MessagePack 学习笔记
封装和解析类似json的 key-value 示例
{"ID" = 333,"name"="zds","3333"="ende"}
msgpack::sbuffer sBuf;
msgpack::packer<msgpack::sbuffer> pker(&sBuf); pker.pack_map();
pker.pack(std::string("ID"));
pker.pack();
pker.pack(std::string("name"));
pker.pack(std::string("zds"));
pker.pack(std::string(""));
pker.pack(std::string("ende")); //unserilized
msgpack::unpacked unpack;
msgpack::unpack(unpack, sBuf.data(), sBuf.size()); msgpack::object obj = unpack.get();
std::cout << obj << std::endl; if (obj.type == msgpack::type::ARRAY)
std::cout << "是array" << std::endl;
else if (obj.type == msgpack::type::MAP)
std::cout << "是map" << std::endl; if(obj.via.map.size > )
{
auto pkv = obj.via.map.ptr;
auto pkv_end = obj.via.map.ptr + obj.via.map.size; do
{
auto key = pkv->key;
auto val = pkv->val;
std::cout << "key:" << key << " value:" << val << std::endl;
++pkv;
} while (pkv < pkv_end);
}
解析Socket示例
各类数据结构:
msgpack::object 他是一个引用,拷贝他的代价少,因为他是浅拷贝
msgpack::object_handle 他管理了一个对象的生命周期。他如果释放了,所有从他生成的object都是无效的引用
解析Socket示例
下列代码解析socke收包数据
unpacker.reserve_buffer 分配要收的数据的内存字节数
unpacker..buffer() 返回数据地址
unpacker.buffer_consumed() 设置实际收到的数据
unpacker.next(object_handle& oh) 循环解析数据
int main() {
boost::asio::io_service ios;
std::uint16_t const port = ;
// Server
std::size_t const window_size = ;
boost::asio::ip::tcp::acceptor ac(ios, boost::asio::ip::tcp::endpoint(boost::asio::ip::tcp::v4(), port));
boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket ss(ios);
std::function<void()> do_accept;
std::function<void()> do_async_read_some;
msgpack::unpacker unp;
do_accept = [&] {
ac.async_accept(
ss,
[&]
(boost::system::error_code const& e) {
if (e) {
std::cout << __LINE__ << ":" << e.message() << std::endl;
return;
}
unp.reserve_buffer(window_size);
do_async_read_some = [&] {
ss.async_read_some(
boost::asio::buffer(unp.buffer(), window_size),
[&](boost::system::error_code const& e, std::size_t bytes_transferred) {
if (e) {
std::cout << __LINE__ << ":" << e.message() << std::endl;
return;
}
std::cout << bytes_transferred << " bytes read." << std::endl;
unp.buffer_consumed(bytes_transferred);
msgpack::object_handle oh;
while (unp.next(oh)) {
std::cout << oh.get() << std::endl;
// In order to finish the program,
// return if one complete msgpack is processed.
// In actual server, don't return here.
return;
}
do_async_read_some();
}
);
};
do_async_read_some();
}
);
};
do_accept();
// Client
auto host = "localhost";
boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver r(ios);
boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver::query q(host, boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(port));
auto it = r.resolve(q);
boost::asio::ip::tcp::socket cs(ios);
boost::asio::async_connect(
cs,
it,
[&]
(boost::system::error_code const& e, boost::asio::ip::tcp::resolver::iterator) {
if (e) {
std::cout << __LINE__ << ":" << e.message() << std::endl;
return;
}
std::cout << __LINE__ << ":client connected" << std::endl;
msgpack::sbuffer sb;
msgpack::pack(sb, std::make_tuple(, false, "hello world", 12.3456));
write(cs, boost::asio::buffer(sb.data(), sb.size()));
}
);
// Start
ios.run();
}
详解:
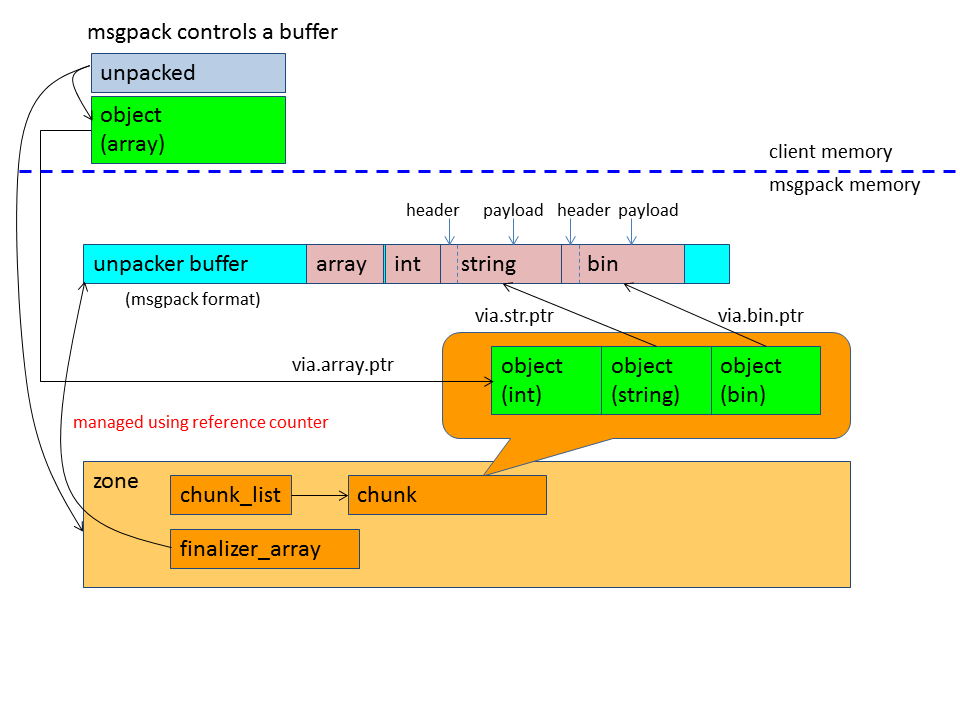
msgpack controls a buffer
msgpack provides a buffer management functionality named msgpack::unpacker. msgpack::unpacker is sutable for the following motivations:
- msgpack data is chopped, and the client doesn't know when it will complete. This is a typical situation when you develop streaming applications.
- You want to minimize copy opperations without careful memory management.
Here is the basic (not all) interface of msgpack::unpacker:
#ifndef MSGPACK_UNPACKER_INIT_BUFFER_SIZE
#define MSGPACK_UNPACKER_INIT_BUFFER_SIZE (64*1024)
#endif #ifndef MSGPACK_UNPACKER_RESERVE_SIZE
#define MSGPACK_UNPACKER_RESERVE_SIZE (32*1024)
#endif class unpacker {
public:
unpacker(unpack_reference_func f = &unpacker::default_reference_func,
void* user_data = nullptr,
std::size_t init_buffer_size = MSGPACK_UNPACKER_INIT_BUFFER_SIZE,
unpack_limit const& limit = unpack_limit());
void reserve_buffer(std::size_t size = MSGPACK_UNPACKER_RESERVE_SIZE);
char* buffer();
void buffer_consumed(std::size_t size);
bool next(unpacked& result);
};
Here is a basic pattern using msgpack::unpacker:
// The size may decided by receive performance, transmit layer's protocol and so on.
std::size_t const try_read_size = 100; msgpack::unpacker unp; // Message receive loop
while (/* block until input becomes readable */) {
unp.reserve_buffer(try_read_size);
// unp has at least try_read_size buffer on this point. // input is a kind of I/O library object.
// read message to msgpack::unpacker's internal buffer directly.
std::size_t actual_read_size = input.readsome(unp.buffer(), try_read_size); // tell msgpack::unpacker actual consumed size.
unp.buffer_consumed(actual_read_size); msgpack::unpacked result;
// Message pack data loop
while(unp.next(result)) {
msgpack::object obj(result.get());
// Use obj
}
// All complete msgpack message is proccessed at this point,
// then continue to read addtional message.
}
msgpack::unpacker::next() returns true if one complete msgpack messege is proccessed. If msgpack message is correct but insufficient, it returns false. However, parsing proccess is proceeded and the context information is preserved in the msgpack::unpacker. It helps leveling the load of parse.
When msgpack message contains binary data, string data, or ext data, they are not copied but referenced from msgpack::object by default. See the following implementation:
inline bool unpacker::default_reference_func(type::object_type type, uint64_t len, void*)
{
return true;
}
You can also customize unpack_reference_func. Even if you use references, you don't need to control buffer's lifetime. The buffers' lifetime is controled by msgpack using msgpack::zone's finalizer_array and msgpack::unpacker's reference counting mechanism.
So, in most cases, the default behavior is enough. If you want to control the peak of memory consumption when receiving msgpack data patterns are predictable, customizing unpack_reference_func might be useful.
You can get a reference information from msgpack::unpacker::next() using the following function:
bool next(unpacked& result, bool& referenced);
However, mostly you don't need to use that version of next() because referenced memories are managed by unpacker.
MessagePack 学习笔记的更多相关文章
- js学习笔记:webpack基础入门(一)
之前听说过webpack,今天想正式的接触一下,先跟着webpack的官方用户指南走: 在这里有: 如何安装webpack 如何使用webpack 如何使用loader 如何使用webpack的开发者 ...
- PHP-自定义模板-学习笔记
1. 开始 这几天,看了李炎恢老师的<PHP第二季度视频>中的“章节7:创建TPL自定义模板”,做一个学习笔记,通过绘制架构图.UML类图和思维导图,来对加深理解. 2. 整体架构图 ...
- PHP-会员登录与注册例子解析-学习笔记
1.开始 最近开始学习李炎恢老师的<PHP第二季度视频>中的“章节5:使用OOP注册会员”,做一个学习笔记,通过绘制基本页面流程和UML类图,来对加深理解. 2.基本页面流程 3.通过UM ...
- 2014年暑假c#学习笔记目录
2014年暑假c#学习笔记 一.C#编程基础 1. c#编程基础之枚举 2. c#编程基础之函数可变参数 3. c#编程基础之字符串基础 4. c#编程基础之字符串函数 5.c#编程基础之ref.ou ...
- JAVA GUI编程学习笔记目录
2014年暑假JAVA GUI编程学习笔记目录 1.JAVA之GUI编程概述 2.JAVA之GUI编程布局 3.JAVA之GUI编程Frame窗口 4.JAVA之GUI编程事件监听机制 5.JAVA之 ...
- seaJs学习笔记2 – seaJs组建库的使用
原文地址:seaJs学习笔记2 – seaJs组建库的使用 我觉得学习新东西并不是会使用它就够了的,会使用仅仅代表你看懂了,理解了,二不代表你深入了,彻悟了它的精髓. 所以不断的学习将是源源不断. 最 ...
- CSS学习笔记
CSS学习笔记 2016年12月15日整理 CSS基础 Chapter1 在console输入escape("宋体") ENTER 就会出现unicode编码 显示"%u ...
- HTML学习笔记
HTML学习笔记 2016年12月15日整理 Chapter1 URL(scheme://host.domain:port/path/filename) scheme: 定义因特网服务的类型,常见的为 ...
- DirectX Graphics Infrastructure(DXGI):最佳范例 学习笔记
今天要学习的这篇文章写的算是比较早的了,大概在DX11时代就写好了,当时龙书11版看得很潦草,并没有注意这篇文章,现在看12,觉得是跳不过去的一篇文章,地址如下: https://msdn.micro ...
随机推荐
- iOS开发-类簇(Class Cluster)
类簇(Class Cluster)是定义相同的接口并提供相同功能的一组类的集合,仅公开接口的抽象类也可以称之为类簇的公共类,每个具体类的接口有公共类的接口抽象化,并隐藏在簇的内部.这些类一般不能够直 ...
- 65. XPages自定义控件(三)高级搜索之三
RecordView控件的两个文件的完整代码在本文末尾给出.虽说完整,仅靠这两个文件,RecordView控件还不能正常工作,因为在这两个文件里还引用了其他自定义控件,调用了作为managed bea ...
- How could I create a custom windows message?
[问题] Our project is running on Windows CE 6.0 and is written in C++ . We have some problems with the ...
- ASP入门(十三)-Server对象
Server 对象用于处理服务器上的一些特殊任务,例如,创建组件实例.获取文件路径.执行ASP脚本文件等. Server 对象是体现 ASP 强大功能的一个对象,之前介绍的对象都是针对获取.请求以及简 ...
- Format Conditions按条件显示表格记录
标记特定记录 DevExpress强大得确实让人觉得它别具一格!现在,我有这样一个需求,把一个表中某字段为False的记录标记出来.下面是效果(某字段的可见性为否): 实现方式 如果是以前,我写个代码 ...
- thinkphp3返回json或jsonp数据
1.返回json数据 public function demo1() { $data = 'ok'; $this->ajaxReturn($data); } public function de ...
- python网络爬虫 - 如何伪装逃过反爬虫程序
有的时候,我们本来写得好好的爬虫代码,之前还运行得Ok, 一下子突然报错了. 报错信息如下: Http 800 Internal internet error 这是因为你的对象网站设置了反爬虫程序,如 ...
- WPF编程:textbox控件文本框数据显示最后一行
WPF编程:textbox控件文本框数据显示最后一行 TextBox控件在接收大量数据的时候,滚动条一般在最上方,如何使滚动条随着数据的接收而向下滚动呢?比如有一个TextBox'控件txbRecvD ...
- Ant详解之-path、classpath和fileset
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/itech/archive/2011/11/01/2231206.html 一 .<path/> 和 <classpath/> ...
- Linux(CentOS)中使用Mono+jexus部署Asp.net4.5网站
一.效果: 二.安装步骤: 1.安装系统CentOS,我这是用CentOs7测试的. 2.接下来安装libgdiplus.Mono.Jexus有问题可以参考安装工具的官网: Libgdiplus下载官 ...
