SpringBoot学习记录(二)
一. SpringBoot日志框架
SpringBoot:底层是Spring框架,Spring框架默认是用JCL(commons-logging);
SpringBoot选用SLF4j和logback;
1.SLF4j使用
(1) 如何在系统中使用SLF4j
以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法;给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和logback的实现jar包
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}
网上找的图例:每一个日志的实现框架都有自己的配置文件。使用slf4j以后,配置文件还是做成日志实现框架自己本身的配置文件

(2) 遗留问题
SpringBoot (slf4j+logback);Spring (commons-logging); Hibernate (jboss-logging); Mybatis
统一日志记录,即使是别的框架如何与SpringBoot一起使用slf4j进行输出?
1. 将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;
2. 用中间包替换原有的日志框架;
3. 导入slf4j其他的实现
(3) SpringBoot日志关系
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
SpringBoot使用它来做日志功能;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐starter‐logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
底层依赖关系
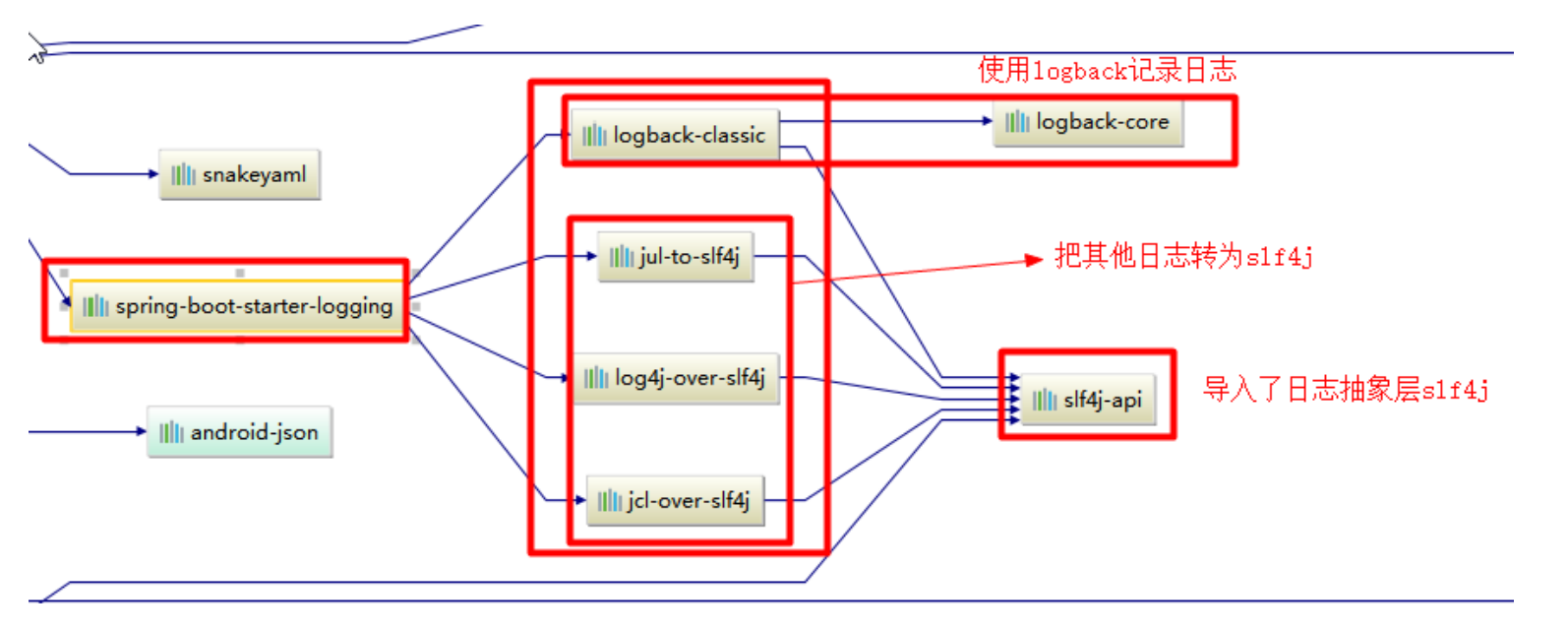
总结:
(1) SPringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录
(2) SpringBoot也罢其他的日志都替换成了slf4j
(3) 中间替换包
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public abstract class LogFactory {
static String UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION_IN_JCL_OVER_SLF4J =
"http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsupported_operation_in_jcl_over_slf4j";
static LogFactory logFactory = new SLF4JLogFactory();

(4) 如果我们要引入其他框架一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉
例如;Spring框架用的是commons-logging;那么如果要使用Spring就需要吧这个依赖移除
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐core</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons‐logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons‐logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架的依赖的日志框架排除掉即可
2. SpringBoot的日志配置
SpringBoot默认帮我们配置了日志;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootLoggingApplicationTests { @Test
public void contextLoads() {
// System.out.println();
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); //日志的级别:由低到高 trace < debug < info < warn < error
//可以调整输出的日志级别;日志就只会在这个级别以及之后的高级别生效
logger.trace("这是trace日志。。。");
logger.debug("这是debug日志。。。"); //SpringBoot默认级别是从info开始,即root级别; 可以通过配置文件进行调节
logger.info("这是info日志。。。");
logger.warn("这是warn日志。。。");
logger.error("这是error日志。。。");
} }
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%‐5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符 %d{yyyy‐MM‐dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %‐5level %logger{50} ‐ %msg%n
SpringBoot修改日志的默认配置
logging.level.com.javaweb=trace #在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹;使用spring.log作为默认文件
logging.path=/spring/log #不指定路径在当前项目下生成springboot.log,也可以指定完胜的路径
#logging.file=springboot.log
#logging.file=D:/springboot.log #在控制台输出日志的格式
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
#在指定文件中日志的输出格式
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} == [%thread == %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
二. SpringBoot的Web开发
1. 使用SpringBoot:
(1) 创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块
(2) SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
(3) 自己编写业务代码
自动配置原理:
这个场景SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改?能修改那些配置?能不能扩展?
xxxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件;
xxxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容;
2. SpringBoot对静态济源的映射规则
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties { public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if(!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if(!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if(!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern}).addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
}
(1) 所有/webjars/**,都去classpath:/META-INF/resource/webjars/ 找资源
以jar包的方式引入静态资源

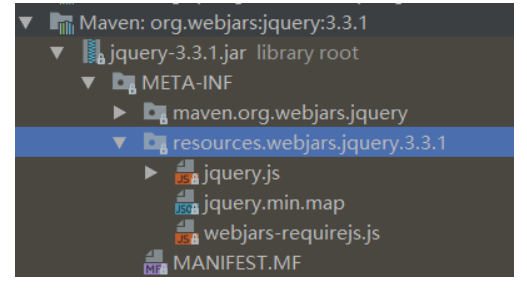
localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
<!-- 引入jquery-webjars 在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</dependency>
(2) /** 访问当前项目的任何资源 (静态资源文件夹)
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/",
"classpath:/static/",
"classpath:/public/",
localhost:8080/abc ===>自动去静态资源文件夹寻找abc资源
(3) 欢迎页;静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;
(4) 所有的**/facivon.ico都是在静态资源文件下找
3. 模板引擎
JSP,Veloctiy,Freemarker,Thymeleaf;
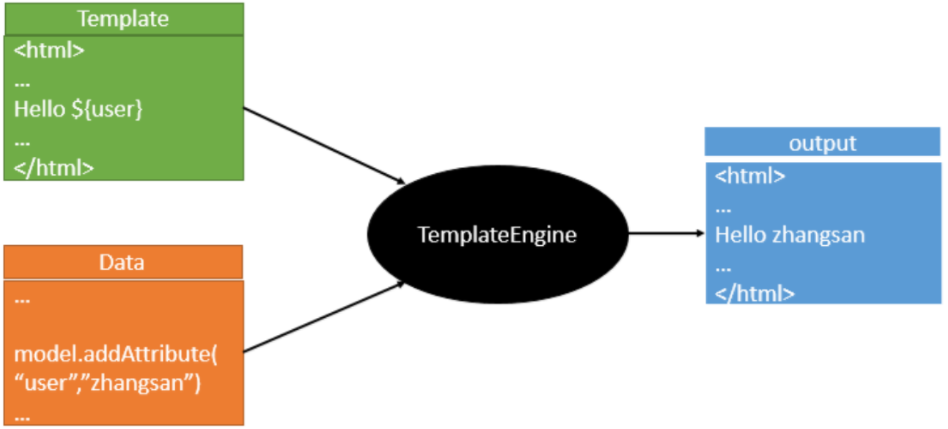

SpringBoot推荐使用Thymeleaf:
语法更简单,功能更强大;
1. 引入thymeleaf
<!-- 引入模板引擎 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 使用thymeleaf
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.thymeleaf"
)
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true; //只要我们把html页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/"; private String suffix = ".html";
private String mode = "HTML";
只需要在页面中导入thymeleaf的空间,就可以使用thymeleaf的语法
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
3. thymeleaf语法规则
(1) th:text:改变当前元素里面的文本内容;
th:任意html属性;来替换原生属性:

<div th:text="${hello}" th:id="${hello}" th:class="${hello}"></div>

(2) 表达式
Simple expressions:(表达式语法)
Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL;
1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法
2)、使用内置的基本对象:
#ctx : the context object.
#vars: the context variables.
#vars: the context variables.
#locale : the context locale.
#request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object.
#response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object.
#session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object.
#servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
${session.foo}
3)、内置的一些工具对象:
#execInfo : information about the template being processed.
#messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the
same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax.
#uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs
#conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any).
#dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : methods for objects in general.
#bools : methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : methods for arrays.
#lists : methods for lists.
#sets : methods for sets.
#maps : methods for maps.
#aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
#ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a
result of an iteration).
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样;
补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}:
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容
Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL;
@{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST')}
Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式
<div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div>
Literals(字面量)
Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,…
Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,…
Boolean literals: true , false
Null literal: null
Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,…
Text operations:(文本操作)
String concatenation: +
Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}|
Arithmetic operations:(数学运算)
Binary operators: + , ‐ , * , / , %
Minus sign (unary operator): ‐
Boolean operations:(布尔运算)
Binary operators: and , or
Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not
Comparisons and equality:(比较运算)
Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le )
Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne )
Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符)
If‐then: (if) ? (then)
If‐then‐else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
Special tokens:
No‐Operation: _
例如:
我在业务层java编写:
/**
* @program: spring-boot-web
* @description:
* @author: Yukai Fan
* @create: 2018-10-20 09:46
**/
@Controller
public class HelloController {
//查处一些数据,在页面展示
@RequestMapping("success")
public String success(Map<String, Object> map) {
map.put("hello","<h1>你好</h1>");
map.put("users", Arrays.asList("zhangsan","lisi","wangwu"));
//classpath:/templates/success.html
return "success";
}
}
根据thymeleaf可以默认从classpath:/templates/下寻找success.html
所以使用tyhmeleaf语法在success.html上:
<body>
<h1>成功</h1>
<!-- th:text 设置文本内容 -->
<div th:text="${hello}"></div>
<div th:utext="${hello}"></div>
<hr/>
<!-- th:each每次遍历都会生成当前标签 3个h4标签-->
<h4 th:text="${user}" th:each="user:${users}"></h4>
<hr/>
<h4>
<span th:each="user:${users}"> [[${user}]] </span>
</h4>
</body>
得到的效果为:


其中审查元素可知,有三个h4标签,3个span标签

SpringBoot学习记录(二)的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot学习记录(二)--thymeleaf模板 - CSDN博客
==他的博客应该不错,没有细看 Spring Boot学习记录(二)--thymeleaf模板 - CSDN博客 http://blog.csdn.net/u012706811/article/det ...
- Material Calendar View 学习记录(二)
Material Calendar View 学习记录(二) github link: material-calendarview; 在学习记录一中简单翻译了该开源项目的README.md文档.接下来 ...
- Springboot学习记录1--概念介绍以及环境搭建
摘要:springboot学习记录,环境搭建: 官方文档地址:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current-SNAPSHOT/reference/ht ...
- JavaScript学习记录二
title: JavaScript学习记录二 toc: true date: 2018-09-13 10:14:53 --<JavaScript高级程序设计(第2版)>学习笔记 要多查阅M ...
- 2.VUE前端框架学习记录二
VUE前端框架学习记录二:Vue核心基础2(完结)文字信息没办法描述清楚,主要看编码实战里面,有附带有一个完整可用的Html页面,有需要的同学到脑图里面自取.脑图地址http://naotu.baid ...
- Spring Boot学习记录(二)–thymeleaf模板
自从来公司后都没用过jsp当界面渲染了,因为前后端分离不是很好,反而模板引擎用的比较多,thymeleaf最大的优势后缀为html,就是只需要浏览器就可以展现页面了,还有就是thymeleaf可以很好 ...
- SpringBoot学习(二)——Spring的Java配置方式
Java配置是Spring4.x推荐的配置方式,可以完全替代xml配置. 一.@Configuration 和 @Bean Spring的Java配置方式是通过@Configuration和@Bean ...
- SpringBoot学习(二)
MyBatis是支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射的优秀的持久层框架,避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.spring Boot 是能支持快速创建 Spring 应用的 ...
- 【java并发编程艺术学习】(四)第二章 java并发机制的底层实现原理 学习记录(二) synchronized
章节介绍 本章节主要学习 Java SE 1.6 中为了减少获得锁 和 释放锁 时带来的性能消耗 而引入的偏向锁 和 轻量级锁,以及锁的存储结构 和 升级过程. synchronized实现同步的基础 ...
随机推荐
- Hadoop集群配置免密SSH登录方法
Hadoop集群包含1个主节点和3个从节点,需要实现各节点之间的免密码登录,下面介绍具体的实现方法. 一.Hadoop集群环境 二.免密登录原理 每台主机authorized_keys文件里面包含的主 ...
- POST和 GET
http GET 和 POST 请求的优缺点.区别以及误区 Get和Post在面试中一般都会问到,一般的区别: (1)post更安全(不会作为url的一部分,不会被缓存.保存在服务器日志.以及 ...
- OJDBC版本区别:ojdbc14.jar,ojdbc5.jar和ojdbc6.jar的区别
classes12.jar - for Java 1.2 and 1.3ojdbc14.jar - for Java 1.4 and 1.5ojdbc5.jar - for Java 1.5ojdbc ...
- JS模块
本文主要内容翻译自<Exploring ES6-upgrade to the next version of javascript> 模块系统 定义模块接口,通过接口 隐藏模块的内部实现, ...
- shell学习(11)- seq
今天是五一劳动节,窗户外边,草长莺飞,惠风和畅,但坐在办公室里值班也需要做点事情,今天就写写seq的用法. 作用:用于以指定增量从首数开始打印数字到尾数,即产生从某个数到另外一个数之间的所有整数,并且 ...
- GHOST来进行备份和还原及菜单介绍
这篇文章主要说的是如何手工操作GHOST来进行备份和还原. GHOST的菜单及功能: 在主菜单中,有以下几项: l Local:本地操作,对本地计算机上的硬盘进行操作. l Peer to peer: ...
- PartTime__学习辅助软件_20161025
1.http://www.680.com/ruanjian/412629.html 1.1.http://www.gysjxjy.com/ 密码:我的名字的拼音(全小写) 使用的身份证信息:http: ...
- windows 7 elasticsearch-5.3.2
# windows elasticsearch- D:\nescafe\elasticsearch-\bin λ java -version java version "1.8.0_121& ...
- CountDownLatch与CyclicBarrier的使用与区别
CountDownLatch的介绍和使用: 一个同步辅助类,在完成一组正在其他线程中执行的操作之前,它允许一个或多个线程一直等待. 用给定的计数 初始化 CountDownLatch.由于调用了 co ...
- Linux中ext2文件系统的结构
1.ext2产生的历史 最早的Linux内核是从MINIX系统过渡发展而来的.Linux最早的文件系统就是MINIX文件系统.MINIX文件系统几乎到处都是bug,采用的是16bit偏移量,最大容量为 ...
