委托发展史(Linq操作符)
嗯~这篇就讲讲Linq吧!
之前讲过Lambda最后进化到了令人发指的地步:
Func<string, int> returnLength;
returnLength = text => text.Length; Console.WriteLine(returnLength("Hellow"));
来,把这个lambda表达式拿出来(text => text.Length),好眼熟啊,好像在某个地方用到过。
*LINQ
这个东西直到现在都是我见过的最好的表达式,他虽然不是银弹,但却是你开发"兵器库"中一个非常强大的兵器。
Linq有两种写法,这篇来讲操作符。先说说组成哈。
IEnumerable.linq操作符 (委托,方法,Lambda);
例如:
list<int>.Select(x => x + 1);
Select:循环集合 条件是 集合里的每一个int + 1;
来说说linq是怎么组成的吧。
算了,直接看linq的源代码吧。Select的哈
public static IEnumerable<TResult> Select<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, TResult> selector)
静态方法有this说明是一个扩展方法,this在IEnumerable前,一个IEnumerable<TResult>的扩展方法,参数是一个Func<TSource, TResult>的泛型委托。
由于参数是委托,所以linq的括号里可放入,符合条件的方法,一个类似的委托,或者Lambda表达式。
其中我们最常用的就是Lambda表达式。因为是委托的终极进化,最简便的一个了。
linq有一个延迟加载的特性,最初我以为是委托的原因(因为委托就是只有在执行Invoke的时候才执行),后来去网上查询资料。
发现延迟加载完全拜一个 yield return 所实现的。
来看一看这个诡异的东西吧。。。
public IEnumerable<int> OutValue(List<int> list)
{
foreach (var a in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(a);
yield return a;
}
}
这是一个yield return返回IEnumerable的方法,内容很简单就是输出一下集合里的值,然后yield return了。
然后我调用它的时候奇怪了。
test.OutValue(list);
输出:
嗯~,换一个思路试一下,既然你不输出啥,那我再循环一次看看吧!
var val = OutValue(list);
foreach (var a in val){}
我没有加任何操作,只是单纯的循环了一下。输出结果却是:
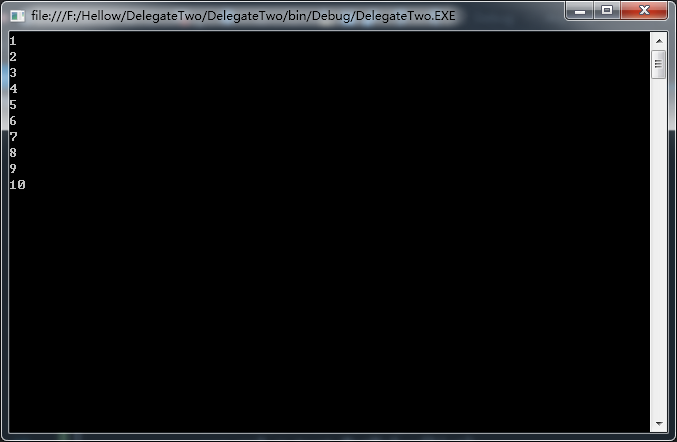
哼哼,显而易见了。延迟加载拜这个yield 所致啊。
如果我们要简单的实现一个Select的话,很简单:
public static IEnumerable<TResult> Select<TSource,TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source,Func<TSource,TResult> selector)
{
foreach (TSource element in source)
yield return selector(element);
}
粗暴明了,当然源代码不是这样的。。。但意思差不多。foreach循环这个集合,yield return 执行这个selector 委托,委托实例是什么?就是你穿的Lambda,方法,委托啦~当然必须是满足条件的。
yield 语句只能出现在 iterator 块中,该块可用作方法、运算符或访问器的体。
当用到Select返回的值时,yield return 会去执行这个Func委托。这就是延迟加载的原理吗?(请各位大佬指正,小弟可能讲的不正确,欢迎指正哈。)
看看别的操作符是怎么实现的
*Max最大值
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public static int Max(this IEnumerable<int> source)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("source");
}
int num = ;
bool flag = false;
foreach (int current in source)
{
if (flag)
{
if (current > num)
{
num = current;
}
}
else
{
num = current;
flag = true;
}
}
if (flag)
{
return num;
}
throw Error.NoElements();
}
Max只支持对int集合的扩展,内部是不是非常简单,就是生命一个int变量存最大值,一个bool类型来判断是否执行了这个foreach循环。
来看看经常用的排序吧!
*Groupby
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public static IEnumerable<IGrouping<TKey, TSource>> GroupBy<TSource, TKey>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, TKey> keySelector)
{
return new GroupedEnumerable<TSource, TKey, TSource>(source, keySelector, IdentityFunction<TSource>.Instance, null);
}
但最后执行的原理在这里。。。
[__DynamicallyInvokable, IteratorStateMachine(typeof(Lookup<, >.<GetEnumerator>d__12))]
public IEnumerator<IGrouping<TKey, TElement>> GetEnumerator()
{
Lookup<TKey, TElement>.Grouping next = this.lastGrouping;
if (next != null)
{
do
{
next = next.next;
yield return next;
}
while (next != this.lastGrouping);
}
yield break;
}
Lookup<Tkey,TValue>是.NET3.5中新增的,它类似与Dictionary<Tkey,TElement>,但把键映射带一个值集上.这个类在程序及System.Core中实现,用System,Linq命名空间定义.
Grouping是最终实现排序的那个程序。取最后一个,判断非空,然后进行do{}while()循环。也是用了yield return延迟加载。
*Where
where里的委托与select是不一样的;
public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, bool> predicate)
Where委托的返回值时bool类型,但扩展方法又要返回IEnumerable<TSource>类型的。
大体上的意思就是这样的:
public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, bool> predicate)
{
foreach (TSource element in source)
{
if (predicate(element))
{
yield return element;
}
}
}
大致上是这样的,我理解的是.当然源代码不是这样的。当委托Func为true时才会yield return。也是有延迟加载的特性的。。。
等等等。。。太多了就不一一列举了。
那么会有人问了,我不想用这个延迟加载怎么办,我就想跟foreach循环一样,我就想立即加载。
肯定是可以的,有要求肯定是会满足的。
很简单,将返回值转换为另外一种类型即可,Linq的查询操作符中包含了转换操作的定义:ToArray(转换为数组)、ToDictionary(转换为字典)、ToList(转换为集合),使用这些转换运算就可以将延迟执行转换为立即执行,也就可以避免延迟执行了。
*总结
就写这么多吧。毕竟我的理解也是有限的,还请各位大佬们指正。
有错误的地方欢迎各位大佬指出来,我会努力进步,努力改正的。
给大家几段比较简单的linq的源码。
SelectMany的源码:将序列的每个元素投影到 IEnumerable(T) 并将结果序列合并为一个序列。
[IteratorStateMachine(typeof(Enumerable.<SelectManyIterator>d__17<, >))]
private static IEnumerable<TResult> SelectManyIterator<TSource, TResult>(IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, IEnumerable<TResult>> selector)
{
foreach (TSource current in source)
{
foreach (TResult current2 in selector(current))
{
yield return current2;
}
IEnumerator<TResult> enumerator2 = null;
}
IEnumerator<TSource> enumerator = null;
yield break;
}
简单的说一下下他的应用吧。看源代码应该能看出它是两个foreach,算了不说了直接上代码。
//班级类
public class Class
{
public List<Student> stuList { get; set; }
}
//学生类
public class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Sex { get; set; }
} static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Class> list = new List<Class>();
//Select
List<List<Student>> result = list.Select(m => m.stuList).ToList();
//SelectMany
List<Student> result = list.SelectMany(m => m.stuList).ToList();
}
Sum的源码:int集合求和
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public static int Sum(this IEnumerable<int> source)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("source");
}
int num = ;
checked
{
foreach (int current in source)
{
num += current;
}
return num;
}
}
All的源码:All表示集合中的所有元素满足表达式条件,即返回true。
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public static bool All<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, bool> predicate)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("source");
}
if (predicate == null)
{
throw Error.ArgumentNull("predicate");
}
foreach (TSource current in source)
{
if (!predicate(current))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
多谢观看!
委托发展史(Linq操作符)的更多相关文章
- linq操作符:分区操作符
Linq中的分区指的是在不重新排列元素的情况下,将输入序列划分为两部分,然后返回其中一个部分的操作. 一.Take操作符 Take(int n)表示将从序列的开头返回数量为n的连续元素,常用于分页.其 ...
- linq操作符:元素操作符
元素操作符仅返回一个元素. 一.Fitst操作符 First操作符将返回序列中的第一个元素.如果序列中不包含任何元素,则First<T>方法将引发异常.来看看First()方法的定义: 从 ...
- linq操作符:聚合操作符
一.Aggregate操作符 Aggregate操作符对集合值执行自定义聚合运算.来看看Aggregate的定义: public static TSource Aggregate<TSource ...
- linq操作符:连接操作符
linq中的连接操作符主要包括Join()和GroupJoin()两个. 一.Join()操作符 Join()操作符非常类似于T-SQL中的inner join,它将两个数据源进行连接,根据两个数据源 ...
- LINQ操作符四:排序操作符
Linq中的排序操作符包括OrderBy.OrderByDescending.ThenBy.ThenByDescending和Reverse,提供了升序或者降序排序. 一.OrderBy操作符 Ord ...
- 普通委托到泛型委托到Linq
private delegate bool delTest(int a); private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { var a ...
- LINQ 操作符
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using System.Linq; namespace LinQ ...
- linq操作符:限定操作符
限定操作符运算返回一个Boolean值,该值指示序列中是否有一些元素满足条件或者是否所有元素都满足条件. 一.All操作符 All方法用来确定是否序列中的所有元素都满足条件.看下面的例子: using ...
- linq操作符:转换操作符
这些转换操作符将集合转换成数组:IEnumerable.IList.IDictionary等.转换操作符是用来实现将输入对象的类型转变为序列的功能.名称以"As"开头的转换方法可更 ...
随机推荐
- Extjs面板和布局初探
面板相当于一张干净的白纸,如果直接在上面添加内容,将很难控制面板中内容的显示位置,面板元素越多就越显得凌乱,所以需要在面板上划分不同的区域,将面板内容展示到希望的位置上.ExtJS通过提供多种布局类来 ...
- [leetcode]314. Binary Tree Vertical Order Traversal二叉树垂直遍历
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from top to bott ...
- jQuery之双下拉框
双下拉框要实现的效果,实际上就是左边下拉选择框里的内容,可以添加到右边,而右边同理.写了个简单的例子,来说明一下. 代码如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ...
- 接触mybatis使用
1.mybatis mybatis是一个自定义sql.存储过程和高级映射的持久层框架,是Apache下的顶级项目. mybatis可以让程序员将主要精力放在sql上,通过mybatis提供的映射方式. ...
- oracle查找特定表的引用
select * from user_source t where upper(t.TEXT) like upper('%table1%') 第二种方法类似于eclipse中的file search ...
- DB2与oracle类型对比
本文摘自http://www.cnblogs.com/cy163/archive/2010/11/17/1880280.html 做过DB2数据库应用迁移的工程师,了解IBM MTK工具在迁移过程中所 ...
- OSGi 系列(二)之 Hello World
OSGi 系列(二)之 Hello World 之前曾介绍过 OSGi 是什么,下面将继续上篇介绍的内容,讲述一个简单的 OSGi Bundle:Hello World 是如何开发的. 在 OSGi ...
- java 事件监听
事件监听实现: 三要素: 1.事件源(数据源,要处理的数据) 2.事件 (承载数据,传递信息并被监听) 3.监听器 (负责对数据的业务处理) --该开发用例采用了Spring的事件监听 1. 定义事 ...
- DB2 like两个表的字段或like一个变量
DB2中的like的使用是有限制的,它后面不能跟一个变量或者是字段,因此,在存储过程或SQL语句中就不能like一个变量或一个字段. 比如有两个表A(a,b,c,d),B(a,b,c,d). 普遍的用 ...
- [转载红鱼儿]delphi 实现微信开发(1)
大体思路: 1.用户向服务号发消息,(这里可以是个菜单项,也可以是一个关键词,如:注册会员.) 2.kbmmw web server收到消息,生成一个图文消息给微信,在图文消息中做好自己的url,在u ...
