TensorRT&Sample&Python[end_to_end_tensorflow_mnist]
本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的end_to_end_tensorflow_mnist例子的分析和介绍。
1 引言
假设当前路径为:
TensorRT-5.0.2.6/samples
其对应当前例子文件目录树为:
# tree python
python
├── common.py
├── end_to_end_tensorflow_mnist
│ ├── model.py
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ └── sample.py
2 基于tensorflow生成模型
其中只有2个文件:
- model:该文件包含简单的训练模型代码
- sample:该文件使用UFF mnist模型去创建一个TensorRT inference engine
首先介绍下model.py
# 该脚本包含一个简单的模型训练过程
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
'''main中第一步:获取数据集 '''
def process_dataset():
# 导入mnist数据集
# 手动下载aria2c -x 16 https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/mnist.npz
# 将mnist.npz移动到~/.keras/datasets/
# tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data会去读取~/.keras/datasets/mnist.npz,而不从网络下载
(x_train, y_train),(x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
# Reshape
NUM_TRAIN = 60000
NUM_TEST = 10000
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (NUM_TRAIN, 28, 28, 1))
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (NUM_TEST, 28, 28, 1))
return x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test
'''main中第二步:构建模型 '''
def create_model():
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
model.add(tf.keras.layers.InputLayer(input_shape=[28,28, 1]))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten())
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation=tf.nn.relu))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.softmax))
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
'''main中第五步:模型存储 '''
def save(model, filename):
output_names = model.output.op.name
sess = tf.keras.backend.get_session()
# freeze graph
frozen_graph = tf.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, sess.graph.as_graph_def(), [output_names])
# 移除训练的节点
frozen_graph = tf.graph_util.remove_training_nodes(frozen_graph)
# 保存模型
with open(filename, "wb") as ofile:
ofile.write(frozen_graph.SerializeToString())
def main():
''' 1 - 获取数据'''
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = process_dataset()
''' 2 - 构建模型'''
model = create_model()
''' 3 - 模型训练'''
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs = 5, verbose = 1)
''' 4 - 模型评估'''
model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
''' 5 - 模型存储'''
save(model, filename="models/lenet5.pb")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
在获得
models/lenet5.pb
之后,执行下述命令,将其转换成uff文件,输出结果如
'''该converter会显示关于input/output nodes的信息,这样你就可以用来在解析的时候进行注册;
本例子中,我们基于tensorflow.keras的命名规则,事先已知input/output nodes名称了 '''
[root@30d4bceec4c4 end_to_end_tensorflow_mnist]# convert-to-uff models/lenet5.pb
Loading models/lenet5.pb
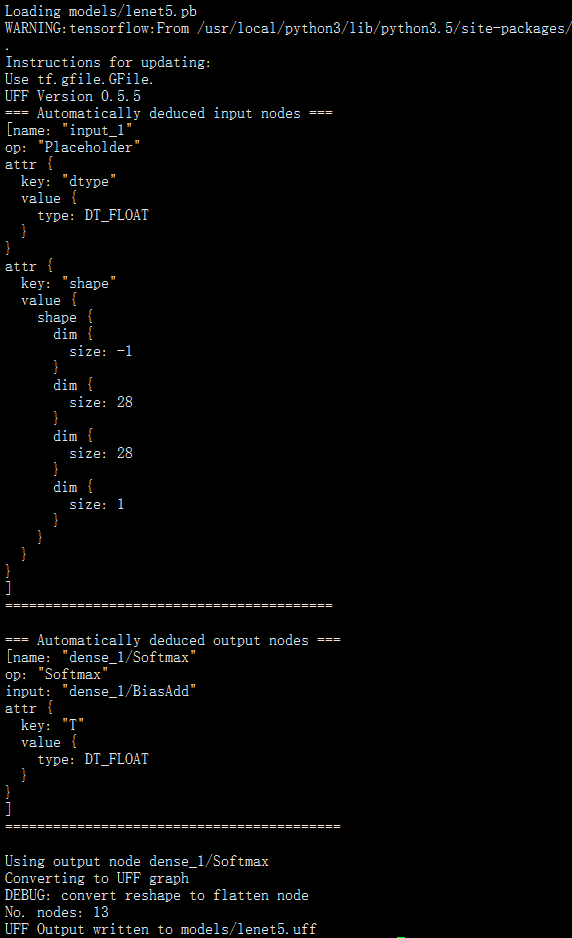
3 基于tensorflow的pb文件生成UFF并处理
# 该例子使用UFF MNIST 模型去创建一个TensorRT Inference Engine
from random import randint
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit # 该import会让pycuda自动管理CUDA上下文的创建和清理工作
import tensorrt as trt
import sys, os
# sys.path.insert(1, os.path.join(sys.path[0], ".."))
# import common
# 这里将common中的GiB和find_sample_data,allocate_buffers,do_inference等函数移动到该py文件中,保证自包含。
def GiB(val):
'''以GB为单位,计算所需要的存储值,向左位移10bit表示KB,20bit表示MB '''
return val * 1 << 30
def find_sample_data(description="Runs a TensorRT Python sample", subfolder="", find_files=[]):
'''该函数就是一个参数解析函数。
Parses sample arguments.
Args:
description (str): Description of the sample.
subfolder (str): The subfolder containing data relevant to this sample
find_files (str): A list of filenames to find. Each filename will be replaced with an absolute path.
Returns:
str: Path of data directory.
Raises:
FileNotFoundError
'''
# 为了简洁,这里直接将路径硬编码到代码中。
data_root = kDEFAULT_DATA_ROOT = os.path.abspath("/TensorRT-5.0.2.6/python/data/")
subfolder_path = os.path.join(data_root, subfolder)
if not os.path.exists(subfolder_path):
print("WARNING: " + subfolder_path + " does not exist. Using " + data_root + " instead.")
data_path = subfolder_path if os.path.exists(subfolder_path) else data_root
if not (os.path.exists(data_path)):
raise FileNotFoundError(data_path + " does not exist.")
for index, f in enumerate(find_files):
find_files[index] = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(data_path, f))
if not os.path.exists(find_files[index]):
raise FileNotFoundError(find_files[index] + " does not exist. ")
if find_files:
return data_path, find_files
else:
return data_path
#-----------------
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
class ModelData(object):
MODEL_FILE = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "models/lenet5.uff")
INPUT_NAME ="input_1"
INPUT_SHAPE = (1, 28, 28)
OUTPUT_NAME = "dense_1/Softmax"
'''main中第二步:构建engine'''
def build_engine(model_file):
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, \
builder.create_network() as network, \
trt.UffParser() as parser:
builder.max_workspace_size = GiB(1)
# 解析 Uff 网络
parser.register_input(ModelData.INPUT_NAME, ModelData.INPUT_SHAPE)
parser.register_output(ModelData.OUTPUT_NAME)
parser.parse(model_file, network)
# 构建并返回一个engine
return builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
'''main中第三步 '''
def allocate_buffers(engine):
inputs = []
outputs = []
bindings = []
stream = cuda.Stream()
for binding in engine:
size = trt.volume(engine.get_binding_shape(binding)) * engine.max_batch_size
dtype = trt.nptype(engine.get_binding_dtype(binding))
# 分配host和device端的buffer
host_mem = cuda.pagelocked_empty(size, dtype)
device_mem = cuda.mem_alloc(host_mem.nbytes)
# 将device端的buffer追加到device的bindings.
bindings.append(int(device_mem))
# Append to the appropriate list.
if engine.binding_is_input(binding):
inputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))
else:
outputs.append(HostDeviceMem(host_mem, device_mem))
return inputs, outputs, bindings, stream
'''main中第四步 '''
# 从pagelocked_buffer.中读取测试样本
def load_normalized_test_case(data_path, pagelocked_buffer, case_num=randint(0, 9)):
test_case_path = os.path.join(data_path, str(case_num) + ".pgm")
# Flatten该图像成为一个1维数组,然后归一化,并copy到host端的 pagelocked内存中.
img = np.array(Image.open(test_case_path)).ravel()
np.copyto(pagelocked_buffer, 1.0 - img / 255.0)
return case_num
'''main中第五步:执行inference '''
# 该函数可以适应多个输入/输出;输入和输出格式为HostDeviceMem对象组成的列表
def do_inference(context, bindings, inputs, outputs, stream, batch_size=1):
# 将数据移动到GPU
[cuda.memcpy_htod_async(inp.device, inp.host, stream) for inp in inputs]
# 执行inference.
context.execute_async(batch_size=batch_size, bindings=bindings, stream_handle=stream.handle)
# 将结果从 GPU写回到host端
[cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(out.host, out.device, stream) for out in outputs]
# 同步stream
stream.synchronize()
# 返回host端的输出结果
return [out.host for out in outputs]
def main():
''' 1 - 寻找模型文件'''
data_path = find_sample_data(
description="Runs an MNIST network using a UFF model file",
subfolder="mnist")
model_file = ModelData.MODEL_FILE
''' 2 - 基于build_engine函数构建engine'''
with build_engine(model_file) as engine:
''' 3 - 分配buffer并创建一个流'''
inputs, outputs, bindings, stream = allocate_buffers(engine)
with engine.create_execution_context() as context:
''' 4 - 读取测试样本,并归一化'''
case_num = load_normalized_test_case(data_path, pagelocked_buffer=inputs[0].host)
''' 5 - 执行inference,do_inference函数会返回一个list类型,此处只有一个元素'''
[output] = do_inference(context, bindings=bindings, inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs, stream=stream)
pred = np.argmax(output)
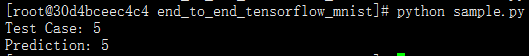
print("Test Case: " + str(case_num))
print("Prediction: " + str(pred))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
结果如:
TensorRT&Sample&Python[end_to_end_tensorflow_mnist]的更多相关文章
- TensorRT&Sample&Python[yolov3_onnx]
本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的yolov3_onnx例子的分析和介绍. 本例子展示一个完整的ONNX的pipline,在tensorrt 5.0的ONNX-TensorRT ...
- TensorRT&Sample&Python[uff_custom_plugin]
本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的uff_custom_plugin例子的分析和介绍. 本例子展示如何使用cpp基于tensorrt python绑定和UFF解析器进行编写pl ...
- TensorRT&Sample&Python[fc_plugin_caffe_mnist]
本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的fc_plugin_caffe_mnist例子的分析和介绍. 本例子相较于前面例子的不同在于,其还包含cpp代码,且此时依赖项还挺多.该例子展 ...
- TensorRT&Sample&Python[network_api_pytorch_mnist]
本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的network_api_pytorch_mnist例子的分析和介绍. 本例子直接基于pytorch进行训练,然后直接导出权重值为字典,此时并未 ...
- TensorRT&Sample&Python[introductory_parser_samples]
本文是基于TensorRT 5.0.2基础上,关于其内部的introductory_parser_samples例子的分析和介绍. 1 引言 假设当前路径为: TensorRT-5.0.2.6/sam ...
- tensorRT使用python进行网络定义
- Python API vs C++ API of TensorRT
Python API vs C++ API of TensorRT 本质上,C++ API和Python API应该在支持您的需求方面接近相同.pythonapi的主要优点是数据预处理和后处理都很容易 ...
- (原)pytorch中使用TensorRT
转载请注明出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/11332155.html 代码网址: https://github.com/darkknightzh/ ...
- 基于TensorRT 3的自动驾驶快速INT8推理
基于TensorRT 3的自动驾驶快速INT8推理 Fast INT8 Inference for Autonomous Vehicles with TensorRT 3 自主驾驶需要安全性,需要一种 ...
随机推荐
- .NET快速信息化系统开发框架 V3.2 -> WinForm“组织机构管理”界面组织机构权限管理采用新的界面,操作权限按模块进行展示
对于某些大型的企业.信息系统,涉及的组织机构较多,模块多.操作权限也多,对用户或角色一一设置模块.操作权限等比较繁琐.我们可以直接对某一组织机构进行权限的设置,这样设置后,同一组织机构的用户就可以拥有 ...
- Magicodes.WeiChat——使用OAuth 2.0获取微信用户信息
使用Magicodes.WeiChat,可以很方便的获取到微信用户的信息.在使用OAuth 2.0之前,你先需要做以下操作: 1)在开发者中心修改[网页授权获取用户基本信息],在弹出的界面输入自己的根 ...
- kubernetes学习01—kubernetes介绍
本文收录在容器技术学习系列文章总目录 一.简介 1.Kubernetes代码托管在GitHub上:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/. 2.Kubern ...
- Android ios嵌套web页面
我们现在做一个活动页面,Android和ios的活动页面用web来做,方便更改,下面有几个小问题: 1.在Android和ios中,虽然web上面可以存localstorage,但是到了Android ...
- [MySQL] mysql的事务隔离和幻读和死锁问题
1.系统要通过严格的ACID测试,ACID表示原子性/一致性/隔离性/持久性原子性:一个事务必须被视为一个不可分割的最小工作单元一致性:数据库总是从一个一致性的状态转换到另外一个一致性的状态隔离性:通 ...
- 理解sort()函数的排序原理
看了很多关于sort()函数的定义和解释还是不太清楚,尤其是初学者很容易看懵,这里讲讲自己是如何理解的. 首先,要理解sort()内部是利用递归进行冒泡排序的: 例如: var arr = [1, 5 ...
- 【代码笔记】Web-CSS-CSS 语法
一,效果图. 二,代码. <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> ...
- Docker 创建 Jira Core(Jira SoftWare) 7.12.3 中文版
目录 目录 1.介绍 1.1.什么是 JIRA Core? 1.2.什么是 JIRA SoftWare 2.JIRA 的官网在哪里? 3.如何下载安装? 4.对 JIRA 进行配置 4.1.JIRA ...
- spring学习总结——装配Bean学习四(导入和混合配置)
情景:在典型的Spring应用中,我们可能会同时使用自动化和显式配置(JavaConfig)或者XML配置,幸好在Spring中,这些配置方案都不是互斥的.你尽可以将JavaConfig的组件扫描和自 ...
- SQL Sever AlwaysOn的数据同步原理
1. SQL Server AlwaysOn数据同步基本工作 AlwaysOn 副本同步需要完成三件事: 1.把主副本上发生的数据变化记录下来. 2.把这些记录传输到各个辅助副本. 3.把数据变化在辅 ...
