AT91 USB Composite Driver Implementation
AT91 USB Composite Driver Implementation
1. Introduction The USB Composite Device is a general way to integrate two or more functions into one single device.
It is defined in the USB Specification Revision 2.0, as "A device that has multiple interfaces controlled independently of each other".
This document introduces basics for USB composite device and gives examples to implement the composite device
that has two functions included, based on the Atmel® AT91 SAM Softpack for its ARM® Thumb® based microcontrollers.
To add more than one functions to the host via one USB port, the USB composite device works.
The available functions are listed as following:
• MSD: To extend hard disk storage capacity.
• HID: USB mouse, USB keyboard, Game controller ...
• Audio: USB Speaker or Recorder for host.
• CDC: To work as virtual COM port, modems or networking devices such as ADSL or Cable modem.
For more detailed information, please refer to the Application Notes of the class related device implementations.
Normally when you use USB functions, you will need one USB cable for each function, which means when you use several functions, many cables are needed.
The composite device helps to reduce the number of cables used at the same time.
This Application Note details the following composite solutions:
• HID + MSD: Adds keys, navigation pads or even handwrite pad with a storage disk.
• HID + Audio: Integrates game controller with Audio codec.
• CDC + MSD: Add more serial ports or modems when extending the storage of your laptop.
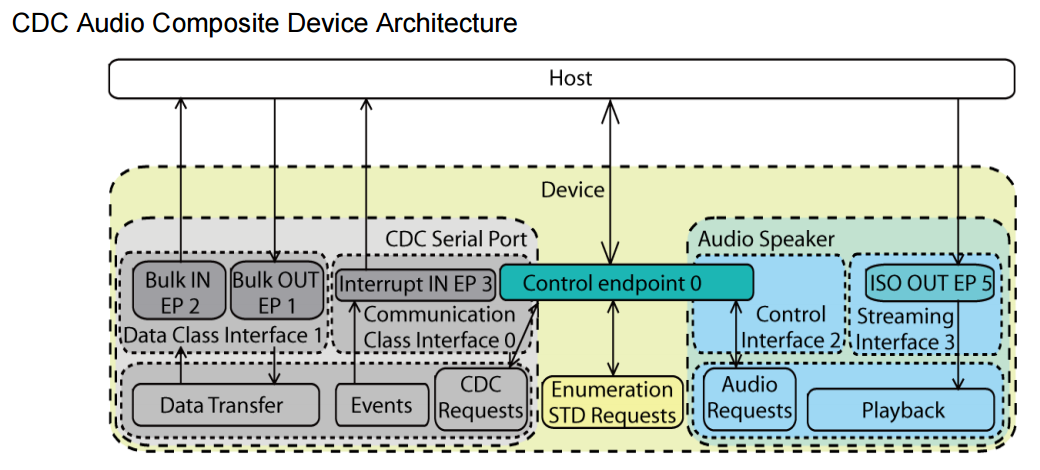
• CDC + Audio: Modem and an audio speaker at the same time. Or extend your serial port when you are playing music.
• CDC + HID: Extends the interface mostly for laptops, which allows extra serial port and mouse/keyboard.
• CDC + CDC: To extends two or more serial ports through one single USB cable, mostly for laptop.
Note that the composite device has several functions that work concurrently.
The host can see all of these functions available simultaneously.
Some of the cellphones that can manually select their connection types as “Modem” or “USB Disk”
is just product with two different USB devices pre-selected and not “composite” one.
3. USB Composite Device Basics
3.1 Purpose The Universal Serial Bus (USB) offers an easy way to connect PC with portable devices and to expand external peripherals.
Usually a USB device provides a single function to the host,
such as a storage disk, serial RS-232 port, digital microphone, or speakers, so one function occupies one USB port.
Nevertheless, to allow several functions through a single physical port, the USB specification mentions two kinds of devices:
• Composite device: a device has multiple logical interfaces controlled independently of each other.
A single physical logical address is used for the device.
• Compound device: a separate hub with multiple functions attached.
Composite devices are an efficient solution to reduce the number of hub and USB cables.
To give an example:
a device being at the same time modem and audio speaker requires only a single USB cable.
3.2 Architecture
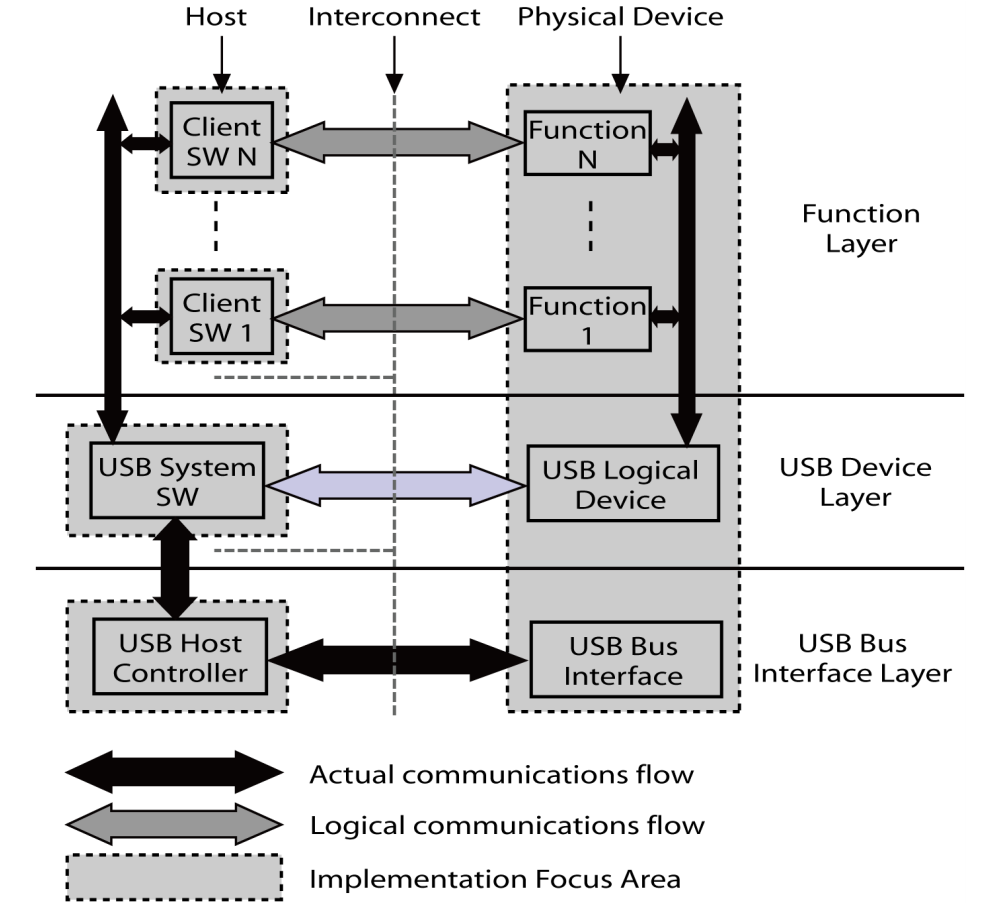
3.2.1 Communication flow
Figure 3-3 highlights logical communication flows between several clients (host side) and functions (device side),
over a single physical USB connection.
The highlighted layer is the function layer. In host side, there is some client software that can operate with the different functions in the same physical device simultaneously. E.g. when a composite device with card reader and printing function is connected to a PC, a new printer device and storage disks may appear for you to explore your pictures on your media card, and to print them with the printer.
3.2.2 Interfaces Interface descriptors for composite devices correspond to the concatenation of interfaces descriptors defined for each functions available in the system.
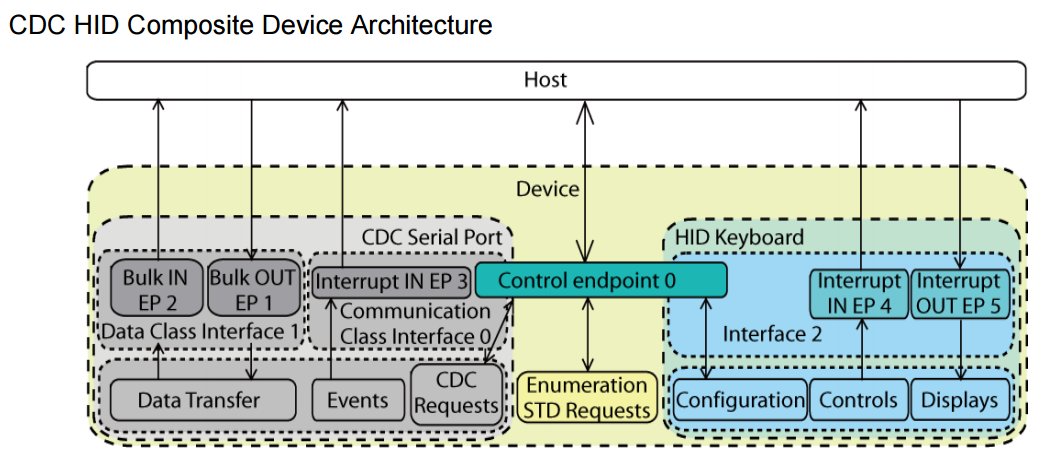
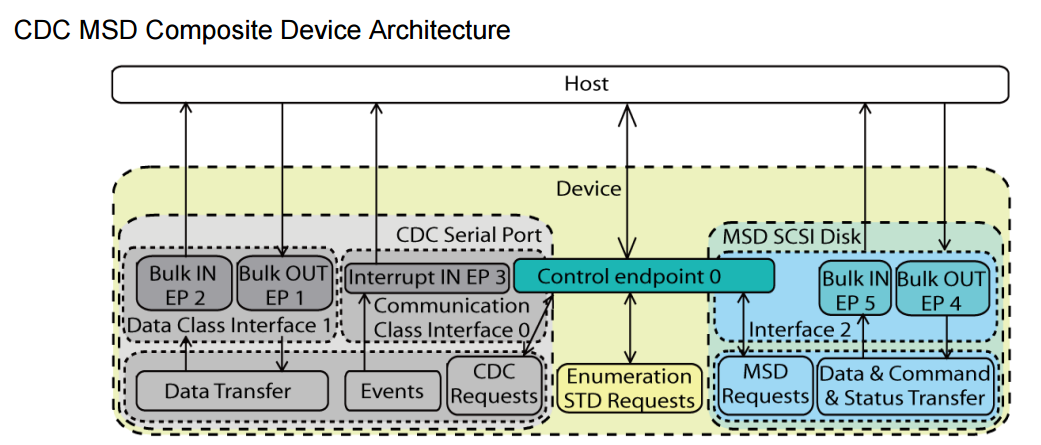
E.g., a composite with HID+CDC needs three interface descriptors (Section 4.7.3 on page 15), while HID+MSD (Section 4.7.1 on page 13) only needs two.
There are some general rules to assemble the interfaces:
• bInterfaceNumber should start from zero and then increase by one;
• the interfaces that use the same function should be placed together, that is, the values of bInterfaceNumber should be contiguous;
• if two or more interfaces are associated to one device function (such as CDC), the Interface Association Descriptor (IAD) is used,
please refer to Section 3.2.4.1 on page 6 for more details.
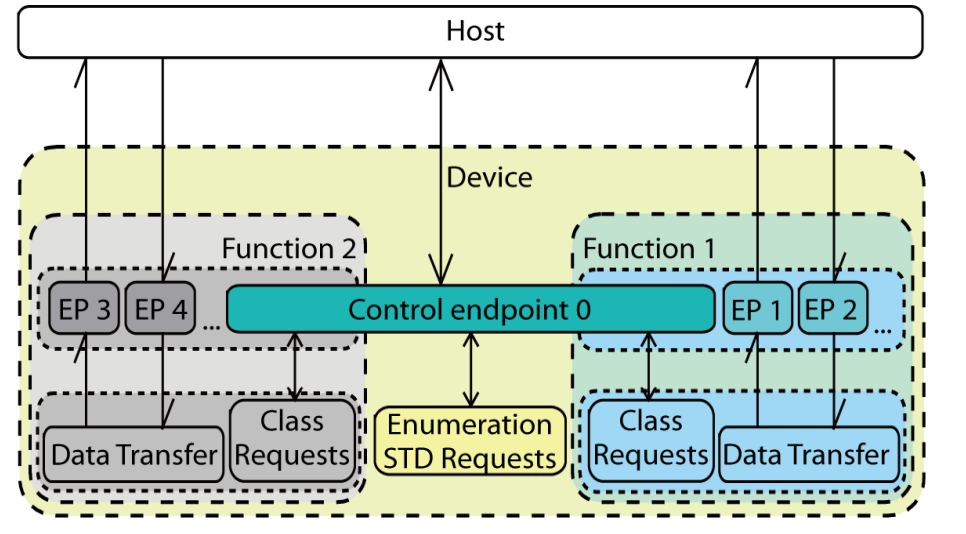
3.2.2.1 Composite with SINGLE-interface functions
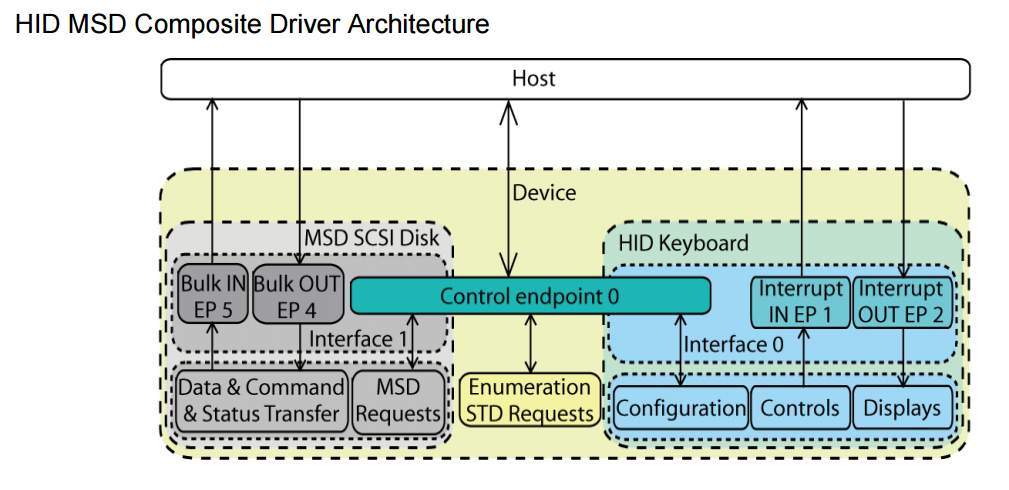
This kind of composite device includes the functions that have only one interface, such as HID+MSD.
The default endpoint (endpoint 0) is shared by all functions.
Each function has one interface only, to handle class-specific requests, control commands and data.
The interface and endpoint settings are function specific.
Figure 3-1. USB Composite Device with SINGLE-interface-functions
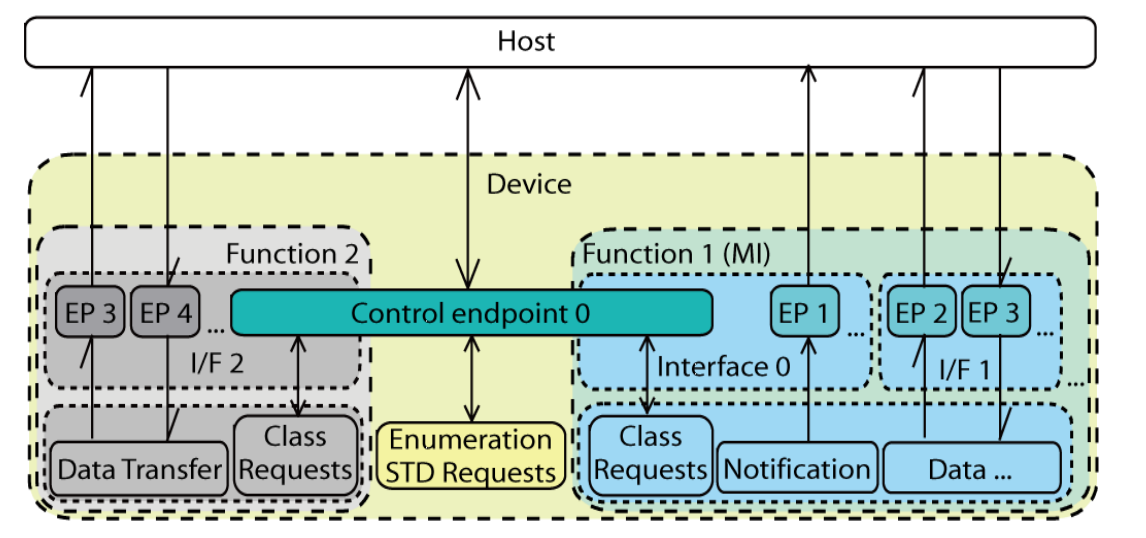
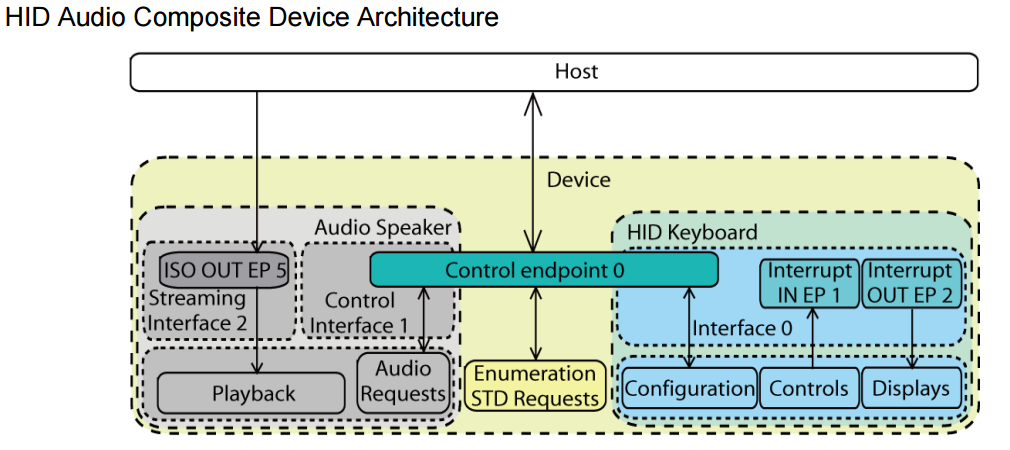
3.2.2.2 Composite with MULTI-interface functions
This kind of composite device includes the functions that are composed of more than one interface,
such as CDC class function, Audio Class function, etc..
The default endpoint (endpoint 0) is usually shared by single-interface-function and the control interface of the multi-interface-function.
There may be other endpoints such as an interrupt IN endpoint for CDC in the control interface for the function to accept control commands or update status.
The interface and endpoint settings are function specific.
The multi-interface function also needs a Interface Association Descriptor (IAD, See Section 3.2.4.1 on page 6) to associate its interfaces.
Figure 3-2. USB Composite Device with MULTI-interface-functions
3.2.3 Endpoints
Excluding the default endpoint, composite devices shall declare a number of endpoints equal to the sum of the number of endpoint required for individual function.
E.g., a composite with HID+CDC needs six endpoint descriptors (Section 4.7.3 on page 15), while HID+MSD (Section 4.7.1 on page 13) only needs five.
Endpoint 0 (default endpoint) is used for standard, class-specific and vendor-specific requests, depending on the implementation of the functions inside.
It can be used to operate on any interface for any device function.
The other endpoints are function-specific, their usage is defined by the class of the function or defined by the vendor.
Figure 3-1 and Figure 3-2 are examples for the composite device architecture with two device functions.
Figure 3-3. USB composite composition
3.2.3.1 Interface & Endpoints compositions for AT91 chip
Since the number of endpoints and the endpoint fifo size is based on hardware,
the assignment of the endpoints should be arranged carefully.
Here are some examples on the endpoint allocation for AT91SAM7SE chip,
since it has 7 endpoints to use.
Please refer to the AT91SAM product datasheet to get the number and the size of endpoints.
Generally, ISO endpoints should be considered firstly, because they always require large FIFO size and double buffer;
the BULK endpoints come the second, which only require a double buffer with transfer speed considered;
the last ones are the Interrupt endpoints, which only require a small FIFO and the lowest speed.
Please refer to the Ping-pong mechanism in the USB device section of the AT91SAM product datasheet.
• HID: For HID device function, only two interrupt endpoints are needed, and since the size is small and speed is low, its endpoints are considered as the lowest priority.
• MSD: For MSD device function, the high speed transaction, two endpoints, bulk transfer, double/triple bank for performance.
• Audio: For Audio device function, the endpoint size should be larger than the audio frame size (here the size is 192 bytes),
more than one endpoint, isochronous transfer and at least double bank.
• CDC: CDC needs three endpoints excluding the default endpoint to work.
Two Bulk endpoints and one Interrupt endpoint. So dual-CDC device will occupy 7 endpoints.
The interrupt endpoints can be assigned to single-buffered endpoints.
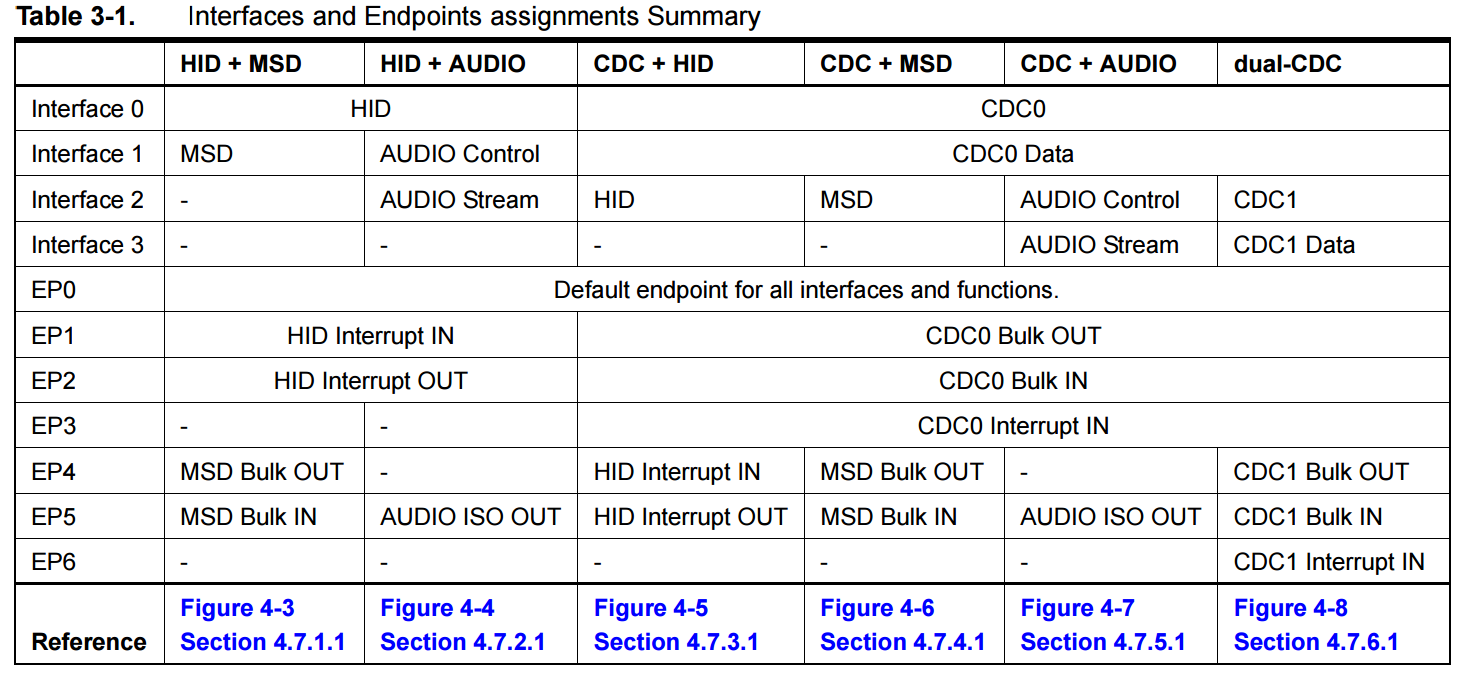
3.2.3.2 Composite Composition Summary
The following is a summary of the interfaces and endpoints assigned.
You can also find reference descriptions and figures in the following sections.
Table 3-1. Interfaces and Endpoints assignments Summary
3.2.4 Specific Descriptors
Since the composite is not for specific class, most of the descriptors for functions are defined in the included class related specifications.
Only one descriptor is necessary to define a multi-interface function:
the Interface Association Descriptor (IAD).
3.2.4.1 Interface Association Descriptor
The Interface Association Descriptor (IAD) is a new standard descriptor defined in USB Engineering Change Notice,
to allow a device to describe which interfaces are associated with the same device function.
This allows the Operation System to bind all of the appropriate interfaces to the same driver instance for the function.
Please see USB ENGINEERING CHANGE NOTICE (Title: Interface Association Descriptors) for detailed information.
The IAD is used to describe that two or more interfaces are associated to the same function.
The ‘association’ includes two or more interfaces and all of their alternative setting interfaces.
A device must use an IAD for each multi-interfaced device function.
An IAD is always returned as part of the configuration information returned by a GetConfigurationDescriptor request.
It must be located before the interface descriptors (including all alternate settings) for the interfaces it associates with.
All of the interface numbers in a particular set of associated interfaces must be contiguous.
Table 3-2 shows the standard interface association descriptor includes function

3.2.5 Specific Requests
No special request is used for a composite device, all requests are defined by the device function that is integrated.
3.3 Host Drivers
Usually the Operating System supports the composite device via two part of drivers - composite driver and the function drivers depending
on the functions that are integrated.
The OS will recognize the USB device as a composite device first then distinguish the included functions and install their driver modules one by one.
Then the functions will appear as normal separated devices for OS to access.
Most OSs now include generic drivers for a wide variety of USB classes.
This makes developing a function device simpler, since the host complexity is now handled by the OS.
Manufacturers can thus concentrate on the device itself, not on developing specific host drivers.
As described before in Section 3.2.4.1 note, the IAD of multi-interface USB devices is a new feature,
there may be issues about how existing USB OS implementations will support devices with IAD.
For Linux®, it is supported now.
For Windows you can refer to Support for USB Interface Association Descriptor in Windows, but patches may needed,
only Windows XP with some hot fix or service pack 3 or later updates fully support this feature now.
Here is a brief list of the various function implementations supported by several OSs
(for CDC maybe additional .inf file is required to install the device but the driver files themselves are from windows source disk):
• Windows (see Windows Supported USB Classes for more)
– MSD: USB Storage disks
– HID: USB Keyboard, Mouse, etc.
– Audio: USB Desktop speaker, recorder.
– CDC: Abstract Control Model, Remote NDIS ...
• Linux (see Linux Device Driver Support for more)
– MSD: USB Storage disks
– HID: USB Keyboard, Mouse, etc.
– CDC: Abstract Control Model
– CDC: Ethernet Model Please refer to the sections about the functions or the class implement application notes for details about the OS compatibility on the device driver.

AT91 USB Composite Driver Implementation的更多相关文章
- USB Compound Device,USB复合设备 ; USB Composite Device,USB组合设备【转】
本文转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/autumn20080101/article/details/52776863 科普下USB复合设备和USB组合设备的区别. 关键字 Commu ...
- usb wifi driver run in ubuntu support 360/xiaodu and with 3.13.0-32-generic
(为了实现usb-wifi用在linux系统上,需求解决方案,过程记录和如何实现) 重点解决3.13.0-32-generic内核编译 mt7601 usb wifi 驱动问题. 1:首先下载MT76 ...
- Security arrangements for extended USB protocol stack of a USB host system
Security arrangements for a universal serial bus (USB) protocol stack of a USB host system are provi ...
- STM32F4 HAL Composite USB Device Example : CDC + MSC
STM32F4 USB Composite CDC + MSC I'm in the process of building a USB composite CDC + MSC device on t ...
- USB组合设备 Interface Association Descriptor (IAD)
Communication Device Class,简称CDCUSB Compound Device,USB复合设备USB Composite Device,USB组合设备 摘要USB复合设备 Co ...
- [置顶] 自娱自乐6之Linux gadget驱动5(自编gadget驱动,包涵与之通讯的主机usb驱动,已调试通过)
这个代码调试,你首先要保证你的udc驱动没用问题,这个有些矛盾,应为我本来要用gadget驱动来调试udc驱动,结果反过来了. 这是在zero基础改的,大概的改动 1. 去掉loop. 2. sink ...
- 设备管理 USB ID
发现个USB ID站点,对于做设备管理识别的小伙伴特别实用 http://www.linux-usb.org/usb.ids 附录: # # List of USB ID's # # Maintain ...
- Linux下usb设备驱动详解
USB驱动分为两块,一块是USB的bus驱动,这个东西,Linux内核已经做好了,我们可以不管,我们只需要了解它的功能.形象的说,USB的bus驱动相当于铺出一条路来,让所有的信息都可以通过这条USB ...
- android的USB MTP && USB CDC/USBnet(ECM, NCM, ACM) && USB gardget
MTP的全称是Media Transfer Protocol(媒体传输协议),它是微软公司提出的一套媒体文件传输协议.早在智能手机普及前,数码相机和MP3播放器等都使用了MTP的前身PTP(Pictu ...
随机推荐
- 原生JS获取元素的位置与尺寸
1.内高度.内宽度: 内边距 + 内容框 element.clientWidth element.clientHeight 2.外高度,外宽度: 边框 + 内边距 + 内容框 element.offs ...
- 数据库优化之mysql【转】
1. 优化流程图 mysql优化(主要增加数据库的select查询,让查询速度更快) 2. 优化mysql的方面 主要从以下四个方面去优化mysql ①存储层:如何选择一个数据库引擎,选择合适的字段列 ...
- 数据库索引和SQL语句使用经验
1.如果检索数据量超过30%的表中记录数,使用索引将没有显著的效率提高 2.在特定情况下,使用索引也许会比全表扫描慢,但这是同一个数量级上的差距:而通常情况下,使用索引比全表扫描要快几倍乃至几千倍! ...
- 基于Apache在本地配置多个虚拟主机站点
简单的说,打开httpd.conf 在最后加入如下内容: <VirtualHost 127.0.0.2:80> DocumentRoot d:/AppServ/www2 Ser ...
- selnium远程机上传图片遇到的坑
一般上传图片方法采取方案如下: input标签的file类型上传图片,使用对象的sendkeys+路径方法 使用js注入,再用使用对象的sendkeys+路径方法 使用autolt生成的exe,打开对 ...
- 使用JS实现俄罗斯方块游戏
简单的JS俄罗斯方块游戏源码 效果图: 代码如下,复制即可使用: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset=&q ...
- Codeforces 219C Color Stripe(思维+字符串)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/219/C 题目大意: 给出一个字符串,只包含k种字符,问最少修改多少个字符(不增长新的种类)能够得到一个新 ...
- Django Celery定时任务和时间设置
1.Celery加入定时任务 Celery除了可以异步执行任务之外,还可以定时执行任务.在实例代码的基础上写个测试方法: #coding:utf- from celery.task.schedules ...
- 20165330《网络对抗技术》Exp0 Kali安装
Kali安装 下载地址 Kali官网 VMware 安装步骤 参考在虚拟机中安装kali linux 安装Kali Linux的镜像和VMware 打开VMware,选择文件-新建虚拟机,出现对话框选 ...
- appium入门级教程(3)—— 安装 Android SDK
前言 搭建Android平台不是必须的,如果你不想使用 Android 模拟器运行测试的话可以跳过,不过,建议安装:原生 Android 好折腾!关键是它自带的一些工具是做 appium 测试必须要用 ...
