Unit02: 参数值注入 、 基于注解的组件扫描
Unit02: 参数值注入 、 基于注解的组件扫描
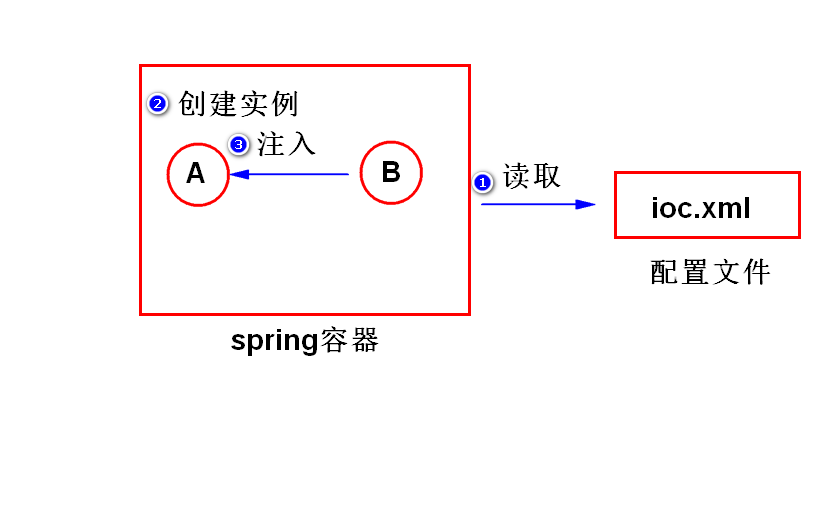
(4)IOC (Inversion Of Controll 控制反转)
什么是IOC?
对象之间的依赖关系由容器来建立。
什么是DI? (Dependency Injection 依赖注入)
容器通过调用set方法或者构造器来建立对象之间的依赖关系。
注: IOC是目标,而DI是手段。
依赖注入的两种方式
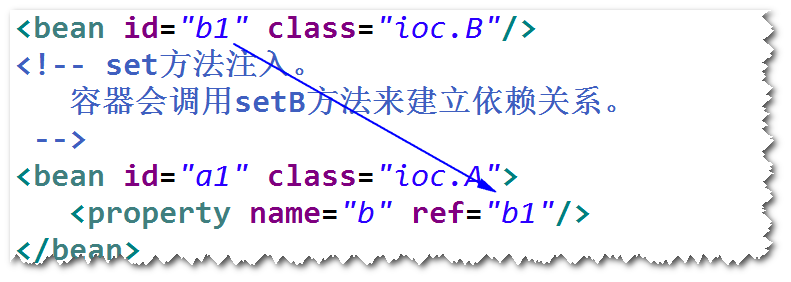
方式一 set方法注入。
step1. 添加set方法。
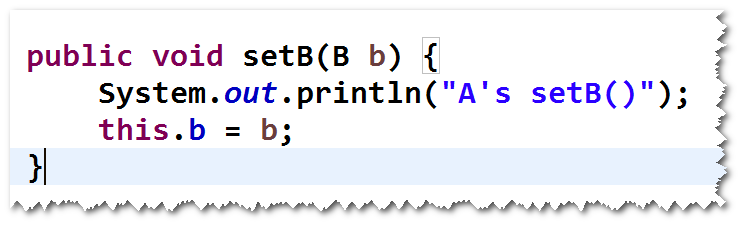
step2. 配置set方法注入。
方式二 构造器注入。
step1. 添加构造器。

step2. 配置构造器注入。

自动装配 (了解)
什么是自动装配?
容器依据某些规则,自动建立对象之间的依赖关系。
注:默认情况下,容器禁止自动装配。

注入基本类型的值
使用value属性来注入。
注入集合类型的值
List,Set,Map,Properties
引用的方式注入集合类型的值

读取properties文件的内容

使用Spring表达式

案例:
auto
package auto;
public class Restaurant {
private Waiter wt;
public void setWt(Waiter wt) {
System.out.println("setWt()");
this.wt = wt;
}
public Restaurant() {
System.out.println("Restaurant");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Restaurant [wt=" + wt + "]";
}
}
Restaurant.java
package auto;
public class Waiter {
public Waiter() {
System.out.println("Waiter()");
}
}
Waiter.java
ioc
package ioc;
public class A {
private B b;
public A() {
System.out.println("A()");
}
public A(B b) {
System.out.println("A(B)");
this.b = b;
}
public void service(){
System.out.println("A's service()");
b.f1();
}
}
A.java
package ioc;
public class B {
public B() {
System.out.println("B()");
}
public void f1(){
System.out.println("B's f1()");
}
}
B.java
value
package value;
public class SpelBean {
private String name;
private String interest;
private double score;
private int pageSize;
public void setPageSize(int pageSize) {
this.pageSize = pageSize;
}
public SpelBean() {
System.out.println("SpelBean");
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public void setInterest(String interest) {
this.interest = interest;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SpelBean [name=" + name + ", interest=" + interest + ", score=" + score + ", pageSize=" + pageSize
+ "]";
}
}
SpelBean.java
package value; import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set; public class ValueBean {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<String> interest;
private Set<String> city;
private Map<String,Double> score;
private Properties db; public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public List<String> getInterest() {
return interest;
}
public Set<String> getCity() {
return city;
}
public Map<String, Double> getScore() {
return score;
}
public Properties getDb() {
return db;
}
public void setInterest(List<String> interest) {
this.interest = interest;
}
public void setDb(Properties db) {
this.db = db;
}
public void setCity(Set<String> city) {
this.city = city;
}
public void setScore(Map<String, Double> score) {
this.score = score;
}
public ValueBean() {
System.out.println("ValueBean()");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ValueBean [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", interest=" + interest + ", city=" + city + ", score="
+ score + ", db=" + db + "]";
} }
ValueBean.java
src/main/resource
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="wt2" class="auto.Waiter"/>
<!--
autowire指定自动装配的规则,有这样三个值:
byName: 容器依据属性名查找对应的bean(即
bean的id等于属性名),找到之后,调用对应的
set方法来完成注入。
注:如果找不到,会注入null值。
byType:容器依据属性类型查找对应的bean(即
bean的类型与属性类型一致),找到之后,调用对
应的set方法来完成注入。
注:如果找不到,会注入null值。
如果找到多个,会出错。
constructor:类似byType,只不过会调用构造器
来完成注入。
-->
<bean id="rest" class="auto.Restaurant"
autowire="byType"/>
</beans>
auto.xml
pagesize=10
config.properties
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="b1" class="ioc.B"/>
<!--
构造器方式注入。
index属性:指定参数的下标(从0开始)
-->
<bean id="a1" class="ioc.A">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="b1"/>
</bean> </beans>
ioc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd">
<!--
使用Spring表达式读取其它bean的属性值。
-->
<bean id="sb1" class="value.SpelBean">
<property name="name"
value="#{vb1.name}"/>
<property name="interest"
value="#{vb1.interest[0]}"/>
<property name="score"
value="#{vb1.score['英语']}"/>
<property name="pageSize"
value="#{config.pagesize}"/>
</bean> <bean id="vb1" class="value.ValueBean">
<property name="name" value="小月"/>
<property name="age" value="22"/>
<property name="interest">
<list>
<value>钓鱼</value>
<value>旅游</value>
<value>看电视</value>
<value>看电视</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="city">
<set>
<value>北京</value>
<value>长沙</value>
<value>南京</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="score">
<map>
<entry key="英语" value="60"/>
<entry key="math" value="80"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="db">
<props>
<prop key="username">King</prop>
<prop key="password">1234</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean> <!-- 引用的方式注入集合类型的值 -->
<util:list id="interestBean">
<value>钓鱼</value>
<value>旅游</value>
<value>上网</value>
</util:list>
<util:set id="cityBean">
<value>北京</value>
<value>上海</value>
<value>武汉</value>
</util:set>
<util:map id="scoreBean">
<entry key="english" value="80"/>
<entry key="math" value="90"/>
</util:map>
<util:properties id="dbBean">
<prop key="username">King</prop>
<prop key="password">1234</prop>
</util:properties>
<bean id="vb2" class="value.ValueBean">
<property name="interest"
ref="interestBean"/>
<property name="city"
ref="cityBean"/>
<property name="score"
ref="scoreBean"/>
<property name="db"
ref="dbBean"/>
</bean> <!-- 读取properties文件的内容 -->
<!--
location属性:指定要 读取的文件的位置,
其中,classpath:表示依据类路径去查找。
-->
<util:properties id="config"
location="classpath:config.properties"/> </beans>
value.xml
src/test/java
test
package test; import java.util.Properties; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import auto.Restaurant;
import ioc.A;
import value.SpelBean;
import value.ValueBean; public class TestCase {
@Test
// 测试 构造器方式的注入
public void test1() {
// 启动Spring容器
String config = "ioc.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
// 获得对象
A a1 = ac.getBean("a1", A.class);
a1.service();
} @Test
// 测试 自动装配
public void test2() {
// 启动Spring容器
String config = "auto.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
// 获得对象
Restaurant rest = ac.getBean("rest", Restaurant.class);
System.out.println(rest);
} @Test
// 测试 注入基本类型的值
public void test3() {
// 启动Spring容器
String config = "value.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
ValueBean vb1 = ac.getBean("vb2", ValueBean.class);
System.out.println(vb1);
} @Test
// 读取properties文件
public void test4() {
// 启动Spring容器
String config = "value.xml";
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config);
Properties props = ac.getBean("config", Properties.class);
System.out.println(props);
} @Test
// 测试 Spring表达式
public void test5() {
// 启动Spring容器
String config = "value.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
SpelBean sb1 =
ac.getBean("sb1",SpelBean.class);
System.out.println(sb1);
}
}
TestCase.java
使用注解简化配置
(1)什么是组件扫描?
Spring容器会扫描base-package指定的包及其子包下面的所有的类, 如果这些类前面有一些特殊的注解(比如@Component),则Spring 容器会将这些类纳入容器进行管理(相当于在配置文件当中有对应的bean)。
(2)如何进行组件扫描?
step1. 在类前面添加特定的注解。比如 @Component。

step2. 在配置文件当中,配置组件扫描。

(3)作用域和延迟加载相关注解

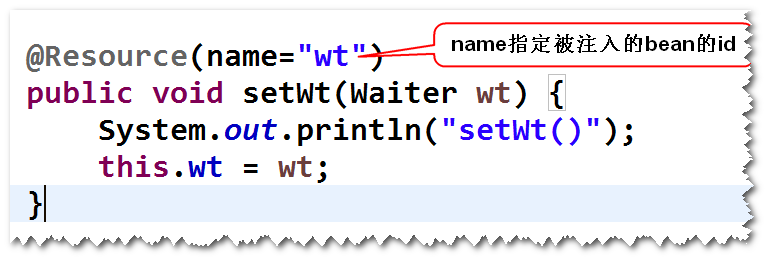
(4)依赖注入相关的注解


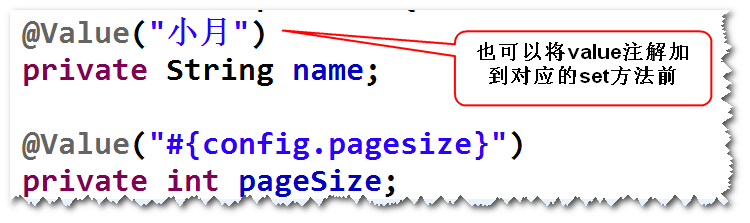
(5)value注解
案例:
annotation
package annotation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("eb")
public class ExampleBean {
@Value("小月")
private String name; @Value("#{config.pagesize}")
private int pageSize; public void setPageSize(int pageSize) {
this.pageSize = pageSize;
} public ExampleBean() {
System.out.println("ExampleBean()");
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "ExampleBean [name=" + name + ", pageSize=" + pageSize + "]";
} }
ExampleBean.java
package annotation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("mg")
public class Manager {
private Waiter wt; public Manager() {
System.out.println("Manager()");
} @Autowired
public Manager(@Qualifier("wt") Waiter wt) {
System.out.println("Manager(wt)");
this.wt = wt;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Manager [wt=" + wt + "]";
} }
Manager.java
package annotation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("rest")
public class Restaurant { @Autowired
@Qualifier("wt")
private Waiter wt; // @Autowired
// public void setWt(@Qualifier("wt") Waiter wt) {
// System.out.println("setWt()");
// this.wt = wt;
// } @Override
public String toString() {
return "Restaurant [wt=" + wt + "]";
} public Restaurant() {
System.out.println("Restaurant()");
} }
Restaurant.java
package annotation;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("school")
public class School {
private Waiter wt;
@Resource(name="wt")
public void setWt(Waiter wt) {
System.out.println("setWt()");
this.wt = wt;
}
public School() {
System.out.println("School()");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "School [wt=" + wt + "]";
}
}
School.java
package annotation; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("stu1")
@Scope("singleton")
@Lazy(true)
public class Student { public Student() {
System.out.println("Student()");
} @PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("init()");
} @PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("destroy()");
} }
Student.java
package annotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("wt")
public class Waiter {
public Waiter() {
System.out.println("Waiter()");
}
}
Waiter.java
src/main/resources
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa-1.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-3.2.xsd">
<!-- 配置组件扫描 -->
<!--
Spring容器会扫描base-package指定的包及
其子包下面的所有的类,如果这些类前面有一
些特殊的注解(比如@Component),则Spring
容器会将这些类纳入容器进行管理(相当于在
配置文件当中有对应的bean)。
-->
<context:component-scan
base-package="annotation"/> <util:properties id="config"
location="classpath:config.properties"/> </beans>
annotation.xml
pagesize=10
config.properties
src/test/java
test
package test; import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import annotation.ExampleBean;
import annotation.Manager;
import annotation.Restaurant;
import annotation.School;
import annotation.Student; public class TestCase {
@Test
//测试 组件扫描
public void test1(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
Student stu1 =
ac.getBean("stu1",
Student.class);
System.out.println(stu1);
} @Test
//测试 作用域
public void test2(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
Student stu1 =
ac.getBean("stu1",
Student.class);
Student stu2 =
ac.getBean("stu1",
Student.class);
System.out.println(stu1 == stu2);
} @Test
// 测试 生命周期
public void test3(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
AbstractApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
Student stu1 =
ac.getBean("stu1",
Student.class);
ac.close();
} @Test
// 测试 延迟加载
public void test4(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
} @Test
// 测试 @Autowired和 @Qualifier
public void test5(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
Restaurant rest =
ac.getBean("rest",Restaurant.class);
System.out.println(rest); Manager mg =
ac.getBean("mg",Manager.class);
System.out.println(mg);
} @Test
//测试 @Resource
public void test6(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
School s =
ac.getBean("school",
School.class);
System.out.println(s);
} @Test
//测试 @Value
public void test7(){
String config = "annotation.xml";
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
config);
ExampleBean eb =
ac.getBean("eb",ExampleBean.class);
System.out.println(eb);
} }
TestCase.java
Unit02: 参数值注入 、 基于注解的组件扫描的更多相关文章
- Spring - 基于注解的组件扫描
关于Spring的书籍都会花很大篇幅来讲解Spring如何注入各种bean的问题,非常令人头疼,自己在工作中还从来没有用到过. 所以就要跳过那些篇章,直接学习基于注解的组件扫描. 发现spring2是 ...
- Spring IoC 源码分析 (基于注解) 之 包扫描
在上篇文章Spring IoC 源码分析 (基于注解) 一我们分析到,我们通过AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类传入一个包路径启动Spring之后,会首先初始化包扫 ...
- Spting:基于注解的组件化管理
@Component,@Controller(控制层),@Service(业务层),@Repository(持久层) 以上四个注解的功能完全相同,不过在实际开发中,要在不同功能的类上加上响应的注解 1 ...
- Spring IOC基础回顾 — 组件扫描和装配
目录 注解形式配置应用IOC 1. 组件自动扫描 2. 组件依赖:为bean添加注解,实现自动注入 3. Spring IOC应用小结 注解形式配置应用IOC 在类定义.方法定义.成员变量定义前使用, ...
- Spring学习笔记之 Spring IOC容器(二) 之注入参数值,自动组件扫描方式,控制Bean实例化方式,使用注解方式
本节主要内容: 1. 给MessageBean注入参数值 2. 测试Spring自动组件扫描方式 3. 如何控制ExampleBean实例化方式 4. 使用注解方式重构Jdb ...
- Spring基于注解及SpringMVC
1.使用注解 (1)组件扫描 指定一个包路径,Spring会自动扫描该包 及其子包所有组件类,当发现组件类定义前有 特定的注解标记时,就将该组件纳入到Spring 容器.等价于原有XML配置中的< ...
- Spring_自动组件扫描和 基于注解配置bean
自动组件扫描 启用Spring组件扫描功能. 使用@Component注释来表示这是类是一个自动扫描组件. package com.tanlei.dao; import org.springfram ...
- 07 Spring框架 依赖注入(四)基于注解的依赖注入
前面几节我们都在使用xml进行依赖的注入,但是在实际的开发中我们往往偏爱于使用注解进行依赖注入,因为这样更符合我们人的思维,并且更加快捷,本节就来讲述Spring基于注解的依赖注入: 信息注入注解 @ ...
- Spring:基于注解的依赖注入的使用
1.什么是pojo?什么是bean? 首先,在之前几篇Spring的介绍文章当中,自己都提到了一个名词叫做POJO类,但是在回顾Spring的注解的使用的时候,去形容java当中的对象还有一个名词是叫 ...
随机推荐
- IRC BOT原来是利用IRC下发C&C命令——在xx云环境遇到了,恶意软件开的是6666端口
Backdoor/IRC.RpcBot 本词条缺少名片图,补充相关内容使词条更完整,还能快速升级,赶紧来编辑吧! Backdoor/IRC.RpcBot是一些批处理文件.脚本文件和执行文件的集合,也是 ...
- python高级内置函数和各种推导式的介绍:一行搞定的代码
一.知识要点 all 都为真 any 有真的 min 最小的 max 最大的 sum 求和 reversed 反转 sorted 排序 zip 对应合并 [] 列表推倒式 () 生成器 {} 字典推倒 ...
- Linux中jar包指定端口启动并记录日志
Linux中jar包指定端口启动并记录日志: java -jar -Dserver.port=38080 group-buying-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar >log.log ...
- 【zznu-2093】毁掉这颗二叉树
题目描述 广寒宫下有株二叉树,树上共有n个节点,通过n-1条树枝连接,树下有一只玉兔,吴刚提着斧子站在一旁. 他恼恨一切同他争夺嫦娥的事物,所以他决定通过砍二叉树上的n-1条树枝来毁掉这颗二叉树. 妙 ...
- kvm虚拟主机安装速度很慢
在c6220 II上部署虚拟化遇到的问题: 1.部署完kvm后,安装虚拟主机的过程非常缓慢,但是最终能成功 原因:宿主机BIOS的virtualization technology设置为Disable ...
- 内存保护机制及绕过方法——利用Ret2Libc绕过DEP之VirtualProtect函数
利用Ret2Libc绕过DEP之VirtualProtect函数 ⑴. 原理分析: i.相关概念: VirtualProtect()函数: BOOL WINAPI VirtualProtect( _ ...
- log4cpp单例类封装
body, table{font-family: 微软雅黑; font-size: 13.5pt} table{border-collapse: collapse; border: solid gra ...
- yii2 联系我们发送邮件报错
为什么会报错,因为国内的邮件服务商要求发送邮件的人和设置的smtp服务器账号要相同,因为联系我们的是用户,也就是发件人是用户,而不是我们配置的邮箱,所有出错. 这里我用了个取巧的办法,发件人改为自己, ...
- html dom SetInterVal()
HTML DOM setInterval() 方法 HTML DOM Window 对象 定义和用法 setInterval() 方法可按照指定的周期(以毫秒计)来调用函数或计算表达式. setInt ...
- TreeSet实现原理及源码分析
类似于HashMap和HashSet之间的关系,HashSet底层依赖于HashMap实现,TreeSet底层则采用一个NavigableMap来保存TreeSet集合的元素.但实际上,由于Navig ...
