Pandas 时间序列处理
Pandas 时间序列处理
1 Python 的日期和时间处理
1.1 常用模块
datetime time calendar
- datetime,以毫秒形式存储日期和时间
- datime.timedelta,表示两个 datetime 对象的时间差
- datetime 模块中包含的数据类型
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| date | 以公历形式存储日历日期(年、月、日) |
| time | 将时间存储为时、分、秒、毫秒 |
| datetime | 存储日期和时间 |
| timedelta | 表示两个 datetime 值之间的差(日、秒、毫秒) |
1.2 字符串和 datetime 转换
datetime -> str
- str(datetime_obj)
dt_obj = datetime(2019, 8, 8)
str_obj = str(dt_obj)
print(type(str_obj))
print(str_obj)
<class 'str'>
2019-08-08 00:00:00
- datetime.strftime()
str_obj2 = dt_obj.strftime('%d/%m/%Y')
print(str_obj2)
08/08/2019
str -> datetime
- datetime.strptime()
需要指定时间表示的形式
dt_str = '2019-08-8'
dt_obj2 = datetime.strptime(dt_str, '%Y-%m-%d')
print(type(dt_obj2))
print(dt_obj2)
<class 'datetime.datetime'>
2019-08-08 00:00:00
- dateutil.parser.parse()
可以解析大部分时间表示形式
from dateutil.parser import parse
dt_str2 = '8-08-2019'
dt_obj3 = parse(dt_str2)
print(type(dt_obj3))
print(dt_obj3)
<class 'datetime.datetime'>
2019-08-08 00:00:00
pd.to_datetime()
可以处理缺失值和空字符串
2 Pandas 的时间处理及操作
2.1 创建与基础操作
基本类型,以时间戳为索引的 Series->Datetimelndex
指定 index 为 datetime 的 list
from datetime import datetime
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# 指定index为datetime的list
date_list = [datetime(2017, 2, 18), datetime(2017, 2, 19),
datetime(2017, 2, 25), datetime(2017, 2, 26),
datetime(2017, 3, 4), datetime(2017, 3, 5)]
time_s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(6), index=date_list)
print(time_s)
print(type(time_s.index))
2017-02-18 -0.230989
2017-02-19 -0.398082
2017-02-25 -0.309926
2017-02-26 -0.179672
2017-03-04 0.942698
2017-03-05 1.053092
dtype: float64
<class 'pandas.core.indexes.datetimes.DatetimeIndex'>
索引
- 索引位置
print(time_s[0])
-0.230988627576
- 索引值
print(time_s[datetime(2017, 2, 18)])
-0.230988627576
- 可以被解析的日期字符串
print(time_s['20170218'])
-0.230988627576
- 按“年份”、“月份”索引
print(time_s['2017-2'])
2017-02-18 -0.230989
2017-02-19 -0.398082
2017-02-25 -0.309926
2017-02-26 -0.179672
dtype: float64
- 切片操作
print(time_s['2017-2-26':])
2017-02-26 -0.179672
2017-03-04 0.942698
2017-03-05 1.053092
dtype: float64
过滤
- 过滤掉日期之前的
time_s.truncate(before='2017-2-25')
2017-02-25 -0.309926
2017-02-26 -0.179672
2017-03-04 0.942698
2017-03-05 1.053092
dtype: float64
- 过滤掉日期之后的
time_s.truncate(after='2017-2-25')
2017-02-18 -0.230989
2017-02-19 -0.398082
2017-02-25 -0.309926
dtype: float64
pd.date_range()
功能:生成日期范围
dates = pd.date_range('2017-02-18', # 起始日期
periods=5, # 周期
freq='W-SAT') # 频率
print(dates)
print(pd.Series(np.random.randn(5), index=dates))
DatetimeIndex(['2017-02-18', '2017-02-25', '2017-03-04', '2017-03-11',
'2017-03-18'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='W-SAT')
2017-02-18 -1.680280
2017-02-25 0.908664
2017-03-04 0.145318
2017-03-11 -2.940363
2017-03-18 0.152681
Freq: W-SAT, dtype: float64
- 传入开始、结束日期,默认生成的该时间段的时间点是按天计算的
date_index = pd.date_range('2017/02/18', '2017/03/18') - 只传入开始或结束日期,还需要传入时间段
print(pd.date_range(start='2017/02/18', periods=10, freq='4D'))
print(pd.date_range(end='2017/03/18', periods=10)) - 规范化时间戳
print(pd.date_range(start='2017/02/18 12:13:14', periods=10))
print(pd.date_range(start='2017/02/18 12:13:14', periods=10, normalize=True))
DatetimeIndex(['2017-02-18 12:13:14', '2017-02-19 12:13:14',
'2017-02-20 12:13:14', '2017-02-21 12:13:14',
'2017-02-22 12:13:14', '2017-02-23 12:13:14',
'2017-02-24 12:13:14', '2017-02-25 12:13:14',
'2017-02-26 12:13:14', '2017-02-27 12:13:14'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
DatetimeIndex(['2017-02-18', '2017-02-19', '2017-02-20', '2017-02-21',
'2017-02-22', '2017-02-23', '2017-02-24', '2017-02-25',
'2017-02-26', '2017-02-27'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
频率与偏移量
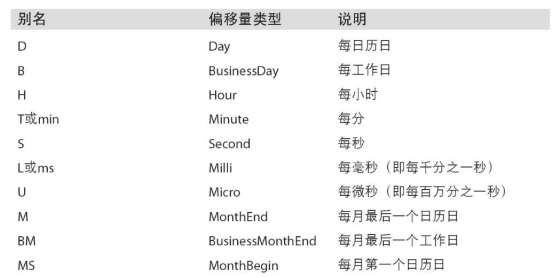
- 频率 Freq,由基础频率的倍数组成,基础频率包括:
1.BM:business end of month,每个月最后一个工作日
2.D:天,M:月等
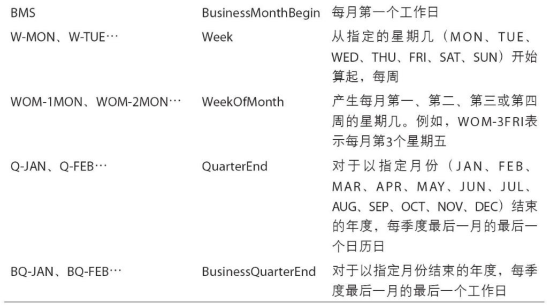
- 偏移量,每个基础频率对应一个偏移量
1.偏移量通过加法连接
sum_offset = pd.tseries.offsets.Week(2) + pd.tseries.offsets.Hour(12)
print(sum_offset)
print(pd.date_range('2017/02/18', '2017/03/18', freq=sum_offset))
14 days 12:00:00
DatetimeIndex(['2017-02-18 00:00:00', '2017-03-04 12:00:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='348H')
移动数据
沿时间轴将数据前移或后移,保持索引不变
ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5), index=pd.date_range('20170218', periods=5, freq='W-SAT'))
print(ts)
2017-02-18 -0.208622
2017-02-25 0.616093
2017-03-04 -0.424725
2017-03-11 -0.361475
2017-03-18 0.761274
Freq: W-SAT, dtype: float64
向后移动一位:print(ts.shift(1))
2017-02-18 NaN
2017-02-25 -0.208622
2017-03-04 0.616093
2017-03-11 -0.424725
2017-03-18 -0.361475
Freq: W-SAT, dtype: float64
pd.to_datetime()
import pandas as pd
s_obj = pd.Series(['2017/02/18', '2017/02/19', '2017-02-25', '2017-02-26'], name='course_time')
s_obj2 = pd.to_datetime(s_obj)
print(s_obj2)
0 2017-02-18
1 2017-02-19
2 2017-02-25
3 2017-02-26
Name: course_time, dtype: datetime64[ns]
# 处理缺失值
s_obj3 = pd.Series(['2017/02/18', '2017/02/19', '2017-02-25', '2017-02-26'] + [None],
name='course_time')
print(s_obj3)
0 2017/02/18
1 2017/02/19
2 2017-02-25
3 2017-02-26
4 None
Name: course_time, dtype: object
时间周期计算
- Period 类,通过字符串或整数及基础频率构造
- Period 对象可进行数学运算,但要保证具有相同的基础频率
- period_range,创建指定规则的时间周期范围,生成 Periodlndex 索引,可用于创建 Series 或 DataFrame
- 时间周期的频率转换,asfreq
- 如:年度周期->月度周期
- 按季度计算时间周期频率
2.2 时间数据重采样
重采样(resampling)
- 将时间序列从一个频率转换到另一个频率的过程,需要
聚合 - 高频率->低频率,downsampling,相反为 upsampling
- pandas 中的 resample 方法实现重采样
- 产生 Resampler 对象
- reample(freq).sum0,resampe(freq).mean).…
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
date_rng = pd.date_range('20170101', periods=100, freq='D')
ser_obj = pd.Series(range(len(date_rng)), index=date_rng)
# 统计每个月的数据总和
resample_month_sum = ser_obj.resample('M').sum()
# 统计每个月的数据平均
resample_month_mean = ser_obj.resample('M').mean()
print('按月求和:', resample_month_sum)
print('按月求均值:', resample_month_mean)
按月求和: 2017-01-31 465
2017-02-28 1246
2017-03-31 2294
2017-04-30 945
Freq: M, dtype: int32
按月求均值: 2017-01-31 15.0
2017-02-28 44.5
2017-03-31 74.0
2017-04-30 94.5
Freq: M, dtype: float64
降采样(downsampling)
- 将数据聚合到规整的低频率
- OHLC重采样,open,high,low,close
# 将数据聚合到5天的频率
five_day_sum_sample = ser_obj.resample('5D').sum()
five_day_mean_sample = ser_obj.resample('5D').mean()
five_day_ohlc_sample = ser_obj.resample('5D').ohlc()
- 使用 groupby 降采样
使用函数对其进行分组操作
ser_obj.groupby(lambda x: x.month).sum()
ser_obj.groupby(lambda x: x.weekday).sum()
升采样(upsampling)
- 将数据从低频转到高频,需要
插值,否则为 NaN (直接重采样会产生空值) - 常用的插值方法
- ffill(limit),空值取前面的值填充,limit 为填充个数
df.resample('D').ffill(2) - bfill(limit),空值取后面的值填充
df.resample('D').bfill() - fillna(fill')或 fllna(‘bfill)
df.resample('D').fillna('ffill') - interpolate,根据插值算法补全数据
线性算法:df.resample('D').interpolate('linear')
具体可以参考:pandas.core.resample.Resampler.interpolate
2.3 滑动窗口
- 在时间窗口上计算各种统计函数
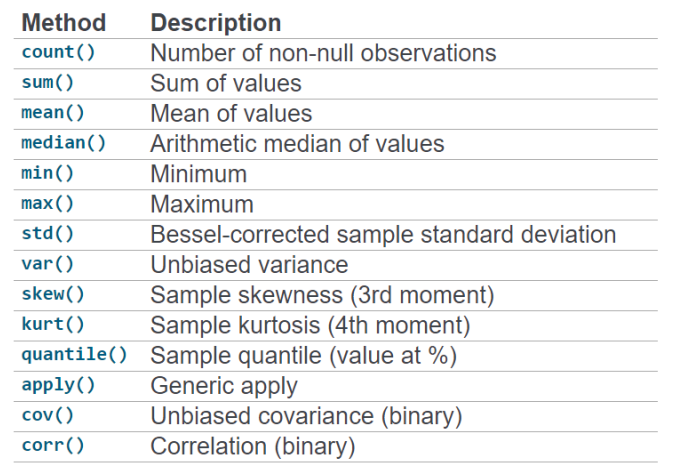
- 窗口函数(window functions)
- 滚动统计(rolling)
obj.rolling().func
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
ser_obj = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000),
index=pd.date_range('20170101', periods=1000))
ser_obj = ser_obj.cumsum()
r_obj = ser_obj.rolling(window=5)
print(r_obj)
Rolling [window=5,center=False,axis=0]
- window
窗口大小 - center
窗口是否居中统计
设置居中:
# 画图查看
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
ser_obj.plot(style='r--')
ser_obj.rolling(window=10, center=True).mean().plot(style='b')
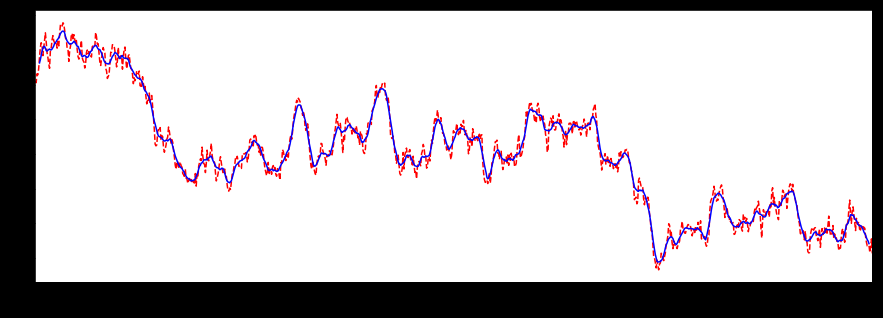
不设置居中:
ser_obj.rolling(window=10, center=False).mean().plot(style='b')

Pandas 时间序列处理的更多相关文章
- Pandas时间序列
Pandas时间序列 pandas 提供了一组标准的时间序列处理工具和数据算法 数据类型及操作 Python 标准库的 datetime datetime 模块中的 datetime. time. c ...
- Python Pandas 时间序列双轴折线图
时间序列pv-gmv双轴折线图 import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt n = 12 date_s ...
- pandas时间序列滑窗
时间序列数据统计-滑动窗口 窗口函数 import pandas as pd import numpy as np ser_obj = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000), ...
- Pandas 时间序列
# 导入相关库 import numpy as np import pandas as pd 在做金融领域方面的分析时,经常会对时间进行一系列的处理.Pandas 内部自带了很多关于时间序列相关的工具 ...
- Pandas时间序列和分组聚合
#时间序列import pandas as pd import numpy as np # 生成一段时间范围 ''' 该函数主要用于生成一个固定频率的时间索引,在调用构造方法时,必须指定start.e ...
- pandas时间序列常用操作
目录 一.时间序列是什么 二.时间序列的选取 三.时间序列的生成 四.时间序列的偏移量 五.时间前移或后移 五.时区处理 六.时期及算术运算 七.频率转换 一.时间序列是什么 时间序列在多个时间点观察 ...
- pandas时间序列学习笔记
目录 创建一个时间序列 pd.date_range() info() asfred() shifted(),滞后函数 diff()求差分 加减乘除 DataFrame.reindex() 通过data ...
- Python——Pandas 时间序列数据处理
介绍 Pandas 是非常著名的开源数据处理库,我们可以通过它完成对数据集进行快速读取.转换.过滤.分析等一系列操作.同样,Pandas 已经被证明为是非常强大的用于处理时间序列数据的工具.本节将介绍 ...
- pandas 时间序列resample
resample与groupby的区别:resample:在给定的时间单位内重取样groupby:对给定的数据条目进行统计 函数原型:DataFrame.resample(rule, how=None ...
随机推荐
- 【leetcode】698. Partition to K Equal Sum Subsets
题目如下: 解题思路:本题是[leetcode]473. Matchsticks to Square的姊妹篇,唯一的区别是[leetcode]473. Matchsticks to Square指定了 ...
- codevs 1026 逃跑的拉尔夫 x
1026 逃跑的拉尔夫 时间限制: 1 s 空间限制: 128000 KB 题目等级 : 黄金 Gold 题目描述 Description 年轻的拉尔夫开玩笑地从一个小镇上偷走了一辆车,但他 ...
- 洛谷P1982 小朋友的数字——题解
题目传送 简单地说,这题就是让我们求前i个数的最大子串和和最值. 对于最大子串和,我们可以设一个变量qian,表示以当前元素结尾的最大子串的子串和.若搜索完第i-1个小朋友,现在看到第i个小朋友时,若 ...
- js基础补漏
1.for...in 和 for...of有何区别 for ... in循环由于历史遗留问题,它遍历的实际上是对象的属性名称.一个Array数组实际上也是一个对象,它的每个元素的索引被视为一个属性. ...
- 在 iTerm2 终端使用 command + ;会弹出最近使用的命令列表
- andriod\iphone视频禁止全屏播放
x-webkit-airplay="true" x5-playsinline="true" webkit-playsinline="true" ...
- edusoho 支持同一账号多人同时登录
文件: ./src/Topxia/WebBundle/Listener/UserLoginTokenListener.php 函数: public function onGetUserLoginLis ...
- leetcode 884. 两句话中的不常见单词 (python)
给定两个句子 A 和 B . (句子是一串由空格分隔的单词.每个单词仅由小写字母组成.) 如果一个单词在其中一个句子中只出现一次,在另一个句子中却没有出现,那么这个单词就是不常见的. 返回所有不常用单 ...
- SpringBoot系列:三、SpringBoot中使用Filter
在springboot中要使用Filter首先要实现Filter接口,添加@WebFilter注解 然后重写三个方法,下图示例是在Filter中过滤上一届中拿配置的接口,如果是这个接口会自动跳转到/P ...
- 015-elasticsearch5.4.3【五】-搜索API【四】Joining 多文档查询、GEO查询、moreLikeThisQuery、script脚本查询、span跨度查询
一.Joining 多文档查询 joining query 像Elasticsearch这样的分布式系统中执行完整的SQL样式连接非常昂贵.相反,Elasticsearch提供两种形式的连接,旨在水平 ...
