编译原理 算法3.8 LR分析 c++11实现
LR分析简介
LR分析是应用最广泛的一类分析方法,它是实用的编译器功能中最强的分析器,其特点是:
1,采用最一般的无回溯移进-规约方法。
2,可分析的文法是LL文法的真超集。
3,能够及时发现错误,及时从左扫描输入序列的最大可能。
4,分析表较为复杂,难以手工构造。
实验内容
根据LR分析表action和goto实现LR分析。
实验步骤
输入 序列$\omega$和文法$G$的LR分析表action与goto。
输出 若$\omega \in L(G)$,得到$\omega$的规范规约,否则指出一个错误。
具体实现
见代码。
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <fstream>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <map>
- #include <set>
- #include <stack>
- #include <vector>
- using namespace std;
- using Production = pair<string, vector<string>>;
- const int max_state = ;
- const int delay_num = 5e8;
- struct ParserLR
- {
- map<string, int> mp_n; //非终结符映射
- map<string, int> mp_t; //终结符映射
- vector<Production> P; //产生式
- vector<string> N, T; //非终结符,终结符
- int state_num, operator_num, nonterminal_num, terminal_num, production_num;
- vector<string> action[max_state];
- vector<int> _goto[max_state];
- int init(string filename)
- {
- N.clear();
- T.clear();
- P.clear();
- mp_n.clear();
- mp_t.clear();
- for (int i = ; i < max_state; i++)
- {
- action[i].clear();
- _goto[i].clear();
- }
- state_num = operator_num = nonterminal_num = terminal_num = production_num = ;
- ifstream in(filename, ios::in);
- if (!in.is_open())
- return ;
- in >> terminal_num;
- for (int i = ; i < terminal_num; i++)
- {
- string tmp;
- in >> tmp;
- T.emplace_back(tmp);
- mp_t[tmp] = i;
- }
- in >> nonterminal_num;
- for (int i = ; i < nonterminal_num; i++)
- {
- string tmp;
- in >> tmp;
- N.emplace_back(tmp);
- mp_n[tmp] = i;
- }
- in >> production_num;
- for (int i = ; i < production_num; i++)
- {
- Production cur;
- in >> cur.first;
- int sz;
- in >> sz;
- for (int j = ; j < sz; j++)
- {
- string t;
- in >> t;
- cur.second.emplace_back(t);
- }
- P.emplace_back(cur);
- }
- in >> state_num;
- for (int i = ; i <= state_num; i++)
- for (int j = ; j < terminal_num; j++)
- {
- string tmp;
- in >> tmp;
- action[i].emplace_back(tmp);
- }
- for (int i = ; i <= state_num; i++)
- for (int j = ; j < nonterminal_num; j++)
- {
- int tmp;
- in >> tmp;
- _goto[i].emplace_back(tmp);
- }
- return ;
- }
- Production getProduction(int idx)
- {
- return P[idx - ];
- }
- pair<int, vector<Production>> analyze(vector<string> input) //first->出错位置,-1代表无错
- {
- vector<Production> error;
- vector<Production> success;
- stack<string> ch; //符号栈
- stack<int> st; //状态栈
- ch.emplace("#");
- st.emplace();
- input.emplace_back("#");
- int sz = input.size();
- for (int i = ; i < sz;)
- {
- string now = input[i];
- if (!mp_t.count(now))
- return make_pair(i, success);
- int ip = mp_t[now];
- int top = st.top(); //栈顶状态
- string at = action[top][ip];
- if (at[] == 'r') //规约
- {
- string res = at.substr(, at.size());
- int num = stoi(res);
- Production trans = getProduction(num);
- for (int i = ; i < trans.second.size(); i++)
- {
- st.pop();
- ch.pop();
- }
- top = st.top();
- string cur = trans.first;
- ch.emplace(cur);
- st.emplace(_goto[top][mp_n[cur]]);
- success.emplace_back(trans);
- }
- else if (at[] == 's') //移进
- {
- string res = at.substr(, at.size());
- int to_state = stoi(res);
- st.emplace(to_state);
- ch.emplace(now);
- i++;
- }
- else if (at == "acc") //接受
- return make_pair(-, success);
- else //error
- {
- if (now == "#")
- return make_pair(i - , success);
- return make_pair(i, success);
- }
- }
- return make_pair(, error);
- }
- };
- inline void delay()
- {
- for (int i = ; i < delay_num; i++)
- ;
- }
- inline void display(const pair<int, vector<Production>> &out)
- {
- if (out.first == -)
- {
- for (int i = ; i < out.second.size(); i++)
- {
- cout << out.second[i].first << "->";
- for (int j = ; j < out.second[i].second.size(); j++)
- cout << out.second[i].second[j];
- cout << "\n";
- }
- }
- else
- cout << "在第" << out.first + << "个终结符出错.\n";
- }
- int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
- {
- ParserLR app;
- string filename = "prj3_8_in.txt";
- if (app.init(filename))
- {
- cout << "构建分析器中";
- delay();
- cout << ".";
- delay();
- cout << ".";
- delay();
- cout << ".\n";
- delay();
- cout << "构建成功.\n";
- cout << "请输入终结符个数:";
- int sz;
- cin >> sz;
- cout << "请输入包含" << sz << "个终结符的待分析序列, 终结符间需用空格分离:";
- vector<string> al;
- for (int i = ; i < sz; i++)
- {
- string tmp;
- cin >> tmp;
- al.emplace_back(tmp);
- }
- cout << "开始分析";
- delay();
- cout << ".";
- delay();
- cout << ".";
- delay();
- cout << ".\n";
- delay();
- cout << "分析结束.\n";
- pair<int, vector<Production>> out = app.analyze(al);
- cout << "分析成功,结果如下:\n";
- display(out);
- }
- return ;
- }
源代码
- id - * #
- E T F
- E E - T
- E T
- T T * F
- T F
- F - F
- F id
- s4 s5 null null
- null s6 null acc
- null r2 s7 r2
- null r4 r4 r4
- null r6 r6 r6
- s4 s5 null null
- s4 s5 null null
- s4 s5 null null
- null r5 r5 r5
- null r1 s7 r1
- null r3 r3 r3
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- -
- - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
输入文件
效果展示
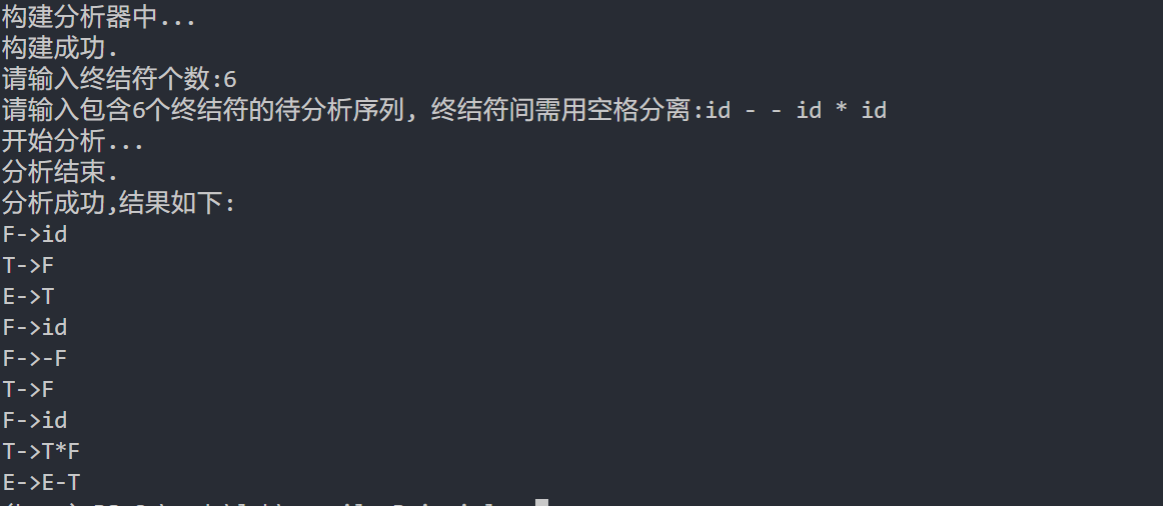
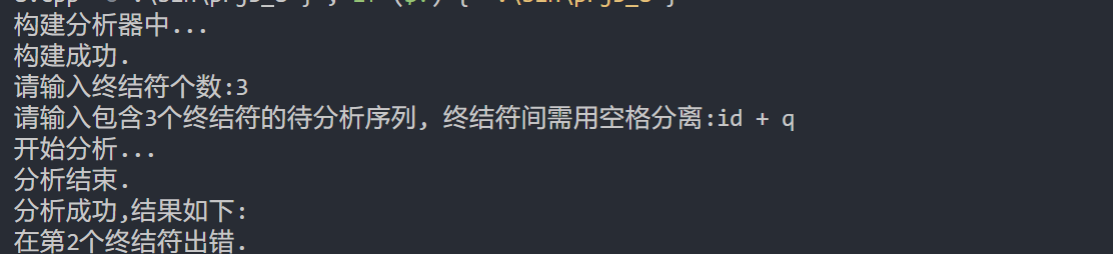
代码使用部分c++11特性,如有本地编译需要,请确认环境。
欢迎下方留言。
编译原理 算法3.8 LR分析 c++11实现的更多相关文章
- 《编译原理》构造 LL(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析
<编译原理>构造 LL(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析 易错点及扩展: 1.求每个产生式的 SELECT 集 2.注意区分是对谁 FIRST 集 FOLLOW 集 3.开始符号的 FOL ...
- 编译原理实验之SLR1文法分析
---内容开始--- 这是一份编译原理实验报告,分析表是手动造的,可以作为借鉴. 基于 SLR(1) 分析法的语法制导翻译及中间代码生成程序设计原理与实现1 .理论传授语法制导的基本概念,目标代码结 ...
- 编译原理(六)自底向上分析之LR分析法
自底向上分析之LR分析法 说明:以老师PPT为标准,借鉴部分教材内容,AlvinZH学习笔记. 基本概念 1. LR分析:从左到右扫描(L)自底向上进行规约(R),是规范规约,也即最右推导(规范推导) ...
- 【编译原理】语法分析LL(1)分析法的FIRST和FOLLOW集
近来复习编译原理,语法分析中的自上而下LL(1)分析法,需要构造求出一个文法的FIRST和FOLLOW集,然后构造分析表,利用分析表+一个栈来做自上而下的语法分析(递归下降/预测分析),可是这个FIR ...
- 编译原理实习(应用预测分析法LL(1)实现语法分析)
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<iomanip> #include<cstdio> #inc ...
- 编译原理 #02# 简易递归下降分析程序(js实现)
// 实验存档 截图: 代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"&g ...
- 【编译原理】c++实现自下而上语法分析器
写在前面:本博客为本人原创,严禁任何形式的转载!本博客只允许放在博客园(.cnblogs.com),如果您在其他网站看到这篇博文,请通过下面这个唯一的合法链接转到原文! 本博客全网唯一合法URL:ht ...
- 编译原理根据项目集规范族构造LR(0)分析表
转载于https://blog.csdn.net/Johan_Joe_King/article/details/79058597?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.n ...
- 《编译原理》LR 分析法与构造 LR(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析
<编译原理>LR 分析法与构造 LR(1) 分析表的步骤 - 例题解析 笔记 直接做题是有一些特定步骤,有技巧.但也必须先了解一些基本概念,本篇会通过例题形式解释概念,会容易理解和记忆,以 ...
随机推荐
- xms跨平台基础框架 - 基于.netcore
背景 敝人经过多年开发,数百个项目“打磨(折磨)”,各种国内外框架平台都有涉及,没有一款称心顺手的,原因有三,一是设计反人类,二是不开源根本无法突破框架限制,三是即使开源也是阉割版,然后xms就开始萌 ...
- [转载]2.8 UiPath中断活动Break的介绍和使用
一.Break的介绍 Break: 用于结束当前循环. 注意: Break控件只能用于For Each 循环中 二.Break在UiPath中结合For Each循环的使用 1.打开设计器,在设计库中 ...
- numpy---python数据分析
最后大图可点开保存 文章目录 最后大图可点开保存 学习目标 3.1.1Numpy介绍 3.1.2 ndarray介绍 3.1.3 ndarray与Python原生list运算效率对比 3.1.4 nd ...
- Scrapy进阶知识点总结(一)——基本命令与基本类(spider,request,response)
一.常见命令 scrapy全局命令可以在任何地方用,项目命令只能在项目路径下用 全局命令: 项目命令: startproject crawl genspider check settings list ...
- 关于vue ui组件
一.vue ui 组件 1: vue 当前很火前端框架vue 针对PC用户 pc 端与移动端区别 (1)屏幕宽度:992px > (2)操作方式:鼠标 事件 手指:触碰操作 -饿了么:基于 ...
- [git]关于github的一些用法笔记(入门)
本视频来自于观看尚硅谷B站教学:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av10475153?from=search&seid=9735863941344749813 而 ...
- 如何基于k8s快速搭建TeamCity(YAML分享)
前言 最近有朋友基于之前的博客<Docker最全教程之使用TeamCity来完成内部CI.CD流程(十七)>搭建TeamCity时出现了一些问题,由于平常比较忙,没有及时答复,非常抱歉. ...
- mysql 创建用户及授权(2)
一. MySQL初始密码 新安装的MySQL默认是没有密码的,设置初始密码可以用以下命 mysqladmin -u root password 'new-password' mysqladmin -u ...
- Anaconda 笔记
Anaconda笔记 conda 功能 管理版本的切换 安装其他的包 conda 创建python27环境 conda create --name python27 python=2.7 conda ...
- 力扣(LeetCode)按奇偶排序数组II 个人题解
给定一个非负整数数组 A, A 中一半整数是奇数,一半整数是偶数. 对数组进行排序,以便当 A[i] 为奇数时,i 也是奇数:当 A[i] 为偶数时, i 也是偶数. 你可以返回任何满足上述条件的数组 ...
