算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——2.5
写在前面
整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp
查找更方便的版本见:https://alg4.ikesnowy.com/
这一节内容可能会用到的库文件有 SortApplication,同样在 Github 上可以找到。
善用 Ctrl + F 查找题目。
习题&题解
2.5.1
解答
如果比较的两个 String 引用的是同一个对象,那么就直接返回相等,不必再逐字符比较。
一个例子:
string s = "abcabc";string p = s;Console.WriteLine(s.CompareTo(p));
2.5.2
解答
将字符串数组 keywords 按照长度排序,于是 keywords[0] 就是最短的字符串。
组合词的最短长度 minLength = 最短字符串的长度 * 2 = keywords[0] * 2。
先找到第一个长度大于等于 minLength 的字符串,下标为 canCombine。
我们从 canCombine 开始,一个个检查是否是组合词。
如果 keywords[canCombine] 是一个组合词,那么它一定是由位于它之前的某两个字符串组合而成的。
组合词的长度一定等于被组合词的长度之和,因此我们可以通过长度快速判断有可能的组合词。
现在题目转化为了如何解决 ThreeSum 问题,即求 a + b = c 型问题,根据 1.4.41 中的解法求解。
keywords[canCombine] 的长度已知,i 从 0 到 canCombine 之间循环,
用二分查找确认 i 到 canCombine 之间有没有符合条件的字符串,注意多个字符串可能长度相等。
代码
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace _2._5._2{/** 2.5.2** 编写一段程序,从标准输入读入一列单词并打印出其中所有由两个单词组成的组合词。* 例如,如果输入的单词为 after、thought 和 afterthought,* 那么 afterthought 就是一个组合词。**/class Program{/// <summary>/// 根据字符串长度进行比较。/// </summary>class StringLengthComparer : IComparer<string>{public int Compare(string x, string y){return x.Length.CompareTo(y.Length);}}/// <summary>/// 二分查找,返回符合条件的最小下标。/// </summary>/// <param name="keys">搜索范围。</param>/// <param name="length">搜索目标。</param>/// <param name="lo">起始下标。</param>/// <param name="hi">终止下标。</param>/// <returns></returns>static int BinarySearch(string[] keys, int length, int lo, int hi){while (lo <= hi){int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;if (keys[mid].Length == length){while (mid >= lo && keys[mid].Length == length)mid--;return mid + 1;}else if (length > keys[mid].Length)lo = mid + 1;elsehi = mid - 1;}return -1;}static void Main(string[] args){string[] keywords = Console.ReadLine().Split(' ');Array.Sort(keywords, new StringLengthComparer());int minLength = keywords[0].Length * 2;// 找到第一个大于 minLength 的字符串int canCombine = 0;while (keywords[canCombine].Length < minLength &&canCombine < keywords.Length)canCombine++;// 依次测试是否可能while (canCombine < keywords.Length){int sum = keywords[canCombine].Length;for (int i = 0; i < canCombine; i++){int start = BinarySearch(keywords, sum - keywords[i].Length, i, canCombine);if (start != -1){while (keywords[start].Length + keywords[i].Length == sum){if (keywords[start] + keywords[i] == keywords[canCombine])Console.WriteLine(keywords[canCombine] + " = " + keywords[start] + " + " + keywords[i]);else if (keywords[i] + keywords[start] == keywords[canCombine])Console.WriteLine(keywords[canCombine] + " = " + keywords[i] + " + " + keywords[start]);start++;}}}canCombine++;}}}}
2.5.3
解答
这样会破坏相等的传递性。
例如 a = 0.005, b=0.000, c=-0.005,则 a == b, c == b,但是 a != c。
2.5.4
解答
先排序,然后用书中的代码进行去重。
static string[] Dedup(string[] a){if (a.Length == 0)return a;string[] sorted = new string[a.Length];for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++){sorted[i] = a[i];}Array.Sort(sorted);// sorted = sorted.Distinct().ToArray();string[] distinct = new string[sorted.Length];distinct[0] = sorted[0];int j = 1;for (int i = 1; i < sorted.Length; i++){if (sorted[i].CompareTo(sorted[i - 1]) != 0)distinct[j++] = sorted[i];}return distinct;}
2.5.5
解答
因为选择排序会交换不相邻的元素。
例如:
B1 B2 AA B2 B1
此时 B1 和 B2 的相对位置被改变,如果将交换限定在相邻元素之间(插入排序)。
B1 B2 AB1 A B2A B2 B2
此时排序就是稳定的了。
2.5.6
解答
非递归官网实现见:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/23quicksort/QuickPedantic.java.html
原本是和快速排序一块介绍的,将数组重新排列,使得 a[k] 正好是第 k 小的元素,k 从 0 开始。
具体思路类似于二分查找,
先切分,如果切分位置小于 k,那么在右半部分继续切分,否则在左半部分继续切分。
直到切分位置正好等于 k,直接返回 a[k] 。
代码
/// <summary>/// 使 a[k] 变为第 k 小的数,k 从 0 开始。/// a[0] ~ a[k-1] 都小于等于 a[k], a[k+1]~a[n-1] 都大于等于 a[k]/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T">元素类型。</typeparam>/// <param name="a">需要调整的数组。</param>/// <param name="k">序号。</param>/// <param name="lo">起始下标。</param>/// <param name="hi">终止下标。</param>/// <returns></returns>static T Select<T>(T[] a, int k, int lo, int hi) where T : IComparable<T>{if (k > a.Length || k < 0)throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("select out of bound");if (lo >= hi)return a[lo];int i = Partition(a, lo, hi);if (i > k)return Select(a, k, lo, i - 1);else if (i < k)return Select(a, k, i + 1, hi);elsereturn a[i];}
另请参阅
2.5.7
解答
参考书中给出的快速排序性能分析方法(中文版 P186,英文版 P293)。
设 $ C_n $ 代表找出 $ n $ 个元素中的最小值所需要的比较次数。
一次切分需要 $ n+1 $ 次比较,下一侧的元素个数从 $ 0 $ 到 $ n-1 $ 都有可能,
于是根据全概率公式,有:
C_n&=&\frac {1}{n} (n+1) +\frac{1}{n} (n+1+C_1)+ \cdots + \frac{1}{n}(n+1+C_{n-1}) \\
C_n&=&n+1+\frac{1}{n}(C_1+C_2+\cdots+C_{n-1}) \\
nC_n&=&n(n+1)+(C_1+C_2+\cdots+C_{n-1}) \\
nC_n-(n-1)C_{n-1}&=&2n+C_{n-1} \\
nC_n&=&2n+nC_{n-1} \\
C_n&=&2+C_{n-1} \\
C_n &=& C_1+2(n-1) \\
C_n &=& 2n-2 < 2n
\end{eqnarray*}
\]
测试结果符合我们的预期。
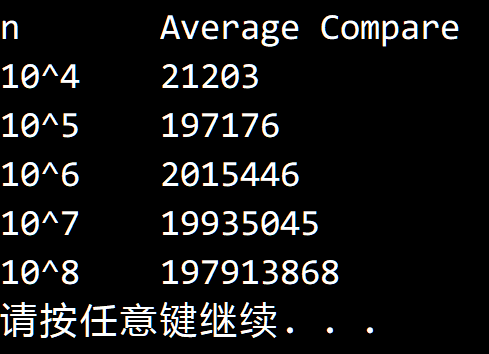
附加:找出第 $ k $ 小的数平均需要的比较次数。
类似的方法也在计算快速排序的平均比较次数时使用,见题 2.3.14。
首先和快速排序类似,select 方法的所有元素比较都发生在切分过程中。
接下来考虑第 $ i $ 小和第 $ j $ 小的元素($ x_i $ ,$ x_j $),
当枢轴选为 $ x_i $ 或 $ x_j $ 时,它们会发生比较;
如果枢轴选为 $ x_i $ 和 $ x_j $ 之间的元素,那么它们会被切分到两侧,不可能发生比较;
如果枢轴选为小于 $ x_i $ 或大于 $ x_j $ 的元素,它们会被切分到同一侧,进入下次切分。
但要注意的是,select 只会对切分的一侧进行再切分,另一侧会被抛弃(快速排序则是两侧都会再切分)。
因此我们需要将第 $ k $ 小的数 $ x_k $ 纳入考虑。
如果 $ x_k>x_j>x_i $ ,且枢轴选了 $ x_k $ 到 $ x_j $ 之间的元素,切分后 $ x_i $ 和 $ x_j $ 会被一起抛弃,不发生比较。
如果 $ x_j > x_k > x_i $ ,枢轴的选择情况和快速排序一致。
如果 $ x_j > x_i > x_k $ ,且枢轴选了 $ x_i $ 到 $ x_k $ 之间的元素,切分后 $ x_i $ 和 $ x_j $ 会被一起抛弃,不发生比较。
综上我们可以得到 $ x_i $ 和 $ x_j $ 之间发生比较的概率 $ \frac{2}{\max(j-i+1, k-i+1,j-k+1)} $ 。
我们利用线性规划的知识把最大值函数的区域画出来,如下图所示:
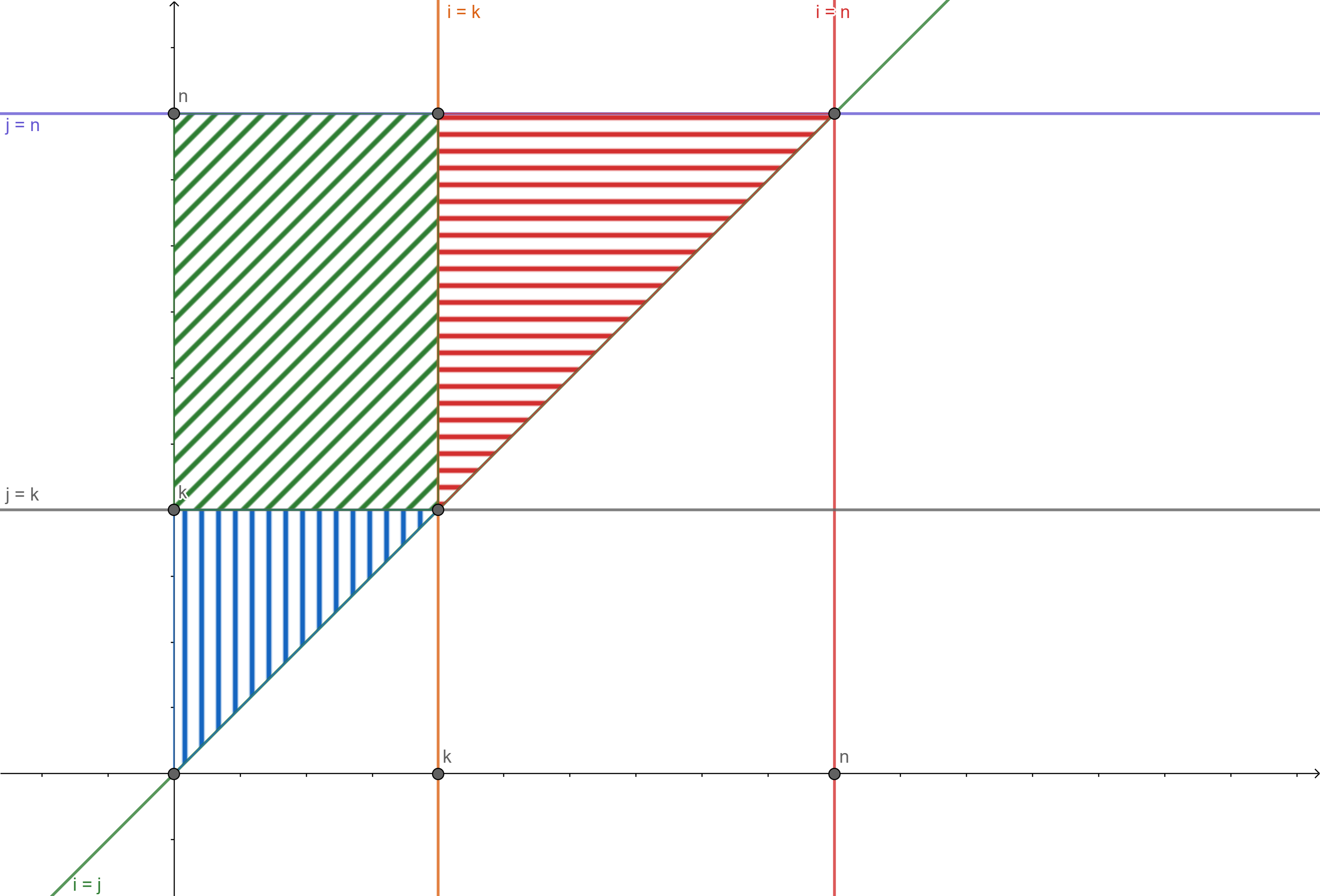

对蓝色区域积分得:
&&\int_{0}^{k} dj \int_{0}^{j} \frac{2}{j-k+1}\ di \\
&=& 2 \int_{0}^{k} \frac{j}{j-k+1} \ dj \\
&<& 2 k
\end{eqnarray*}
\]
对红色区域积分得:
&& \int_{k}^{n} di \int_{i}^{n} \frac{2}{k-i+1} dj \\
&=& 2\int_{k}^{n} \frac{n-i}{k-i+1} di \\
&<& 2(n-k)
\end {eqnarray*}
\]
对绿色区域积分得:
&& \int_{0}^{k}di\int_{k}^{n} \frac{2}{j-i+1} dj \\
&<& \int_{0}^{k}di\int_{k}^{n} \frac{2}{j-i} dj \\
&=& 2\int_{0}^{k} \ln (n-i) di - 2\int_{0}^{k} \ln(k-i)di \\
&=& 2i\ln(n-i) \bigg|_{0}^{k} + 2\int_{0}^{k}\frac{i}{n-i} di -
\left[ i\ln(k-i) \bigg|_{0}^{k} + 2\int_{0}^{k} \frac{i}{k-i} di \right] \\
&=& 2k\ln(n-k)+2\int_{0}^{k}\frac{n}{n-i}-1 \ di -2\int_{0}^{k} \frac{k}{k-i}-1 \ di \\
&=& 2k\ln(n-k)+2\int_{0}^{k}\frac{n}{n-i} \ di -2k - 2\int_{0}^{k} \frac{k}{k-i} \ di +2k \\
&=& 2k\ln(n-k) -2n\ln(n-i) \bigg|_{0}^{k} +2k\ln(k-i)\bigg|_{0}^{k} \\
&=& 2k\ln(n-k)-2n\ln(n-k)+2n\ln n -2k\ln k
\end{eqnarray*}
\]
全部相加得到:
&& 2k+2(n-k)+2k\ln(n-k)-2n\ln(n-k)+2n\ln n -2k\ln k \\
&=& 2n + 2k\ln(n-k)-2n\ln(n-k)+2n\ln n -2k\ln k \\
&=& 2n + 2k\ln(n-k)-2n\ln(n-k)+2n\ln n-2k\ln k +2k\ln n-2k\ln n \\
&=& 2n + 2k\ln n-2k\ln k+2n\ln n-2n\ln(n-k) - 2k\ln n + 2k\ln(n-k) \\
&=& 2n + 2k\ln \left(\frac{n}{k} \right)+2n\ln\left(\frac{n}{n-k} \right) - 2k\ln\left(\frac{n}{n-k} \right) \\
&=& 2n+2k\ln\left(\frac{n}{k}\right)+2(n-k)\ln\left(\frac{n}{n-k} \right)
\end{eqnarray*}
\]
于是得到了命题 U 中的结果(中文版 P221,英文版 P347)。
另请参阅
Blum-style analysis of Quickselect
2.5.8
解答
官网实现见:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/Frequency.java.html
用到的数据来自(右键另存为):https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/tale.txt
先把所有单词读入,然后排序,一样的单词会被放在一起,
接下来遍历一遍记录每个单词出现的次数。
然后按照频率排序,倒序输出即可。
定义了一个嵌套类 Record 来记录单词及出现次数,实现的比较器按照出现次数排序。
class Record : IComparable<Record>{public string Key { get; set; } // 单词public int Value { get; set; } // 频率public Record(string key, int value){this.Key = key;this.Value = value;}public int CompareTo(Record other){return this.Value.CompareTo(other.Value);}}
测试结果(前 1% 的单词):

代码
using System;using System.IO;namespace _2._5._8{class Program{class Record : IComparable<Record>{public string Key { get; set; } // 单词public int Value { get; set; } // 频率public Record(string key, int value){this.Key = key;this.Value = value;}public int CompareTo(Record other){return this.Value.CompareTo(other.Value);}}static void Main(string[] args){string filename = "tale.txt";StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead(filename));string[] a = sr.ReadToEnd().Split(new char[] { ' ', '\n', '\r' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);Array.Sort(a);Record[] records = new Record[a.Length];string word = a[0];int freq = 1;int m = 0;for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++){if (!a[i].Equals(word)){records[m++] = new Record(word, freq);word = a[i];freq = 0;}freq++;}records[m++] = new Record(word, freq);Array.Sort(records, 0, m);// 只显示频率为前 1% 的单词for (int i = m - 1; i >= m * 0.99; i--)Console.WriteLine(records[i].Value + " " + records[i].Key);}}}
2.5.9
解答
右侧给出的是道琼斯指数,官方数据(右键另存为):DJI
设计一个类保存日期和交易量,然后按照交易量排序即可。
/// <summary>/// 道琼斯指数。/// </summary>class DJIA : IComparable<DJIA>{public string Date { get; set; }public long Volume { get; set; }public DJIA(string date, long vol){this.Date = date;this.Volume = vol;}public int CompareTo(DJIA other){return this.Volume.CompareTo(other.Volume);}}
2.5.10
解答
用一个 int 数组来保存版本号,按顺序进行比较。
如果两个版本号不等长且前缀相同,那么较长的版本号比较高,例如:1.2.1 和 1.2。
using System;namespace _2._5._10{/// <summary>/// 版本号。/// </summary>class Version : IComparable<Version>{private int[] versionNumber;public Version(string version){string[] versions = version.Split('.');this.versionNumber = new int[versions.Length];for (int i = 0; i < versions.Length; i++){this.versionNumber[i] = int.Parse(versions[i]);}}public int CompareTo(Version other){for (int i = 0; i < this.versionNumber.Length && i < other.versionNumber.Length; i++){if (this.versionNumber[i].CompareTo(other.versionNumber[i]) != 0)return this.versionNumber[i].CompareTo(other.versionNumber[i]);}return this.versionNumber.Length.CompareTo(other.versionNumber.Length);}public override string ToString(){string result = "";for (int i = 0; i < this.versionNumber.Length - 1; i++){result += this.versionNumber[i] + ".";}result += this.versionNumber[this.versionNumber.Length - 1].ToString();return result;}}}
2.5.11
解答
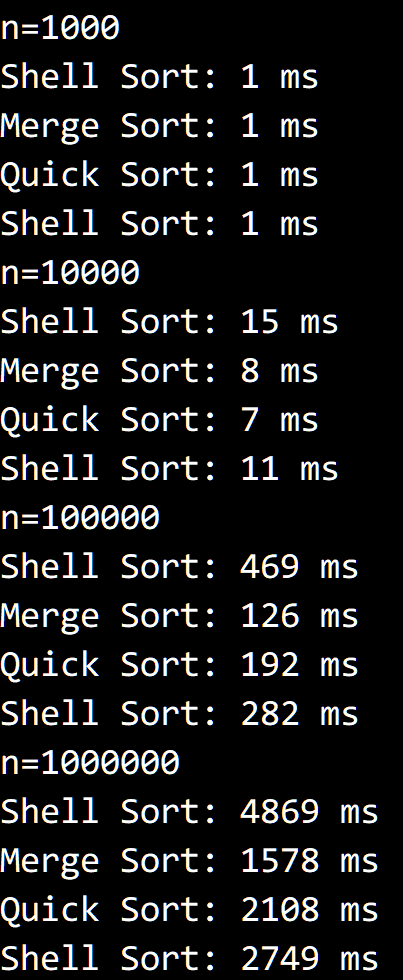
结果如下,其中快速排序去掉了一开始打乱数组的步骤:
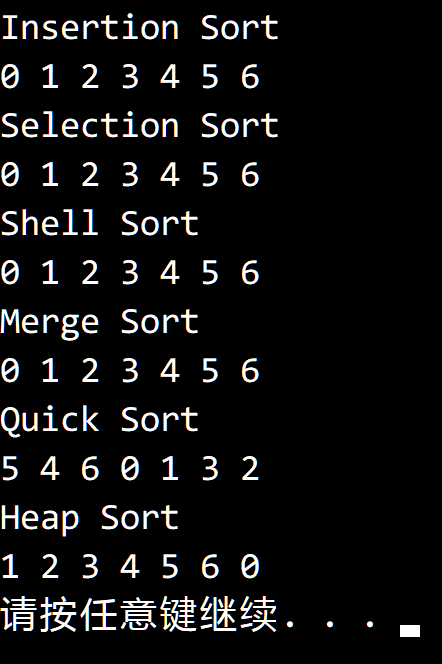
只有快速排序和堆排序会进行交换,剩下四种排序都不会进行交换。
插入排序在排序元素完全相同的数组时只会进行一次遍历,不会交换。
选择排序第 i 次找到的最小值就是 a[i] ,只会让 a[i] 和 a[i] 交换,不会影响顺序。
希尔排序和插入排序类似,每轮排序都不会进行交换。
归并排序是稳定的,就本例而言,只会从左到右依次归并,不会发生顺序变化。
快速排序在遇到相同元素时会交换,因此顺序会发生变化,且每次都是对半切分。
堆排序在删除最大元素时会将第一个元素和最后一个元素交换,使元素顺序发生变化。
代码
using System;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._11{class Program{/// <summary>/// 用来排序的元素,记录有自己的初始下标。/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>class Item<T> : IComparable<Item<T>> where T : IComparable<T>{public int Index;public T Key;public Item(int index, T key){this.Index = index;this.Key = key;}public int CompareTo(Item<T> other){return this.Key.CompareTo(other.Key);}}static void Main(string[] args){// 插入排序Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort");Test(new InsertionSort(), 7, 1);// 选择排序Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort");Test(new SelectionSort(), 7, 1);// 希尔排序Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort");Test(new ShellSort(), 7, 1);// 归并排序Console.WriteLine("Merge Sort");Test(new MergeSort(), 7, 1);// 快速排序Console.WriteLine("Quick Sort");QuickSortAnalyze quick = new QuickSortAnalyze{NeedShuffle = false,NeedPath = false};Test(quick, 7, 1);// 堆排序Console.WriteLine("Heap Sort");Item<int>[] array = new Item<int>[7];for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)array[i] = new Item<int>(i, 1);Heap.Sort(array);for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)Console.Write(array[i].Index + " ");Console.WriteLine();}static void Test(BaseSort sort, int n, int constant){Item<int>[] array = new Item<int>[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)array[i] = new Item<int>(i, constant);sort.Sort(array);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)Console.Write(array[i].Index + " ");Console.WriteLine();}}}
另请参阅
2.5.12
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/SPT.java.html
把任务按照处理时间升序排序即可。
建立 Job 类,保存任务的名称和处理时间,并实现了 IConparable<Job> 接口。
class Job : IComparable<Job>{public string Name;public double Time;public Job(string name, double time){this.Name = name;this.Time = time;}public int CompareTo(Job other){return this.Time.CompareTo(other.Time);}}
代码
using System;namespace _2._5._12{class Program{class Job : IComparable<Job>{public string Name;public double Time;public Job(string name, double time){this.Name = name;this.Time = time;}public int CompareTo(Job other){return this.Time.CompareTo(other.Time);}}static void Main(string[] args){// 官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/SPT.java.htmlint n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());Job[] jobs = new Job[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){string[] input = Console.ReadLine().Split(' ');jobs[i] = new Job(input[0], double.Parse(input[1]));}Array.Sort(jobs);for (int i = 0; i < jobs.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(jobs[i].Name + " " + jobs[i].Time);}}}}
2.5.13
解答
官方解答见:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/LPT.java.html
使用上题的 Job 类,在本题建立 Processor 类来代表处理器,定义如下:
class Processor : IComparable<Processor>{private List<Job> jobs = new List<Job>();private double busyTime = 0;public Processor() { }public void Add(Job job){this.jobs.Add(job);this.busyTime += job.Time;}public int CompareTo(Processor other){return this.busyTime.CompareTo(other.busyTime);}public override string ToString(){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();Job[] nowList = this.jobs.ToArray();for (int i = 0; i < nowList.Length; i++){sb.AppendLine(nowList[i].Name + " " + nowList[i].Time);}return sb.ToString();}}
按照读入所有的任务并排序,再将所有的处理器放进一个最小堆里。
从最小堆取出任务最轻的处理器,按取耗时最长的任务分配给它,再将它放回最小堆中。
最后依次打印处理器的任务分配即可。
代码
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Text;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._13{class Program{class Job : IComparable<Job>{public string Name;public double Time;public Job(string name, double time){this.Name = name;this.Time = time;}public int CompareTo(Job other){return this.Time.CompareTo(other.Time);}}class Processor : IComparable<Processor>{private List<Job> jobs = new List<Job>();private double busyTime = 0;public Processor() { }public void Add(Job job){this.jobs.Add(job);this.busyTime += job.Time;}public int CompareTo(Processor other){return this.busyTime.CompareTo(other.busyTime);}public override string ToString(){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();Job[] nowList = this.jobs.ToArray();for (int i = 0; i < nowList.Length; i++){sb.AppendLine(nowList[i].Name + " " + nowList[i].Time);}return sb.ToString();}}static void Main(string[] args){int processorNum = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());int jobNum = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());Job[] jobs = new Job[jobNum];for (int i = 0; i < jobNum; i++){string[] jobDesc = Console.ReadLine().Split(' ');jobs[i] = new Job(jobDesc[0], double.Parse(jobDesc[1]));}Array.Sort(jobs);MinPQ<Processor> processors = new MinPQ<Processor>(processorNum);for (int i = 0; i < processorNum; i++){processors.Insert(new Processor());}for (int i = jobs.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--){Processor min = processors.DelMin();min.Add(jobs[i]);processors.Insert(min);}while (!processors.IsEmpty()){Console.WriteLine(processors.DelMin());}}}}
另请参阅
2.5.14
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/Domain.java.html
按照逆域名排序,例如输入的是 com.google 和 com.apple ,
比较的时候是按照 google.com 和 apple.com 进行比较的。
排序结果自然是 apple.com, google.com。
编写的 Domain 类,CompareTo() 中是按照倒序进行比较的。
using System;using System.Text;namespace _2._5._14{/// <summary>/// 域名类。/// </summary>class Domain : IComparable<Domain>{private string[] fields;private int n;/// <summary>/// 构造一个域名。/// </summary>/// <param name="url">域名的 url。</param>public Domain(string url){this.fields = url.Split('.');this.n = this.fields.Length;}public int CompareTo(Domain other){int minLength = Math.Min(this.n, other.n);for (int i = 0; i < minLength; i++){int c = this.fields[minLength - i - 1].CompareTo(other.fields[minLength - i - 1]);if (c != 0)return c;}return this.n.CompareTo(other.n);}public override string ToString(){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < this.fields.Length; i++){if (i != 0)sb.Append('.');sb.Append(this.fields[i]);}return sb.ToString();}}}
代码
using System;namespace _2._5._14{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Domain[] domains = new Domain[5];domains[0] = new Domain("edu.princeton.cs");domains[1] = new Domain("edu.princeton.ee");domains[2] = new Domain("com.google");domains[3] = new Domain("edu.princeton");domains[4] = new Domain("com.apple");Array.Sort(domains);for (int i = 0; i < domains.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(domains[i]);}}}}
2.5.15
解答
利用上一题的逆域名排序将域名相同的电子邮件分在一起。
代码
using System;namespace _2._5._15{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){// 利用上一题的逆域名排序,将相同的域名放在一起。Domain[] emails = new Domain[5];emails[0] = new Domain("wayne@cs.princeton.edu");emails[1] = new Domain("windy@apple.com");emails[2] = new Domain("rs@cs.princeton.edu");emails[3] = new Domain("ike@ee.princeton.edu");emails[4] = new Domain("admin@princeton.edu");Array.Sort(emails);for (int i = 0; i < emails.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(emails[i]);}}}}
2.5.16
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/California.java.html
数据来源:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/california-gov.txt
建立一个 string 的比较器,按照题目给定的顺序比较。
private class CandidateComparer : IComparer<string>{private static readonly string order = "RWQOJMVAHBSGZXNTCIEKUPDYFL";public int Compare(string x, string y){int n = Math.Min(x.Length, y.Length);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int a = order.IndexOf(x[i]);int b = order.IndexOf(y[i]);if (a != b)return a.CompareTo(b);}return x.Length.CompareTo(y.Length);}}
代码
using System;using System.IO;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace _2._5._16{class Program{// 官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/California.java.htmlprivate class CandidateComparer : IComparer<string>{private static readonly string order = "RWQOJMVAHBSGZXNTCIEKUPDYFL";public int Compare(string x, string y){int n = Math.Min(x.Length, y.Length);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int a = order.IndexOf(x[i]);int b = order.IndexOf(y[i]);if (a != b)return a.CompareTo(b);}return x.Length.CompareTo(y.Length);}}static void Main(string[] args){// 数据来源:https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/data/california-gov.txtStreamReader sr = new StreamReader(File.OpenRead("california-gov.txt"));string[] names =sr.ReadToEnd().ToUpper().Split(new char[] { '\n', '\r' },StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);Array.Sort(names, new CandidateComparer());for (int i = 0; i < names.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(names[i]);}}}}
2.5.17
解答
用一个 Wrapper 类包装准备排序的元素,在排序前同时记录元素的内容和下标。
随后对 Wrapper 数组排序,相同的元素会被放在一起,检查它们的下标是否是递增的。
如果不是递增的,则排序算法就是不稳定的;否则排序算法就有可能是稳定的。
(不稳定的排序算法也可能不改变相同元素的相对位置,比如用选择排序对有序数组排序)
代码
using System;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._17{class Program{class Wrapper<T> : IComparable<Wrapper<T>> where T : IComparable<T>{public int Index;public T Key;public Wrapper(int index, T elements){this.Index = index;this.Key = elements;}public int CompareTo(Wrapper<T> other){return this.Key.CompareTo(other.Key);}}static void Main(string[] args){int[] data = new int[] { 7, 7, 4, 8, 8, 5, 1, 7, 7 };MergeSort merge = new MergeSort();InsertionSort insertion = new InsertionSort();ShellSort shell = new ShellSort();SelectionSort selection = new SelectionSort();QuickSort quick = new QuickSort();Console.WriteLine("Merge Sort: " + CheckStability(data, merge));Console.WriteLine("Insertion Sort: " + CheckStability(data, insertion));Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort: " + CheckStability(data, shell));Console.WriteLine("Selection Sort: " + CheckStability(data, selection));Console.WriteLine("Quick Sort: " + CheckStability(data, quick));}static bool CheckStability<T>(T[] data, BaseSort sort) where T : IComparable<T>{Wrapper<T>[] items = new Wrapper<T>[data.Length];for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)items[i] = new Wrapper<T>(i, data[i]);sort.Sort(items);int index = 0;while (index < data.Length - 1){while (index < data.Length - 1 && items[index].Key.Equals(items[index + 1].Key)){if (items[index].Index > items[index + 1].Index)return false;index++;}index++;}return true;}}}
另请参阅
2.5.18
解答
用和上题一样的 Wrapper 类进行排序。
排序之后,相同的元素会被放在一起,形成一个个子数组。
根据事先保存的原始下标对它们进行排序,即可将不稳定的排序稳定化。
结果:
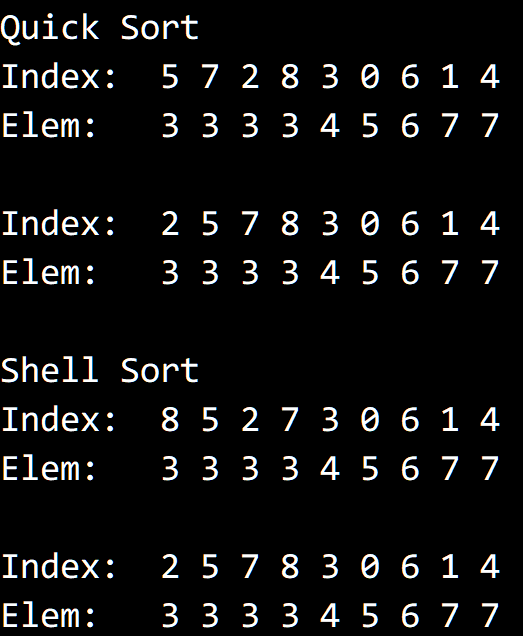
代码
using System;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._18{class Program{class Wrapper<T> : IComparable<Wrapper<T>> where T : IComparable<T>{public int Index;public T Key;public Wrapper(int index, T elements){this.Index = index;this.Key = elements;}public int CompareTo(Wrapper<T> other){return this.Key.CompareTo(other.Key);}}static void Main(string[] args){int[] data = new int[] { 5, 7, 3, 4, 7, 3, 6, 3, 3 };QuickSort quick = new QuickSort();ShellSort shell = new ShellSort();Console.WriteLine("Quick Sort");Stabilize(data, quick);Console.WriteLine();Console.WriteLine("Shell Sort");Stabilize(data, shell);}static void Stabilize<T>(T[] data, BaseSort sort) where T : IComparable<T>{Wrapper<T>[] items = new Wrapper<T>[data.Length];for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++){items[i] = new Wrapper<T>(i, data[i]);}sort.Sort(items);Console.Write("Index:\t");for (int i = 0; i < items.Length; i++){Console.Write(items[i].Index + " ");}Console.WriteLine();Console.Write("Elem:\t");for (int i = 0; i < items.Length; i++){Console.Write(items[i].Key + " ");}Console.WriteLine();Console.WriteLine();int index = 0;while (index < items.Length - 1){while (index < items.Length - 1 &&items[index].Key.Equals(items[index + 1].Key)){// 插入排序for (int j = index + 1; j > 0 && items[j].Index < items[j - 1].Index; j--){if (!items[j].Key.Equals(items[j - 1].Key))break;Wrapper<T> temp = items[j];items[j] = items[j - 1];items[j - 1] = temp;}index++;}index++;}Console.Write("Index:\t");for (int i = 0; i < items.Length; i++){Console.Write(items[i].Index + " ");}Console.WriteLine();Console.Write("Elem:\t");for (int i = 0; i < items.Length; i++){Console.Write(items[i].Key + " ");}Console.WriteLine();}}}
另请参阅
2.5.19
解答
官方解答:
Kendall Tau:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/KendallTau.java.html
Inversion:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort/Inversions.java.html
由书中 2.5.3.2 节得,两个数组之间的 Kendall Tau 距离即为两数组之间顺序不同的数对数目。
如果能够把其中一个数组变成标准排列(即 1,2,3,4... 这样的数组),
那么此时 Kendall Tau 距离就等于另一个数组中的逆序对数量。
现在我们来解决如何把一个数组 a 变成标准排列的方法。
也就是找到函数 $ f(x) $,使得 $ f(a[i])=i $ ,这样的函数其实就是数组 a 的逆数组。
如下图所示,逆数组 ainv 即为满足 ainv[a[i]] = i 的数组。
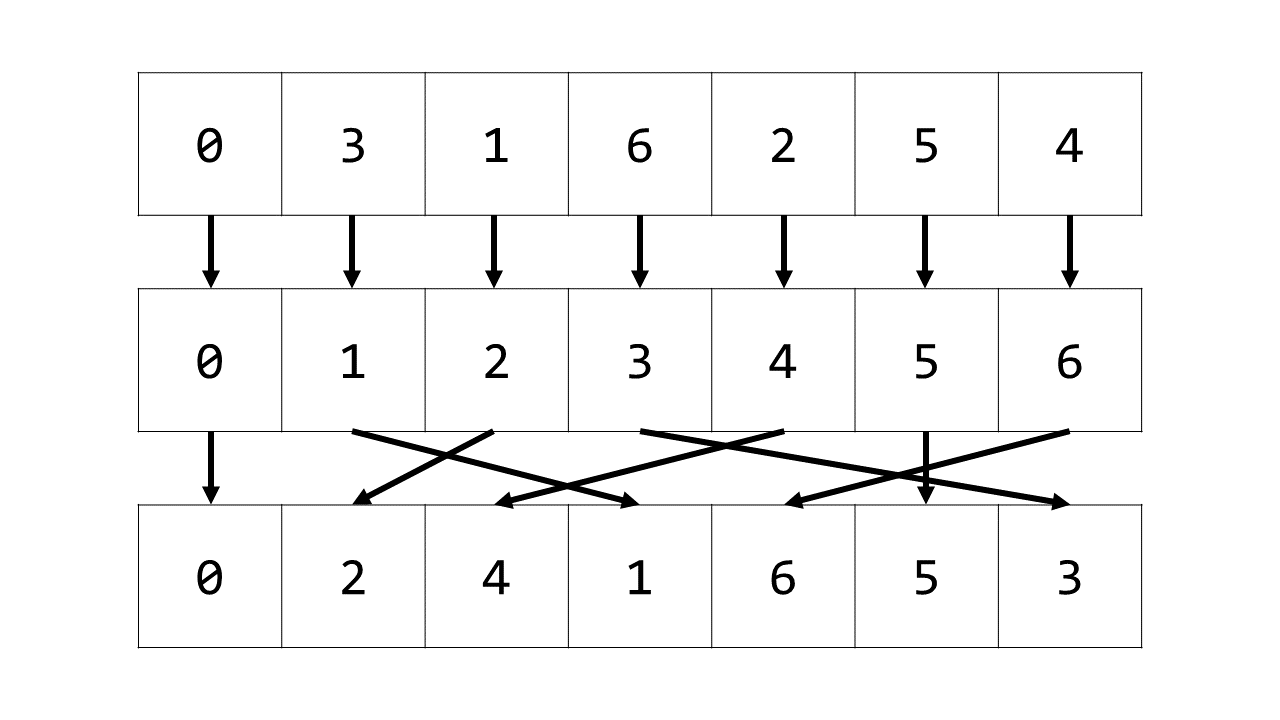
获得逆数组之后,对另一个数组 b 做同样的变换,令数组 bnew[i] = ainv[b[i]] 。
即 ainv[a[i]] = i, ainv[b[i]] = bnew[i] 。
于是问题转化为了 bnew 和标准排列之间的 Kendall Tau 距离,即 bnew 的逆序对数量。
逆序对数量的求法见题 2.2.19。
代码
using System;namespace _2._5._19{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){// 官方解答:// https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/KendallTau.java.html// https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort/Inversions.java.htmlint[] testA = { 0, 3, 1, 6, 2, 5, 4 };int[] testB = { 1, 0, 3, 6, 4, 2, 5 };Console.WriteLine(Distance(testA, testB));}public static long Distance(int[] a, int[] b){if (a.Length != b.Length)throw new ArgumentException("Array dimensions disagree");int n = a.Length;int[] ainv = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){ainv[a[i]] = i;}int[] bnew = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){bnew[i] = ainv[b[i]];}Inversions inversions = new Inversions();inversions.Count(bnew);return inversions.Counter;}}}
2.5.20
解答
我们以事件为单位进行处理,每个事件包含任务名,记录时刻和开始/结束标记。
随后按照时间从小到大排序,遍历事件数组。
设开始的时候机器空闲,设置计数器,作为当前正在运行的任务数量。
当遇到开始事件时,计数器加一;遇到结束事件时,计数器减一。
如果计数器加一之前计数器为 0,说明空闲状态结束,记录并更新空闲时间,当前时间为忙碌开始的时间。
如果计数器减一之后计数器为 0,说明忙碌状态结束,记录并更新忙碌时间,当前时间为空闲开始的时间。
测试结果:
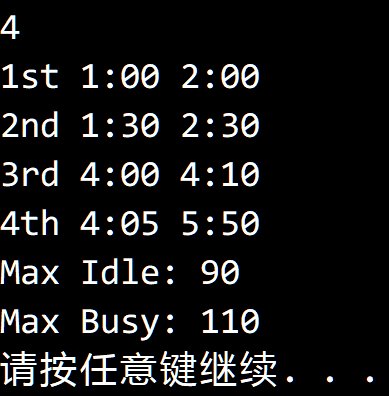
代码
using System;namespace _2._5._20{class Program{/// <summary>/// 任务变化事件。/// </summary>class JobEvent : IComparable<JobEvent>{public string JobName;public int Time;public bool IsFinished = false; // false = 开始,true = 结束public int CompareTo(JobEvent other){return this.Time.CompareTo(other.Time);}}static void Main(string[] args){// 输入格式: JobName 15:02 17:02int nowRunning = 0; // 正在运行的程序数量int maxIdle = 0;int maxBusy = 0;int items = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());JobEvent[] jobs = new JobEvent[items * 2];for (int i = 0; i < jobs.Length; i += 2){jobs[i] = new JobEvent();jobs[i + 1] = new JobEvent();jobs[i].IsFinished = false; // 开始事件jobs[i + 1].IsFinished = true; // 停止事件string[] record = Console.ReadLine().Split(new char[] { ' ', ':' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);jobs[i].JobName = record[0];jobs[i + 1].JobName = record[0];jobs[i].Time = int.Parse(record[1]) * 60 + int.Parse(record[2]);jobs[i + 1].Time = int.Parse(record[3]) * 60 + int.Parse(record[4]);}Array.Sort(jobs);// 事件处理int idleStart = 0;int busyStart = 0;for (int i = 0; i < jobs.Length; i++){// 启动事件if (!jobs[i].IsFinished){// 空闲状态结束if (nowRunning == 0){int idle = jobs[i].Time - idleStart;if (idle > maxIdle)maxIdle = idle;// 开始忙碌busyStart = jobs[i].Time;}nowRunning++;}else{nowRunning--;// 忙碌状态结束if (nowRunning == 0){int busy = jobs[i].Time - busyStart;if (busy > maxBusy)maxBusy = busy;// 开始空闲idleStart = jobs[i].Time;}}}Console.WriteLine("Max Idle: " + maxIdle);Console.WriteLine("Max Busy: " + maxBusy);}}}
2.5.21
解答
与之前的版本号比较十分类似,对数组进行包装,然后按照次序依次比较即可。
using System;using System.Text;namespace _2._5._21{class Vector : IComparable<Vector>{private int[] data;public int Length { get; set; }public Vector(int[] data){this.data = data;this.Length = data.Length;}public int CompareTo(Vector other){int maxN = Math.Max(this.Length, other.Length);for (int i = 0; i < maxN; i++){int comp = this.data[i].CompareTo(other.data[i]);if (comp != 0)return comp;}return this.Length.CompareTo(other.Length);}public override string ToString(){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < this.Length; i++){if (i != 0)sb.Append(' ');sb.Append(this.data[i]);}return sb.ToString();}}}
2.5.22
解答
建立最小堆和最大堆,最小堆保存卖家的报价,最大堆保存买家的报价。
如果最小堆中的最低卖出价低于最大堆的最高买入价,交易达成,交易份额较大的一方需要重新回到堆内。
测试结果:
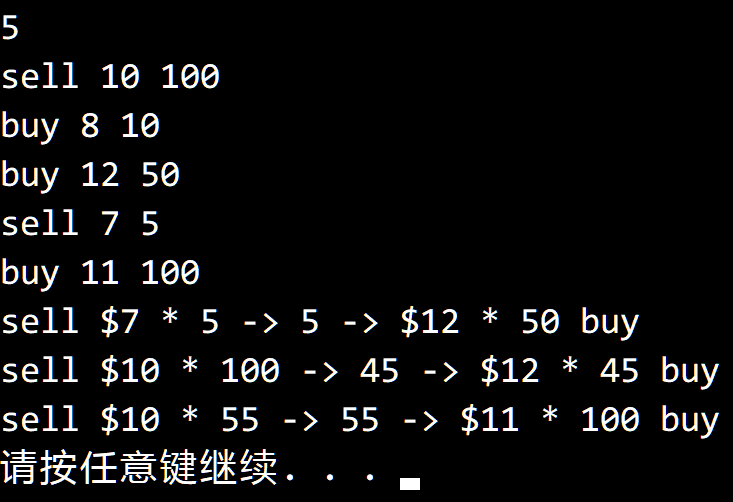
代码
using System;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._22{class Program{class Ticket : IComparable<Ticket>{public double Price;public int Share;public int CompareTo(Ticket other){return this.Price.CompareTo(other.Price);}}static void Main(string[] args){// 输入格式: buy 20.05 100MaxPQ<Ticket> buyer = new MaxPQ<Ticket>();MinPQ<Ticket> seller = new MinPQ<Ticket>();int n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){Ticket ticket = new Ticket();string[] item = Console.ReadLine().Split(' ');ticket.Price = double.Parse(item[1]);ticket.Share = int.Parse(item[2]);if (item[0] == "buy")buyer.Insert(ticket);elseseller.Insert(ticket);}while (!buyer.IsEmpty() && !seller.IsEmpty()){if (buyer.Max().Price < seller.Min().Price)break;Ticket buy = buyer.DelMax();Ticket sell = seller.DelMin();Console.Write("sell $" + sell.Price + " * " + sell.Share);if (buy.Share > sell.Share){Console.WriteLine(" -> " + sell.Share + " -> $" + buy.Price + " * " + buy.Share + " buy");buy.Share -= sell.Share;buyer.Insert(buy);}else if (buy.Share < sell.Share){sell.Share -= buy.Share;seller.Insert(sell);Console.WriteLine(" -> " + buy.Share + " -> $" + buy.Price + " * " + buy.Share + " buy");}else{Console.WriteLine(" -> " + sell.Share + " -> $" + buy.Price + " * " + buy.Share + " buy");}}}}}
另请参阅
2.5.23
解答
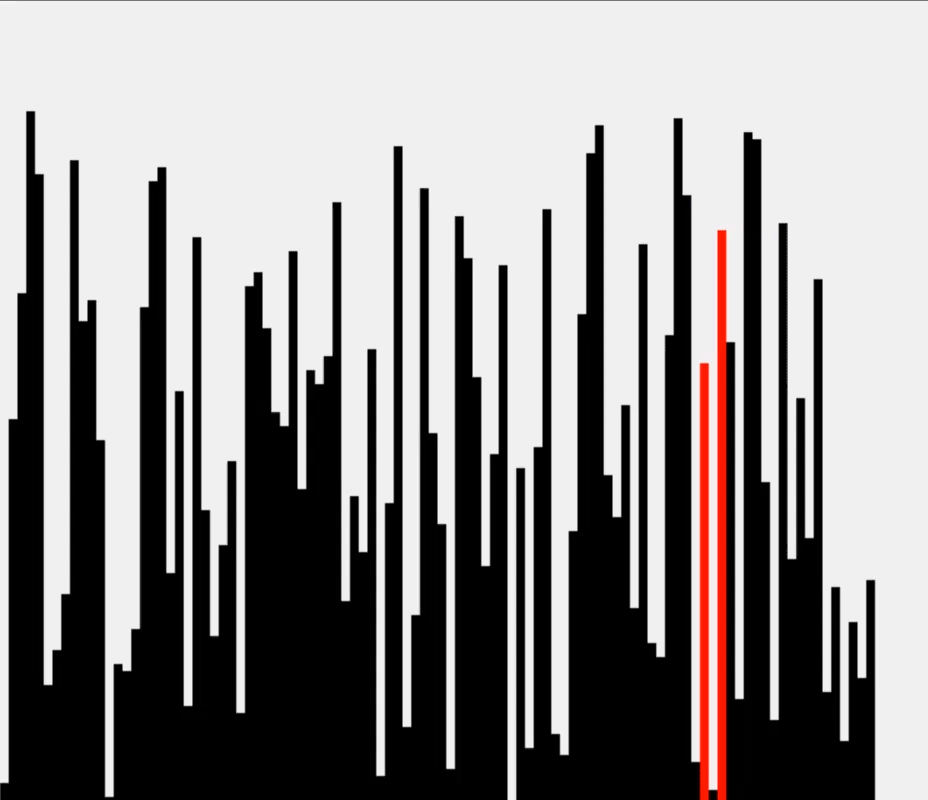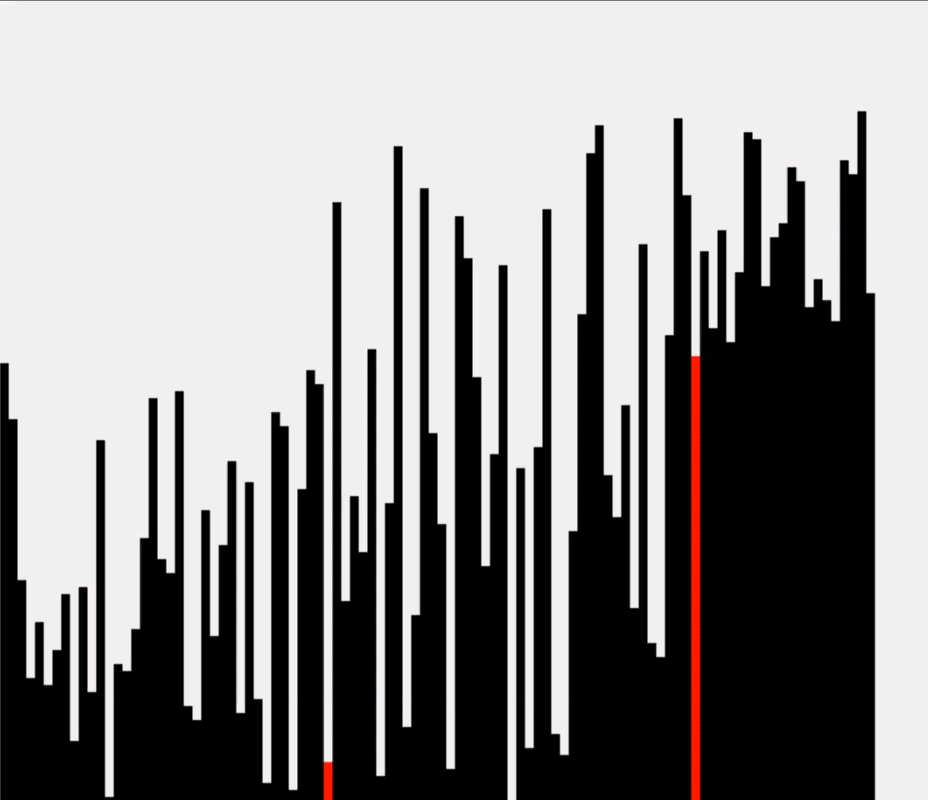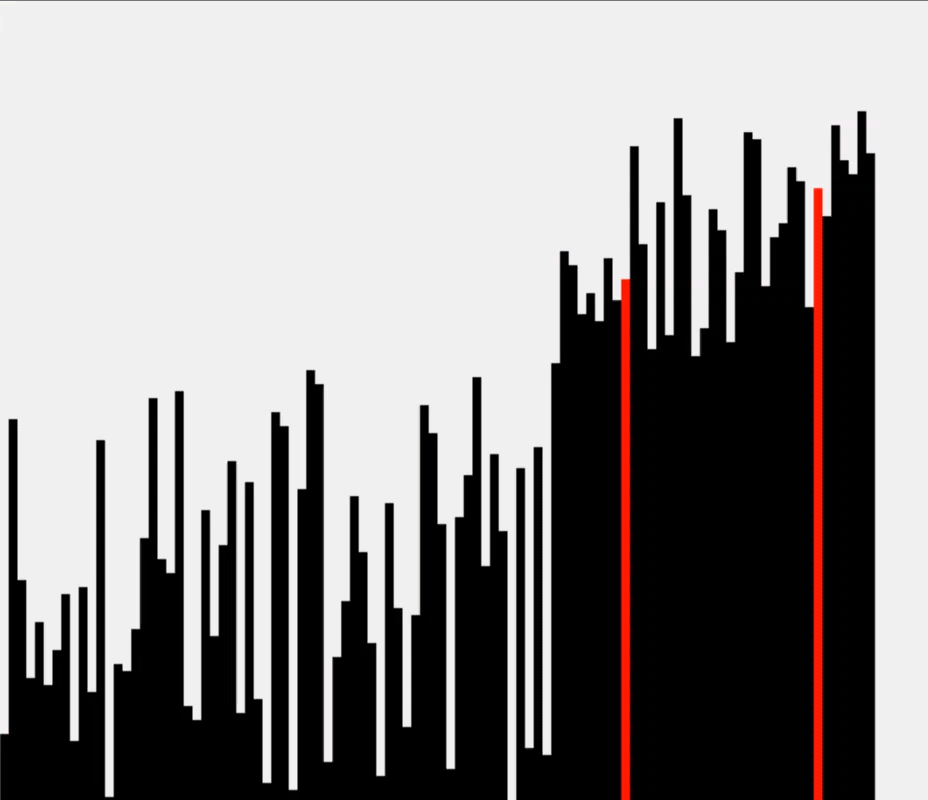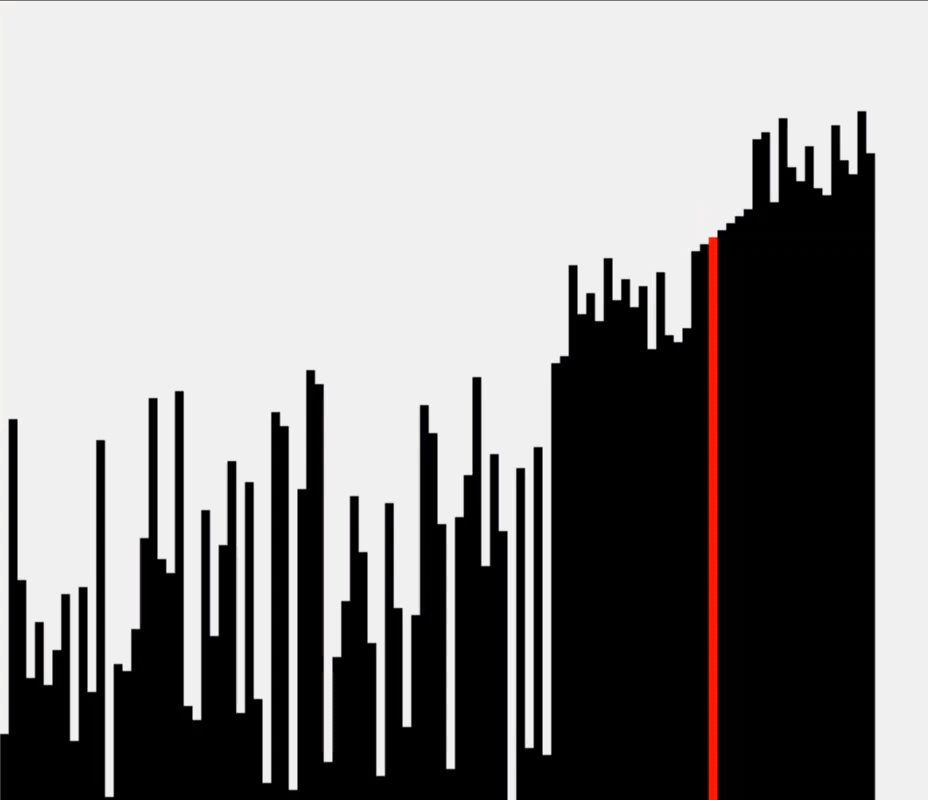
这里我们使用 Floyd-Rivest 算法进行优化,大致思想是:
我们期望第 $ k $ 大的元素位于 a[k] 附近,因此优先对 a[k] 附近的区域进行选择。
每次切分时枢轴都选择 a[k],先递归对样本区域选择,再对整个数组进行选择。
运行示意图:
测试结果:

代码
/// <summary>/// Floyd–Rivest 方法优化,令 a[k] 变成第 k 小的元素。/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T">元素类型。</typeparam>/// <param name="a">需要排序的数组。</param>/// <param name="k">序号</param>/// <returns></returns>static T Select<T>(T[] a, int lo, int hi, int k) where T : IComparable<T>{if (k < 0 || k > a.Length)throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Select elements out of bounds");while (hi > lo){if (hi - lo > 600){int n = hi - lo + 1;int i = k - lo + 1;int z = (int)Math.Log(n);int s = (int)(Math.Exp(2 * z / 3) / 2);int sd = (int)Math.Sqrt(z * s * (n - s) / n) * Math.Sign(i - n / 2) / 2;int newLo = Math.Max(lo, k - i * s / n + sd);int newHi = Math.Min(hi, k + (n - i) * s / n + sd);Select(a, newLo, newHi, k);}Exch(a, lo, k);int j = Partition(a, lo, hi);if (j > k)hi = j - 1;else if (j < k)lo = j + 1;elsereturn a[j];}return a[lo];}
另请参阅
Floyd–Rivest algorithm - Wikipedia
2.5.24
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/StableMinPQ.java.html
在元素插入的同时记录插入顺序,比较的时候把插入顺序也纳入比较。
对于值一样的元素,插入顺序在前的的元素比较小。
交换的时候需要同时交换插入次序。
代码
using System;using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace SortApplication{/// <summary>/// 稳定的最小堆。(数组实现)/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="Key">最小堆中保存的元素类型。</typeparam>public class MinPQStable<Key> : IMinPQ<Key>, IEnumerable<Key> where Key : IComparable<Key>{protected Key[] pq; // 保存元素的数组。protected int n; // 堆中的元素数量。private long[] time; // 元素的插入次序。private long timeStamp = 1; // 元素插入次序计数器。/// <summary>/// 默认构造函数。/// </summary>public MinPQStable() : this(1) { }/// <summary>/// 建立指定容量的最小堆。/// </summary>/// <param name="capacity">最小堆的容量。</param>public MinPQStable(int capacity){this.time = new long[capacity + 1];this.pq = new Key[capacity + 1];this.n = 0;}/// <summary>/// 删除并返回最小元素。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public Key DelMin(){if (IsEmpty())throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("Priority Queue Underflow");Key min = this.pq[1];Exch(1, this.n--);Sink(1);this.pq[this.n + 1] = default(Key);this.time[this.n + 1] = 0;if ((this.n > 0) && (this.n == this.pq.Length / 4))Resize(this.pq.Length / 2);Debug.Assert(IsMinHeap());return min;}/// <summary>/// 向堆中插入一个元素。/// </summary>/// <param name="v">需要插入的元素。</param>public void Insert(Key v){if (this.n == this.pq.Length - 1)Resize(2 * this.pq.Length);this.pq[++this.n] = v;this.time[this.n] = ++this.timeStamp;Swim(this.n);//Debug.Assert(IsMinHeap());}/// <summary>/// 检查堆是否为空。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public bool IsEmpty() => this.n == 0;/// <summary>/// 获得堆中最小元素。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public Key Min() => this.pq[1];/// <summary>/// 获得堆中元素的数量。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public int Size() => this.n;/// <summary>/// 获取堆的迭代器,元素以降序排列。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public IEnumerator<Key> GetEnumerator(){MaxPQ<Key> copy = new MaxPQ<Key>(this.n);for (int i = 1; i <= this.n; i++)copy.Insert(this.pq[i]);while (!copy.IsEmpty())yield return copy.DelMax(); // 下次迭代的时候从这里继续执行。}/// <summary>/// 获取堆的迭代器,元素以降序排列。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator(){return GetEnumerator();}/// <summary>/// 使元素上浮。/// </summary>/// <param name="k">需要上浮的元素。</param>private void Swim(int k){while (k > 1 && Greater(k / 2, k)){Exch(k, k / 2);k /= 2;}}/// <summary>/// 使元素下沉。/// </summary>/// <param name="k">需要下沉的元素。</param>private void Sink(int k){while (k * 2 <= this.n){int j = 2 * k;if (j < this.n && Greater(j, j + 1))j++;if (!Greater(k, j))break;Exch(k, j);k = j;}}/// <summary>/// 重新调整堆的大小。/// </summary>/// <param name="capacity">调整后的堆大小。</param>private void Resize(int capacity){Key[] temp = new Key[capacity];long[] timeTemp = new long[capacity];for (int i = 1; i <= this.n; i++){temp[i] = this.pq[i];timeTemp[i] = this.time[i];}this.pq = temp;this.time = timeTemp;}/// <summary>/// 判断堆中某个元素是否大于另一元素。/// </summary>/// <param name="i">判断是否较大的元素。</param>/// <param name="j">判断是否较小的元素。</param>/// <returns></returns>private bool Greater(int i, int j){int cmp = this.pq[i].CompareTo(this.pq[j]);if (cmp == 0)return this.time[i].CompareTo(this.time[j]) > 0;return cmp > 0;}/// <summary>/// 交换堆中的两个元素。/// </summary>/// <param name="i">要交换的第一个元素下标。</param>/// <param name="j">要交换的第二个元素下标。</param>protected virtual void Exch(int i, int j){Key swap = this.pq[i];this.pq[i] = this.pq[j];this.pq[j] = swap;long temp = this.time[i];this.time[i] = this.time[j];this.time[j] = temp;}/// <summary>/// 检查当前二叉树是不是一个最小堆。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>private bool IsMinHeap() => IsMinHeap(1);/// <summary>/// 确定以 k 为根节点的二叉树是不是一个最小堆。/// </summary>/// <param name="k">需要检查的二叉树根节点。</param>/// <returns></returns>private bool IsMinHeap(int k){if (k > this.n)return true;int left = 2 * k;int right = 2 * k + 1;if (left <= this.n && Greater(k, left))return false;if (right <= this.n && Greater(k, right))return false;return IsMinHeap(left) && IsMinHeap(right);}}}
另请参阅
2.5.25
解答
官方解答见:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/Point2D.java.html
这些比较器都以嵌套类的形式在 Point2D 中定义。
静态比较器直接在类中以静态成员的方式声明。
非静态比较器则需要提供工厂方法,该方法新建并返回对应的比较器对象。
代码
/// <summary>/// 按照 X 顺序比较。/// </summary>private class XOrder : Comparer<Point2D>{public override int Compare(Point2D x, Point2D y){if (x.X < y.X)return -1;if (x.X > y.X)return 1;return 0;}}/// <summary>/// 按照 Y 顺序比较。/// </summary>private class YOrder : Comparer<Point2D>{public override int Compare(Point2D x, Point2D y){if (x.Y < y.Y)return -1;if (x.Y > y.Y)return 1;return 0;}}/// <summary>/// 按照极径顺序比较。/// </summary>private class ROrder : Comparer<Point2D>{public override int Compare(Point2D x, Point2D y){double delta = (x.X * x.X + x.Y * x.Y) - (y.X * y.X + y.Y * y.Y);if (delta < 0)return -1;if (delta > 0)return 1;return 0;}}/// <summary>/// 按照 atan2 值顺序比较。/// </summary>private class Atan2Order : Comparer<Point2D>{private Point2D parent;public Atan2Order() { }public Atan2Order(Point2D parent){this.parent = parent;}public override int Compare(Point2D x, Point2D y){double angle1 = this.parent.AngleTo(x);double angle2 = this.parent.AngleTo(y);if (angle1 < angle2)return -1;if (angle1 > angle2)return 1;return 0;}}/// <summary>/// 按照极角顺序比较。/// </summary>private class PolorOrder : Comparer<Point2D>{private Point2D parent;public PolorOrder() { }public PolorOrder(Point2D parent){this.parent = parent;}public override int Compare(Point2D q1, Point2D q2){double dx1 = q1.X - this.parent.X;double dy1 = q1.Y - this.parent.Y;double dx2 = q2.X - this.parent.X;double dy2 = q2.Y - this.parent.Y;if (dy2 >= 0 && dy2 < 0)return -1;else if (dy2 >= 0 && dy1 < 0)return 1;else if (dy1 == 0 && dy2 == 0){if (dx1 >= 0 && dx2 < 0)return -1;else if (dx2 >= 0 && dx1 < 0)return 1;return 0;}elsereturn -CCW(this.parent, q1, q2);}}/// <summary>/// 按照距离顺序比较。/// </summary>private class DistanceToOrder : Comparer<Point2D>{private Point2D parent;public DistanceToOrder() { }public DistanceToOrder(Point2D parent){this.parent = parent;}public override int Compare(Point2D p, Point2D q){double dist1 = this.parent.DistanceSquareTo(p);double dist2 = this.parent.DistanceSquareTo(q);if (dist1 < dist2)return -1;else if (dist1 > dist2)return 1;elsereturn 0;}}/// <summary>/// 提供到当前点极角的比较器。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public Comparer<Point2D> Polor_Order(){return new PolorOrder(this);}/// <summary>/// 提供到当前点 Atan2 值的比较器。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public Comparer<Point2D> Atan2_Order(){return new Atan2Order(this);}/// <summary>/// 提供到当前点距离的比较器。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public Comparer<Point2D> DistanceTo_Order(){return new DistanceToOrder(this);}
另请参阅
2.5.26
解答
提示中已经给出了方法,使用上一题编写的比较器进行排序即可。
效果演示:

代码
绘图部分代码:
using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Drawing;using System.Windows.Forms;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._26{public partial class Form2 : Form{Graphics panel;List<Point2D> points;Point2D startPoint;double maxX = 0, maxY = 0;public Form2(){InitializeComponent();}/// <summary>/// 显示并初始化绘图窗口。/// </summary>public void Init(){Show();this.panel = CreateGraphics();this.points = new List<Point2D>();this.startPoint = null;}/// <summary>/// 向画板中添加一个点。/// </summary>/// <param name="point"></param>public void Add(Point2D point){this.points.Add(point);if (this.startPoint == null){this.startPoint = point;this.maxX = point.X * 1.1;this.maxY = point.Y * 1.1;}else if (this.startPoint.Y > point.Y)this.startPoint = point;else if (this.startPoint.Y == point.Y && this.startPoint.X > point.X)this.startPoint = point;if (point.X > this.maxX)this.maxX = point.X * 1.1;if (point.Y > this.maxY)this.maxY = point.Y * 1.1;this.points.Sort(this.startPoint.Polor_Order());RefreashPoints();}public void RefreashPoints(){double unitX = this.ClientRectangle.Width / this.maxX;double unitY = this.ClientRectangle.Height / this.maxY;double left = this.ClientRectangle.Left;double bottom = this.ClientRectangle.Bottom;this.panel.Clear(this.BackColor);Pen line = (Pen)Pens.Red.Clone();line.Width = 6;Point2D before = this.startPoint;foreach (var p in this.points){this.panel.FillEllipse(Brushes.Black,(float)(left + p.X * unitX - 5.0),(float)(bottom - p.Y * unitY - 5.0),(float)10.0,(float)10.0);this.panel.DrawLine(line,(float)(left + before.X * unitX),(float)(bottom - before.Y * unitY),(float)(left + p.X * unitX),(float)(bottom - p.Y * unitY));before = p;}this.panel.DrawLine(line,(float)(left + before.X * unitX),(float)(bottom - before.Y * unitY),(float)(left + this.startPoint.X * unitX),(float)(bottom - this.startPoint.Y * unitY));}}}
另请参阅
2.5.27
解答
类似于索引排序的做法,访问数组都通过一层索引来间接实现。
首先创建一个数组 index,令 index[i] = i。
排序时的交换变成 index 数组中元素的交换,
读取元素时使用 a[index[i]] 而非 a[i] 。
代码
/// <summary>/// 间接排序。/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>/// <param name="keys"></param>/// <returns></returns>static int[] IndirectSort<T>(T[] keys) where T : IComparable<T>{int n = keys.Length;int[] index = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)index[i] = i;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = i; j > 0 && keys[index[j]].CompareTo(keys[index[j - 1]]) < 0; j--){int temp = index[j];index[j] = index[j - 1];index[j - 1] = temp;}return index;}
2.5.28
解答
官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/FileSorter.java.html
先获得目录里的所有文件名,然后排序输出即可。
代码
using System;using System.IO;namespace _2._5._28{class Program{// 官方解答:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/25applications/FileSorter.java.htmlstatic void Main(string[] args){// 输入 ./ 获得当前目录文件。string directoryName = Console.ReadLine();if (!Directory.Exists(directoryName)){Console.WriteLine(directoryName + " doesn't exist or isn't a directory");return;}string[] directoryFiles = Directory.GetFiles(directoryName);Array.Sort(directoryFiles);for (int i = 0; i < directoryFiles.Length; i++)Console.WriteLine(directoryFiles[i]);}}}
2.5.29
解答
首先定义一系列比较器,分别根据文件大小、文件名和最后修改日期比较。
然后修改 Less 的实现,接受一个比较器数组,使用数组中的比较器依次比较,直到比较结果为两者不相同。
最后使用插入排序作为稳定排序,传入比较器数组用于 Less 函数。
代码
using System;using System.IO;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace _2._5._29{class Program{class FileSizeComparer : Comparer<FileInfo>{public override int Compare(FileInfo x, FileInfo y){return x.Length.CompareTo(y.Length);}}class FileNameComparer : Comparer<FileInfo>{public override int Compare(FileInfo x, FileInfo y){return x.FullName.CompareTo(y.FullName);}}class FileTimeStampComparer : Comparer<FileInfo>{public override int Compare(FileInfo x, FileInfo y){return x.LastWriteTime.CompareTo(y.LastWriteTime);}}static void InsertionSort<T>(T[] keys, Comparer<T>[] comparers){for (int i = 0; i < keys.Length; i++)for (int j = i; j > 0 && Less(keys, j, j - 1, comparers); j--){T temp = keys[j];keys[j] = keys[j - 1];keys[j - 1] = temp;}}static bool Less<T>(T[] keys, int x, int y, Comparer<T>[] comparables){int cmp = 0;for (int i = 0; i < comparables.Length && cmp == 0; i++){cmp = comparables[i].Compare(keys[x], keys[y]);}return cmp < 0;}static void Main(string[] args){string[] arguments = Console.ReadLine().Split(' ');string directoryPath = arguments[0];string[] filenames = Directory.GetFiles(directoryPath);FileInfo[] fileInfos = new FileInfo[filenames.Length];for (int i = 0; i < filenames.Length; i++)fileInfos[i] = new FileInfo(filenames[i]);List<Comparer<FileInfo>> comparers = new List<Comparer<FileInfo>>();for (int i = 1; i < arguments.Length; i++){string command = arguments[i];switch (command){case "-t":comparers.Add(new FileTimeStampComparer());break;case "-s":comparers.Add(new FileSizeComparer());break;case "-n":comparers.Add(new FileNameComparer());break;}}InsertionSort(fileInfos, comparers.ToArray());for (int i = 0; i < fileInfos.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(fileInfos[i].Name + "\t" + fileInfos[i].Length + "\t" + fileInfos[i].LastWriteTime);}}}}
2.5.30
解答
不妨按照升序排序,$ x_{ij} $ 代表第 $ i $ 行第 $ j $ 列的元素。
首先保证每列都是有序的。
对第一行排序,对于第一行的元素 $ x_{1i} $ ,排序结果无非两种。
要么 $ x_{1i} $ 不改变,要么和更小的元素进行交换。
显然,无论哪种情况,第 $ i $ 列都是有序的。
因此对第一行排序之后,第一行有序,每一列都分别有序。
之后我们对第二行排序,考虑元素 $ x_{11} $。
此时 $ x_{11} $ 小于第一列的所有其他元素,也小于第一行的所有其他元素。
又每一列都分别有序,因此 $ x_{11} $ 是整个矩阵的最小值,第二行不存在比它小的元素。
考虑使用选择排序,我们把第二行的最小值和 $ x_{21} $ 交换,第一列仍然有序。
现在去掉第一列,对剩下的矩阵做一样的操作,可以将第二行依次排序。
同时保证第二行的元素都小于同列的第一行元素。
接下来的行都可以依次类推,最终将整个矩阵的所有行排序,定理得证。
2.5.31
解答
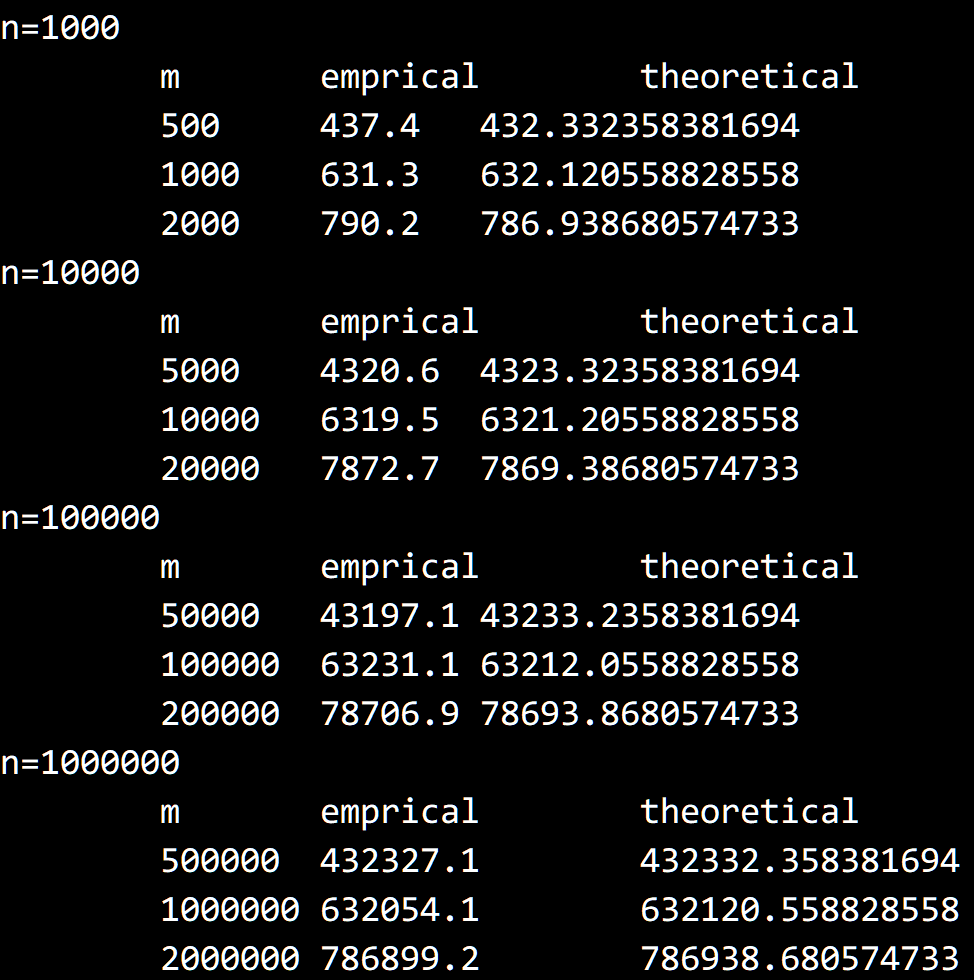
编写代码进行实验即可,实验结果如下,可以发现十分接近:
代码
using System;namespace _2._5._31{class Program{/// <summary>/// 计算数组中重复元素的个数。/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>/// <param name="a">需要计算重复元素的数组。</param>/// <returns></returns>static int Distinct<T>(T[] a) where T : IComparable<T>{if (a.Length == 0)return 0;Array.Sort(a);int distinct = 1;for (int i = 1; i < a.Length; i++)if (a[i].CompareTo(a[i - 1]) != 0)distinct++;return distinct;}static void Main(string[] args){int T = 10; // 重复次数int n = 1000; // 数组初始大小int nMultipleBy10 = 4; // 数组大小 ×10 的次数int mMultipleBy2 = 3; // 数据范围 ×2 的次数Random random = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < nMultipleBy10; i++){Console.WriteLine("n=" + n);Console.WriteLine("\tm\temprical\ttheoretical");int m = n / 2;for (int j = 0; j < mMultipleBy2; j++){int distinctSum = 0;for (int k = 0; k < T; k++){int[] data = new int[n];for (int l = 0; l < n; l++)data[l] = random.Next(m);distinctSum += Distinct(data);}double empirical = (double)distinctSum / T;double alpha = (double)n / m;double theoretical = m * (1 - Math.Exp(-alpha));Console.WriteLine("\t" + m + "\t" + empirical + "\t" + theoretical);m *= 2;}n *= 10;}}}}
2.5.32
解答
(前置知识:提前了解 Dijkstra 算法能够降低理解 A* 算法的难度。)
A* 算法是 Dijkstra 算法和最佳优先算法的一种结合。
Dijkstra 算法需要遍历所有结点来找到最短路径,唯一的优化条件就是路径长度。
建立队列 queue ,把所有的结点加入 queue 中;建立数组 d,d[v] 代表起点到点 v 的距离。
开始时只有起点到起点的距离为 0,其他都为无穷大,然后重复如下步骤:
从队列中取出已知距离最短的结点 u,检查该结点的所有边。
如果通过这个点能够以更近的距离到达 v,更新起点到 v 的距离 d[v] = d[u] + distance(u, v)。
等到队列为空之后数组 d 中就存放着起点到其他所有结点的最短距离。
Dijkstra 算法会计算起点到所有点的最短路径,因此会均匀的遍历所有结点,效率较低。
很多时候,我们只需要找到起点到某一终点的最短路径即可,为此遍历整个图显然是不必要的。
通过修改算法,使得比较接近终点的结点优先得到搜索,我们就可能在遍历完全部结点之前获得结果。
在 Dijkstra 算法中,离起点最近的点会被优先搜索,记结点离起点的距离为 g[n] 。
现在引入新的条件,用于估计结点和终点的接近程度,记结点离终点的估计距离为 h[n] 。
令 f[n] = g[n] + h[n],我们按照 f[n] 对等待搜索的结点进行排序。
同时令 h[n] 始终小于 g[n] ,保证离起点的距离 g[n] 权重大于离终点的估计距离 h[n] 。
(h[n]也被称之为容许估计)
于是在离起点距离接近的条件下,离终点比较近的点会被优先搜索,减少搜索范围。
接下来就是算法的具体内容,与 Dijkstra 算法不同,A* 算法不一定需要访问所有结点,
因此 A* 算法需要维护两个集合,openSet 保存等待搜索的结点,closeSet 保存已经搜索过的结点。
和 Dijkstra 算法类似,一开始 openSet 中只有起点,closeSet 则是空的。
然后重复执行如下步骤,直到 openSet 为空:
从 openSet 中取出 f[n] 最小的结点 u ,放入 closeSet。(标记为已访问)
如果 u 就是终点,算法结束。
计算结点 u 直接可达的周围结点,放入集合 neighbors。
遍历 neighbors 中的所有结点 v,做如下判断:
如果 v 已经存在于 closeSet ,忽略之。(防止走回头路)
如果经过 u 不能缩短起点到 v 的路径长度 g[v],忽略之。(和 Dijkstra 算法一样的做法)
否则将 v 放入 openSet,更新 g[v] = g[u] + distance(u, v) ,计算 f[v] = g[v] + h[v]。(更新结点)
以上是 A* 算法的核心逻辑,
为了结合具体问题,我们需要自定义计算 g[n] 和 h[n] 的方法,以及获得某个结点周围结点的方法。
这里有个问题,openSet 和 closeSet 应该用什么数据结构?
closeSet 比较简单,只需要添加和查找即可,哈希表 HashSet 是不二选择。
openSet 需要读取并删除最小元素,以及添加和查找元素,用最小堆 MinPQ 会是比较方便的方法。
书中给出的最小堆 MinPQ 没有实现 Contains 方法,需要自己实现一个,简单顺序查找就够用了。
同时 MinPQ 的 Greater 比较方法也需要重新实现,需要使用基于 f[n] 进行比较的比较器。
现在我们考虑 8 字谜题如何用 A* 算法实现。
棋盘的每一个状态就是一个结点,每走一步就能进入下一个状态,结点可以这么定义:
class SearchNode{int[] Board; // 棋盘状态int Steps; // 已经使用的步数}
g(start, goal) 直接就是 goal.Steps - start.Steps,h(start, goal) 则根据题意有不同的实现。
获得周围结点的方法 GetNeighbors(current),会返回一个数组,其中有从 current 上下左右走获得的棋盘状态。
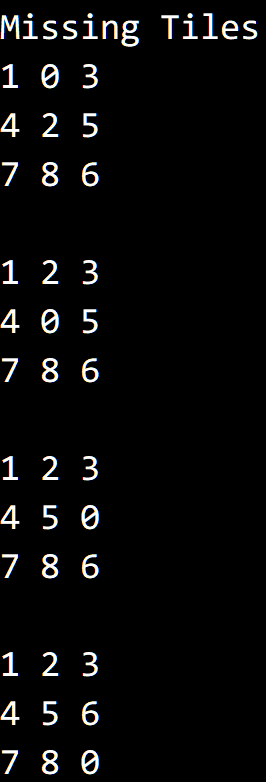
运行结果,初始状态为:
0 1 34 2 57 9 6

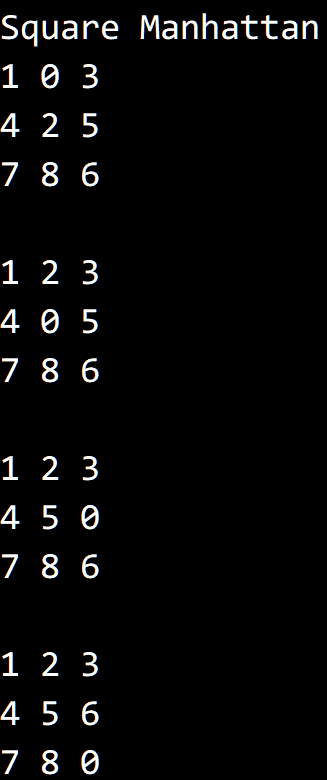
代码
A* 算法的泛型实现
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;namespace SortApplication{/// <summary>/// A* 搜索器。/// </summary>/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>public abstract class AStar<T> where T : IComparable<T>{/// <summary>/// 相等比较器。/// </summary>private readonly IEqualityComparer<T> equalityComparer;/// <summary>/// 默认相等比较器。/// </summary>class DefaultEqualityComparer : IEqualityComparer<T>{public bool Equals(T x, T y){return x.Equals(y);}public int GetHashCode(T obj){return obj.GetHashCode();}}/// <summary>/// 根据 FScore 进行比较的比较器。/// </summary>class FScoreComparer : IComparer<T>{Dictionary<T, int> fScore;public FScoreComparer(Dictionary<T, int> fScore){this.fScore = fScore;}public int Compare(T x, T y){if (!this.fScore.ContainsKey(x))this.fScore[x] = int.MaxValue;if (!this.fScore.ContainsKey(y))this.fScore[y] = int.MaxValue;return this.fScore[x].CompareTo(this.fScore[y]);}}/// <summary>/// 新建一个 Astar 寻路器,使用元素默认相等比较器。/// </summary>protected AStar() : this(new DefaultEqualityComparer()) { }/// <summary>/// 新建一个 AStar 寻路器。/// </summary>/// <param name="equalityComparer">用于确定状态之间相等的比较器。</param>protected AStar(IEqualityComparer<T> equalityComparer){this.equalityComparer = equalityComparer;}/// <summary>/// 获得最短路径。/// </summary>/// <param name="start">起始状态。</param>/// <param name="goal">终止状态。</param>/// <returns></returns>public T[] GetPath(T start, T goal){Dictionary<T, T> comeFrom = new Dictionary<T, T>(this.equalityComparer);Dictionary<T, int> gScore = new Dictionary<T, int>(this.equalityComparer);Dictionary<T, int> fScore = new Dictionary<T, int>(this.equalityComparer);MinPQ<T> openSet = new MinPQ<T>(new FScoreComparer(fScore), this.equalityComparer);HashSet<T> closeSet = new HashSet<T>(this.equalityComparer);openSet.Insert(start);gScore.Add(start, 0);fScore.Add(start, HeuristicDistance(start, goal));while (!openSet.IsEmpty()){T current = openSet.DelMin();if (this.equalityComparer.Equals(current, goal))return ReconstructPath(comeFrom, current);closeSet.Add(current);T[] neighbors = GetNeighbors(current);foreach (T neighbor in neighbors){if (closeSet.Contains(neighbor))continue;int gScoreTentative = gScore[current] + ActualDistance(current, neighbor);// 新状态if (!openSet.Contains(neighbor))openSet.Insert(neighbor);else if (gScoreTentative >= gScore[neighbor])continue;// 记录新状态comeFrom[neighbor] = current;gScore[neighbor] = gScoreTentative;fScore[neighbor] = gScore[neighbor] + HeuristicDistance(neighbor, goal);}}return null;}/// <summary>/// 倒回重建最佳路径。/// </summary>/// <param name="status">包含所有状态的数组。</param>/// <param name="from">记载了状态之间顺序的数组。</param>/// <param name="current">当前状态位置。</param>/// <returns></returns>private T[] ReconstructPath(Dictionary<T, T> comeFrom, T current){Stack<T> pathReverse = new Stack<T>();while (comeFrom.ContainsKey(current)){pathReverse.Push(current);current = comeFrom[current];}T[] path = new T[pathReverse.Count];for (int i = 0; i < path.Length; i++){path[i] = pathReverse.Pop();}return path;}/// <summary>/// 计算两个状态之间的估计距离,即 h(n)。/// </summary>/// <param name="start">初始状态。</param>/// <param name="goal">目标状态。</param>/// <returns></returns>protected abstract int HeuristicDistance(T start, T goal);/// <summary>/// 计算两个状态之间的实际距离,即 g(n)。/// </summary>/// <param name="start">初始状态。</param>/// <param name="goal">目标状态。</param>/// <returns></returns>protected abstract int ActualDistance(T start, T goal);/// <summary>/// 获得当前状态的周围状态。/// </summary>/// <param name="current">当前状态。</param>/// <returns></returns>protected abstract T[] GetNeighbors(T current);}}
另请参阅
A* search algorithm-Wikipedia
SortApplication 库
2.5.33
解答
编写代码实验即可,结果如下:
代码
随机交易生成器 TransactionGenerator
using System;using System.Text;using SortApplication;namespace _2._5._33{/// <summary>/// 随机交易生成器。/// </summary>class TransactionGenerator{private static Random random = new Random();/// <summary>/// 生成 n 条随机交易记录。/// </summary>/// <param name="n">交易记录的数量。</param>/// <returns></returns>public static Transaction[] Generate(int n){Transaction[] trans = new Transaction[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){trans[i] = new Transaction(GenerateName(),GenerateDate(),random.NextDouble() * 1000);}return trans;}/// <summary>/// 获取随机姓名。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>private static string GenerateName(){int nameLength = random.Next(4, 7);StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.Append(random.Next('A', 'Z' + 1));for (int i = 1; i < nameLength; i++)sb.Append(random.Next('a', 'z' + 1));return sb.ToString();}/// <summary>/// 获取随机日期。/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>private static Date GenerateDate(){int year = random.Next(2017, 2019);int month = random.Next(1, 13);int day;if (month == 2)day = random.Next(1, 29);else if ((month < 8 && month % 2 == 1) ||(month > 7 && month % 2 == 0))day = random.Next(1, 32);elseday = random.Next(1, 31);Date date = new Date(month, day, year);return date;}}}
另请参阅
算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——2.5的更多相关文章
- 算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1
算法(第四版)C#题解——2.1 写在前面 整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csh ...
- 算法第四版 在Eclipse中调用Algs4库
首先下载Eclipse,我选择的是Eclipse IDE for Java Developers64位版本,下载下来之后解压缩到喜欢的位置然后双击Eclipse.exe启动 然后开始新建项目,File ...
- 算法第四版jar包下载地址
算法第四版jar包下载地址:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/code/
- 算法第四版-文字版-下载地址-Robert Sedgewick
下载地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/moshenglv/10777447 算法第四版,文字版,可复制,方便copy代码 目录: 第1章 基 础 ...... ...
- 二项分布。计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数(算法第四版1.1.27)
算法第四版35页问题1.1.27,估计用一下代码计算binomial(100,50,0.25)将会产生的递归调用次数: public static double binomial(int n,int ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之优先队列--Priority Queues
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.4优先队列(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:API 与初级实现 2:堆得定义 3:堆排序 4:事件驱动的仿真 优先队列最重要的操作就是删 ...
- 算法第四版学习笔记之快速排序 QuickSort
软件:DrJava 参考书:算法(第四版) 章节:2.3快速排序(以下截图是算法配套视频所讲内容截图) 1:快速排序 2:
- C程序设计(第四版)课后习题完整版 谭浩强编著
//复习过程中,纯手打,持续更新,觉得好就点个赞吧. 第一章:程序设计和C语言 习题 1.什么是程序?什么是程序设计? 答:程序就是一组计算机能识别和执行的指令.程序设计是指从确定任务到得到结果,写出 ...
- 算法第四版 coursera公开课 普林斯顿算法 ⅠⅡ部分 Robert Sedgewick主讲《Algorithms》
这是我在网上找到的资源,下载之后上传到我的百度网盘了. 包含两部分:1:算法视频的种子 2:字幕 下载之后,请用迅雷播放器打开,因为迅雷可以直接在线搜索字幕. 如果以下链接失效,请在下边留言,我再更新 ...
- 相似度分析,循环读入文件(加入了HanLP,算法第四版的库)
相似度分析的,其中的分词可以采用HanLP即可: http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1421978002609.htm /****************** ...
随机推荐
- Digest of Overview of Linux Kernel Security Features
Linux kernel Security: I. DAC: Discretionary Access Control, the core security model of UNIX. II. PO ...
- TNS-12560: TNS: 协议适配器错误同时伴有TNS-00584: 有效节点检查配置错误的解决方法
:修改/home/oracle/app/product/11.2.0/db_1/network/admin/sqlnet.ora(与listener.ora同一目录) 增加白名单: tcp.valid ...
- ADB——keyevent命令
基本格式 adb shell input keyevent xxx # xxx为具体操作对应的数字 keycode 官方 KEYCODE 链接:戳这里 0 KEYCODE_UNKNOWN 未知按键 1 ...
- mysql表类型导致的 setRollbackOnly() 事务不回滚
在SpringBoot 中,使用事务非常简单,只需在方法上面加入 @Transactional 注解就可以实现.也可加在类上,此时则类中所有方法都支持事务. 而当我使用下面代码时,发现事务却没有回滚 ...
- PHP防CC攻击代码
PHP防CC攻击代码: empty($_SERVER['HTTP_VIA']) or exit('Access Denied'); //代理IP直接退出 session_start(); $secon ...
- 实验吧MD5之守株待兔解题思路
解题链接 http://ctf5.shiyanbar.com/misc/keys/keys.php 解题思路 首先我们多打开几次解题链接,发现系统密钥大约在一秒钟左右变一次,所以联想到时间戳. 解题过 ...
- 杂记:解决Android扫描BLE设备名称不刷新问题
背景 个人开发过一种BLE设备有这样一种需求:当设备处于状态A时,广播设备名称A:处于状态B时,广播设备名称B. 问题 我们发现,当Android在进行Ble扫描的时候,扫描回调函数onScanRes ...
- 1、写在开头的话——Tinking in Java 绪论之我见
新兵道歉!版式不懂,技术若有错误,请指正,或发我邮箱1300431700@qq.com 不胜感激! 本文力图通过文章总结的形式,阐述自己的观点,迫使自己思考书中精髓,即使跟技术无关! 正文开始! “上 ...
- java中进程与线程的区别
进程是一个正在运行的应用程序.一个进程包含一个或多个线程.它可以是一段完整的代码或部分程序的动态执行.系统资源分配与调度的基本单位.而线程是CPU调度与运行的基本单位,它是一组指令的集合或是程序的特殊 ...
- Halcon一维运算相关算子整理
Halcon一维离散函数算子 1. abs_funct_1d 计算一维数组的绝对值 2. compose_funct_1将两个离散的一维函数合并为一个函数 3. cre ...
