poj 3368 Frequent values -Sparse-Table
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 16537 | Accepted: 5981 |
Description
You are given a sequence of n integers a1 , a2 , ... , an in non-decreasing order. In addition to that, you are given several queries consisting of indices i and j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n). For each query, determine the most frequent value among the integers ai , ... , aj.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case starts with a line containing two integers n and q (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 100000). The next line contains n integers a1 , ... , an (-100000 ≤ ai ≤ 100000, for each i ∈ {1, ..., n}) separated by spaces. You can assume that for each i ∈ {1, ..., n-1}: ai ≤ ai+1. The following q lines contain one query each, consisting of two integers i and j (1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ n), which indicate the boundary indices for the
query.
The last test case is followed by a line containing a single 0.
Output
For each query, print one line with one integer: The number of occurrences of the most frequent value within the given range.
Sample Input
- -
Sample Output
Source
先讲一下题目大意,给出一个有n个数的不下降数列,和q个问题每个问题是求[a,b]中出现次数最多的数出现的次数,
有多组测试数据,当n = 0时测试结束
方法有多种,第一种直接暴力枚举,就不讲了
第二种用线段树,很多时候都不是完整的区间,怎么查?
左右两端不完整区间连续的个数是可以求出来的,这个就比较简单,记录一下每个区间开始的位置
,然后再弄个数组,记录第i个数属于的区间的新编号,如果a不是一个短的开始就就用下一个区间的
开始减去a (就把编号 + 1就是下一个区间的编号),结束部分就基本一样了
中间完整的区间就交给线段树查,最好是
把一个区间当成长度为1的线段,建树,查的时候就对应这个编号就行了。
由于我不想写,所以就不给代码了,可以在网上查查
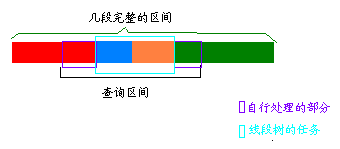
第三种使用RMQ,反正又不会更新,再比较查询的时间复杂度,线段树的查询是O(log2N),而ST算法的查询时间O(1)(自行忽略
log函数执行的时间或者打表的时间),线段树建树的时间复杂度貌似是O(2N)左右(大约实际有效的节点是原数组的2
倍),ST算法的预处理时间是O(nlog2n)看起来差不多
ST算法的思路和上面差不多,两端单独处理,中间交给ST算法去查。
另外:
1.用位运算时一定要加上括号,位运算优先级很低,之前没在意,RE了几次
2.每次完成一轮计算该清0的清0,该还原的还原
Code
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef class MyData{
private:
MyData(int from,int end,int _count):from(from),end(end),_count(_count){}
public:
int from;
int end;
int _count;
MyData(){}
static MyData getNULL(){
return MyData(,,);
}
}MyData;
vector<MyData> list;
int a = -,b;
int *pos;
int count1;
int f[][];
int t;
int n,q;
void init(){
const int limit = list.size();
for(int i = ;i < limit;i++)
f[i][] = list[i]._count;
for(int j = ; ( << j) < limit;j++){
t = << j;
for(int i = ; i < limit && (i + t) < limit; i++){
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j - ], f[ i + ( << j - ) ][j - ]); //位运算优先级低!!!打括号
}
}
}
int main(){
while(true){
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n == ) break;
scanf("%d",&q);
pos = new int[(const int)(n + )];
for(int i = ;i <= n;i++){
scanf("%d",&b);
if(a == b){
list[list.size() - ]._count++;
pos[i] = pos[i - ];
}else{
if(!list.empty())
list[list.size() - ].end = i - ;
list.push_back(MyData::getNULL());
pos[i] = count1++;
list[list.size() - ].from = i;
list[list.size() - ]._count = ;
}
a = b;
}
list[list.size() - ].end = n;
init();
for(int i = ;i <= q;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(pos[a] == pos[b]){
printf("%d\n",b - a + );
continue;
}
if(pos[b] - pos[a] == ){
int result = max(list[pos[a]].end - a + ,b - list[pos[b]].from + );
printf("%d\n",result);
continue;
}
int ans = ;
ans = max(list[pos[a]].end-a+,b-list[pos[b]].from+);
b = pos[b] - ;
a = pos[a] + ;
int k = (int)(log((double)b-a+1.0)/log(2.0));
int t2 = max(f[a][k],f[b-(<<k)+][k]);
ans = max(ans,t2);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
delete[] pos;
list.clear();
count1 = ;
a = -;
}
return ;
}
[后记]
附赠调试这道题时所用的对拍器、比较程序和数据生成器
cmp.cpp:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char buf1[];
char buf2[];
FILE *fin1;
FILE *fin2;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
fin1 = fopen(argv[],"r");
fin2 = fopen(argv[],"r");
while(!(feof(fin1))&&!(feof(fin2))){
fscanf(fin1,"%s",buf1);
fscanf(fin2,"%s",buf2);
if(strcmp(buf1, buf2) != ) return ;
}
if(feof(fin1) != feof(fin2)) return ;
return ;
}
md_fv.cpp:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
ofstream fout("fv.in");
int main(){ srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int n = rand()% + ;
int q = rand()% + ; fout<<n<<" "<<q<<endl; int start = rand()% - ;
for(int i =; i<= n;i++){
start += rand()%;
fout<<start<<" ";
} fout<<endl;
for(int i = ;i < q;i++){
start = rand()%n + ;
int end = min(rand()%(n - start + ) + start,n);
fout<<start<<" "<<end<<endl;
} fout<<""<<endl;
return ;
}
test_fv.cpp:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
int statu;
boolean aFlag;
int main(){
system("g++ fv.cpp -o fv.exe");
system("g++ cmp.cpp -o cmp.exe");
system("g++ md_fv.cpp -o md_fv.exe");
system("g++ std.fv.cpp -o std.fv.exe");
for(int i = ;i < ;i++){
aFlag = true;
system("md_fv");
system("std.fv");
clock_t begin = clock();
statu = system("fv");
clock_t end = clock();
cout<<"测试数据#"<<i<<":";
if(statu != ){
cout<<"RuntimeError";
}else if(system("cmp fv1.out fv.out") != ){
cout<<"WrongAnswer";
}else{
cout<<"Accepted";
aFlag = false;
}
cout<<"\t\tTime:"<<(end - begin)<<"ms"<<endl;
if(aFlag){
system("pause");
}
}
return ;
}
poj 3368 Frequent values -Sparse-Table的更多相关文章
- POJ 3368 Frequent values 【ST表RMQ 维护区间频率最大值】
传送门:http://poj.org/problem?id=3368 Frequent values Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total S ...
- poj 3368 Frequent values(RMQ)
/************************************************************ 题目: Frequent values(poj 3368) 链接: http ...
- POJ 3368 Frequent values (基础RMQ)
Frequent values Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 14742 Accepted: 5354 ...
- poj 3368 Frequent values(段树)
Frequent values Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 13516 Accepted: 4971 ...
- POJ 3368 Frequent values RMQ ST算法/线段树
Frequent values Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Lim ...
- POJ 3368 Frequent values(RMQ 求区间出现最多次数的数字的次数)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem? id=3368 Description You are given a sequence of n integers a1 , a2 , .. ...
- poj 3368 Frequent values(RMQ)
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=3368 题意:给定n个数,顺序为非下降,询问某个区间内的数出现最多的数的 出现次数.. 大白书上的 例题..算是RMQ变形了, 对 原数组重 ...
- (简单) POJ 3368 Frequent values,RMQ。
Description You are given a sequence of n integers a1 , a2 , ... , an in non-decreasing order. In ad ...
- POJ 3368 Frequent values(线段树区间合并)
[题目链接] http://poj.org/problem?id=3368 [题目大意] 有一个有序序列,要求区间查询出现次数最多的数 [题解] 维护每个区间左端点和右端点,以及左右的长度,还有区间的 ...
随机推荐
- Why is long2ip conversion important?
Frequently Asked Questions about Convert long to IP address https://long2ip.com/faq/ What is long2ip ...
- queue hardware os
Computer Science An Overview 11th Edition Queues are often used as the underlying structure of a buf ...
- vim编辑器的基本用法
使用linux时候,个人比较喜欢用vim编辑器,对文本进行操作. 为了方便我使用vim编辑器,特地搜索了一下教程记录于此,防止自己忘记了. 下面就是一些vim使用的基础操作: 使用vim打开软件 vi ...
- vue.js个人学习心得
2017.4.7开始辞职刚好一个月时间,一个月时间里我开始彷徨,迷惘,失业带来的痛苦,打算转行,不再搞机械行业,因为不想再做低端的产品设计(本身不是研究生也不是说天资卓越,只是不甘于平凡). 好了,不 ...
- 解决eslint空格报错等问题
eslint检查代码风格是好的,不过 有些换行报错 空格报错 还有在代码中有 console也是报错 这有些烦人 为了把这些烦人的报错给禁止掉 我们可以在package.json文件中 找到 ...
- 【F12】谷歌浏览器F12前端调试工具 Console
谷歌浏览器F12前端调试工具 Console 前言 先上图:不知道有多少人发现,在浏览器开发工具的“Console”上的百度首页的关于百度招聘的信息: 今天要给大家介绍的就是是Web前端调试工具中的C ...
- java-JProfiler(二)-进行本地JVM的性能监控-tomcat
监视本地的Tomcat, 看似是本地,其实JProfiler GUI在一个单独的JVM里启动,他与被监视的目标jvm之间通过socket通讯,目的为了不干扰目标JVM.所以监视本地Tomcat与监视远 ...
- 64位win10+cuda8.0+vs2013+cuDNN V5下Caffe的编译安装教程并配置matlab2014a 接口
一.需要安装的软件 1)vs2013,我是在http://www.52pojie.cn/thread-492326-1-1.html这个网址安装的.我之前用的是vs2012,按照网上的配置教程会爆各种 ...
- 详解Linux(centos7)下安装OpenSSL安装图文方法
OpenSSL是一个开源的ssl技术,由于我需要使用php相关功能,需要获取https的文件所以必须安装这个东西了,下面我整理了两种关于OpenSSL安装配置方法. 安装环境: 操作系统:CentO ...
- JMS规范与Kafka
一.为什么需要消息队列 消息队列的核心作用就是三点:解耦一个系统中各个子模块的互相绑定与依赖,异步执行后台耗时逻辑,并行处理一个请求中涉及的多个操作. 以我们常见的下订单场景来说明,我们熟悉的淘宝,后 ...
