AI数据分析(二)
NumPy库
NumPy数组对象
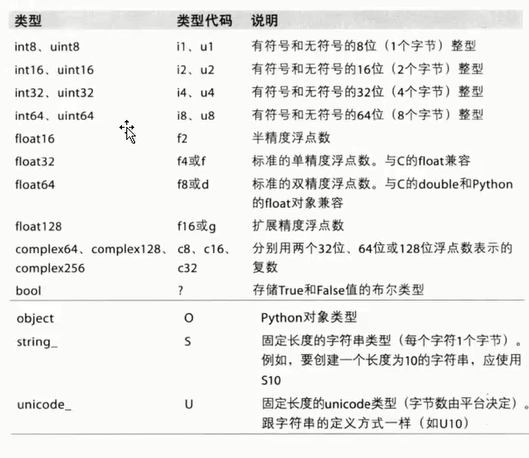
NumPy数据类型
数组的索引
数组的切片
数组的组合
数组的分割
数组的属性
NumPy数组对象
NumPy数据类型
#numpy数据类型
print "In: float64(42)"
print np.float64(42) print "In: int8(42.0)"
print np.int8(42.0) print "In: bool(42)"
print np.bool(42) print np.bool(0) print "In: bool(42.0)"
print np.bool(42.0) print "In: float(True)"
print np.float(True)
print np.float(False) print "In: arange(7, dtype=uint16)"
print np.arange(7, dtype=np.uint16) print "In: int(42.0 + 1.j)"
数据类型
# 数据类型转换
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
arr.dtype
float_arr = arr.astype(np.float64)
float_arr.dtype arr = np.array([3.7, -1.2, -2.6, 0.5, 12.9, 10.1])
arr
arr.astype(np.int32) numeric_strings = np.array(['1.25', '-9.6', ''], dtype=np.string_)
numeric_strings.astype(float)
数据类型转换
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
print(a.dtype.byteorder) #= print(a.dtype.itemsize) #
数据类型对象
print np.arange(7, dtype='f')
print np.arange(7, dtype='D') print np.dtype(float) print np.dtype('f') print np.dtype('d') print np.dtype('f8') print np.dtype('Float64')
类型代码
#dtype类的属性
t = np.dtype('Float64') print t.char print t.type print t.str #创建自定义数据类型
t = np.dtype([('name', np.str_, 40), ('numitems', np.int32), ('price', np.float32)])
print t print t['name'] itemz = np.array([('Meaning of life DVD', 42, 3.14), ('Butter', 13, 2.72)], dtype=t) print itemz[1]
dtype类的属性、创建自定义数据类型
数组操作
数组与标量之间的运算
#创建多维数组
m=np.array([np.arange(2),np.arange(2)])
print(m)
print(m.shape)
print(m.dtype)
#数组与标量的运算
arr = np.array([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]])
arr
arr * arr
结果: array([[ 1., 4., 9.],
[16., 25., 36.]])
arr - arr 1 / arr
arr ** 0.5
数组的索引
#布尔型索引
names = np.array(['Bob', 'Joe', 'Will', 'Bob', 'Will', 'Joe', 'Joe'])
data = randn(7, 4)
names
data names == 'Bob'
data[names == 'Bob'] data[names == 'Bob', 2:]
data[names == 'Bob', 3] names != 'Bob'
data[-(names == 'Bob')] mask = (names == 'Bob') | (names == 'Will')
mask
data[mask] data[data < 0] = 0
data data[names != 'Joe'] = 7
data
布尔型索引
#花式索引
arr = np.empty((8, 4))
for i in range(8):
arr[i] = i
arr arr[[4, 3, 0, 6]] arr[[-3, -5, -7]] arr = np.arange(32).reshape((8, 4))
arr
arr[[1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2]] arr[[1, 5, 7, 2]][:, [0, 3, 1, 2]] arr[np.ix_([1, 5, 7, 2], [0, 3, 1, 2])]
花式索引
数组的切片
#多维数组的切片与索引
b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4) #生成二维数组,三行四列 print b.shape print b
#array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]]) print b[0,0,0] print b[:,0,0] print b[0] print b[0, :, :] print b[0, ...] print b[0,1] print b[0,1,::2] print b[...,1] print b[:,1] print b[0,:,1] print b[0,:,-1] print b[0,::-1, -1] print b[0,::2,-1] print b[::-1] s = slice(None, None, -1)
print b[(s, s, s)]
数组的组合
#数组转置
arr = np.arange(15).reshape((3, 5))
arr
arr.T #改变数组的维度
b = np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4) print b print b.ravel() print b.flatten() b.shape = (6,4) print b print b.transpose() b.resize((2,12)) print b
数组转置、改变数组的维度
#组合数组
a = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3) print a b = 2 * a print b print np.hstack((a, b)) 水平组合 print np.concatenate((a, b), axis=1) print np.vstack((a, b)) 垂直组合 print np.concatenate((a, b), axis=0) print np.dstack((a, b)) 深度组合 oned = np.arange(2) print oned twice_oned = 2 * oned print twice_oned print np.column_stack((oned, twice_oned)) 列组合 print np.column_stack((a, b)) print np.column_stack((a, b)) == np.hstack((a, b)) print np.row_stack((oned, twice_oned)) print np.row_stack((a, b)) print np.row_stack((a,b)) == np.vstack((a, b))
组合数组
数组的分割
#数组的分割
a = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3) print a print np.hsplit(a, 3) 水平分割 print np.split(a, 3, axis=1) print np.vsplit(a, 3) 垂直分割 print np.split(a, 3, axis=0) c = np.arange(27).reshape(3, 3, 3) print c print np.dsplit(c, 3)
数组的分割
数组的属性
#数组的属性
b=np.arange(24).reshape(2,12)
b.ndim 维度
b.size 数组元素总个数
b.itemsize 元素占的字节数
b.nbytes b = np.array([ 1.+1.j, 3.+2.j])
b.real 实部
b.imag 虚部 b=np.arange(4).reshape(2,2)
b.flat
b.flat[2] #数组的转换
b = np.array([ 1.+1.j, 3.+2.j])
print b print b.tolist() 转化成python中的列表 print b.tostring() print np.fromstring('\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xf0?\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xf0?\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x08@\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00@', dtype=complex) print np.fromstring('20:42:52',sep=':', dtype=int) print b print b.astype(int) print b.astype('complex')
数组的属性
AI数据分析(二)的更多相关文章
- SPSS数据分析—二分类Logistic回归模型
对于分类变量,我们知道通常使用卡方检验,但卡方检验仅能分析因素的作用,无法继续分析其作用大小和方向,并且当因素水平过多时,单元格被划分的越来越细,频数有可能为0,导致结果不准确,最重要的是卡方检验不能 ...
- Python数据分析(二): Numpy技巧 (1/4)
In [1]: import numpy numpy.__version__ Out[1]: '1.13.1' In [2]: import numpy as np
- Python数据分析(二): Numpy技巧 (2/4)
numpy.pandas.matplotlib(+seaborn)是python数据分析/机器学习的基本工具. numpy的内容特别丰富,我这里只能介绍一下比较常见的方法和属性. 昨天晚上发了第一 ...
- Python数据分析(二): Numpy技巧 (3/4)
numpy.pandas.matplotlib(+seaborn)是python数据分析/机器学习的基本工具. numpy的内容特别丰富,我这里只能介绍一下比较常见的方法和属性. 昨天晚上发了第一 ...
- Python数据分析(二): Numpy技巧 (4/4)
numpy.pandas.matplotlib(+seaborn)是python数据分析/机器学习的基本工具. numpy的内容特别丰富,我这里只能介绍一下比较常见的方法和属性. 第一部分: ht ...
- 【python数据分析实战】电影票房数据分析(二)数据可视化
目录 图1 每年的月票房走势图 图2 年票房总值.上映影片总数及观影人次 图3 单片总票房及日均票房 图4 单片票房及上映月份关系图 在上一部分<[python数据分析实战]电影票房数据分析(一 ...
- Python+Requests+Bs4(解析)爬取某诗词信息(数据分析二)
1.环境安装 - 需要将pip源设置为国内源,阿里源.豆瓣源.网易源等 - windows (1)打开文件资源管理器(文件夹地址栏中) (2)地址栏上面输入 %appdata% (3)在这里面新建一个 ...
- [USB波形分析] 全速USB波形数据分析(二)
在上一篇文章全速USB波形数据分析(一)介绍了全速USB的数据包(Packet)的组成,数据的类型等基本知识.这篇文章介绍USB的几种传输方式 事务(Transaction) USB协议定义了三种不同 ...
- Python数据分析(二): Pandas技巧 (1)
第一部分: ipython http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7623347.html 第二部分: numpy http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7 ...
随机推荐
- Eclipse 设置背景色
window -> preferences -> General -> Editors -> Test Editors -> Background color 勾掉Sy ...
- 洛谷 p1090 合并果子
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1090 优先队列的经典题目 体现了stl的优越性 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using ...
- ORM关于表那些事
一.. ORM表和表之间的关系 1. 一对多 --> 外键(ForeignKey) 2. 多对多 --> 另外一张关系表(ManyToManyField) 1. 三种方式 1. 自己建立第 ...
- 爬虫与request模块
一.爬虫简介 1.介绍 网络爬虫(又被称为网页蜘蛛,网络机器人,在FOAF社区中间,更经常的称为网页追逐者),是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本.另外一些不常使用的名字还有蚂蚁. ...
- Centos7 systemctl服务脚本
systemd.service 参考文档 RHEL6和之前的版本使用的初始进程是init,init是一个线性的启动过程,一个接一个的启动,比较慢:systemd则可以多进程启动,速度提高很多. sev ...
- 第十八节、基于传统图像处理的目标检测与识别(HOG+SVM附代码)
其实在深度学习中我们已经介绍了目标检测和目标识别的概念.为了照顾一些没有学过深度学习的童鞋,这里我重新说明一次:目标检测是用来确定图像上某个区域是否有我们要识别的对象,目标识别是用来判断图片上这个对象 ...
- (二分查找 拓展) leetcode 69. Sqrt(x)
Implement int sqrt(int x). Compute and return the square root of x, where x is guaranteed to be a no ...
- usb的hid鼠标键盘报告描述符(五)
title: usb的hid鼠标键盘报告描述符 tags: linux date: 2018/12/20/ 18:05:08 toc: true --- usb的hid鼠标键盘报告描述符 https: ...
- Tomcat设计模式
omcat 系统架构与设计模式,第 2 部分 设计模式分析 系列内容: 此内容是该系列 2 部分中的第 2 部分: Tomcat 系统架构与设计模式 门面设计模式 门面设计模式在 Tomcat 中有多 ...
- MongoDB实战性能优化
1. 性能优化分类 mongodb性能优化分为软件层面和操作系统层面. 软件层面,一般通过修改mongodb软件配置参数来达到,这个需要非常熟悉mongodb里面的各种配置参数: 而操作系统层面,相对 ...