Spring 4.x (一)
1 Spring是什么?
- Spring是一个开源框架
- Spring是为简化企业级应用开发而生的,使用Spring可以使得简单的JavaBean能够实现以前只有EJB才能实现的功能。
- Spring是一个IOC(DI)和AOP的容器。
- Spring的特点:
- 轻量级:Spring是非侵入性的。基于Spring开发的应用中对象可以不依赖Spring的API。
- 依赖注入
- 面向切面编程
- 容器:Spring是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理应用搞对象的生命周期。
- 框架:Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用在Spring中可以使用xml和java朱姐组合这些对象。
- 一站式:在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库(Spring自身也提供了展现层的Spring MVC 和持久层的Spring JDBC)。
2 Spring的模块
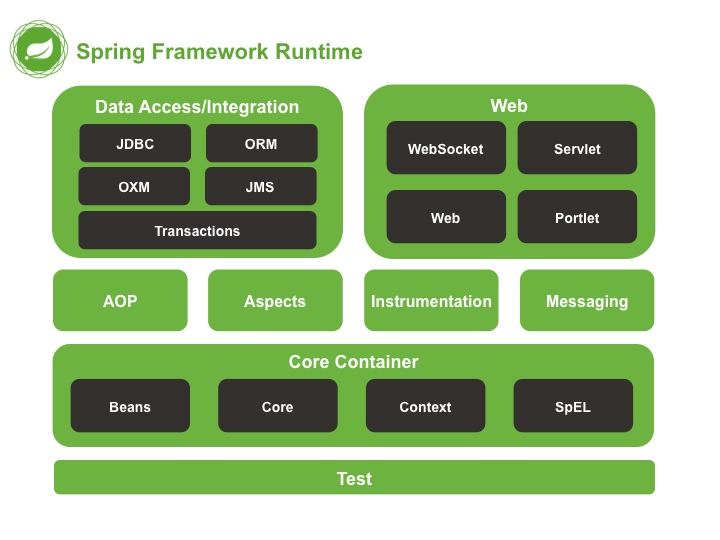
3 传统的HelloWorld VS Spring的HelloWorld
- 传统式HelloWorld
- HelloWorld.java
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好:"+name);
}
}
- HelloWorldTest.java
@Test
public void testHello(){
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
helloWorld.setName("许威威");
helloWorld.hello();
}
- Spring式的HelloWorld
- HelloWorld.java
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好:"+name);
}
}
- applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.xuweiwei.HelloWorld">
<property name="name" value="许威威"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- HelloWorldTest.java
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
4 IOC和DI
- IOC:控制反转,反转资源获取的方向。其实,就是将创建对象的方式交给Spring。
- class A{} class B{ private A a; public void setA(A a){ this.a = a; } }
- 传统方式:组件向容器发送请求查找资源,作为回应,容器将返回资源。
A a = new A(); B b = new B(); b.setA(a);
- IOC方式:容器主动的将资源推送给它所管理的组件,组件所需要做的仅仅是选择一种合适的方式接受资源。
B b = (B)applicationContext.getBean("b");
- DI:依赖注入,组件以一些预先定义好的方式接受来自容器的资源注入。比如setter方法或构造方法等。
5 Spring容器
- 在Spring的IOC容器读取Bean配置创建Bean实例之前,必须对它进行实例化。只有在容器实例化之后,才可以从IOC容器中获取Bean实例使用。
- Spring提供了两种类型的IOC容器
- BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现。
- ApplicationContext:提供更多的高级特性,是BeanFactory的子类。
5.1 ApplicationContext
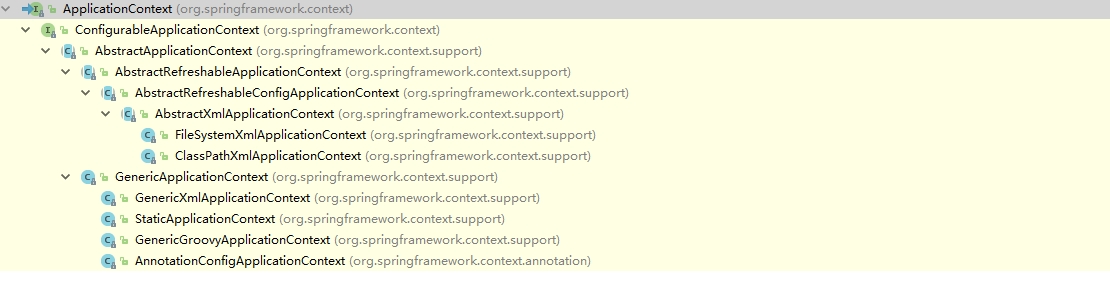
- ApplicationContext的两个主要实现类如下:
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统中加载配置文件
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下加载配置文件。
- ApplicationContext在初始化的上下文的时候就创建所有的单例Bean。
- WebApplicationContext是专门为WEB应用而准备的,它允许从相对于WEB根目录的路径中完成初始化。
6 配置Bean---基于XML方式
- 在xml文件中通过bean节点来配置bean
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.xuweiwei.HelloWorld">
<property name="name" value="许威威"/>
</bean>
- 在IOC容器中,id必须是唯一的,如果没有指定id,那么Spring容器会自动的将类名首字母小写作为Bean的id值。
- 依赖注入的方式:
- 属性注入
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好:"+name);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.xuweiwei.HelloWorld">
<property name="name" value="许威威"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
- 构造方法注入
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public HelloWorld(){
}
public HelloWorld(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好:"+name);
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.xuweiwei.HelloWorld">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="许威威" type="java.lang.String"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
- 工厂方法注入,很少使用
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public HelloWorld(){
}
public HelloWorld(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好:"+name);
}
}
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorldFactory {
public static HelloWorld getInstance(){
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
helloWorld.setName("许威威");
return helloWorld;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorld" factory-method="getInstance" class="com.xuweiwei.HelloWorldFactory" ></bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
- 实例工厂(很少使用)
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorld {
private String name;
public HelloWorld(){
}
public HelloWorld(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好:"+name);
}
}
package com.xuweiwei;
public class HelloWorldNewInstanceFactory {
public HelloWorld helloWorld(){
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
helloWorld.setName("许威威");
return helloWorld;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="helloWorldNewInstanceFactory" class="com.xuweiwei.HelloWorldNewInstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="helloWorld" factory-bean="helloWorldNewInstanceFactory" factory-method="helloWorld"></bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld helloWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
helloWorld.hello();
}
- 属性注入的示例:
- 引用类型的注入:比如主人和猫
package com.xuweiwei;
//猫
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.xuweiwei;
//主人
public class Master {
private String name;
private Cat cat ;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 创建猫的bean -->
<bean id="cat" class="com.xuweiwei.Cat">
<property name="name" value="helloKetty"/>
</bean>
<!-- 创建主人的bean -->
<bean id="master" class="com.xuweiwei.Master">
<property name="name" value="许威威"/>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Master master = (Master) context.getBean("master");
System.out.println("猫的名称是:"+master.getCat().getName());
System.out.println("猫的主人的名称是:"+master.getName());
}
- 其它类型的注入:比如数组,Map等
package com.xuweiwei;
import java.util.*;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Integer[] nums;
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String,Integer> map;
private Properties properties;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer[] getNums() {
return nums;
}
public void setNums(Integer[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Map<String, Integer> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, Integer> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nums=" + Arrays.toString(nums) +
", list=" + list +
", set=" + set +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.xuweiwei.Person">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name">
<value>许威威</value>
</property>
<property name="nums">
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>哈哈</value>
<value>呵呵</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>嘻嘻</value>
<value>笨笨</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map >
<entry key="许威威" value="1"></entry>
<entry key="王伟" value="2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<props >
<prop key="helloWorld">你好世界</prop>
<prop key="what">什么鬼?</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person) context.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
7 Bean的配置---基于注解
- 使用注解自动注入(DI)
package com.xuweiwei;
//猫
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.xuweiwei;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
//主人
public class Master {
private String name;
@Resource(name = "cat")
private Cat cat ;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Master{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!--
配置注解
-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<bean id="cat" class="com.xuweiwei.Cat">
<property name="name" value="helloketty"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="master" class="com.xuweiwei.Master">
<property name="name" value="许威威"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Master master = (Master) context.getBean("master");
System.out.println(master);
}
- 【注意】:@Resource是用来注入Bean,并且是根据bean的名称
- 使用@AutoWired和@Qualifier注解进行注入
package com.xuweiwei;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
//猫
public class Cat {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Qualifier("hello ketty")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.xuweiwei;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
//主人
public class Master {
private String name;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("cat")
private Cat cat ;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Master{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!--
配置注解
-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<bean id="cat" class="com.xuweiwei.Cat">
<property name="name" value="helloketty"/>
</bean>
<bean id="master" class="com.xuweiwei.Master">
<property name="name" value="许威威"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Master master = (Master) context.getBean("master");
System.out.println(master);
}
- 使用注解进行IOC和DI
package com.xuweiwei;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//猫
@Component("cat")
public class Cat {
private String name ="hello ketty";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Cat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.xuweiwei;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//主人
@Component("master")
public class Master {
private String name = "许威威";
@Autowired
@Qualifier("cat")
private Cat cat ;
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public void setCat(Cat cat) {
this.cat = cat;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Master{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", cat=" + cat +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!--
此注解会自动扫描包下的所有类,并为@Component注解的类自动创建对象
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xuweiwei"/>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpring(){
//启动Spring容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Master master = (Master) context.getBean("master");
System.out.println(master);
}
8 软件三层开发--基于XML
- 实体类:Person.java
package com.xuweiwei.vo;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- DAO层:
- PersonDAO.java
package com.xuweiwei.dao;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public interface PersonDAO {
public void insertPersonInfo(Person person);
}
- PersonDAOImpl.java
package com.xuweiwei.dao.impl;
import com.xuweiwei.dao.PersonDAO;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public class PersonDAOImpl implements PersonDAO {
@Override
public void insertPersonInfo(Person person) {
System.out.println("保存个人信息");
}
}
- Service层
- PersonService
package com.xuweiwei.service;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public interface PersonService {
public void savePersonInfo(Person person);
}
- PersonServiceImpl
package com.xuweiwei.service.impl;
import com.xuweiwei.dao.PersonDAO;
import com.xuweiwei.service.PersonService;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService {
private PersonDAO personDAO;
public PersonDAO getPersonDAO() {
return personDAO;
}
public void setPersonDAO(PersonDAO personDAO) {
this.personDAO = personDAO;
}
@Override
public void savePersonInfo(Person person) {
personDAO.insertPersonInfo(person);
}
}
- action层:PersonAction
package com.xuweiwei.action;
import com.xuweiwei.service.PersonService;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public class PersonAction {
private PersonService personService;
public PersonService getPersonService() {
return personService;
}
public void setPersonService(PersonService personService) {
this.personService = personService;
}
public void add(){
Person p = new Person();
personService.savePersonInfo(p);
}
}
- applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="personDAO" class="com.xuweiwei.dao.impl.PersonDAOImpl"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="com.xuweiwei.service.impl.PersonServiceImpl">
<property name="personDAO" ref="personDAO"/>
</bean>
<bean id="personAction" class="com.xuweiwei.action.PersonAction">
<property name="personService" ref="personService"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 测试
package com.xuweiwei.test;
import com.xuweiwei.action.PersonAction;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestSave {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
PersonAction personAction = (PersonAction) context.getBean("personAction");
personAction.add();
}
}
9 软件三层开发---基于注解
- 实体类:Person.java
package com.xuweiwei.vo;
public class Person {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- DAO层
- PersonDAO
package com.xuweiwei.dao;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public interface PersonDAO {
public void insertPersonInfo(Person person);
}
- PersonDAOImpl
package com.xuweiwei.dao.impl;
import com.xuweiwei.dao.PersonDAO;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("personDAO")
public class PersonDAOImpl implements PersonDAO {
@Override
public void insertPersonInfo(Person person) {
System.out.println("保存个人信息");
}
}
- Service层
- PersonService
package com.xuweiwei.service;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
public interface PersonService {
public void savePersonInfo(Person person);
}
- PersonServiceImpl
package com.xuweiwei.service.impl;
import com.xuweiwei.dao.PersonDAO;
import com.xuweiwei.service.PersonService;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service("personService")
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService {
@Resource(name = "personDAO")
private PersonDAO personDAO;
@Override
public void savePersonInfo(Person person) {
personDAO.insertPersonInfo(person);
}
}
- action层:PersonAction
package com.xuweiwei.action;
import com.xuweiwei.service.PersonService;
import com.xuweiwei.vo.Person;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller("personAction")
public class PersonAction {
@Resource(name="personService")
private PersonService personService;
public void add(){
Person p = new Person();
personService.savePersonInfo(p);
}
}
- applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xuweiwei"/>
</beans>
- 测试
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
PersonAction personAction = (PersonAction) context.getBean("personAction");
personAction.add();
}
Spring 4.x (一)的更多相关文章
- 基于spring注解AOP的异常处理
一.前言 项目刚刚开发的时候,并没有做好充足的准备.开发到一定程度的时候才会想到还有一些问题没有解决.就比如今天我要说的一个问题:异常的处理.写程序的时候一般都会通过try...catch...fin ...
- 玩转spring boot——快速开始
开发环境: IED环境:Eclipse JDK版本:1.8 maven版本:3.3.9 一.创建一个spring boot的mcv web应用程序 打开Eclipse,新建Maven项目 选择quic ...
- Spring基于AOP的事务管理
Spring基于AOP的事务管理 事务 事务是一系列动作,这一系列动作综合在一起组成一个完整的工作单元,如果有任何一个动作执行失败,那么事务 ...
- [Spring]IoC容器之进击的注解
先啰嗦两句: 第一次在博客园使用markdown编辑,感觉渲染样式差强人意,还是github的样式比较顺眼. 概述 Spring2.5 引入了注解. 于是,一个问题产生了:使用注解方式注入 JavaB ...
- 学习AOP之透过Spring的Ioc理解Advisor
花了几天时间来学习Spring,突然明白一个问题,就是看书不能让人理解Spring,一方面要结合使用场景,另一方面要阅读源代码,这种方式理解起来事半功倍.那看书有什么用呢?主要还是扩展视野,毕竟书是别 ...
- 学习AOP之深入一点Spring Aop
上一篇<学习AOP之认识一下SpringAOP>中大体的了解了代理.动态代理及SpringAop的知识.因为写的篇幅长了点所以还是再写一篇吧.接下来开始深入一点Spring aop的一些实 ...
- 学习AOP之认识一下Spring AOP
心碎之事 要说知道AOP这个词倒是很久很久以前了,但是直到今天我也不敢说非常的理解它,其中的各种概念即抽象又太拗口. 在几次面试中都被问及AOP,但是真的没有答上来,或者都在面上,这给面试官的感觉就是 ...
- 为什么做java的web开发我们会使用struts2,springMVC和spring这样的框架?
今年我一直在思考web开发里的前后端分离的问题,到了现在也颇有点心得了,随着这个问题的深入,再加以现在公司很多web项目的控制层的技术框架由struts2迁移到springMVC,我突然有了一个新的疑 ...
- Spring之旅(2)
Spring简化Java的下一个理念:基于切面的声明式编程 3.应用切面 依赖注入的目的是让相互协作的组件保持松散耦合:而AOP编程允许你把遍布应用各处的功能分离出来形成可重用的组件. AOP面向切面 ...
- Spring之旅
Java使得以模块化构建复杂应用系统成为可能,它为Applet而来,但为组件化而留. Spring是一个开源的框架,最早由Rod Johnson创建.Spring是为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性而创建 ...
随机推荐
- VS2015配置内核WDK7600环境,32位下.
VS2015配置内核WDK7600环境,32位下. 学习内核驱动的编写,就要会配置环境.不然总是用记事本编写.比较不方便. 环境配置如下. 1.首先下载WDK7600, 课堂资料代码中已经上传.链接: ...
- Django-- 多数据库联用
django项目中使用多个数据库的方法, 多个数据库的联用 以及多数据库时数据导入导出的方法. 直接给出一种简单的方法吧,想了解更多的到官方教程,点击此处 给每个app都可以单独的设置一个数据库 se ...
- HttpWebRequest中GetResponse或者说GetRequestStream偶尔超时,或者是各种操作超时造成的假死的一些解决方案
今天用了将近一天的时间来查找这个问题的存在,不停的百度查找原因测试原因,发现解决方案很是简单,不过最好还好哦啊都解决了,在这里纪录一下,希望可以帮到你们 payload = System.Text.E ...
- 一步一步创建ASP.NET MVC5程序[Repository+Autofac+Automapper+SqlSugar](四)
前言 上一篇<一步一步创建ASP.NET MVC5程序[Repository+Autofac+Automapper+SqlSugar](三)>,我们完成了: * 引用SqlSugar * ...
- Jfinal拦截器源码解读
本文对Jfinal拦截器源码做以下分析说明
- 一步一步从原理跟我学邮件收取及发送 3.telnet命令行发一封信
首先要感谢博客园管理员的及时回复,本系列的第二篇文章得以恢复到首页,这是对作者的莫大鼓励.说实在的本来我真的挺受打击的.好在管理员说只是排版上有些问题,要用代码块修饰下相关的信息.说来惭愧因为常年编码 ...
- [国嵌攻略][092][UDP网络程序设计]
server.c #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <strings.h> #inc ...
- [国嵌攻略][091][TCP网络程序设计]
server.c #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include <strings.h> #inc ...
- 【自制工具类】Java删除字符串中的元素
这几天做项目需要把多个item的id存储到一个字符串中,保存进数据库.保存倒是简单,只需要判断之前是否为空,如果空就直接添加,非空则拼接个"," 所以这个字符串的数据结构是这样的 ...
- jQuery:图片自动变换
<script type="text/javascript"> var aa=0; //设置变换时间为2s var timeChange=2000; //定义数组 va ...
