Pandas系列(十四)- 实战案例
一、series
- import pandas as pd
- import string
- #创建Series的两种方式
- #方式一
- t = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,43],index=list('asdfg'))
- print(t)
- #方式二
- temp_dict = {'name':'xiaohong','age':30,'tel':10086}
- t2 = pd.Series(temp_dict)
- print(t2)
- #字典推导式
- a = {string.ascii_uppercase[i]:i for i in range(10)}
- print(a)
- print(pd.Series(a))
- print(pd.Series(a,index=list(string.ascii_uppercase[5:15])))
二、read_file
- import pandas as pd
- from pymongo import MongoClient
- #pandas读取csv文件
- # df = pd.read_csv('dogNames2.csv')
- # print(df)
- client = MongoClient()
- collection = client['meipai']['meipai_video']
- data = collection.find()
- data_list = []
- for i in data:
- temp = {}
- temp['cut_url'] = i['cut_url']
- temp['create_time'] = i['create_time']
- temp['title'] = i['title']
- temp['video_url'] = i['video_url']
- data_list.append(temp)
- # print(data)
- # t1 = data[0]
- # t1 = pd.Series(t1)
- # print(t1)
- df = pd.DataFrame(data_list)
- print(df.info())
- print(df.describe())
- # print(df.head())
- # print('*'*100)
- # print(df.tail())
三、dataframe
示例一
- import pandas as pd
- temp_dict = {'name':['xiaohong','xiaozhang'],'age':[30,23],'tel':[10086,10010]}
- t1 = pd.DataFrame(temp_dict)
- print(t1)
- temp_dict1 = [{'name':'xiaohong','age':23,'tel':10086},{'name':'xiaogang','age':12},{'name':'xiaozhang','tel':10010}]
- t2 = pd.DataFrame(temp_dict1)
- print(t2)
示例二
- import pandas as pd
- #pandas读取csv文件
- df = pd.read_csv('dogNames2.csv')
- # print(df.head())
- # print(df.info())
- #DataFrame中排序的方法
- df = df.sort_values(by='Count_AnimalName',ascending=False)
- # print(df.head())
- #pandas取行和列的注意事项
- # - 方括号写数组,表示取行,对行进行操作
- # - 写字符串,表示取列索引,对列进行操作
- print(df[:20])
- print(df[:20]['Row_Labels'])
- print(type(df['Row_Labels']))
- #bool索引
- print(df[(df['Row_Labels'].str.len()>4)&(df['Count_AnimalName']>800)])
四、电影数据案例
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- file_path = './IMDB-Movie-data.csv'
- df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
- # print(df.head(1))
- # print(df.info())
- # rating,runtime分布情况
- # 选择图形:直方图
- # 准备数据
- runtime_data = df['Runtime (Minutes)'].values
- max_runtime = runtime_data.max()
- min_runtime = runtime_data.min()
- #计算组距
- num_bin = (max_runtime-min_runtime)//5
- #设置图行大小
- plt.figure(figsize=(13,6),dpi=80)
- #画直方图
- plt.hist(runtime_data,num_bin)
- plt.xticks(range(min_runtime,max_runtime+5,5))
- #显示
- plt.show()
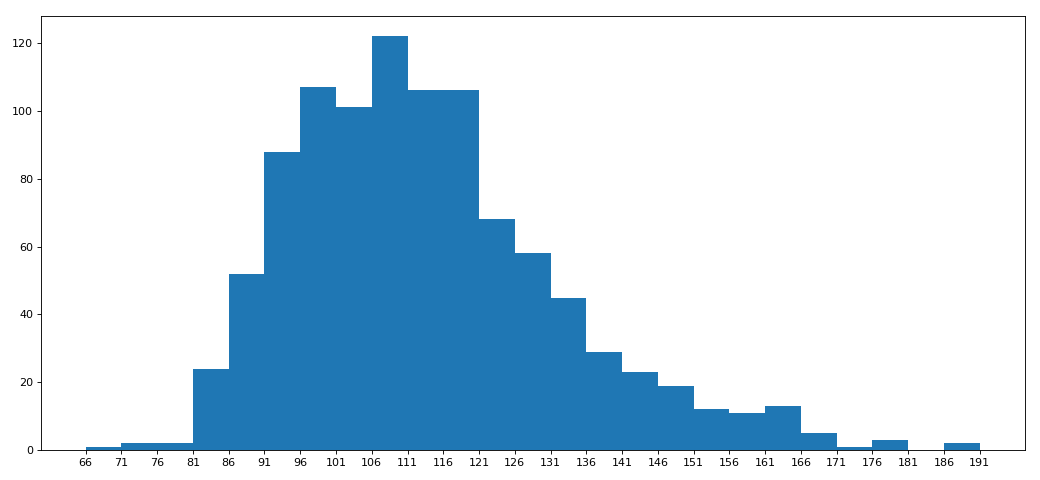
电影案例二
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- from functools import reduce
- file_path = './IMDB-Movie-data.csv'
- df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
- # print(df.head(1))
- # print(df.info())
- # rating,runtime分布情况
- # 选择图形:直方图
- # 准备数据
- # runtime_data = df['Runtime (Minutes)'].values
- rate_data = df['Rating'].values
- max_rate = rate_data.max()
- min_rate = rate_data.min()
- #设置不等宽组距,hist方法中取到的会是一个左闭右开的区间[1,9,3.5)
- num_bin_list = [1.9,3.5]
- i = 3.5
- while i<=max_rate:
- i += 0.5
- num_bin_list.append(i)
- print(num_bin_list)
- #设置图形大小
- plt.figure(figsize=(13,6),dpi=80)
- #画直方图
- plt.hist(rate_data,num_bin_list)
- #xticks让之前的组距能够对上
- plt.xticks(num_bin_list)
- #显示
- plt.show()

- [1.9, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 9.0, 9.5]
五。常用统计方法
- import numpy
- import pandas as pd
- df = pd.read_csv('IMDB-Movie-Data.csv')
- print(df.info())
- print(df.describe())
- #获取评分的均分
- rate_mean = df.Rating.mean()
- print(rate_mean)
- #获取导演的人数
- print(df.Director.value_counts().count())
- print(len(set(df.Director.tolist())))
- print(len(df.Director.unique()))
- #获取演员的人数
- temp_actors_list = df.Actors.str.split(',').tolist()
- actors_list = [i for j in temp_actors_list for i in j]
- # numpy.array(temp_actors_list).flatten()
- actors_num = len(set(actors_list))
- print(actors_num)
- <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
- RangeIndex: 1000 entries, 0 to 999
- Data columns (total 12 columns):
- Rank 1000 non-null int64
- Title 1000 non-null object
- Genre 1000 non-null object
- Description 1000 non-null object
- Director 1000 non-null object
- Actors 1000 non-null object
- Year 1000 non-null int64
- Runtime (Minutes) 1000 non-null int64
- Rating 1000 non-null float64
- Votes 1000 non-null int64
- Revenue (Millions) 872 non-null float64
- Metascore 936 non-null float64
- dtypes: float64(3), int64(4), object(5)
- memory usage: 93.8+ KB
- None
- Rank Year ... Revenue (Millions) Metascore
- count 1000.000000 1000.000000 ... 872.000000 936.000000
- mean 500.500000 2012.783000 ... 82.956376 58.985043
- std 288.819436 3.205962 ... 103.253540 17.194757
- min 1.000000 2006.000000 ... 0.000000 11.000000
- 25% 250.750000 2010.000000 ... 13.270000 47.000000
- 50% 500.500000 2014.000000 ... 47.985000 59.500000
- 75% 750.250000 2016.000000 ... 113.715000 72.000000
- max 1000.000000 2016.000000 ... 936.630000 100.000000
- [8 rows x 7 columns]
六、统计分类情况
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Datetime: 2018/11/19
- @Author: Zhang Yafei
- """
- """
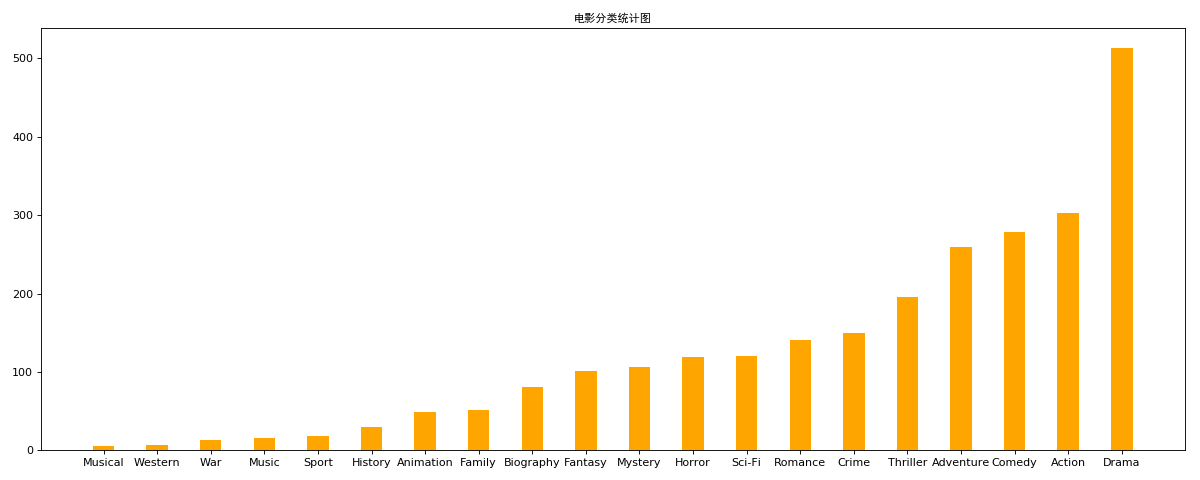
- 对于这一组电影数据,如果我们希望统计电影分类(genre)的情况,应该如何处理数据?
- 思路:重新构造一个全为0的数组,列名为分类,如果某一条数据中分类出现过,就让0变为1
- """
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- from matplotlib import font_manager
- #中文字体
- my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(family='SimHei')
- #显示完整的列
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
- df = pd.read_csv('IMDB-Movie-Data.csv')
- #统计分类列表
- temp_list = df.Genre.str.split(',').tolist()
- genre_list = list(set([i for j in temp_list for i in j]))
- #构造全为0的数组
- zero_df = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((df.shape[0],len(genre_list))),columns=genre_list)
- # print(zero_df)
- #给每个电影出现分类的位置赋值1
- for i in range(df.shape[0]):
- zero_df.loc[i,temp_list[i]] = 1
- # print(zero_df.head(1))
- genre_count = zero_df.sum(axis=0)
- print(genre_count)
- #排序
- genre_count = genre_count.sort_values()
- _x = genre_count.index
- _y = genre_count.values
- #画图
- plt.figure(figsize=(15,6),dpi=80)
- plt.bar(range(len(_x)),_y,width=0.4,color="orange")
- plt.xticks(range(len(_x)),_x)
- plt.title('电影分类统计图',fontproperties=my_font)
- plt.show()
七、数据分组与聚合
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Datetime: 2018/11/19
- @Author: Zhang Yafei
- """
- """
- 现在我们有一组关于全球星巴克店铺的统计数据,如果我想知道美国的星巴克数量和中国的哪个多,或者我想知道中国每个省份星巴克的数量的情况,那么应该怎么办?
- 思路:遍历一遍,每次加1 ???
- """
- import pandas as pd
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
- df = pd.read_csv('starbucks_store_worldwide.csv')
- # print(df.head(1))
- # print(df.info())
- grouped = df.groupby(by='Country')
- # print(grouped)
- # DataFrameGroupBy
- # 可以进行遍历
- # for i,j in grouped:
- # print(i)
- # print('-'*100)
- # print(j)
- # print('*'*100)
- country_count = grouped['Brand'].count()
- # print(country_count['US'])
- # print(country_count['CN'])
- #统计中国每个省份店铺的数量
- china_data = df[df.Country == 'CN']
- china_grouped = china_data.groupby(by='State/Province').count()['Brand']
- # print(china_grouped)
- #数据按照多个条件进行分组
- brand_grouped = df['Brand'].groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()
- # print(brand_grouped)
- # print(type(brand_grouped))
- #数据按照多个条件进行分组,返回dataframe
- brand_grouped1 = df[['Brand']].groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()
- brand_grouped2 = df.groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']])[['Brand']].count()
- brand_grouped3 = df.groupby(by=[df['Country'],df['State/Province']]).count()[['Brand']]
- # print(brand_grouped1)
- # print(brand_grouped2)
- # print(brand_grouped3)
- #索引的方法和属性
- print(brand_grouped1)
- print(brand_grouped1.index)
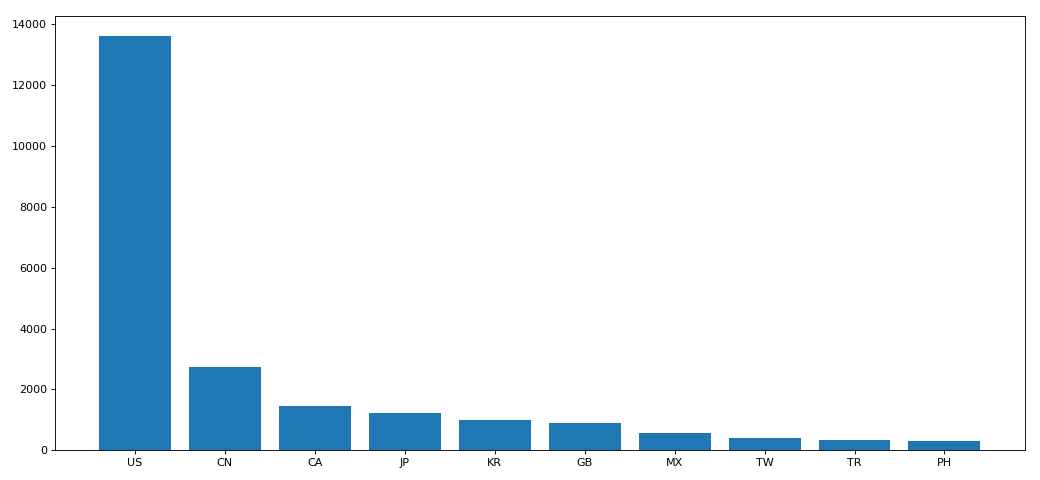
八、分组聚合
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
- df = pd.read_csv('starbucks_store_worldwide.csv')
- df = df.groupby(by='Country').count()['Brand'].sort_values(ascending=False)[:10]
- _x = df.index
- _y = df.values
- #画图
- plt.figure(figsize=(13,6),dpi=80)
- plt.bar(_x,_y)
- plt.show()
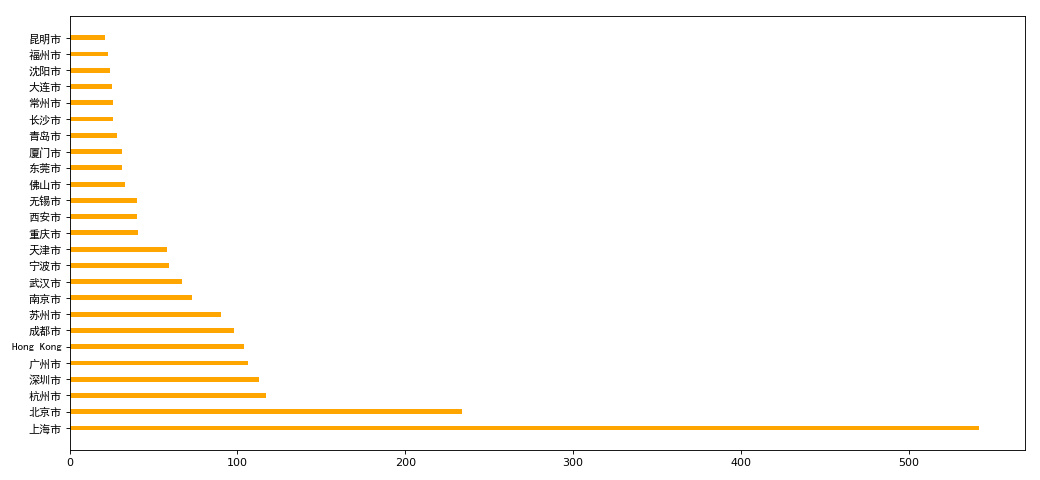
分组聚合二
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- from matplotlib import font_manager
- my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(family='SimHei')
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
- df = pd.read_csv('starbucks_store_worldwide.csv')
- df = df[df['Country']=='CN']
- print(df.head(1))
- df = df.groupby(by='City').count()['Brand'].sort_values(ascending=False)[:25]
- _x = df.index
- _y = df.values
- #画图
- plt.figure(figsize=(13,6),dpi=80)
- # plt.bar(_x,_y,width=0.3,color='orange')
- plt.barh(_x,_y,height=0.3,color='orange')
- # plt.xticks(_x,fontproperties=my_font)
- plt.yticks(_x,fontproperties=my_font)
- plt.show()
九、book_data
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
- df = pd.read_csv('books.csv')
- # print(df.info())
- data = df[pd.notnull(df['original_publication_year'])]
- grouped = data.groupby(by='original_publication_year').count()['title']
- # print(grouped)
- grouped1 = data.average_rating.groupby(by=data['original_publication_year']).mean()
- # print(grouped1)
- _x = grouped1.index
- _y = grouped1.values
- plt.figure(figsize=(15,6),dpi=80)
- plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y)
- plt.xticks(range(len(_x))[::10],_x[::10].astype(int),rotation=45)
- plt.show()
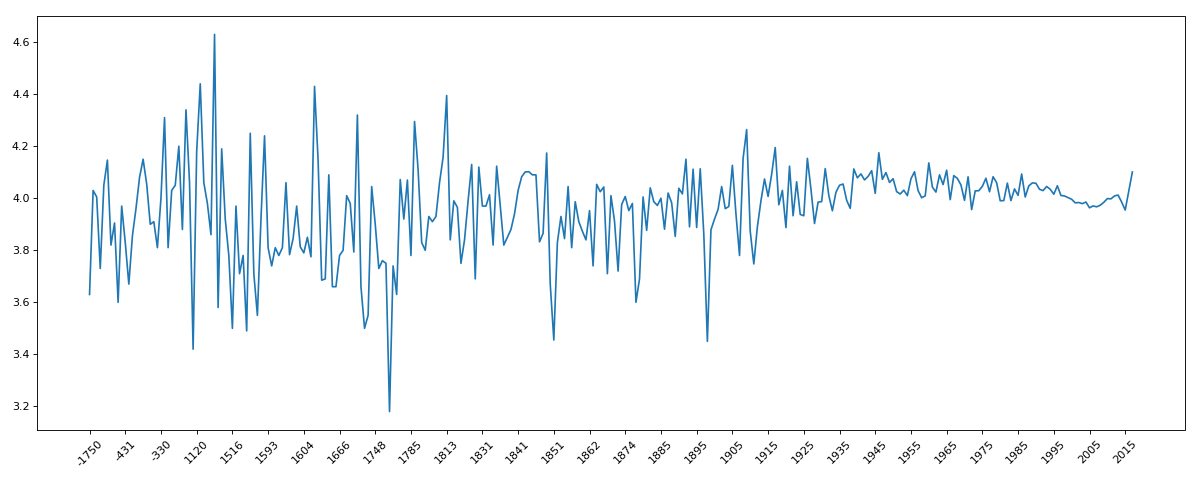
十、911data
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None)
- df = pd.read_csv('911.csv')
- # print(df.head(1))
- # print(df.info())
- #获取分类
- temp_list = df.title.str.split(':').tolist()
- cate_list = list(set([i[0] for i in temp_list]))
- # print(cate_list)
- #构造全为0的数组
- zeros_df = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((df.shape[0],len(cate_list))),columns=cate_list)
- #赋值
- for cate in cate_list:
- zeros_df[cate][df.title.str.contains(cate)] = 1
- print(zeros_df)
- sum_ret = zeros_df.sum(axis=0)
- print(sum_ret)
示例二
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None)
- df = pd.read_csv('911.csv')
- # print(df.head(1))
- # print(df.info())
- #获取分类
- temp_list = df.title.str.split(':').tolist()
- cate_list = [i[0] for i in temp_list]
- df['cate'] = pd.DataFrame(np.array(cate_list).reshape(df.shape[0],1))
- print(df.groupby(by='cate').count()['title'])
十一、时间序列
实例一
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Datetime: 2018/11/19
- @Author: Zhang Yafei
- """
- """
- 统计出911数据中不同月份电话次数的变化情况
- """
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None)
- df = pd.read_csv('911.csv')
- df.drop_duplicates()
- df.timeStamp = pd.to_datetime(df.timeStamp) #时间字符串转时间格式
- df.set_index('timeStamp',inplace=True) #设置时间格式为索引
- # print(df.head())
- #统计出911数据中不同月份电话次数
- count_by_month = df.resample('M').count()['title']
- print(count_by_month)
- #画图
- _x = count_by_month.index
- _y = count_by_month.values
- plt.figure(figsize=(15,8),dpi=80)
- plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y)
- plt.xticks(range(len(_x)),_x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'),rotation=45)
- plt.show()
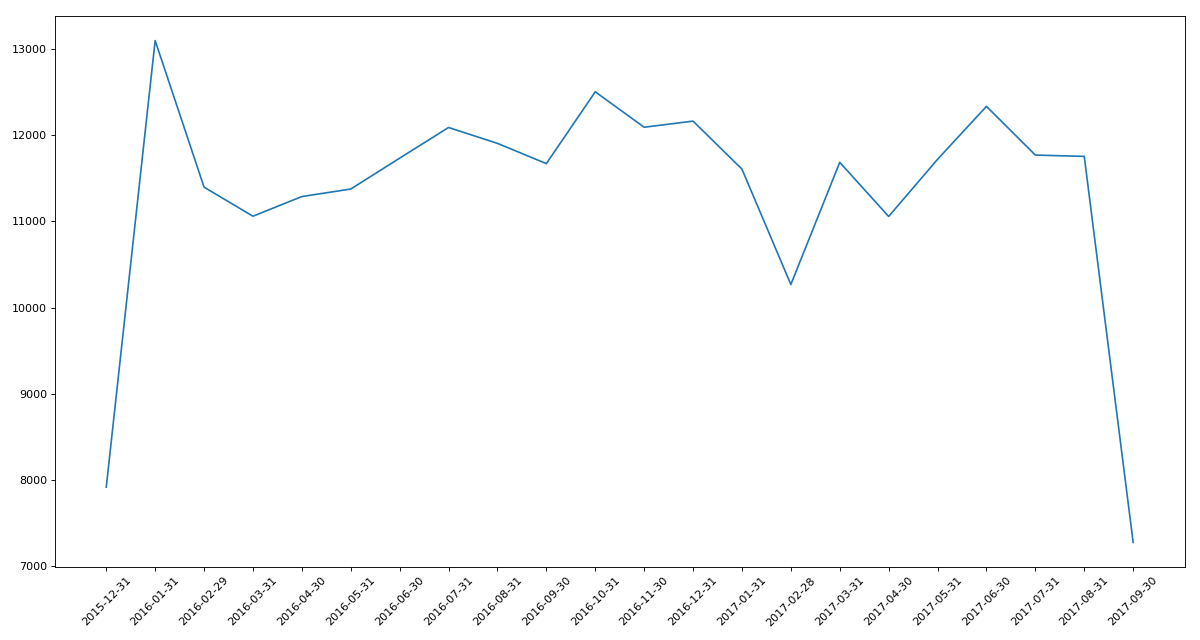
实例二
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Datetime: 2018/11/19
- @Author: Zhang Yafei
- """
- """
- 统计出911数据中不同月份不同类型的电话的次数的变化情况
- """
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None)
- df = pd.read_csv('911.csv')
- #把时间字符串转化为时间类型设置为索引
- df.timeStamp = pd.to_datetime(df.timeStamp)
- #添加列,表示分类
- temp_list = df.title.str.split(':').tolist()
- cate_list = [i[0] for i in temp_list]
- df['cate'] = pd.DataFrame(np.array(cate_list).reshape(df.shape[0],1))
- df.set_index('timeStamp',inplace=True)
- plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8), dpi=80)
- #分组
- for group_name,group_data in df.groupby(by='cate'):
- #对不同的分类都进行绘图
- count_by_month = group_data.resample('M').count()['title']
- # 画图
- _x = count_by_month.index
- _y = count_by_month.values
- plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y,label=group_name)
- plt.xticks(range(len(_x)), _x.strftime('%Y-%m-%d'), rotation=45)
- plt.legend(loc='best')
- plt.show()
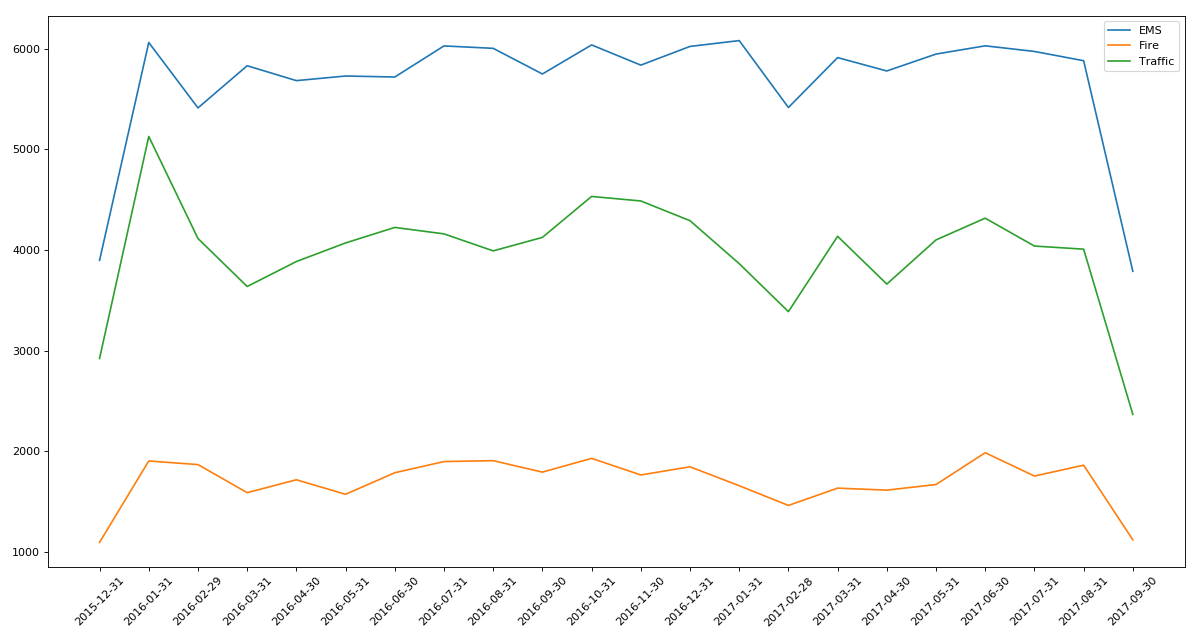
实例三:pm2.5
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- """
- @Datetime: 2018/11/19
- @Author: Zhang Yafei
- """
- """
- 绘制美国和中国PM2.5随时间的变化情况
- """
- import pandas as pd
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- pd.set_option('display.max_columns',None)
- df = pd.read_csv('PM2.5/BeijingPM20100101_20151231.csv')
- # print(df.head())
- #把分开的时间字符串通过periodIndex的方法转化为pandas的时间类型
- period = pd.PeriodIndex(year=df.year,month=df.month,day=df.day,hour=df.hour,freq='H')
- df['datetime'] = period
- print(df.head(10))
- #把datetime设置为索引
- df.set_index('datetime',inplace=True)
- #进行降采样
- df = df.resample('7D').mean()
- #处理缺失值,删除缺失数据
- # data = df['PM_US Post'].dropna()
- # china_data = df['PM_Nongzhanguan'].dropna()
- data = df['PM_US Post']
- china_data = df['PM_Nongzhanguan']
- #画图
- _x = data.index
- _y = data.values
- _x_china = china_data.index
- _y_china = china_data.values
- plt.figure(figsize=(13,8),dpi=80)
- plt.plot(range(len(_x)),_y,label='US_POST',alpha=0.7)
- plt.plot(range(len(_x_china)),_y_china,label='CN_POST',alpha=0.7)
- plt.xticks(range(0,len(_x_china),10),list(_x_china.strftime('%Y%m%d'))[::10],rotation=45)
- plt.show()
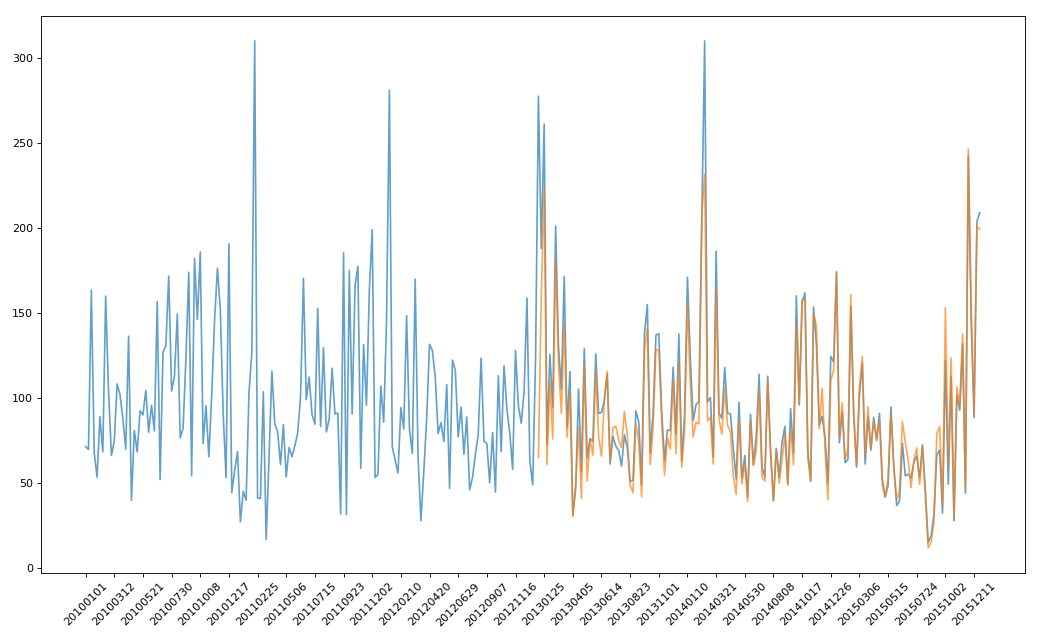
Pandas系列(十四)- 实战案例的更多相关文章
- struts2官方 中文教程 系列十四:主题Theme
介绍 当您使用一个Struts 2标签时,例如 <s:select ..../> 在您的web页面中,Struts 2框架会生成HTML,它会显示外观并控制select控件的布局.样式和 ...
- MP实战系列(十四)之分页使用
MyBatis Plus的分页,有插件式的,也有其自带了,插件需要配置,说麻烦也不是特别麻烦,不过觉得现有的MyBatis Plus足以解决,就懒得配置插件了. MyBatis Plus的资料不算是太 ...
- 闯祸了,生成环境执行了DDL操作《死磕MySQL系列 十四》
由于业务随着时间不停的改变,起初的表结构设计已经满足不了如今的需求,这时你是不是想那就加字段呗!加字段也是个艺术活,接下来由本文的主人咔咔给你吹. 试想一下这个场景 事务A在执行一个非常大的查询 事务 ...
- 学习ASP.NET Core Razor 编程系列十四——文件上传功能(二)
学习ASP.NET Core Razor 编程系列目录 学习ASP.NET Core Razor 编程系列一 学习ASP.NET Core Razor 编程系列二——添加一个实体 学习ASP.NET ...
- Netty实战十四之案例研究(一)
1.Droplr——构建移动服务 Bruno de Carvalho,首席架构师 在Droplr,我们在我的基础设施的核心部分.从我们的API服务器到辅助服务的各个部分都使用了Netty. 这是一个关 ...
- shiro实战系列(十四)之配置
Shiro 被设计成能够在任何环境下工作,从最简单的命令行应用程序到最大的的企业群集应用.由于环境的多样性,使得许多配置机制适用于它的配置. 一. 许多配置选项 Shiro的SecurityManag ...
- SpringCloud系列十四:实现容错的手段
1. 回顾 前面已用Eureka实现了微服务的注册与发现,Ribbon实现了客户端侧的负载均衡,Feign实现了声明式的API调用. 2. 实现容错的手段 如果服务提供者响应非常慢,那么消费者对提供者 ...
- WPF入门教程系列十四——依赖属性(四)
六.依赖属性回调.验证及强制值 我们通过下面的这幅图,简单介绍一下WPF属性系统对依赖属性操作的基本步骤: 借用一个常见的图例,介绍一下WPF属性系统对依赖属性操作的基本步骤: 第一步,确定Base ...
- Pandas系列(四)-文本数据处理
内容目录 1. 为什么要用str属性 2. 替换和分割 3. 提取子串 3.1 提取第一个匹配的子串 3.2 匹配所有子串 3.3 测试是否包含子串 3.4 生成哑变量 3.5 方法摘要 一.为什么要 ...
- 单点登录(十四)-----实战-----cas5.0.x登录mongodb验证方式常规的四种加密的思考和分析
我们在上一篇文章中已经讲解了cas4.2.X登录启用mongodb验证方式 单点登录(十三)-----实战-----cas4.2.X登录启用mongodb验证方式完整流程 但是密码是明文存储的,也就是 ...
随机推荐
- Yii2.0调用sql server存储过程并获取返回值
1.首先展示创建sql server存储过程的语句,创建一个简单的存储过程,测试用. SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO CREATE P ...
- Redhat安装Oracle 11g (转)
1.1 安装前准备 1.1.1 修改操作系统核心参数 在Root用户下执行以下步骤: 1.1.1.1 修改/etc/security/limits.conf文件 输入命令:vi /et ...
- LeetCode算法题-Longest Harmonious Subsequence(Java实现)
这是悦乐书的第270次更新,第284篇原创 01 看题和准备 今天介绍的是LeetCode算法题中Easy级别的第136题(顺位题号是594).我们定义一个和谐数组是一个数组,其最大值和最小值之间的差 ...
- AI 强化学习
强化学习(reinforcement learning,简称RL), agent policy state action 目标 最大化累计reward 参考链接: https://en.wikipe ...
- UI Automator 常用 API 整理
主要类: import android.support.test.uiautomator.UiDevice; 作用:设备封装类,测试过程中获取设备信息和设备交互. import android.sup ...
- Linux笔记-ps -aux的结果解析
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/flyingleo1981/article/details/7739490 ps 的参数说明ps 提供了很多的选项参数,常用的有以下几个: l 长格 ...
- Unable to start web server; nested exception is org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean.
SpringBoot启动时的异常信息如下: "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_161\bin\java" ......... com.fangxing ...
- SQL 无法连接服务器
错误信息:provider:SQL Network Interfaces, error:52-无法定位 LOCA Database Runtime 安装.请验证SQL Server Express是否 ...
- sqlalchemy常用
一.SQLAlchemy 创建表 from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base from sqlalchemy import Colu ...
- mysql 5.7 json
项目中使用的mysql5.6数据库,数据库表一张表中存的字段为blob类型的json串数据.性能压测中涉及该json串处理效率比较低,开发人员提到mysql5.7版本后json串提供了原生态的json ...
