codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(数学 or 数论+线段树)(两种方法)
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
F1 = 1; F2 = 1; Fn = Fn - 1 + Fn - 2 (n > 2).
DZY loves Fibonacci numbers very much. Today DZY gives you an array consisting of n integers: a1, a2, ..., an. Moreover, there are mqueries, each query has one of the two types:
- Format of the query "1 l r". In reply to the query, you need to add Fi - l + 1 to each element ai, where l ≤ i ≤ r.
- Format of the query "2 l r". In reply to the query you should output the value of
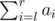 modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
Help DZY reply to all the queries.
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300000). The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — initial array a.
Then, m lines follow. A single line describes a single query in the format given in the statement. It is guaranteed that for each query inequality 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n holds.
For each query of the second type, print the value of the sum on a single line.
题目大意:维护一个序列,每次给一段序列加上一个斐波那契数列,或者询问一段序列的和。
思路1:两个斐波那契的定理,用数学归纳法很容易证明:
①定义F[1] = a, F[2] = b, F[n] = F[n - 1] + F[n - 2](n≥3)。有F[n] = b * fib[n - 1] + a * fib[n - 2](n≥3),其中fib[i]为斐波那契数列的第 i 项。
②定义F[1] = a, F[2] = b, F[n] = F[n - 1] + F[n - 2](n≥3)。有F[1] + F[2] + …… + F[n] = F[n + 2] - b。
这题还有一个事实,就是两个上述定义的数列,相加,仍然符合F[n] = F[n - 1] + F[n - 2]的递推公式。
利用这两个定理,用线段树维护序列,线段树的每个结点记录这一段的前两项是什么,预处理好斐波那契数列,便能O(1)地计算出每一个结点中间的数是多少、每一个结点的和。
代码(1513MS):
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define ll (x << 1)
#define rr ((x << 1) | 1)
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1) const int MOD = 1e9 + ; const int MAXN = ;
const int MAXT = MAXN << ; int f1[MAXT], f2[MAXT], sum[MAXT];
int a[MAXN], fib[MAXN];
int n, m; void init() {
fib[] = fib[] = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n + ; ++i) {
fib[i] = fib[i - ] + fib[i - ];
if(fib[i] >= MOD) fib[i] -= MOD;
}
} int get_fib(int a, int b, int n) {
if(n == ) return a;
if(n == ) return b;
return (LL(b) * fib[n - ] + LL(a) * fib[n - ]) % MOD;
} int get_sum(int a, int b, int n) {
return (get_fib(a, b, n + ) - b + MOD) % MOD;
} void add_fib(int x, int l, int r, int a, int b) {
(f1[x] += a) %= MOD;
(f2[x] += b) %= MOD;
(sum[x] += get_sum(a, b, r - l + )) %= MOD;
} void pushdown(int x, int l, int r) {
add_fib(ll, l, mid, f1[x], f2[x]);
add_fib(rr, mid + , r, get_fib(f1[x], f2[x], mid + - l + ), get_fib(f1[x], f2[x], mid + - l + ));
f1[x] = f2[x] = ;
} void maintain(int x) {
sum[x] = (sum[ll] + sum[rr]) % MOD;
} void build(int x, int l, int r) {
if(l == r) {
sum[x] = a[l];
} else {
build(ll, l, mid);
build(rr, mid + , r);
maintain(x);
}
} void update(int x, int l, int r, int a, int b) {
if(a <= l && r <= b) {
add_fib(x, l, r, fib[l - a + ], fib[l + - a + ]);
} else {
pushdown(x, l, r);
if(a <= mid) update(ll, l, mid, a, b);
if(mid < b) update(rr, mid + , r, a, b);
maintain(x);
}
} int query(int x, int l, int r, int a, int b) {
if(a <= l && r <= b) {
return sum[x];
} else {
int ret = ;
pushdown(x, l, r);
if(a <= mid) (ret += query(ll, l, mid, a, b)) %= MOD;
if(mid < b) (ret += query(rr, mid + , r, a, b)) %= MOD;
return ret;
}
} int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
init();
build(, , n);
int op, l, r;
while(m--) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &op, &l, &r);
if(op == ) update(, , n, l, r);
if(op == ) printf("%d\n", query(, , n, l, r));
}
}
思路2:按官方题解的说法,有通项公式$ fib_n = \frac{ \sqrt 5 } 5 * (( \frac {1 + \sqrt 5} 2) ^ n - ( \frac {1 - \sqrt 5} 2) ^ n) $。
5是1e9+9的二次剩余,383008016^2=5(mod 1e9+9)。
利用逆元,可计算出:$ \frac {\sqrt 5} 5、\frac {1 + \sqrt 5} 2、 \frac {1 - \sqrt 5} 2 $在模1e9+9意义下的值。
然后,变成用线段树维护两个等比数列。预处理出$\frac {1 + \sqrt 5} 2$和$\frac {1 - \sqrt 5} 2$的1~n的次方的值,设他们为q,还要求出1-q的逆元(用于计算等比数列的和)。
线段树每个结点记录两个等比数列的首项,跟上面的方法差不多,也是这样维护一个线段树即可。
代码(1996MS):
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define ll (x << 1)
#define rr ((x << 1) | 1)
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1) const int MOD = 1e9 + ;
const int SQRT5 = ; const int MAXN = ;
const int MAXT = MAXN << ; int powa[MAXN], powb[MAXN];
int coe, ta, tb, invta, invtb;
int fa[MAXT], fb[MAXT], sum[MAXT];
int a[MAXN];
int n, m; int inv(int x) {
if(x == ) return ;
return (LL(MOD - MOD / x) * inv(MOD % x)) % MOD;
} void init() {
coe = inv(SQRT5);
ta = (LL( + SQRT5) * inv()) % MOD;
tb = (LL( - SQRT5 + MOD) * inv()) % MOD;
invta = inv( - ta + MOD);
invtb = inv( - tb + MOD);
//cout<<coe<<endl<<ta<<endl<<tb<<endl;
powa[] = powb[] = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
powa[i] = LL(powa[i - ]) * ta % MOD;
powb[i] = LL(powb[i - ]) * tb % MOD;
}
} void maintain(int x) {
sum[x] = (sum[ll] + sum[rr]) % MOD;
} void add_fib(int x, int l, int r, int a, int b) {
(fa[x] += a) %= MOD;
(fb[x] += b) %= MOD;
(sum[x] += LL(a) * ( - powa[r - l + ] + MOD) % MOD * invta % MOD) %= MOD;
(sum[x] -= LL(b) * ( - powb[r - l + ] + MOD) % MOD * invtb % MOD) %= MOD;
if(sum[x] < ) sum[x] += MOD;
} void pushdown(int x, int l, int r) {
add_fib(ll, l, mid, fa[x], fb[x]);
add_fib(rr, mid + , r, LL(fa[x]) * powa[mid + - l] % MOD, LL(fb[x]) * powb[mid + - l] % MOD);
fa[x] = fb[x] = ;
} void build(int x, int l, int r) {
if(l == r) {
sum[x] = a[l];
} else {
build(ll, l, mid);
build(rr, mid + , r);
maintain(x);
}
} void update(int x, int l, int r, int a, int b) {
if(a <= l && r <= b) {
add_fib(x, l, r, LL(coe) * powa[l - a + ] % MOD, LL(coe) * powb[l - a + ] % MOD);
} else {
pushdown(x, l, r);
if(a <= mid) update(ll, l, mid, a, b);
if(mid < b) update(rr, mid + , r, a, b);
maintain(x);
}
} int query(int x, int l, int r, int a, int b) {
if(a <= l && r <= b) {
return sum[x];
} else {
int ret = ;
pushdown(x, l, r);
if(a <= mid) (ret += query(ll, l, mid, a, b)) %= MOD;
if(mid < b) (ret += query(rr, mid + , r, a, b)) %= MOD;
return ret;
}
} int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
init();
build(, , n);
int op, l, r;
while(m--) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &op, &l, &r);
if(op == ) update(, , n, l, r);
if(op == ) printf("%d\n", query(, , n, l, r));
}
}
codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(数学 or 数论+线段树)(两种方法)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 446-C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 同余 线段树 斐波那契数列
C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- ACM学习历程—Codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(线段树 && 数论)
Description In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence ...
- codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 数论+线段树成段更新
DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers Time Limit:4000MS Memory Limit:262144KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d &a ...
- Codeforces 446C —— DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(线段树)
题目:DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 题意比較简单,不解释了. 尽管官方的题解也是用线段树,但还利用了二次剩余. 可是我没有想到二次剩余,然后写了个感觉非常复杂度的线段树,还是 ...
- Codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers [线段树,数论]
洛谷 Codeforces 思路 这题知道结论就是水题,不知道就是神仙题-- 斐波那契数有这样一个性质:\(f_{n+m}=f_{n+1}f_m+f_{n}f_{m-1}\). 至于怎么证明嘛-- 即 ...
- Codeforces 446C - DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers(斐波那契数列+线段树)
Codeforces 题目传送门 & 洛谷题目传送门 你可能会疑惑我为什么要写 *2400 的题的题解 首先一个很明显的想法是,看到斐波那契数列和 \(10^9+9\) 就想到通项公式,\(F ...
- codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 线段树
假如F[1] = a, F[2] = B, F[n] = F[n - 1] + F[n - 2]. 写成矩阵表示形式可以很快发现F[n] = f[n - 1] * b + f[n - 2] * a. ...
- Codeforces Round #FF 446 C. DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
參考:http://www.cnblogs.com/chanme/p/3843859.html 然后我看到在别人的AC的方法里还有这么一种神方法,他预先设定了一个阈值K,当当前的更新操作数j<K ...
- [CodeForces - 447E] E - DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
E DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is define ...
随机推荐
- MySQL- 锁(2)
InnoDB行锁实现方式 InnoDB行锁是通过给索引上的索引项加锁来实现的,这一点MySQL与Oracle不同,后者是通过在数据块中对相应数据行加锁来实现的.InnoDB这种行锁实现特点意味着:只有 ...
- textview自适应高度的计算方法
http://blog.csdn.net/smking/article/details/22221441
- yum安装node.js
1.安装EPEL库 yum install epel-release 2.安装Node.js yum install nodejs 3.安装nodejs中常用的npm软件包管理器 yum instal ...
- LightOj1418 - Trees on My Island(Pick定理)
题目链接:http://lightoj.com/volume_showproblem.php?problem=1418 题意:给你多边形中的顶点,n个点按顺时针或逆时针方向给出,然后求出多边形内部有多 ...
- App 上线流程
http://www.cocoachina.com/bbs/read.php?tid=330302
- 《Maven实战》阅读笔记
java -versionmvn -vmvn help:system m2eclipse maven->install MAVEN_OPTS: -Xms128m -Xmx512mmvn clea ...
- cannot open /proc/bus/usb/devices, No such file or directory
由于kernel config中没有打开对应的配置. make menuconfig 选择: Device Drivers ---> [*] USB support ---> [*] US ...
- 通过css3实现开关选择按钮
通过css属性实现如图所示按钮 要点:通过checkbox选中与否的状态与兄弟选择器实现相关功能 1.设置开关大小并设置定位方式为relative .swift-btn { positio ...
- $.ajax所犯的错误。success后面不执行
$.ajax({ type: 'post', url: '../AshxHandler/HandlerAddPhoto.ashx', data: { clientPath: photoName }, ...
- iOS 证书及配置文件介绍
1.Certification(证书) 证书是对电脑开发资格的认证,每个开发者帐号有一套,分为两种: 1)Developer Certification(开发证书) 安装在电脑上提供权限:开发人员通过 ...
