mysql 更新(九) pymysql模块的使用
本节重点:
- pymysql的下载和使用
- execute()之sql注入
- 增、删、改:conn.commit()
- 查:fetchone、fetchmany、fetchall
一、pymysql的下载和使用
之前我们都是通过MySQL自带的命令行客户端工具mysql来操作数据库,那如何在python程序中操作数据库呢?这就用到了pymysql模块,该模块本质就是一个套接字客户端软件,使用前需要事先安装。
(1)pymysql模块的下载
pip3 install pymysql
(2)pymysql的使用
数据库和数据都已存在
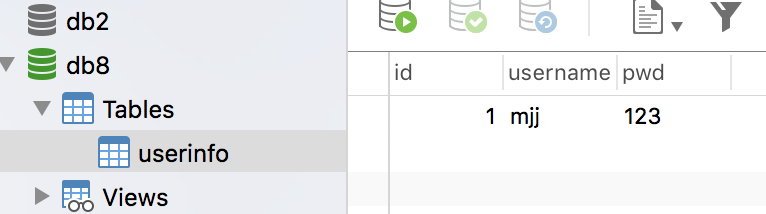

# 实现:使用Python实现用户登录,如果用户存在则登录成功(假设该用户已在数据库中)
import pymysql
user = input('请输入用户名:')
pwd = input('请输入密码:')
# 1.连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
# 2.创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
#注意%s需要加引号
sql = "select * from userinfo where username='%s' and pwd='%s'" %(user, pwd)
print(sql)
# 3.执行sql语句
cursor.execute(sql)
result=cursor.execute(sql) #执行sql语句,返回sql查询成功的记录数目
print(result)
# 关闭连接,游标和连接都要关闭
cursor.close()
conn.close()
if result:
print('登陆成功')
else:
print('登录失败')

二、execute()之sql注入

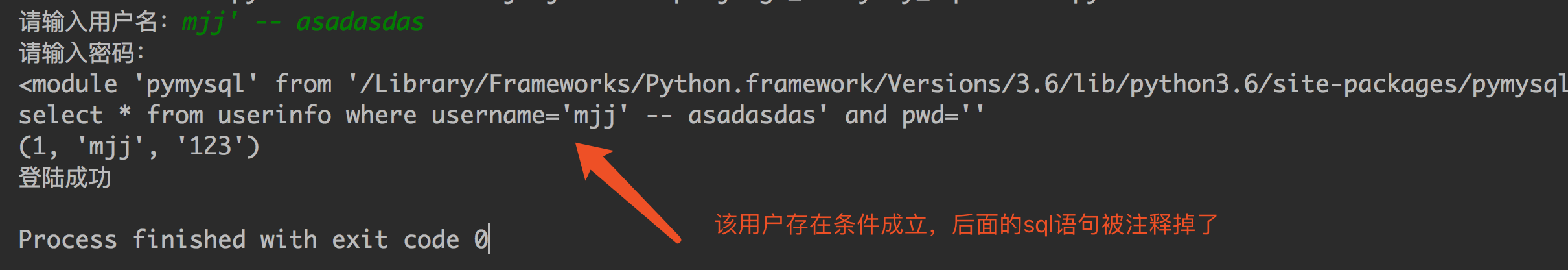
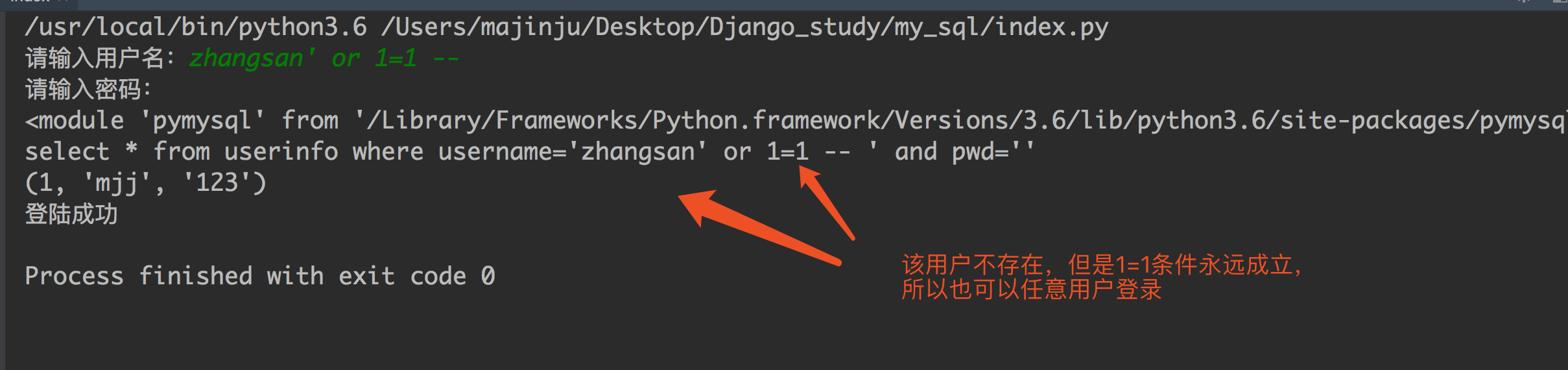
最后那一个空格,在一条sql语句中如果遇到select * from userinfo where username='mjj' -- asadasdas' and pwd='' 则--之后的条件被注释掉了(注意--后面还有一个空格) #1、sql注入之:用户存在,绕过密码 mjj' -- 任意字符 #2、sql注入之:用户不存在,绕过用户与密码 xxx' or 1=1 -- 任意字符

解决方法:

# 原来是我们对sql进行字符串拼接 # sql="select * from userinfo where name='%s' and password='%s'" %(username,pwd) # print(sql) # result=cursor.execute(sql) #改写为(execute帮我们做字符串拼接,我们无需且一定不能再为%s加引号了) sql="select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s" #!!!注意%s需要去掉引号,因为pymysql会自动为我们加上 result=cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #pymysql模块自动帮我们解决sql注入的问题,只要我们按照pymysql的规矩来。

三、增、删、改:conn.commit()
commit()方法:在数据库里增、删、改的时候,必须要进行提交,否则插入的数据不生效。

import pymysql
username = input('请输入用户名:')
pwd = input('请输入密码:')
# 1.连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
# 2.创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 操作
# 增
# sql = "insert into userinfo(username,pwd) values (%s,%s)"
# effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,(username,pwd))#同时插入多条数据#cursor.executemany(sql,[('李四','110'),('王五','119')])
# print(effect_row)#
# 改
# sql = "update userinfo set username = %s where id = 2"
# effect_row = cursor.execute(sql,username)
# print(effect_row)
# 删
sql = "delete from userinfo where id = 2"
effect_row = cursor.execute(sql)
print(effect_row)
#一定记得commit
conn.commit()
# 4.关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 5.关闭连接
conn.close()

四、查:fetchone、fetchmany、fetchall
fetchone():获取下一行数据,第一次为首行; fetchall():获取所有行数据源 fetchmany(4):获取4行数据
查看一下表内容:

mysql> select * from userinfo; +----+----------+-----+ | id | username | pwd | +----+----------+-----+ | 1 | mjj | 123 | | 3 | 张三 | 110 | | 4 | 李四 | 119 | +----+----------+-----+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)

使用fetchone():

import pymysql # 1.连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8') # 2.创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor() sql = 'select * from userinfo' cursor.execute(sql) # 查询第一行的数据 row = cursor.fetchone() print(row) # (1, 'mjj', '123') # 查询第二行数据 row = cursor.fetchone() print(row) # (3, '张三', '110') # 4.关闭游标 cursor.close() # 5.关闭连接 conn.close()

使用fetchall():

import pymysql # 1.连接 conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8') # 2.创建游标 cursor = conn.cursor() sql = 'select * from userinfo' cursor.execute(sql) # 获取所有的数据 rows = cursor.fetchall() print(rows) # 4.关闭游标 cursor.close() # 5.关闭连接 conn.close() #运行结果 ((1, 'mjj', '123'), (3, '张三', '110'), (4, '李四', '119'))

默认情况下,我们获取到的返回值是元组,只能看到每行的数据,却不知道每一列代表的是什么,这个时候可以使用以下方式来返回字典,每一行的数据都会生成一个字典:
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) #在实例化的时候,将属性cursor设置为pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
在fetchone示例中,在获取行数据的时候,可以理解开始的时候,有一个行指针指着第一行的上方,获取一行,它就向下移动一行,所以当行指针到最后一行的时候,就不能再获取到行的内容,所以我们可以使用如下方法来移动行指针:
cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动 cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动 第一个值为移动的行数,整数为向下移动,负数为向上移动,mode指定了是相对当前位置移动,还是相对于首行移动

# 1.Python实现用户登录
# 2.Mysql保存数据
import pymysql
# 1.连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
# 2.创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
sql = 'select * from userinfo'
cursor.execute(sql)
# 查询第一行的数据
row = cursor.fetchone()
print(row) # (1, 'mjj', '123')
# 查询第二行数据
row = cursor.fetchone() # (3, '张三', '110')
print(row)
cursor.scroll(-1,mode='relative') #设置之后,光标相对于当前位置往前移动了一行,所以打印的结果为第二行的数据
row = cursor.fetchone()
print(row)
cursor.scroll(0,mode='absolute') #设置之后,光标相对于首行没有任何变化,所以打印的结果为第一行数据
row = cursor.fetchone()
print(row)
# 4.关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 5.关闭连接
conn.close()
#结果如下
{'id': 1, 'username': 'mjj', 'pwd': '123'}
{'id': 3, 'username': '张三', 'pwd': '110'}
{'id': 3, 'username': '张三', 'pwd': '110'}
{'id': 1, 'username': 'mjj', 'pwd': '123'}

fetchmany():

import pymysql
# 1.连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='db8', charset='utf8')
# 2.创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
sql = 'select * from userinfo'
cursor.execute(sql)
# 获取2条数据
rows = cursor.fetchmany(2)
print(rows)
# 4.关闭游标
# rows = cursor.fetchall()
# print(rows)
cursor.close()
# 5.关闭连接
conn.close()
#结果如下:
[{'id': 1, 'username': 'mjj', 'pwd': '123'}, {'id': 3, 'username': '张三', 'pwd': '110'}]

核心代码 哈哈哈 自己看
import pymysql #开启 连接数据库conn=pymysql.Connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', password='', db='pc') #存入数据库cursor=conn.cursor()#创建游标对象 ,用游标对象创建sq语句sql='insert into pc.woshishui values (NULL ,"网","三")' #处理自增字段 直接把id设置为NULL print(sql)cursor.execute(sql) conn.commit() #关闭数据库cursor.close()conn.close()
mysql 更新(九) pymysql模块的使用的更多相关文章
- Mysql(九):Python连接MySQL数据库之pymysql模块使用
Python3连接MySQL 本文介绍Python3连接MySQL的第三方库--PyMySQL的基本使用. PyMySQL介绍 PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服 ...
- MySQL学习12 - pymysql模块的使用
一.pymysql的下载和使用 1.pymysql模块的下载 2.pymysql的使用 二.execute()之sql注入 三.增.删.改:conn.commit() 四.查:fetchone.fet ...
- Python连接MySQL数据库之pymysql模块使用
安装PyMySQL pip install pymysql PyMySQL介绍 PyMySQL是在python3.x版本中用于连接MySQL服务器的一个库,2中则使用mysqldb. Django中也 ...
- 操作mysql(import pymysql模块)
pymysql模块 import pymysql #1.连上数据库.账号.密码.ip.端口号.数据库 #2.建立游标 #3.执行sql #4.获取结果 #5.关闭游标 #6.连接关闭 #charest ...
- Python连接MySQL数据库之pymysql模块
pymysql 在python3.x 中用于连接MySQL服务器的一个库:Python2中则使用mysqldb pymysql的模块的基本的使用 # 导入pymysql模块 import pymysq ...
- mysql五:pymysql模块
一.介绍 之前都是通过MySQ自带的命令行客户端工具Mysql来操作数据库,那如何在Python程序中操作数据库呢?这就需要用到pymysql模块了. 这个模块本质就是一个套接字客户端软件,使用前需要 ...
- python关于MySQL的API -- pymysql模块
1.模块安装 pip install pymysql 2.执行sql语句 import pymysql #添加数据 conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', p ...
- MySQL:记录的增删改查、单表查询、约束条件、多表查询、连表、子查询、pymysql模块、MySQL内置功能
数据操作 插入数据(记录): 用insert: 补充:插入查询结果: insert into 表名(字段1,字段2,...字段n) select (字段1,字段2,...字段n) where ...; ...
- Python 3.5 连接Mysql数据库(pymysql 方式)
由于 MySQLdb 模块还不支持 Python3.x,官方的Mysql连接包只支持到3.4,所以 Python3.5 如果想连接MySQL需要安装 pymysql 模块. pymysql 模块可以通 ...
随机推荐
- am335x Qt SocketCAN Demo hacking
/*********************************************************************************** * am335x Qt Soc ...
- caffe编译问题-nvcc fatal:Unsupported gpu architecture 'compute_20'
错误描述 nvcc fatal : Unsupported gpu architecture 'compute_20' Makefile:: recipe for target '.build_rel ...
- 使用Nginx实现灰度发
灰度发布是指在黑与白之间,能够平滑过渡的一种发布方式.AB test就是一种灰度发布方式,让一部分用户继续用A,一部分用户开始用B,如果用户对B没有什么反对意见,那么逐步扩大范围,把所有用户都迁移到 ...
- nginx服务相关操作
安装目录 和大多软件一样一般安装在 /usr/local/ 目录下 /usr/local/ 命令man Usage: nginx [-?hvVt] [-s signal] [-c filename] ...
- dfs、遍历与for
dfs实际上就是若干个递归式连续使用,从而把所有情况全部遍历的方法 首先是递归式的连用,然后注意参数的选取以及变化就行了 1.参数一般有状态参数与开关参数 最简单的dfs就是每次选择只是改变自身状态( ...
- Springboot集成mybatis(mysql),mail,mongodb,cassandra,scheduler,redis,kafka,shiro,websocket
https://blog.csdn.net/a123demi/article/details/78234023 : Springboot集成mybatis(mysql),mail,mongodb,c ...
- CH4201 楼兰图腾
题意 4201 楼兰图腾 0x40「数据结构进阶」例题 描述 在完成了分配任务之后,西部314来到了楼兰古城的西部.相传很久以前这片土地上(比楼兰古城还早)生活着两个部落,一个部落崇拜尖刀('V'), ...
- width百分比
table中的td可以在页面中直接在元素上设置width:但是li不能只能在页面中写style: <!-- <li width="20%" class="p- ...
- sys目录下常用文件汇总
1. /sys/kernel/debug/gpio 可以实时反馈系统中感兴趣的gpio引脚的状态 root@g6s:/sys/kernel/debug# cat gpio gpiochip7: GPI ...
- Linux下软件包安装
编译dbus下载地址 :http://dbus.freedesktop.org/releases/dbus/tar zxvf dbus-1.10.0echo ac_cv_have_abstract_s ...
