BTrace 问题辅助排查工具使用手册
BTrace是调试神器,可以通过自己编写的脚本,获取应用的一切调用信息。而不需要重启应用!
Btrace 项目源码信息(你行你上~)
项目地址:http://github.com/btraceio/btrace
但是应用下载地址是: https://github.com/btraceio/btrace/releases (因为一般你并不想编译这些代码)
小白的打开姿势,操作步骤:
1. 打开 jvisualVm 工具;
2. 加载 BTrace 工具, 先把 插件中心地址更改掉: https://visualvm.github.io/uc/8u131/updates.xml.gz ;
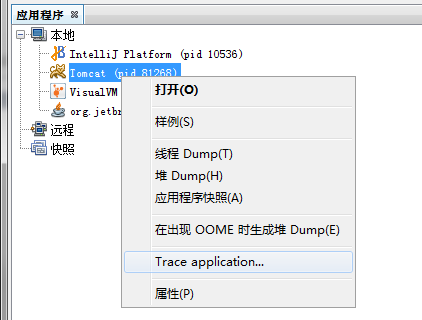
3. 连接到想要 trace 的服务器, 如本地 tomcat;
4. 右击tomcat进程,> Trace application...
5. 写debug程序,样例如下:(在IDE中编写)
6. 直接使用 brace监控: btrace <pid> BtraceScript.java
来个例子:(拦截 spring 的 doService 方法)
/* BTrace Script Template */ import com.sun.btrace.AnyType;
import com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.BTrace;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.Duration;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.Kind;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.Location;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.OnMethod;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.ProbeClassName;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.ProbeMethodName; import static com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils.currentThread;
import static com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils.probeLine;
import static com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils.threadId; @BTrace
public class TracingScript {
/* put your code here */
@OnMethod(
clazz = "/org.springframework.servlet.+/",
method = "/doService.*/",
location = @Location(Kind.RETURN)
)
public static void traceExecute(AnyType[] args, @ProbeClassName String name, @ProbeMethodName String method, @Duration long time) {
long durationTime = time/1000000;
if(durationTime > 0){
String output = name + "." + method + "#" + probeLine() + " cost: " + durationTime + "ms, ThreadId:" + threadId(currentThread());
BTraceUtils.println(output);
// 打印整体参数
BTraceUtils.printArray(args);
// 调用应用的各字段进行反射调用
BTraceUtils.printFields(args[1]);
BTraceUtils.printFields(args[2]);
BTraceUtils.println("over...");
// 结束符
BTraceUtils.println("");
}
}
}
在IDE中编写时,需要导入 pom.xml 如下:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.sun.tools.btrace/btrace-agent -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.tools.btrace</groupId>
<artifactId>btrace-agent</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.sun.tools.btrace/btrace-boot -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.tools.btrace</groupId>
<artifactId>btrace-boot</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.sun.tools.btrace/btrace-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.tools.btrace</groupId>
<artifactId>btrace-client</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
2. 拦截方法定义,也说是 @OnMethod 注解的作用
Btrace使用@OnMethod注解定义需要分析的方法入口,在@OnMethod注解中,需要指定class、method以及location等,class表明需要监控的类,method表明需要监控的方法!
@OnMethod(
clazz = "/org.springframework.servlet.+/",
method = "/doService.*/",
location = @Location(Kind.RETURN)
)
1. 正则表达式定位(全匹配是正则的一种特例)
可以用表达式,批量定义需要监控的类与方法。正则表达式需要写在两个 "/" 中间。
通过在拦截函数的定义里注入@ProbeClassName String probeClass, @ProbeMethodName String probeMethod 参数,告诉脚本实际匹配到的类和方法名。
2. 按接口,父类,Annotation定位
比如我想匹配所有的Filter类,在接口或基类的名称前面,加个+ 就行
@OnMethod(clazz="+com.vip.demo.Filter", method="doFilter")
也可以按类或方法上的annotaiton匹配,也就是注解匹配,前面加上@就行
@OnMethod(clazz="@javax.jws.WebService", method="@javax.jws.WebMethod")
3. 构造方法匹配 <init>
@OnMethod(clazz="java.net.ServerSocket", method="<init>")
4. 静态内部类的写法,在类与内部类之间加上"$"
@OnMethod(clazz="com.vip.MyServer$MyInnerClass", method="hello")
3. 拦截时机, 即@Location注解的作用
// Location 的定义
/**
* This annotation specifies a particular "location" within a
* traced/probed java method for BTrace probe specifications.
*
* @author A. Sundararajan
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Location {
/**
* Kind of the location.
*
* @see Kind
*/
Kind value() default Kind.ENTRY; /**
* Specifies where do want to probe with
* respect to the location of interest.
*
* @see Where
*/
Where where() default Where.BEFORE; /**
* Specifies the fully qualified class name for
* certain kind of probe locations.
*
* <p>
* <h3>Since 1.3.11</h3>
* The specification can contain references to user arguments.
* These references are using Ant style substitution patterns.
* If a reference is not resolvable the whole probe point will be effectively disabled.
* <br>
* <pre>
* {@code @OnMethod(clazz = "MyClass", method = "myMethod", location = @Location(clazz = "${package}.OtherClass"))}
* </pre>
* </p>
*/
String clazz() default ""; /**
* Specifies the method name for
* certain kind of probe locations.
*
* <p>
* <h3>Since 1.3.11</h3>
* The specification can contain references to user arguments.
* These references are using Ant style substitution patterns.
* If a reference is not resolvable the whole probe point will be effectively disabled.
* <br>
* <pre>
* {@code @OnMethod(clazz = "MyClass", method = "myMethod", location = @Location(clazz = "OtherClass", method = "${method}"))}
* </pre>
* </p>
*/
String method() default ""; /**
* Specifies the field name for Kind.FIELD_SET
* and Kind.FIELD_GET probes.
*
* @see Kind#FIELD_GET
* @see Kind#FIELD_SET
*
* <p>
* <h3>Since 1.3.11</h3>
* The specification can contain references to user arguments.
* These references are using Ant style substitution patterns.
* If a reference is not resolvable the whole probe point will be effectively disabled.
* <br>
* <pre>
* {@code @OnMethod(clazz = "MyClass", method = "myMethod", location = @Location(clazz = "OtherClass", field = "${field}"))}
* </pre>
* </p>
*/
String field() default ""; /**
* Specifies field or method type for
* certain kind of probe locations. The type
* is specified like in Java source - except
* the method or field name and parameter names
* are not included.
*
* <p>
* <h3>Since 1.3.11</h3>
* The specification can contain references to user arguments.
* These references are using Ant style substitution patterns.
* If a reference is not resolvable the whole probe point will be effectively disabled.
* <br>
* <pre>
* {@code @OnMethod(clazz = "MyClass", method = "myMethod", location = @Location(clazz = "OtherClass", type = "${ret} ()"))}
* </pre>
* </p>
*/
String type() default ""; /**
* Specifies the line number for Kind.LINE probes.
*
* @see Kind#LINE
*/
int line() default 0;
} // Kind 的定义
public enum Kind {
/**
* <h2>Array element load</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@code type[]} - the array instance</li>
* <li>{@link int int} - array index</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Return} - the return value of the method call (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER})</li>
* </ul>
*/
ARRAY_GET, /**
* <h2>Array element store</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@code type[]} - the array instance</li>
* <li>{@link int int} - array index</li>
* <li>{@link java.lang.Object Object} - new value</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* </ul>
*/
ARRAY_SET, /**
* <h2>Method call</h2>
* <p>
* The order and number of unannotated parameters (if provided) must
* fully match the called method signature. Instead of specific parameter
* types one can use {@linkplain AnyType} to match any type.
* <p>
* If the only unannotated parameter is of type {@link AnyType AnyType[]}
* it will contain the called method parameters in the order defined by
* its signature.
*
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the target instance of the method call
* or null if the method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetMethodOrField} - the name of the method which is called</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Return} - the return value of the method call (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER})</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Duration} - the method call duration in nanoseconds (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER}</li>
* </ul>
*/
CALL, /**
* <h2>Exception catch</h2>
*
* <p>
* The order and number of unannotated parameters (if provided) must
* fully match the probed method signature. Instead of specific parameter
* types one can use {@linkplain AnyType} to match any type.
* <p>
* If the only unannotated parameter is of type {@link AnyType AnyType[]}
* it will contain the probed method parameters in the order defined by
* its signature.
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the caught {@linkplain Throwable} (@since 1.3.11)</li>
* </ul>
*/
CATCH, /**
* <h2>Checkcast</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.String String} - type to cast to</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the casted instance ({@linkplain AnyType})</li>
* </ul>
*/
CHECKCAST, /**
* <h2>Method entry</h2>
* <p>
* The order and number of unannotated parameters (if provided) must
* fully match the probed method signature. Instead of specific parameter
* types one can use {@linkplain AnyType} to match any type.
* <p>
* If the only unannotated parameter is of type {@link AnyType AnyType[]}
* it will contain the probed method parameters in the order defined by
* its signature.
*
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* </ul>
*/
ENTRY, /**
* <h2>"return" because of no-catch</h2>
*
* <p>
* The order and number of unannotated parameters (if provided) must
* fully match the probed method signature. Instead of specific parameter
* types one can use {@linkplain AnyType} to match any type.
* <p>
* If the only unannotated parameter is of type {@link AnyType AnyType[]}
* it will contain the probed method parameters in the order defined by
* its signature.
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Duration} - the method call duration in nanoseconds (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER}</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the {@linkplain Throwable} instance (@since 1.3.11)</li>
* </ul>
*/
ERROR, /**
* <h2>Getting a field value</h2>
*
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the field owner instance or null
* if the field is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetMethodOrField} - the name of the method which is called</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Return} - the return value of the method call (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER})</li>
* </ul>
*/
FIELD_GET, /**
* <h2>Setting a field value</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.Object Object} - new field value</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that field is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the field owner instance or null
* if the field is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetMethodOrField} - the name of the method which is called</li>
* </ul>
*/
FIELD_SET, /**
* <h2>instanceof check</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.String String} - type to check against</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the checked instance ({@linkplain AnyType})</li>
* </ul>
*/
INSTANCEOF, /**
* <h2>Source line number</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link int int} - line number</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* </ul>
*/
LINE, /**
* <h2>New object created</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.String String} - object type name</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Return} - the return value of the method call (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER})</li>
* </ul>
*/
NEW, /**
* <h2>New array created</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.String String} - array type name</li>
* <li>{@link int int} - number of dimensions</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Return} - the return value of the method call (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER})</li>
* </ul>
*/
NEWARRAY, /**
* <h2>Return from method</h2>
* <p>
* The order and number of unannotated probe handler parameters (if provided)
* must fully match the probed method signature. Instead of specific parameter
* types one can use {@linkplain AnyType} to match any type.
* <p>
* If the only unannotated parameter is of type {@link AnyType AnyType[]}
* it will contain the probed method parameters in the order defined by
* its signature.
*
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Return} - the return value of the method call (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER})</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Duration} - the method call duration in nanoseconds (only for {@linkplain Where#AFTER}</li>
* </ul>
*/
RETURN, /**
* <h2>Entry into a synchronized block</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.Object Object} - lock object</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* </ul>
*/
SYNC_ENTRY, /**
* <h2>Exit from a synchronized block</h2>
*
* <h3>Unannotated probe handler parameters:</h3>
* <ol>
* <li>{@link java.lang.Object Object} - lock object</li>
* </ol>
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* </ul>
*/
SYNC_EXIT, /**
* <h2>Throwing an exception</h2>
*
* <p>
* The order and number of unannotated parameters (if provided) must
* fully match the probed method signature. Instead of specific parameter
* types one can use {@linkplain AnyType} to match any type.
* <p>
* If the only unannotated parameter is of type {@link AnyType AnyType[]}
* it will contain the probed method parameters in the order defined by
* its signature.
* <h3>Allowed probe handler parameter annotations:</h3>
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeClassName} - the name of the enclosing class</li>
* <li>{@linkplain ProbeMethodName} - the name of the enclosing method</li>
* <li>{@linkplain Self} - the instance enclosing the declaring method or null
* if that method is static</li>
* <li>{@linkplain TargetInstance} - the thrown exception (@since 1.3.11)</li>
* </ul>
*/
THROW
};
Location 主要属性有 value 和 where, 而 value 则是几个常用的定义点!
定义Btrace对方法的拦截位置,通过@Location注解指定,默认为Kind.ENTRY。可以为同一个函数的不同的Location,分别定义多个拦截函数。
1. Kind.Entry与Kind.Return
Kind.ENTRY:在进入方法时,调用Btrace脚本
Kind.RETURN:方法执行完时,调用Btrace脚本,只有把拦截位置定义为Kind.RETURN,才能获取方法的返回结果@Return和执行时间@Duration
duration的单位是纳秒,要除以 1,000,000 才是毫秒。
2. Kind.Error, Kind.Throw和 Kind.Catch
异常抛出(Throw),异常被捕获(Catch),异常没被捕获被抛出函数之外(Error),主要用于对某些异常情况的跟踪。
在拦截函数的参数定义里注入一个Throwable的参数,代表异常。
3. Kind.Call与Kind.Line
Kind.CALL:分析方法中调用其它方法的执行情况,比如在execute方法中,想获取add方法的执行耗时,必须把where设置成Where.AFTER.
Kind.LINE:通过设置line,可以监控代码是否执行到指定的位置.
下例定义监控bind()函数里调用的所有其他函数:
@OnMethod(clazz = "java.net.ServerSocket", method = "bind", location = @Location(value = Kind.CALL, clazz = "/.*/", method = "/.*/", where = Where.AFTER))
public static void onBind(@Self Object self, @TargetInstance Object instance, @TargetMethodOrField String method, @Duration long duration)
所调用的类及方法名所注入到@TargetInstance与 @TargetMethodOrField中。
下例监控代码是否到达了Socket类的第363行。
@OnMethod(clazz = "java.net.ServerSocket", location = @Location(value = Kind.LINE, line = 363))
4. 如何使用Btrace定位问题
1. 打印this,参数 与 返回值
@OnMethod(clazz = "java.io.File", method = "createTempFile", location = @Location(value = Kind.RETURN))
public static void o(@Self Object self, String prefix, String suffix, @Return AnyType result)
如果想打印它们,首先按顺序定义用@Self 注释的this, 完整的参数列表,以及用@Return 注释的返回值。
需要打印哪个就定义哪个,不需要的就不要定义。但定义一定要按顺序,比如参数列表不能跑到返回值的后面。
Self:
如果是静态函数, self为空。
前面提到,如果上述使用了非JDK的类,命令行里要指定classpath。不过,如前所述,因为BTrace里不允许调用类的方法,所以定义具体类很多时候也没意 思,所以self定义为Object就够了。
参数数列表要么不要定义,要定义就要定义完整,否则BTrace无法处理不同参数的同名函数。
用AnyType来定义任意类型的参数,类似于 Object 。
2. 方法执行时,查看对象的实例属性值
再次强调,为了保证性能不受影响,Btrace不允许调用任何实例方法。
比如不能调用getter方法(怕在getter里有复杂的计算),只会通过直接反射来读取属性名。
又比如,除了JDK类,其他类toString时只会打印其类名+System.IdentityHashCode。
println, printArray,都按上面的规律进行,所以只能打打基本类型。
如果想打印一个Object的属性,用printFields()来反射。
如果只想反射某个属性,参照下面打印Port属性的写法。从性能考虑,应把field用静态变量缓存起来。
注意JDK类与非JDK类的区别:
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
//JDK的类这样写就行
private static Field fdFiled = field("java.io,FileInputStream", "fd");
//非JDK的类,要给出ClassLoader,否则ClassNotFound
private static Field portField = field(classForName("com.vip.demo.MyObject", contextClassLoader()), "port");
public static void onChannelRead(@Self Object self) {
println("port:" + getInt(portField, self));
}
3.TLS,拦截函数间的通信机制
如果要多个拦截函数之间要通信,可以使用@TLS定义 ThreadLocal的变量来共享
@TLS
private static int port = -1;
@OnMethod(clazz = "java.net.ServerSocket", method = "<init>")
public static void onServerSocket(int p){
port = p;
}
@OnMethod(clazz = "java.net.ServerSocket", method = "bind")
public static void onBind(){
println("server socket at " + port);
}
4. 谁调用了这个函数(原理:拦截到方法后,把堆栈打出来)
@OnMethod(clazz = "java.lang.System", method = "gc")
public static void onSystemGC() {
println("entered System.gc()");
jstack();
}
5. 统计方法的调用次数,且每隔1分钟打印调用次数
@Export static AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong();
@OnMethod(class="com.**.MyObject",method="add")
public static void run(){
counter.getAndIncrement();
}
@OnTimer(1000*60)
public static void run(){
BTraceUtils.println("count: " + connter.get());
counter.set(0);
}
5. linux 上使用 btrace!
1. 下载压btrace缩包: wget https://github.com/btraceio/btrace/releases/download/v1.3.11.3/btrace-bin-1.3.11.3.zip ;
2. 解压: unzip btrace-bin-1.3.11.3.zip -d btrace-bin-1.3.11.3;
3. cd btrace-bin-1.3.11.3, ./btrace <pid> TracingScript.java, 就可以看效果了;
4. 修改脚本以解决问题;
5. 通过反射机制,可以很方法的得到当前实例的属性值;
//print one field
Field oneFiled = BTraceUtils.field("com.xx.test", "name");
BTraceUtils.println("print one field: " + BTraceUtils.get(oneFiled, args[0]));
6. BTraceUtils.printFields(args[1]); 调用封装好的打印复杂对象;
// 调用应用的各字段进行反射调用
BTraceUtils.printFields(args[1]);


注意: btrace 是字节码注入,是可能导致jvm退出的,所以,应尽量先在测试环境验证ok后,再到线上调用,或者把注入的类范围尽量的缩小,而非大的正则匹配如: clazz="/com.xxx.*/", method="/.*/",就会导致大量的变更,影响性能也提高了运行风险!
快速定位你的线上问题!
最后,附上几个调试过程的几个经验之坑:
1. BTRACE_HOME 的设置,在 /etc/profile.d/btraceenv.sh 中设置即可; 如果不想设置BTRACE_HOME, 可以直接切换到btrace的bin目录操作即可;
2. 使用 JVisualVm 可以运行的trace代码,不代表使用命令行也运行,最好都使用命令行验证下脚本;
3. JVisualVm 及一些jdk环境,支持 unsafe=true, 而在其他环境则不一定允许; JVisualVm 中如果去除 unsafe=true, 则有些函数会受限制;
4. btrace 脚本如果正常情况无法运行如: btrace 7311 TracingScriptTemplate.java, 则可以切换到debug模式查看: btrace -v 7311 TracingScriptTemplate.java,这里面会出现很多btrace的调试日志,如果不想看这些日志,可以直接过滤掉: btrace -v 7311 TracingScriptTemplate.java | grep -v "DEBUG: ";
5. 借助IDE编写的Trace脚本,可以直接运行,即 trace 脚本可包含package包名,也可以没有包名;但文件必须要以.java结尾(没有试过其他小语种),否则编译时会报错;
6. 代码中如果本身就使用了一些开发脚本,如springboot的开发组件 spring-boot-devtools , 则可能导致 btrace 脚本无法注入, 最好先去掉这些组件再上线;
最后,再附一个完整的链路监控的 script 供参考:
/* BTrace Script Template */ import com.sun.btrace.AnyType;
import com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils;
import com.sun.btrace.annotations.*; import static com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils.currentThread;
import static com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils.probeLine;
import static com.sun.btrace.BTraceUtils.threadId; @BTrace
public class TracingScript { private static final String clazzForTracePattern = "/com.alipay.common.event.tbnotify.adapter.+/";
private static final String methodForTracePattern = "/.*/"; @OnMethod(
clazz = clazzForTracePattern,
method = methodForTracePattern,
location = @Location(Kind.ENTRY)
)
public static void traceExecuteEnter(AnyType[] args, @ProbeClassName String name, @ProbeMethodName String method) {
String output = "enter in: " + name + "." + method + "#" + probeLine() + ", ThreadId:" + threadId(currentThread());
BTraceUtils.println(output);
// 打印整体参数
BTraceUtils.printArray(args);
// 调用应用的各字段进行反射调用
printPerFields(args);
BTraceUtils.println("enter over...");
// 结束符
BTraceUtils.println("");
} @OnMethod(
clazz = clazzForTracePattern,
method = methodForTracePattern,
location = @Location(Kind.RETURN)
)
public static void traceExecuteReturn(AnyType[] args, @ProbeClassName String name, @ProbeMethodName String method, @Return AnyType result, @Duration long time) {
long durationTime = time/1000000;
if(durationTime > 0){
String output = "return from: " + name + "." + method + "#" + probeLine() + " cost: " + durationTime + "ms, ThreadId:" + threadId(currentThread());
BTraceUtils.println(output);
// 打印整体参数
BTraceUtils.printArray(args);
printPerFields(args);
BTraceUtils.printFields(result);
BTraceUtils.println("return over...");
// 结束符
BTraceUtils.println("");
}
} // -----------------------------------------------------
// ================= 以下为捕获异常代码 ================
// -----------------------------------------------------
@TLS
private static Throwable currentException; @OnMethod(
clazz = "java.lang.Throwable",
method = "<init>"
)
public static void onthrow(@Self Throwable self) {
currentException = self;
} @OnMethod(
clazz = "java.lang.Throwable",
method = "<init>"
)
public static void onthrow1(@Self Throwable self, String s) {
currentException = self;
} @OnMethod(
clazz = "java.lang.Throwable",
method = "<init>"
)
public static void onthrow1(@Self Throwable self, String s, Throwable cause) {
currentException = self;
} @OnMethod(
clazz = "java.lang.Throwable",
method = "<init>"
)
public static void onthrow2(@Self Throwable self, Throwable cause) {
currentException = self;
} @OnMethod(
clazz = "java.lang.Throwable",
method = "<init>",
location = @Location(Kind.RETURN)
)
public static void onThrownReturn() {
if (currentException != null) {
BTraceUtils.jstack(currentException);
BTraceUtils.print("<--------------->");
currentException = null;
}
} private static void printPerFields(AnyType[] args) {
// 调用应用的各字段进行反射调用
if(args.length > 0) {
BTraceUtils.printFields(args[0]);
}
if(args.length >= 2) {
BTraceUtils.printFields(args[1]);
}
if(args.length >= 3) {
BTraceUtils.printFields(args[2]);
}
} }
BTrace 问题辅助排查工具使用手册的更多相关文章
- BTrace:线上问题排查工具
BTrace简介 GitHub地址:BTrace 下载地址:v1.3.11.3 官方使用教程:Btrace使用教程 使用场景 BTrace 是一个事后工具,所谓事后工具就是在服务已经上线了,但是发现存 ...
- erlang 故障排查工具
系统级别perf top, dstat -tam, vtune 都能很好分析beam 瓶颈,本文主要erlang 级别排查: 1. 反编译 确认线上运行代码是否正确,reltools没掌握好,升级偶尔 ...
- 各种工具使用手册:http://www.itshouce.com.cn/linux/linux-tcpdump.html 关于tcpdump!!!!
各种工具使用手册:http://www.itshouce.com.cn/linux/linux-tcpdump.html 关于tcpdump!!!! 实用tcpdump命令 //查看本机与mysql的 ...
- Html - 仿Ios assistiveTouch 悬浮辅助球工具
仿Ios assistiveTouch 悬浮辅助球工具 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="u ...
- WPF 辅助开发工具
原文:WPF 辅助开发工具 以下介绍的工具均为免费版,有些是源代码开放,希望对大家有用. Kaxaml 轻量级XAML 编辑器,可以同时进行图像和XAML 代码的编辑.最终生成开发人员想要的XAML ...
- Android辅助开发工具合集
https://github.com/389273716/android-skill-summary/blob/master/开发工具使用指南/辅助开发工具.md
- SQuirrel-GUI工具安装手册-基于phoenix驱动
背景描述: SQuirrel sql client 官方地址:http://www.squirrelsql.org/index.php?page=screenshots 一个图形界面的管理工具 安装手 ...
- arcconf工具操作手册V1.0
arcconf工具操作手册 1.1.1 arcconf工具初始化和去初始化硬盘 [命令功能] PMC阵列卡系统下初始化硬盘,可以将raw盘状态变成ready状态,以便进一步组建raid和设置热备盘: ...
- 系统重装 Windows_VHD_辅助处理工具说明文档1
菜鸟也玩 VHD Windows VHD 辅助处理工具是一个用于创建.安装.维护 VHD 的辅助工具,把一个比较复杂的操作过程傻瓜化,使您轻松体验 VHD 的强大功能.您需要预备的就是一个准备装入 V ...
随机推荐
- Android 打造编译时注解解析框架 这只是一个开始
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/43452969 ,本文出自:[张鸿洋的博客] 1.概述 记得很久以前,写过几篇博客 ...
- Python软件目录结构规范
设计项目目录结构和'代码编码风格'一样, 是为了达到以下两点: 可读性高 可维护性高 目录组织方式 Stackoverflow上有一些比较好的范式.
- 【小白学C#】浅谈.NET中的IL代码
一.前言 前几天群里有位水友提问:”C#中,当一个方法所传入的参数是一个静态字段的时候,程序是直接到静态字段拿数据还是从复制的函数栈中拿数据“.其实很明显,这和方法参数的传递方式有关,如果是引用传递的 ...
- js默认参数实现方法
function simue (){ var a = arguments[0] ? arguments[0] : 1; var b = arguments[1] ? arguments[1] : 2; ...
- MYSQL———正则表达式查询!
在使用select查询的过程中,有时会用到正则表达式对结果进行查询,将学习到的内容进行总结! 一 语法结构如下: 二 常用匹配方式进行示例说明 首先创建表student,表的结构如下: 1·^:查询s ...
- Docker 堆栈
1. Stack stack(译:堆叠,堆栈)是一组相互关联的服务,它们共享依赖关系,并且可以一起编排和伸缩. 在上一篇<Docker 服务>中我们知道可以通过创建一个docker-co ...
- Solr 17 - Solr的时间为什么比本地少8小时 (附修改方法)
目录 1 为什么少8小时 2 如何查看Solr的时区 3 修改Solr的时区 3.1 Solr从数据库中同步数据的原理 3.2 为什么要修改时区 3.3 如何修改时区 1 为什么少8小时 (1) 原因 ...
- Group Convolution分组卷积,以及Depthwise Convolution和Global Depthwise Convolution
目录 写在前面 Convolution VS Group Convolution Group Convolution的用途 参考 博客:blog.shinelee.me | 博客园 | CSDN 写在 ...
- Asp.NetCore轻松学-使用Supervisor进行托管部署
前言 上一篇文章 Asp.NetCore轻松学-部署到 Linux 进行托管 介绍了如何在 Centos 上部署自托管的 .NET Core 应用程序,接下来的内容就是介绍如何使用第三方任务管理程序来 ...
- 联发科MT8788基带处理器介绍
MT8788设备具有集成的蓝牙.fm.wlan和gps模块,是一个高度集成的基带平台,包括调制解调器和应用处理子系统,启用LTE/LTE-A和C2K智能设备应用程序.该芯片集成了工作在2.0GHz的A ...
