4:
- 13时50分51秒 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 pidstat
- 平均时间: UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command
- 平均时间: 0.00 8.58 0.00 1.60 8.58 - kworker/u4:
- 平均时间: 1.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.40 - mono
- 平均时间: 1.00 62.08 0.00 3.59 63.07 - stress
- 平均时间: 0.00 14.77 0.00 1.60 14.77 - kworker/u4:
- 平均时间: 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.00 0.20 - pidstat
可以发现是stress进程导致的。
场景三:大量进程
第一个终端使用stress命令模拟10个进程
- [root@localhost ~]# stress -c --timeout
第二个终端用uptime查看平均负载变化情况
- [root@localhost ~]# watch -d uptime
第三个终端pidstat查看进程情况
- [root@localhost ~]# pidstat -u
- Linux 3.10.-957.10..el7.x86_64 (localhost.localdomain) 2019年04月02日 _x86_64_ ( CPU)
- 13时55分59秒 UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command
- 13时56分04秒 1.38 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.58 mono
- 13时56分04秒 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.53 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.72 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.53 0.00 0.00 78.90 19.53 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.72 0.00 0.00 80.08 19.72 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 stress
- 13时56分04秒 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 stress
- 13时56分04秒 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.39 0.20 pidstat
- 平均时间: UID PID %usr %system %guest %wait %CPU CPU Command
- 平均时间: 1.38 0.20 0.00 0.00 1.58 - mono
- 平均时间: 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.53 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.49 19.72 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.68 19.72 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.53 0.00 0.00 78.90 19.53 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.72 0.00 0.00 80.08 19.72 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.53 0.00 0.00 79.09 19.53 - stress
- 平均时间: 19.72 0.00 0.00 79.29 19.72 - stress
- 平均时间: 0.00 0.20 0.00 0.39 0.20 - pidstat
总结:
平均负载高有可能是cpu密集型进程导致的;
平均负载高不一定是cpu使用率高,还有可能是I/O更繁忙
当发现负载高的时候,可以使用mpstat、pidstat等工具辅助分析负载高的根源。
参考文献
https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/69618
Linux性能优化-理解平均负载的更多相关文章
- linux性能优化cpu-02平均负载
每次我们系统变慢时,我们通常做的第一件事就是top命令或者uptime命令,看一下系统的负载情况,比如下面: 我在命令行中输入uptime 22:15:51 表示当前系统时间 up 13 min ...
- 1 linux性能优化之平均负载uptime
不知道onenote的笔记复制出来就是图片了...
- linux性能分析之平均负载
平均负载 1,执行 top 或者 uptime 命令 来了解系统负载 uptime 分析显示 当前时间,系统运行时间,正在登录用户数 平均负载是指单位时间内,系统处于可运行状态和不可中断状态的平均进程 ...
- Linux性能优化-平均负载
Linux性能优化-平均负载 目录 Linux性能优化-平均负载 平均负载的含义 平均负载为多少时合理 平均负载与 CPU 使用率 平均负载案例分析 场景一:CPU 密集型进程 场景二:I/O 密集型 ...
- 《Linux 性能优化实战—倪朋飞 》学习笔记 CPU 篇
平均负载 指单位时间内,系统处于可运行状态和不可中断状态的平均进程数,即平均活跃进程数 可运行状态:正在使用CPU或者正在等待CPU 的进程,也就是我们常用 ps 命令看到的,处于 R 状态 (Run ...
- 如何学习Linux性能优化?
如何学习Linux性能优化? 你是否也曾跟我一样,看了很多书.学了很多 Linux 性能工具,但在面对 Linux 性能问题时,还是束手无策?实际上,性能分析和优化始终是大多数软件工程师的一个痛点.但 ...
- Linux性能优化从入门到实战:01 Linux性能优化学习路线
我通过阅读各种相关书籍,从操作系统原理.到 Linux内核,再到硬件驱动程序等等. 把观察到的性能问题跟系统原理关联起来,特别是把系统从应用程序.库函数.系统调用.再到内核和硬件等不同的层级贯 ...
- Linux性能优化实战CPU篇之总结(四)
一.分析CPU瓶颈 1,性能指标 a>CPU使用率 CPU使用率描述了非空闲时间占总CPU时间的百分比,根据CPU上运行任务的不同可以分为:用户CPU.系统CPU.等待I/O CPU.软中断和硬 ...
- Linux 性能优化之 IO 子系统 系列 图
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/articlelist_1029388674_11_1.html Linux 性能优化之 IO 子系统(一) 本文介绍了对 Linux IO 子系统 ...
随机推荐
- 工厂参观记:.NET Core 中 HttpClientFactory 如何解决 HttpClient 臭名昭著的问题
在 .NET Framework 与 .NET Core 中 HttpClient 有个臭名昭著的问题,HttpClient 实现了 IDispose 接口,但当你 Dispose 它时,它不会立即关 ...
- DjangoRestFramework学习三之认证组件、权限组件、频率组件、url注册器、响应器、分页组件
DjangoRestFramework学习三之认证组件.权限组件.频率组件.url注册器.响应器.分页组件 本节目录 一 认证组件 二 权限组件 三 频率组件 四 URL注册器 五 响应器 六 分 ...
- zhuan: WAN simulating tool - Netem : command tc qdisc
Last weekly meeting we talked about a WAN simulating tool in order to test WPG, I find a great tool ...
- 在Fastreport里使用的CRC函数
如标题, 是在Fastreport的脚本里运行的CRC计算函数, 包括CRC-16/CRC-32 基本是从网上找的代码, 然后改出来的 至于为什么要在FR的脚本里运行....呵呵 不要在意这些细节(找 ...
- laravel读取excel
$filePath = 'storage/exports/成员信息.xls'; Excel::load($filePath, function ($reader) {// $data = $reade ...
- [git] git怎样fork一个repo
描述 我定制了一下strongswan的工程.然后想把我自己的定制变成一个repo push到远端git.tong.com与大家分享. 这个时候,应该怎么做? 如果你用过github的话.那么你可以理 ...
- Jmeter设置默认中文页面
方法一(从网上看到的) 启动Jmeter找到 options >choose language >chinese(简体繁体自己选). 这样设置后界面就变成了中文,但是当我们下次打开时又恢复 ...
- char和QChar(Unicode的编码与内存里的值还不是一回事)
char类型是c/c++中内置的类型,描述了1个字节的内存信息的解析.比如: char gemfield=’g’;那么在由gemfield标记的这块内存的大小就是1个字节,信息就是01100111,8 ...
- iTerm2 与 Oh My Zsh的配套使用
详见: https://www.jianshu.com/p/7de00c73a2bb https://github.com/sirius1024/iterm2-with-oh-my-zsh https ...
- 007-chrome插件系列
1.Axure RP Extension for Chrome 2.Charset 3.CLEAN crxMouse Gestures 4.Google 翻译 5.JSONView 6.restlet
