ELK Stack总结
ELK Stack
本文基于ELK 6.0,主要针对Elasticsearch和Kibana。
介绍
Elasticsearch is a realtime, distributed search and analytics engine that is horizontally scalable and capable of solving a wide variety of use cases.
优势
- Schemaless, document-oriented:存储JSON documents,更加灵活(不规定每条数据的必须具备哪些列)
- Searching:全文text检索,日期、数字、地理位置、IP地址等都可以。
- Analytics:尤其是明细数据
- Rich client library support and the REST API Easy to operate and easy to scale 部署简单、外部依赖少
- Near real time, Lightning fast, Fault tolerant
缺点:资源更多,需要更多机器。在数据量大时聚合统计方面查询延迟与并发不如Druid。
组成
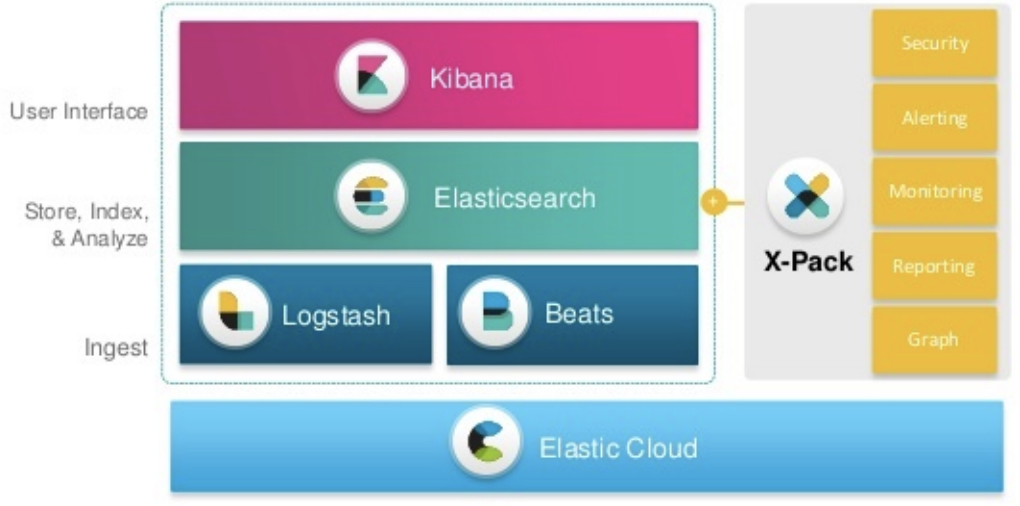
Elasticsearch:作为核心,存储所有数据,提供搜索和分析。
Logstash:集中数据,包括日志、指标等(类似flume)。集中时可以对数据进行各种转换,定位为ETL引擎。
Logstash的Shipper、Broker、Indexer分别和Flume的Source、Channel、Sink各自对应!只不过是Logstash集成了,Broker可以不需要,而Flume需要单独配置,且缺一不可。总体来说Flume的配置比较繁琐,偏向数据传输,Logstash更简单且功能也更多,如解析预处理。
Kibana:ES的可视化工具。
Elasticsearch
概念1(基础)
Elasticsearch是文件导向型存储,JSON文件是第一公民。
索引:含有相同属性的文档集合(小写不含下划线),相当于database。分结构化和非结构化
类型:索引可以定义一个或多个类型,文档必须属于一个类型,相当于table
文档:可以被索引的基本数据单位,相当于record。
在6.0后,索引只能有一个类型。
分片:每个索引都有很多个分片,每个分片是一个Lucene索引。只能创建索引时指定数量,默认为5。
备份:拷贝一份分片就完成了分片的备份
数据类型
text data, numbers, booleans, binary objects, arrays, objects, nested types, geo-points, geo-shapes, and many other specialized datatypes such as IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
6.0引入scaled_float,其存储价格数据效率高,例如10.05在内部实际上是1005的integer。
elasticsearch采用倒排索引的数据结构,分为Term,Frequency和Documents (Postings)三列。其中term为词,Documents列也可能存储改词在文本中的位置。默认elasticsearch会对所有field创建倒排索引。当插入document时,elasticsearch就会解析这个document所有的filed,并添加到倒排索引中。
CRUD基本用法
Restful API基本格式:http://<ip>:<port>/<索引>/<类型>/<文档id>
常用的四种请求方式:GET、PUT、POST、DELETE
PUT: 创建索引和文档增加
POST: 文档增加、查询索引和文档修改
GET: 查询文档
DELETE: 删除文档和删除索引
如果不想自己设置文档id,那就需要用post而不是put
创建结构化索引
如果不创建而直接put来插入数据,elasticsearch会自动创建索引和类型,但一些默认设置可能不会符合预期。所以这里就直接放手动创建index的例子了。另外,如果put的数据包含新的field,elasticsearch也会自动创建新的field。
在postman中put下面json到localhost:9200/index_name
例子1,下面的json会创建索引和类型(名为man)
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"man": { // 类型
"properties": {
"country": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss || yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
}
// 添加新类型。下面假设已经创建了catalog index,那么执行下面语句就会新增一个category类型。如果第二次执行下面代码,换成不同的field,那么就是添加新field
PUT /catalog/_mapping/category
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
例子2
{
"settings": {
"number_of_replicas": 0,
"number_of_shards": 5, // 一般将分片限制在10~20G
"index.store.type": "niofs" ,// 性能更好
"index.query.default_field": "title", // 默认查询字段
"index.unassigned.node_left.delayed_timeout": "5m" // 当某个节点挂掉时,不马上回复分片
"analysis": { // 解析器,看下面概念2
"analyzer": {
"std": {
"type": "standard",
"stopwords": "_english_"
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"house": {
"dynamic": false, // 用"strict"就完全不让结构变化
"_all": {
"enabled": false // 6已经废除,默认为true。会将全部字段拼接为整体作全文索引
},
"properties": {
"houseId": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text", // text类型都会在建立索引前会被分词来支持全文搜索
"index": "analyzed" // 需要分词
},
"price": {
"type": "integer"
},
"createTime": {
"type": "date",
"format": "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis"
},
"cityEnName": {
"type": "keyword" // 内部使用keyword解析器(noop tokenizer),即作为整体不需要分词,支持sorting, filtering, and aggregations
},
"regionEnName": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"tags": { // 这个filed内部还有一个fields,名为raw,实际上这个field的全称为type.raw结果tags会以两种方式存储。text和keyword。
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"raw": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
插入数据
在postman用put + http://<ip>:<port>/<索引>/<类型>/<文档id> + json代码即可
自动生成id的话,用post + 去掉<文档id>
读取数据
用get
修改
直接修改:post + http://<ip>:<port>/<索引>/<类型>/<文档id>/_update
json{"doc":{"属性": "值"}}
脚本修改(painless是内置语言)
{
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"inline": "ctx._source.age = params.age",
"params": {
"age": 100
}
}
}
Elasticsearch内部实现是针对原数据添加一个新版本。
删除
在postman用delete,或者在插件中操作。
概念2(文本解析器)
文本分析基础
Elasticsearch的解析器会将分本分割成词,这会发生在indexing和searching两个阶段。之后还需根据这些词建立索引。每个field可以用不同的解析器。
解析器按顺序分为三个部分:
0个或多个Character filters:可以增加、删除或修改character,例如过滤掉无意义的词,替换词,使得某些词的意义更明显(表情变为文字)。
1个Tokenizer:生成标记/词。另外它产出每个token在输入流中的位置。
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"text": "Tokenizer breaks characters into tokens!"
}上面使用Standard Tokenizer对文本进行分析,结果之一如下
{
"token": "Tokenizer",
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 9,
"type": "<ALPHANUM>",
"position": 0
}0个或多个连续的Token filters:可以增加、删除或修改tokens,例如lowercase、stop token
查询
在postman用post + http://<ip>:<port>/<索引>/_search
- Searching all documents in all indices:
GET /_search - Searching all documents in one index:
GET /catalog/_search - Searching all documents of one type in an index:
GET /catalog/product/_search - Searching all documents in multiple indices:
GET /catalog,my_index/_search - Searching all documents of a particular type in all indices:
GET /_all/product/_search
子条件查询
特定字段查询所指特定值。分为Query context和Filter context。
- Query context:除了判断文档是否满足条件外,还会计算_score来标识匹配度。
全文本查询full-text query:针对文本类型数据。分模糊匹配、习语匹配、多个字段匹配、语法查询。match, match phrase, mulit match。如果针对keyword类型,并不会在查询时进行分词,即变成term query。全文本查询的流程如下:
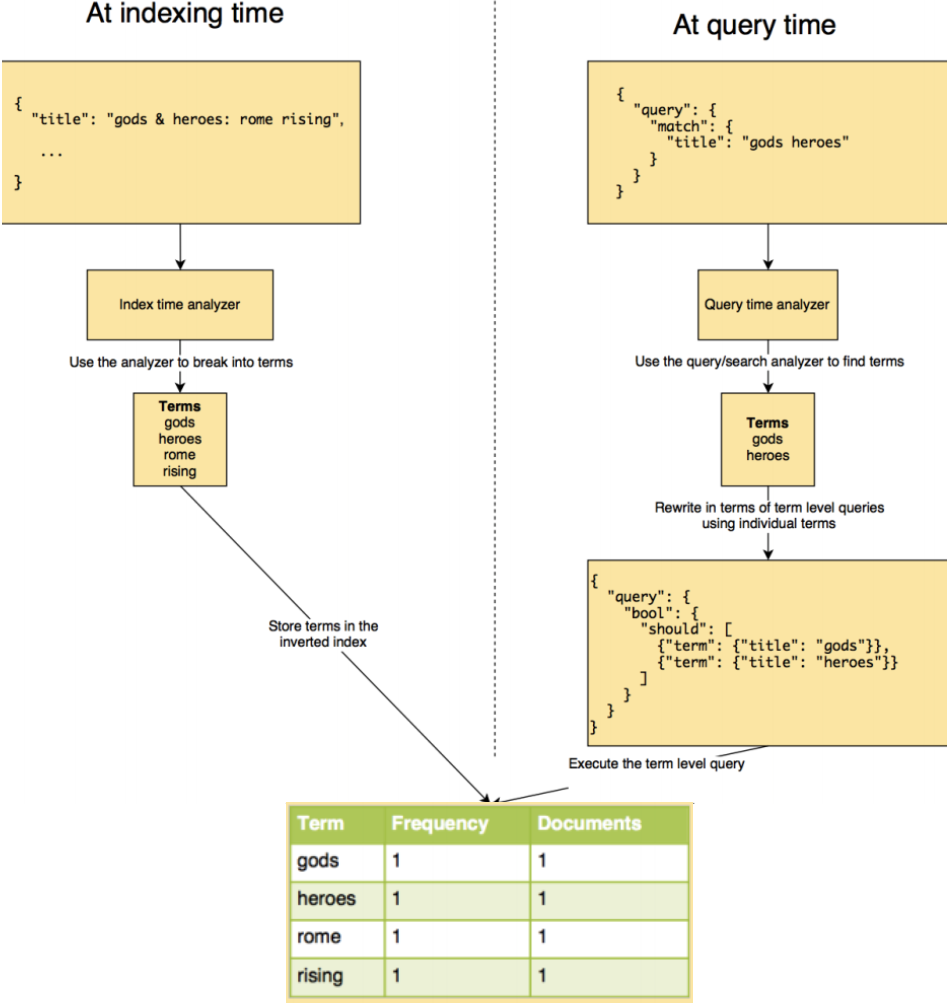
可以添加的选项:
- match:operator,默认or;minimum_should_match;fuzziness
- match_phrase:slop,默认0,可以有多少个字不同
字段级别查询term query:针对结构化数据,如数字、日期等。这种级别在查询阶段不会像上面那样进行分词和重写查询。range, term
- Filter context:返回准确的匹配,比Query快。这类查询还有助于elasticsearch缓存结果(01数组)exists
// 模糊查询,下面匹配会返回含有China或Country的数据。改为match_phrase就是准确匹配(China Country作为一个词组)。
// from是从哪一行开始search,size是返回多少条符合的数据。
{
"query": {
"match": { // 默认排序得分:China和Country按正确顺序且相邻的分数会比“正确顺序不相邻”或”不正确顺序相邻”高,只有其中之一的分数更低。默认operator是or
"country": "China Country"
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 2,
"sort": [
{"age": {"order": "desc"}}
]
}
{// 多字段查询,下面address和country列中有apple的都会查询出来
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "apple",
"fields": ["address", "country^2"] // 表示country的权重更大
}
}
}
{// 语法查询
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "apple OR pear"
}
}
}
{// 字段查询,准确匹配(和习语的区别?)。下面有两种选择,term和constant_score,前者Query context会算分,后者Filter context不会
"query": {
"term": {
"author": "apple"
}
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"manufacturer.raw": "victory multimedia"
}
}
}
}
}
{ // range可以用于数值、日期、 score boosting的数据(即让通过range的数据获得更高的分数,默认为1,从而在混合查询中设置权重)
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 10, // "01/09/2017", "now-7d/d", "now"等针对日期,其中加上"/d"表示round
"lte": 50,
"boost": 2.2,
"format": "dd/MM/yyyy" // 针对日期
}
}
}
}
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "description"
}
}
}
filter
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"age": 20
}
}
}
}
}
复合查询
以一定逻辑组合子条件查询。常用的分为固定分数查询、布尔查询等
// 固定分数查询,这里把查询的分数固定为2,即filter中返回yes的数据分数为2
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"title": "apple"
}
},
"boost": 2
}
}
}
// 布尔查询,这里should表示满足一个条件就够了。must就是都要满足。must和should在query context中执行子句,除非整个bool查询包含在filter context。must not和filter属于filter context。
{
"query": {
"constant_score": { // 整个bool查询包含在filter context。
"filter": {
"bool": {
"should": [{ // 相当于or复合
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 13
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"manufacturer.raw": {
"value": "valuesoft"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
{ // 这个查询同样是整个bool查询包含在filter context。
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
....original query to be negated...
}
}
}
}
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"author": "apple"
}
},
{
"match": {
"tittle": "fruit"
}
}
],
"filter": [
{
"term": {
"age": 20
}
}
]
}
}
}
其他复合查询还有:Dis Max query, Function Score query, Boosting query, Indices query
分析/聚合
POST /<index_name>/<type_name>/_search
聚合类型
Bucket aggregations:类似group by,group的数量可以是自定义规则的一个或多个,可以固定数量,可以动态增加。group可以根据固定数值、时间间隔、自定义范围、基数(cardinality)、filter(自定义条件)、GeoHash Grid进行划分。
Bucketing on string data: terms,如果get的结尾是
_search?size=0,那么只返回count排第一的。这和terms内部的size参数不一样,后者是考虑的bucket的数量,下面“返回结果指标”中提及默认为10。Bucketing on numeric data
histogram:设置
"interval": 1000表示每隔1000为一个bucket,然后返回每个bucket的所含document的数量。另外可设置min_doc_count,规定能划分为bucket的最小document数量。range:更灵活地设置范围。下面key可选。
"ranges": [
{ "key": "Upto 1 kb", "to": 1024},
{ "key": "1 kb to 100 kb", "from": 1024, "to": 102400 },
{ "key": "100 kb and more", "from": 102400 }
]
Aggregating filtered data:agg前添加query/filter
Nesting aggregations:在Bucket agg内部进行Metric agg。参考下面的阅读理解
Bucketing on custom conditions:
filter,创建根据自定义filter规则一个bucket
filters,创建多个bucket
"aggs": {
"messages": {
"filters": {
"filters": {
"chat": {"match": {"category": "Chat"}},
"skype": {"match": {"application": "Skype"}},
"other_than_skype": {
"bool": {
"must": {"match": {"category": "Chat"}},
"must_not": {"match": {"application": "Skype"}}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Bucketing on date/time data:可参考下面阅读理解
"aggs": {
"counts_over_time": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "time",
"interval": "1d",
"time_zone": "+05:30"
}
}
}
Bucketing on geo-spatial data(略)
返回结果指标:
- doc_count_error_upper_bound表示
- sum_other_doc_count:total count of documents that are not included in the buckets returned 默认10个,所以如果bucket少于10个,就会是0。如果多于10个,那么该指标表示的就是排10之后的类别的数据总量。
Metric aggregations:sum, average, minimum, maximum等,里面不能包含其他agg。
Matrix aggregations:5.0的新特征
Pipeline aggregations:(略)
// 较为完整的json
{
"aggs": {
...type of aggregation...
},
"query": { // optional query part
...type of query...
},
"size": 0 // 搜索返回的数量,如果只需要聚合,可以把这个设置为0
}
{ // 下面得出各个年龄的数据行数。terms可改为stats(如果同时需要sum, avg, min, max, and count,这个效率更高), extended stats(更多指标),min, max, sum,cardinality等
"query": { // 缩小聚合范围
"term": {
"customer": "Linkedin"
}
},
"aggs": {
"group_by_age": { // 自己起的名字
"terms": {
"field": "age"
}
},
"group_by_xxx": {
//...
}
}
}
// 阅读理解Nesting aggregations。考虑特定时段和公司的每个用户消耗的总带宽,每个部门中排名前两位的用户
// GET /bigginsight/usageReport/_search?size=0
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [{
"term": {
"customer": "Linkedin"
}
},
{
"range": {
"time": {
"gte": 1506257800000,
"lte": 1506314200000
}
}
}
]
}
},
"aggs": {
"by_departments": {
"terms": {
"field": "department"
},
"aggs": {
"by_users": {
"terms": {
"field": "username",
"size": 2,
"order": {
"total_usage": "desc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"total_usage": {
"sum": {
"field": "usage"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 阅读理解Bucketing on date/time data
// GET /bigginsight/usageReport/_search?size=0
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"term": {"customer": "Linkedin"}},
{"range": {"time": {"gte": 1506277800000}}}
]
}
},
"aggs": {
"counts_over_time": {
"date_histogram": {
"field": "time",
"interval": "1h",
"time_zone": "+05:30"
},
"aggs": {
"hourly_usage": {
"sum": {"field": "usage"}
}
}
}
}
}
概念3(架构原理的补充)
数据存储:
一个分片实际指一个单机上的Lucene索引。Lucene索引由多个倒排索引文件组成,一个文件称为一个segment。Lucene通过commit文件记录所有的segment。每当有信息插入时,会把他们写到内存buffer,达到时间间隔便写到文件系统缓存,然后文件系统缓存真正同步到磁盘上,commit文件更新。当然,这里也会有translog文件来防治commit完成前的数据丢失(translog也有更新间隔、清空间隔参数)。与Hbase类似,segment也有merge过程,也可以设置各种归并策略。
数据存储到哪个shard取决于shard = hash(routing) % number_of_primary_shards.rounting默认情况下为_id值。
请求处理
elasticsearch收到请求时,实际上是master节点收到,它会作为coordinator节点,通过上面提到的公式,告诉其他相关node处理请求,当处理结束后会收集响应并发回给client。这个处理过程与Kafka类似,也有写完主分片返回还是等备份完成才返回。所以分片的数量会影响并行度。
Logstash基础
log作用:troubleshoot、监控、预测等
log的挑战:格式不统一、非中心化、时间格式不统一、数据非结构化
Logstash:构建一个管道,从各种输入源收集数据,并在到达各种目的地前解析,丰富,统一这些数据。
架构:datasource - inputs(create events) - filters(modify the input events) - outputs - datadestination。中间三个组成logstash管道,每个组成之间使用in-memory bounded queues,也可以选择persistent queues。
简单运行例子:logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output {stdout {} }'
logstash -f simple.conf -r # -r可以在conf更新时自动重置配置
#simple.conf
#A simple logstash configuration
input {
stdin {}
}
filter {
mutate {
uppercase => ["message"]
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => rubydebug # codec is used to encode or decode incoming or outgoing events from Logstash
}
}
Overview of Logstash plugins
./bin/logstash-plugin list --verbose:list of plugins that are part of the current installation,verbose版本,--group filter属于filter的。
input
file{
path => ["D:\es\app*","D:\es\logs*.txt"]
start_position => "beginning"
exclude => ["*.csv]
discover_interval => "10s"
type => "applogs"
}
beats {
host => "192.168.10.229"
port => 1234
}
JDBC
input {
jdbc { # 一个jdbc只能一个sql查询
# path of the jdbc driver
jdbc_driver_library => "/path/to/mysql-connector-java-5.1.36-bin.jar "
# The name of the driver class
jdbc_driver_class => "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
# Mysql jdbc connection string to company database
jdbc_connection_string => "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/company"
# user credentials to connect to the DB
jdbc_user => "user"
jdbc_password => "password"
# when to periodically run statement, cron format(ex: every 30 minutes)
schedule => "30 * * * *"
# query parameters
parameters => {
"department" => "IT"
}
# sql statement。可以用statement_filepath
statement => "SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department=: department AND
created_at >=: sql_last_value "
# 其他参数
jdbc_fetch_size =>
last_run_metadata_path => # 存储sql_last_value的位置,这个配置是按照这个元数据来schedule的。可以设置根据某column值来schedule。
}
jdbc { ... }
}
output {
elasticsearch {
index => "company"
document_type => "employee"
hosts => "localhost:9200"
}
}
output
elasticsearch {
...
}
csv {
fields => ["message", "@timestamp","host"]
path => "D:\es\logs\export.csv"
}
kafka {
bootstrap_servers => "localhost:9092"
topic_id => 'logstash'
}
Ingest node(略)
用Logstash构建数据管道(略)
Kibana的数据可视化
测试数据来源:https://github.com/elastic/elk-index-size-tests/blob/master/logs.gz
通过Logstash加上下面的conf把数据导入elasticsearch
input {
file {
path => ".../Elastic_Stack/data/logs"
type => "logs"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => {
"message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}"
}
}
mutate {
convert => {
"bytes" => "integer"
}
}
date {
match => ["timestamp", "dd/MMM/YYYY:HH:mm:ss Z"]
locale => en
remove_field => "timestamp"
}
geoip {
source => "clientip"
}
useragent {
source => "agent"
target => "useragent"
}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => dots
}
elasticsearch {}
}
curl -X GET http://localhost:9200/logstash-*/_count如无意外有300,000条。
使用Kibana进行分析的前提是数据已经加载到Elasticsearch,然后在management处指定index。index通常有两类:time-series indexes:(通常有多个index,其名字以时间结尾)、regular index。如果第一次使用Logstash加载数据到elasticsearch,把Index Name or Pattern设置为logstash-*,Time Filter field name设置为@timestamp即可。
Discover
指定index后在Discover Page处设置时间段,2014-05-28 00:00:00.000和 2014-07-01 00:00:00.000
这份数据是www.logstash.net 的网站log,访问这个网站的top1中国城市无疑是北京,但之后的居然是广州、厦门、福州、深圳...
搜索栏
使用与Google、百度有点类似。
a b:只要有a或b的document都返回"a b":精确搜索field1: a:在field1中搜索AND, OR, - (must not match):boolean搜索。注意“-”与value之间没有空格(...):grouping搜索field1:[start_value TO end_value]:用{}则不包含边界- 通配符:即便是Elasticsearch也不推荐前缀模糊
- 正则:相当耗CPU
- 之前提到的elasticsearch查询
其他自己摸索基本都知道怎么用。
Visualization
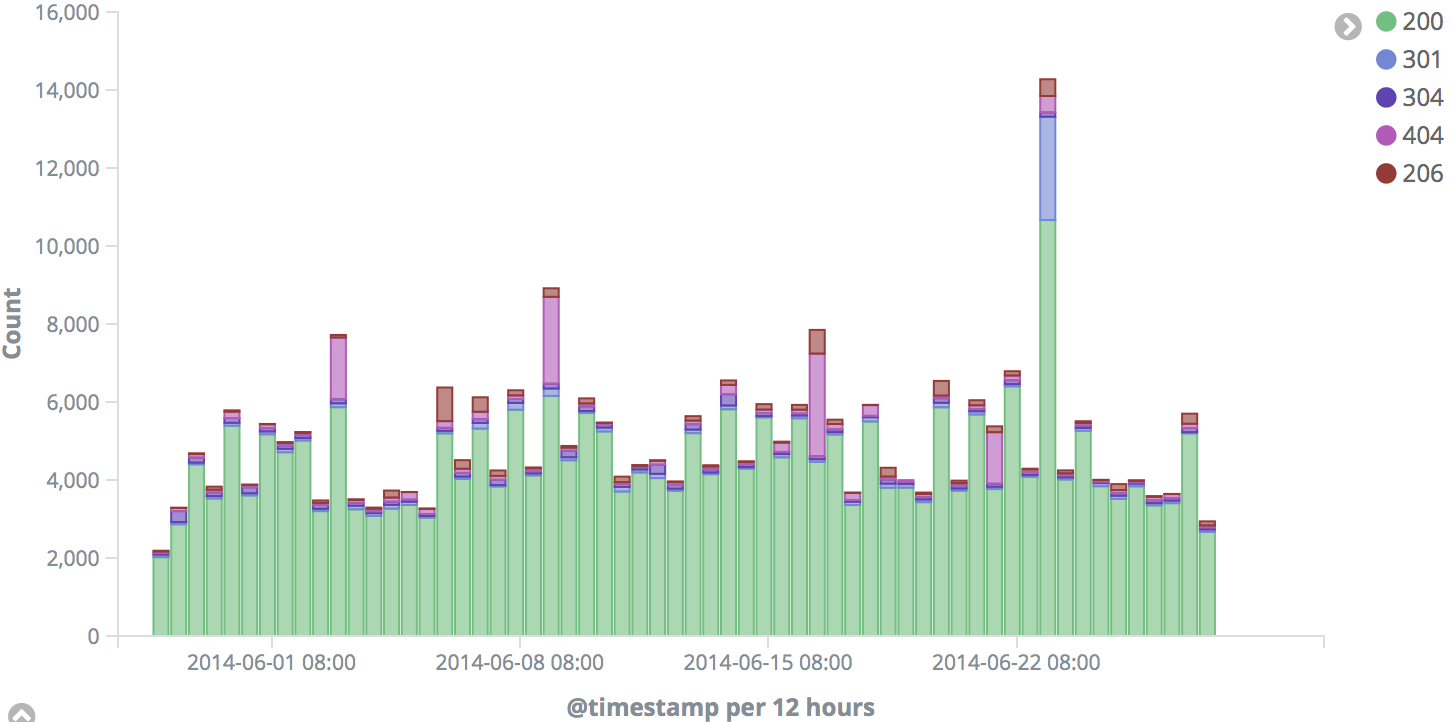
- Analyzing the response codes over time
- Click on
Newand selectVertical Bar - Select
Logstash-*underFrom a New Search, Select Index - In the X axis, select
Date Histogramand@timestampas the field - Click
Add sub-bucketsand selectSplit Series - Select
Termsas the sub aggregation - Select
response.keywordas the field
- Click on
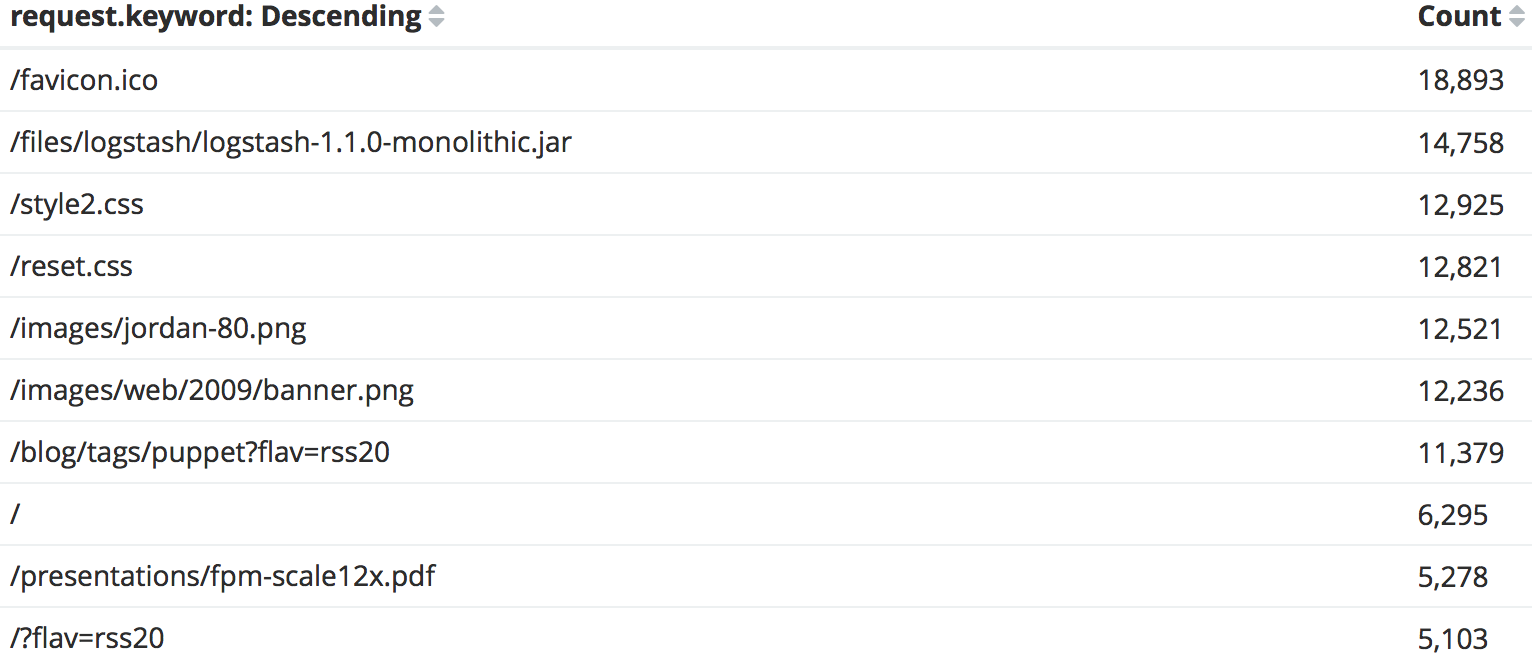
Finding the top 10 URLs requested
新建,选择Data Table,index选择同上。buckets type选择
Split Rows,Aggregation选择Terms,field选择request.keyword,size选择10,结果如下:
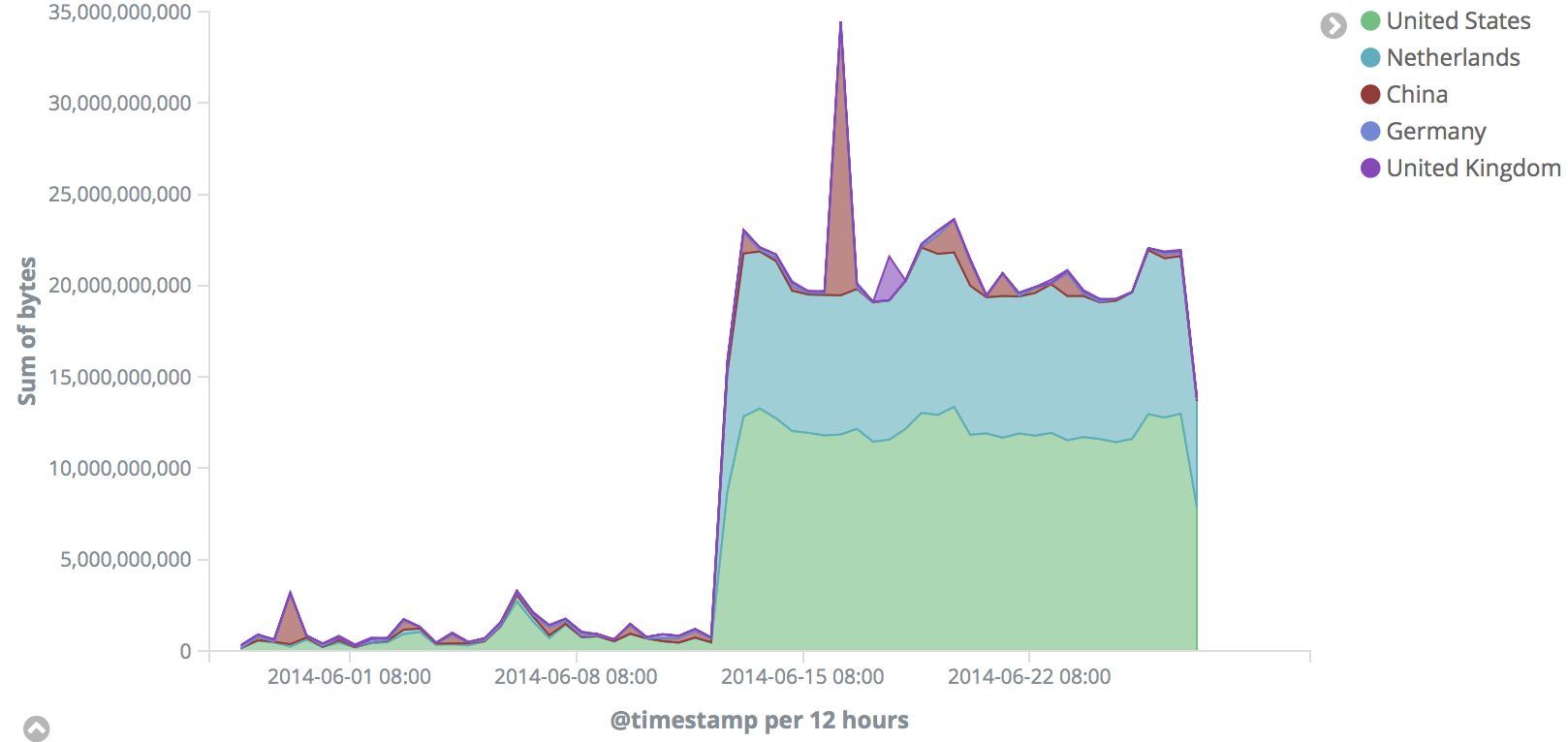
Analyzing the bandwidth usage of the top five countries over time
新建,选择Area,index选择同上。Y轴选择
sum,bytes;X轴选择DateHistogram,@timestamp;sub-buckets选择Split Series,Terms,geoip.country_name.keyword。最后要把sub-buckets拉到X轴前面。这样才是先找到前5的国家,然后对时间轴进行划分。
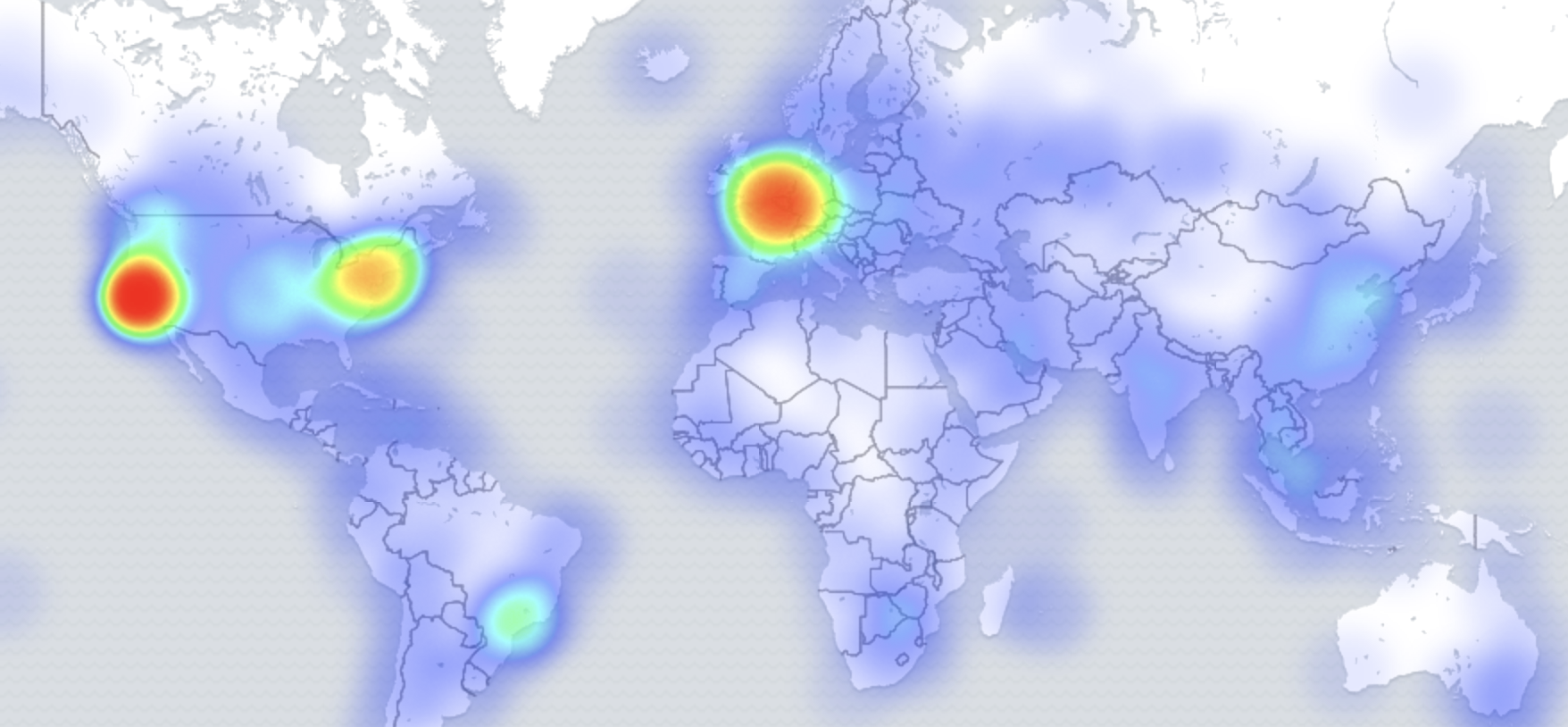
Finding the most used user agent
新建,选择Coordinate Map,index选择同上。bucket选择
Geo Coordinates,Geohash,geoip.location, Options处选择Map类型为Heatmap
Analyzing the web traffic originating from different countries
新建,选择Tag Cloud,index选择同上。bucket选择
Tags,Terms,useragent.name.keyword

Dashboards(略)
Timelion
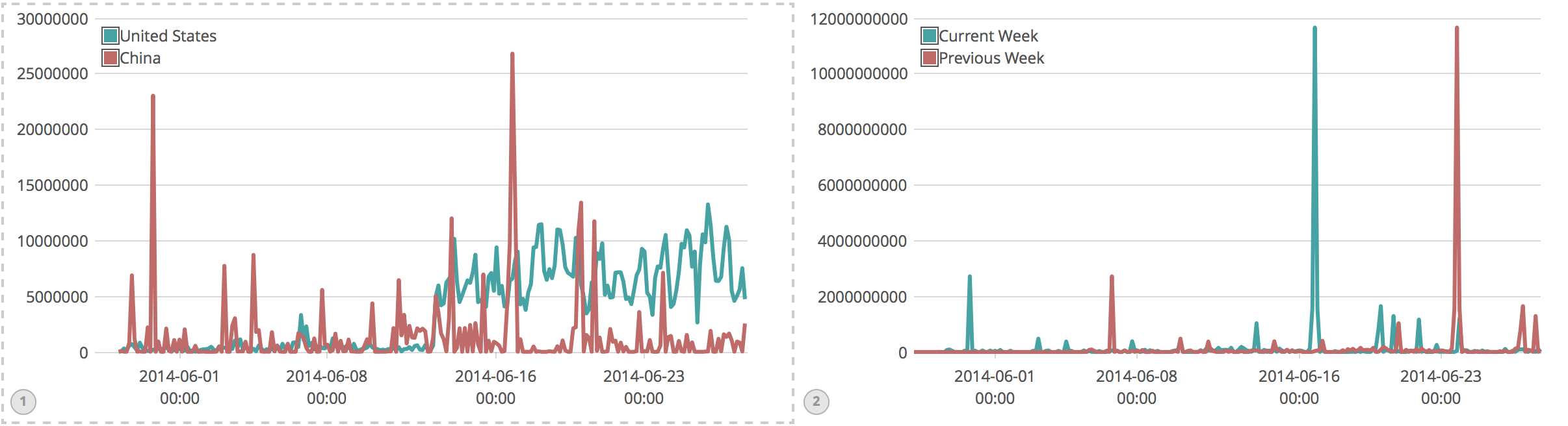
中美比较
.es(q='geoip.country_code3:US',metric='avg:bytes').label('United States'), .es(q='geoip.country_code3:CN',metric='avg:bytes').label('China')
与之后一周的比较
.es(q='geoip.country_code3:CN',metric='sum:bytes').label('Current Week'),
.es(q='geoip.country_code3:CN',metric='sum:bytes',
offset=-1w).label('Previous Week')
Metricbeat
metricbeat由modules和metricsets组成。modules定义收集指标的基本逻辑,如连接方式、收集频率、收集哪些指标。每个modules有一到多个metricsets。metricsets是通过给监控对象发送单个请求来收集其列指标的组件,它构建event数据并把数据转移到output。metricbeat的result guarantees是at least once。
好处:
- 即便所监控的对象不能访问,也会返回错误事件
- 整合多个相关指标到单一事件数据
- 会发送元数据,这有利于数据的mapping、确认、查询、过滤等。
- 没有数据转换功能,返回的都是raw data
event structure
{ // 下面@timestamp,metricset,beat的信息是每条常规event都有的。
"@timestamp": "2017-11-25T11:48:33.269Z",
"@metadata": {
"beat": "metricbeat",
"type": "doc",
"version": "6.0.0"
},
"system": {
// metric 信息
},
"metricset": {
"name": "xxx", // Name of the metricset that the data is from
"rtt": 2000, // Round trip time of the request in microseconds
"module": "system"
},
"beat": {
"version": "6.0.0",
"name": "SHMN-IN",
"hostname": "SHMN-IN"
}
}
配置metricbeat
Module configuration
6.0开始有modules.d目录,里面各个服务都有各自的yml,如mysql.yml,相关配置在里面设置。样式参考system.yml。
General settings :name、tags、max_procs
Output configuration
output.elasticsearch:
enabled: true
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
username: "elasticuser" # 如果设置了权限
password: "password"
pipeline: "ngnix_log_pipeline" # 如果要用ingest node的话
index: "metricbeat-%{[beat.version]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}" # 默认index格式
# 下面是index的另一种实现。当index被重写时注意要设置setup.dashboards.enabled: false和setup.template.enabled: false,除非提供 setup.template.name 和 setup.template.pattern
index: "logs-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
indices:
- index: "debug-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
when.contains:
message: "DEBUG"
- index: "error-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
when.contains:
message: "ERR" output.logstash:
hosts: ["localhost:5045", "localhost:5046"]
loadbalance: true # 测试
output.console:
enabled: true
pretty: true
在metricbeat.yml中开启dashboard功能。这样打开kibana的dashboard就会有默认提供的dashboard模版了。
运行
./metricbeat -e
在Kibana中查看
下图为6.0以上的dashboard,需要elasticsearch和kibana都是6.0以上才可以。比5.0的好看不少。
下面是system overview
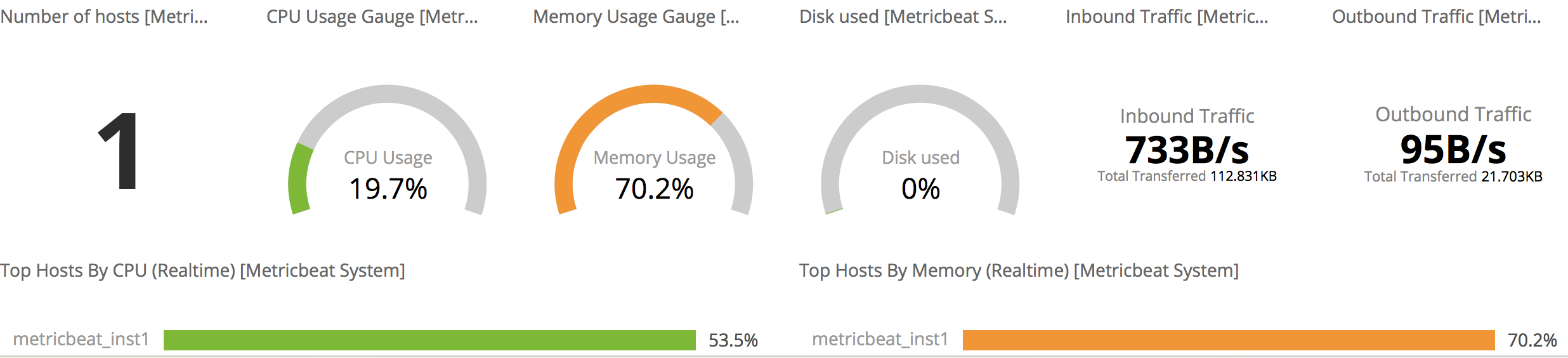
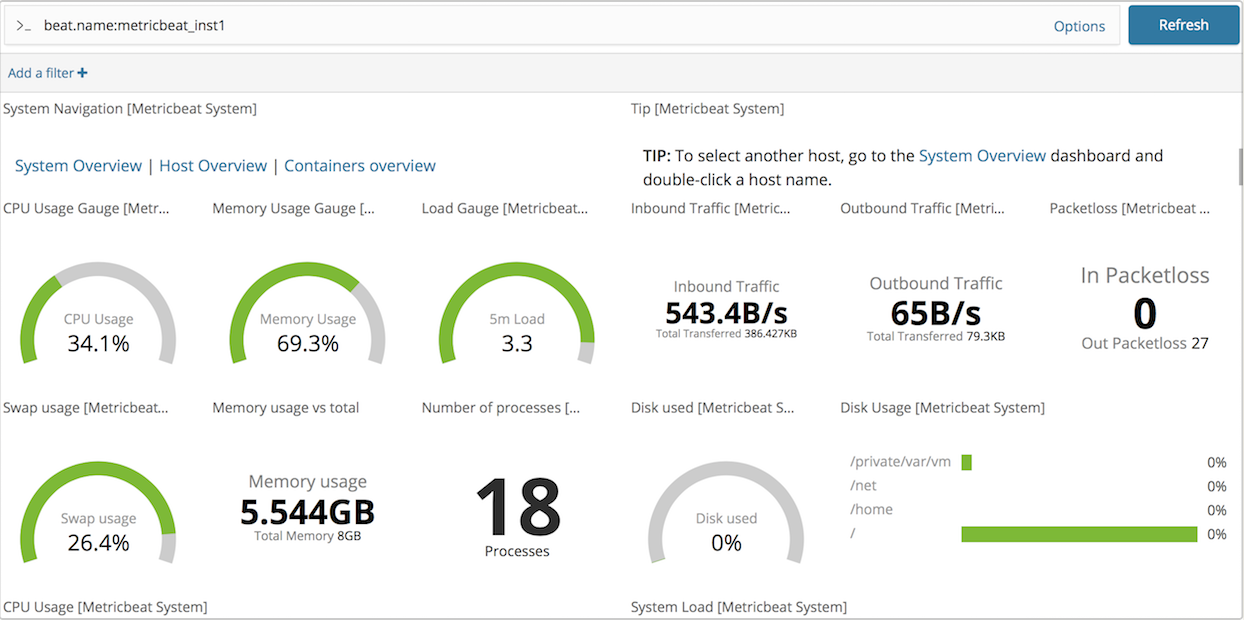
下面是host overview部分信息,注意如果metricbeat.yml的general setting中的那么改变了,要在搜索上写上自己设置的名字。
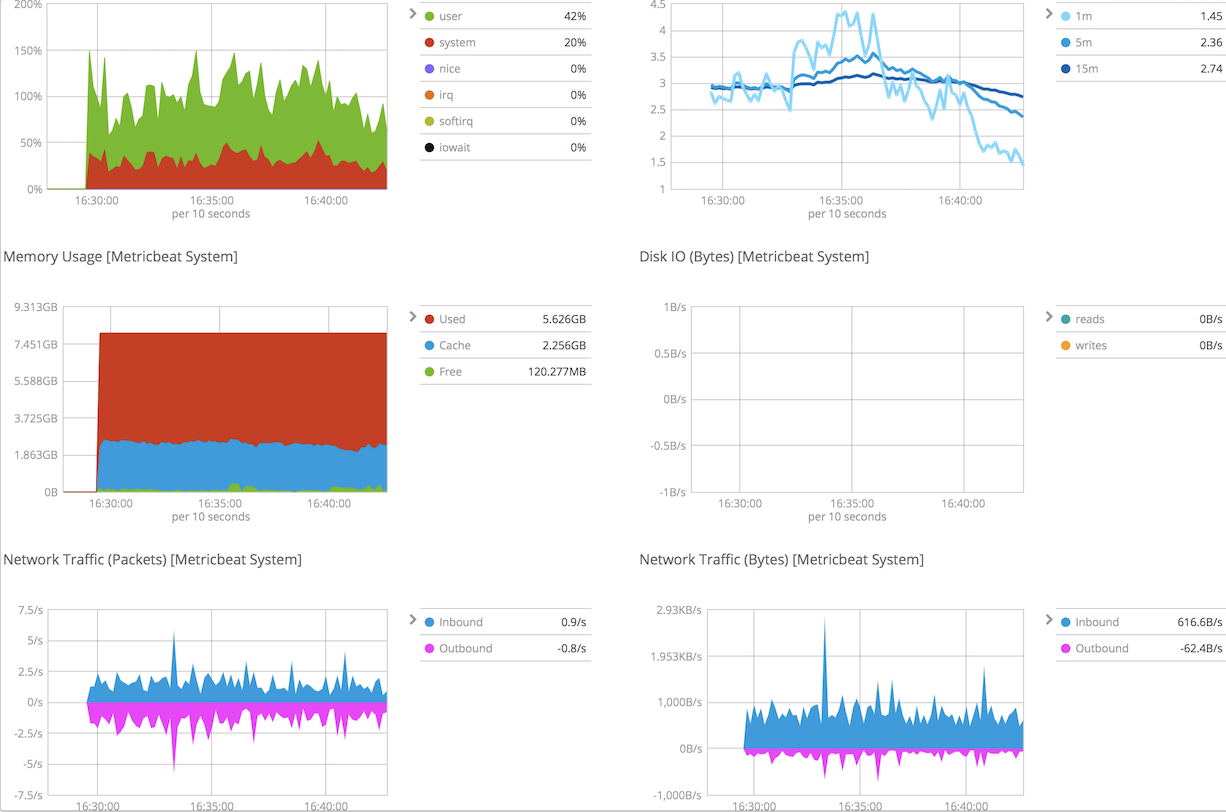
部署和配置
备份与恢复
在所有节点的elasticsearch.yml文件配置hdfs存储备份的位置path.repo: ["/mount/es_backups"]
然后在此注册文件夹下注册命名存储库,名字下面用backups。
curl -XPUT 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/backups' -H 'Content-Type:
application/json' -d '{
"type": "fs",
"settings": {
"location": "/mount/es_backups/backups",
"compress": true
}
}'
快照(参考,到时候写进脚本),默认是incremental的。
curl -XPUT
'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/backups/backup_201710101930?pretty' -H
'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"indices": "bigginsight,logstash-*",
"ignore_unavailable": true,
"include_global_state": false
}'
查看快照
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/backups/_all?pretty'
恢复
curl -XPOST 'http://localhost:9200/_snapshot/backups/backup_201710101930/_restore'
index aliases
生产环境通常是为production index创建链接,并让应用使用这些链接而不是直接使用production index
POST /_aliases
{
"actions" : [
{ "remove" : { "index" : "index1", "alias" : "current_index" } },
{ "add" : { "index" : "index2", "alias" : "current_index" } }
]
}
index templates
设置下面index模版后,每当插入的数据采用新的index,且匹配reading,就会自动执行模版创建index。
PUT _template/readings_template
{
"index_patterns": ["readings*"], // 任何新索引如果匹配到这个模式就会使用这个模版
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"reading": {
"properties": {
"sensorId": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "date"
},
"reading": {
"type": "double"
}
}
}
}
}
时间序列数据
一个index存储大量时间序列数据并非好事,通常以时间,如天、周作为单位新增索引。这主要考虑到shard数量、mapping的变化、过时数据的处理:
shard数量
需要根据当前业务的数据量来估计,但shard一旦设定就不能修改了。不合理的shard数量会影响相关评分和聚合准确度:
- 评分:相对频率是基于各个分片内而不是基于所有分片。
- 聚合:聚合同样是基于各个分片,例如top10则取个分片的top10。如果某个bucket位于其中一个分片返回的前n个bucket中,并且该bucket不是任何其他分片的前n个bucket之一,则协调节点聚合的最终计数会忽略这个bucket。
mapping的变化
随着业务的变化,fields可能会增加,有些fields会过时,过多deprecated field耗费资源
其他
client.transport.sniff为true来使客户端去嗅探整个集群的状态,把集群中其它机器的ip地址自动加到客户端中
当ES服务器监听使用内网服务器IP而访问使用外网IP时,不要使用client.transport.sniff为true,在自动发现时会使用内网IP进行通信,导致无法连接到ES服务器,而直接使用addTransportAddress方法进行指定ES服务器。
// 一些优化说明
post
localhost:9200/index_name/type_name/_search?explain=true
禁止删除索引时使用通配符
put + http://<ip>:<port>/_cluster/settings 动态方式改设置
{
"transient": {
"action.destructive_requires_name": true
}
}
put + http://<ip>:<port>/_all/_settings?preserve_existing=true
{
index.refresh_interval: "30s"
}
非动态改设置,即在config文件中改
discovery.zen.fd.ping_interval: 10s
discovery.zen.fd.ping_timemout: 120s
discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 3
master节点一般不存储数据
node.master: true
node.data: false
针对数据节点,关闭http功能。从而减少一些插件安装到这些节点,浪费资源。
http.enable: false
负载均衡节点:master和data都为false,但一般不用自带的
内存设定:JVM针对内存小于32G才会优化,所以每个节点不要大于这个值。另外堆内存至少小于可用内存的50%,留空间给Apache Lucene。
写入数据从index改为bulk
参考:
Learning Elastic Stack 6.0
ELK Stack总结的更多相关文章
- A session of Log Collect, Retrieval and Analysis using ELK Stack
Motivation 运维过程中对问题的定位往往需要跟踪和定位日志.分布式和弹性计算的引入,使得日志的定位和分析变得越发复杂. 本次实践主要的目的是考察现有成熟的日志收集.检索和分析方案:Kafka+ ...
- 【ELK Stack】ELK+KafKa开发集群环境搭建
部署视图 运行环境 CentOS 6.7 x64 (2核4G,硬盘100G) 需要的安装包 Runtime jdk1.8 : jdk-8u91-linux-x64.gz (http://www.ora ...
- ELK stack elasticsearch/logstash/kibana 关系和介绍
ELK stack elasticsearch 后续简称ES logstack 简称LS kibana 简称K 日志分析利器 elasticsearch 是索引集群系统 logstash 是日志归集集 ...
- 快速搭建日志系统——ELK STACK
什么是ELK STACK ELK Stack是Elasticserach.Logstash.Kibana三种工具组合而成的一个日志解决方案.ELK可以将我们的系统日志.访问日志.运行日志.错误日志等进 ...
- 2019你该掌握的开源日志管理平台ELK STACK
转载于https://www.vtlab.io/?p=217 在企业级开源日志管理平台ELK VS GRAYLOG一文中,我简单阐述了日志管理平台对技术人员的重要性,并把ELK Stack和Gra ...
- ELK Stack 笔记
ELK Stack ELK Stack ELK Stack ELK 介绍 架构 Elasticsearch 安装 常见问题 关闭 Elasticsearch Elasticsearch-head Ki ...
- ELK Stack (2) —— ELK + Redis收集Nginx日志
ELK Stack (2) -- ELK + Redis收集Nginx日志 摘要 使用Elasticsearch.Logstash.Kibana与Redis(作为缓冲区)对Nginx日志进行收集 版本 ...
- ELK Stack (1) —— ELK + Redis安装
ELK Stack (1) -- ELK + Redis安装 摘要 安装Elasticsearch.Logstash.Kibana与Redis以实现一个日志收集平台 版本 elasticsearch版 ...
- ELK Stack 5.2.2 安装文档
简介: ELK Stack 安装文档,这次都使用最新版本(5.2.2).RPM 包的方式搭建 ELK Stack. 下载地址: https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloa ...
- 大数据日志分析产品——SaaS Cloud, e.g. Papertrail, Loggly, Sumo Logic;Open Source Frameworks, e.g. ELK stack, Graylog;Enterprise Products, e.g. TIBCO LogLogic, IBM QRadar, Splunk
Learn how you can maximize big data in the cloud with Apache Hadoop. Download this eBook now. Brough ...
随机推荐
- Discuz论坛广告横幅大图在百度app内无法显示,百度app默认开启了广告屏蔽
问题由来 前段时间搭的一个Discuz论坛上挂了2个广告横幅,网站的话收录还不错,然后客户就反应百度app上无法看到横幅. 由于我没有下载百度app,看不到效果我将信将疑,因为电脑,手机浏览器都是ok ...
- 防火墙内设置FileZilla Server注意事项
开启了Windows下的防火墙,如何设置FileZilla Server 相关选项,能在服务器端只开启21,23端口就可以正常连接使用 方法/步骤 1. 开启windows防火墙,同时 ...
- 学习使用windows下类似iptables的防火墙软件
项目地址:http://wipfw.sourceforge.net一.下载地址:http://sourceforge.net/projects/wipfw/files/安装:解压软件包后执行insta ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 020 D - Min Max Repetition
q<=1000个询问,每次问a,b,c,d:f(a,b)表示含a个A,b个B的字符串中,连续A或连续B最小的串中,字典序最小的一个串,输出这个串的c到d位.a,b<=5e8,d-c+1&l ...
- 【周期性执行事件】MySQL事件(Event)&任务调度
1.事件简介 事件(event)是MySQL在相应的时刻调用的过程式数据库对象.一个事件可调用一次,也可周期性的启动,它由一个特定的线程来管理的,也就是所谓的“事件调度器”. 事件和触发器类似,都是在 ...
- 二级域名相同的情况下子页面调用父页面的js方法
这两天项目遇到这种需求.项目是一个平台级系统,其中嵌入了多款应用.在平台上可以使用这些应用操作业务. 现在产品提出了个需求:即在A应用中需要调用js方法来打开B应用. 处理方法是:平台js中给出个打开 ...
- maven的安装与环境变量配置
1.下载maven 地址:http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi 点击下载 apache-maven-3.2.1-bin.zip. 2.安装配置,假设maven 解压 ...
- 学习日常笔记<day10>servlet编程
1 如何开发一个Servlet 1.1 步骤: 1)编写java类,继承HttpServlet类 2)重新doGet和doPost方法 3)Servlet程序交给tomcat服务器运行!! 3.1 s ...
- Ubuntu 16.04在搭建Redis Cluster搭建时,使用gem install redis时出现:ERROR: While executing gem ... (Gem::FilePermissionError) You don't have write permissions for the /var/lib/gems/2.3.0 directory.
注意:千万不要使用sudo来执行gem install redis. 解决方法: sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install git-core curl zlib ...
- java常用工具类 - 全角转半角、半角转全角
全角转半角.半角转全角代码 /** * <PRE> * 提供对字符串的全角->半角,半角->全角转换 * codingwhy.com * </PRE> */ pub ...
