7、nginx的upstream及fastcgi模块应用
ngx_http_proxy_module, ngx_http_upstream_module
ngx_http_proxy_module:实现反向代理及缓存功能
proxy_pass http://{SERVER_IP|UPSTREAM_NAME}/uri
proxy_cache_path path [levels=levels] keys_zone=name:size [inactive=time] [max_size=size];
proxy_cache zone_name; //缓存名称
proxy_cache_valid [code] time; //指明不同响应码内容的缓存时长
proxy_cache_method //只对哪些方法获取的资源进行缓存,一般使用get
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout ... //是否使用过期的缓存进行响应
proxy_cache_min_uses //某资源至少响应请求多少次后才被缓存下来
proxy_cache_bypass string: 设置在何种情形下nginx将不从cache取数据的;比如邮件
例如:$cookie_nocache、$arg_nocache 、$http_authorization
proxy_set_header
ngx_http_upstream_module:定义服务器组 http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_module.html
可以调用服务器组反向代理有:proxy_pass, fastcgi_pass, uwsgi_pass,
upstream name {
server address [parameters];
ip_hash; //基于源地址绑定,比ip_hash更精确的是session绑定机制是cookie记录,但LVS是没办法识别cookie的,因为cookie是应用层数据
}
nginx(2)
1、SNAT模式的大量Client
基于sticky实现session绑定:对应于工作在应用层的程序才拥有的功能
(1)cookie:基于cookie的绑定
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com;
server backend2.example.com;
sticky cookie srv_id expires=1h domain=.example.com path=/;
}
(2)route:基于路由的绑定
map $cookie_jsessionid $route_cookie {
~.+\.(?P<route>\w+)$ $route;
}
map $request_uri $route_uri {
~jsessionid=.+\.(?P<route>\w+)$ $route;
}
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com route=a;
server backend2.example.com route=b;
sticky route $route_cookie $route_uri;
}
(3)learn () :基于学习的绑定
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com:8080;
server backend2.example.com:8081;
sticky learn
create=$upstream_cookie_examplecookie
lookup=$cookie_examplecookie
zone=client_sessions:1m;
}
2、least_conn: 调度方法,最少连接(相当于LVS中的wlc算法);
3、keeplive: 激活代理服务器nginx和后端服务器之间的持久连接功能的,专用在upstream,
| Syntax: | keepalive |
|---|---|
| Default: | — |
| Context: | upstream |
例子:keepalive一般用在上游服务器是非http服务器时才使用,因为keepalive会损坏http的并发性能,如果后端是专用存储时(比如基于键值存储的memcache),基于keepalive指令可以使链接处于一段时间的长连接,提高查询性能。
upstream memcached_backend {
server 127.0.0.1:11211;
server 10.0.0.2:11211;
keepalive 32;
}
health_check:只能同在location
使用health_check时建议关闭访问日志,因为后端服务器不能检测health_check的检测是正常请求还是只是用来检测的

自定义响应首部:
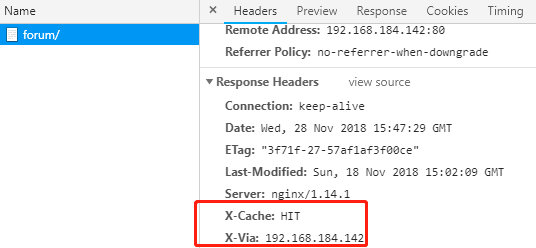
add_header X-Via $server_addr; 自定义响应首部通知客户端是由谁响应的
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status; 告诉客户端响应是否命中
首先编辑代理服务器的server配置文件
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
server {
listen ;
server_name localhost;
add_header X-Via $server_addr;
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
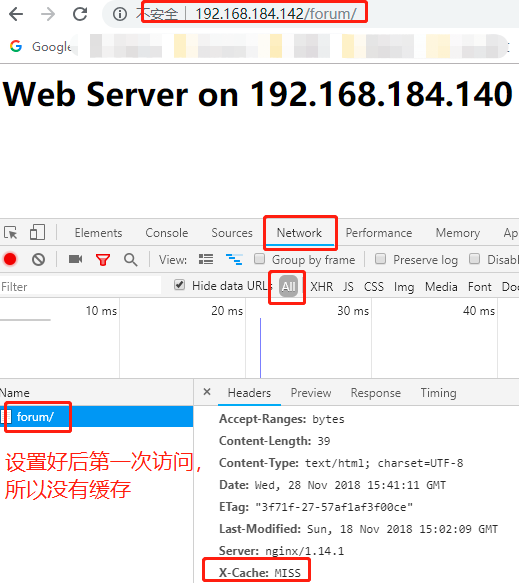
location /forum/ {
proxy_cache mycache;
proxy_cache_valid 1d;
proxy_cache_valid 10m;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
proxy_cache_use_stale error timeout http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_pass http://upservers/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
add_header X-Via $server_addr; //启用添加自定义头部
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
}

Module ngx_http_fastcgi_module模块介绍
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_fastcgi_module.html
proxy_pass http://{SERVER_IP|UPSTREAM_NAME}/uri //proxy_pass指令是把用户的请求反向代理至上有的web服务器,所以这里的协议是http协议,如果上有的协议不是http协议而是fastcgi协议,就必须使用fastcgi模块来实现。
fastcgi模块的意义是:
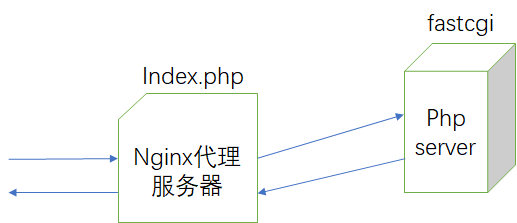
nginx作为代理服务器,当客户端发起对nginx代理服务器的php类型资源的请求,比如是index.php,此时nginx代理服务器只是一个静态内容服务器,所以nginx就会把index.php的文件内容拿过来包装成响应报文后直接返回给客户端,但此时响应报文是源代码,客户端是看不懂的。
所以应该让nginx自持php应用代码的运行,但是nginx自己不支持,所以需要做一个php的服务器。此后nginx在接收到报文时就可以根据请求资源的后缀名进行判断,一旦是php,nginx就会使用特定协议将请求报文反向代理至php的server上,php服务器将会执行index.php上的代码并将执行后的结果返回值nginx代理服务器上,然后nginx就会把响应报文进行封装并返回给客户端。这又是一种反向代理,但是使用的协议是fastcgi协议而不是http协议。
如何让nginx支持LNMP:
php是无法作为nginx的模块的,所以php只能工作于fpm模式
# yum list all *fpm* //查找是否有fpm模块
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Repodata is over 2 weeks old. Install yum-cron? Or run: yum makecache fast
Determining fastest mirrors
* base: mirrors.nwsuaf.edu.cn
* extras: mirrors.neusoft.edu.cn
* updates: mirrors.neusoft.edu.cn
Available Packages
php-fpm.x86_64 5.4.16-45.el7 base
# yum info php-fpm //查看此模块的详细信息
# yum install php-fpm //安装php-fpm模块
# rpm -ql php-fpm //查看php-fpm安装信息
/etc/logrotate.d/php-fpm
/etc/php-fpm.conf //主配置文件
/etc/php-fpm.d
/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf //这里可以查看php监听的地址,如果php和nginx不在同一主机的话,就需要修改php监听的地址了
/etc/sysconfig/php-fpm //服务脚本
/run/php-fpm
/usr/lib/systemd/system/php-fpm.service
/usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/php-fpm.conf
/usr/sbin/php-fpm //可执行程序
/usr/share/doc/php-fpm-5.4.16
/usr/share/doc/php-fpm-5.4.16/fpm_LICENSE
/usr/share/doc/php-fpm-5.4.16/php-fpm.conf.default
/usr/share/fpm
/usr/share/fpm/status.html
/usr/share/man/man8/php-fpm.8.gz
/var/log/php-fpm
# systemctl start php-fpm //启动
# ss -tunl //查看端口
下面让nginx将用户的请求基于fastcgi协议发送给php
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf //编辑此文件,启用php配置段
location ~ \.php$ {
root html; //这里的页面要和上面nginx的web页面保持一致,修改如下
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; //向后端传递的参数
//SCRIPT_FILENAME是变量名指令,用户请求的文件名(即变量名$fastcgi_script_name),
通过uri(~ \.php$)的方式传递给后端的服务器(127.0.0.1:9000)
include fastcgi_params; //包含另外一个文件
} # cd /usr/share/nginx/html/ //对主页面进行修改
# vim index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm; //并在根这里添加index.php
要对/etc/nginx/fastcgi_params做修改
/etc/nginx //在这个文件目录下有一个fastcgi_params配置文件
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_SCHEME $scheme;
fastcgi_param HTTPS $https if_not_empty; fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1;
fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx/$nginx_version; fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name; # PHP only, required if PHP was built with --enable-force-cgi-redirect
fastcgi_param REDIRECT_STATUS ;
编辑/etc/nginx/fastcgi_params,将其内容更改为如下内容:
fastcgi_param GATEWAY_INTERFACE CGI/1.1;
fastcgi_param SERVER_SOFTWARE nginx;
fastcgi_param QUERY_STRING $query_string;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_METHOD $request_method;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_TYPE $content_type;
fastcgi_param CONTENT_LENGTH $content_length;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_NAME $fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param REQUEST_URI $request_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_URI $document_uri;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PROTOCOL $server_protocol;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr;
fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr;
fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port;
fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name;
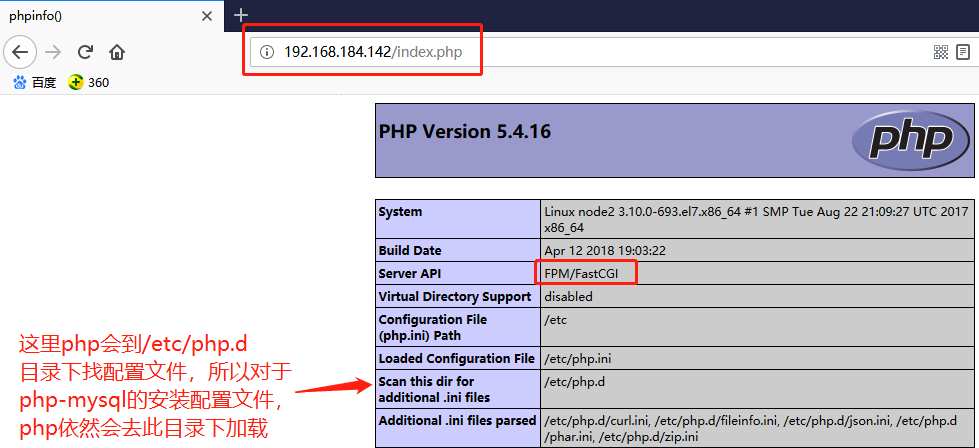
此时nginx已经可以和php结合工作了,下面就要解决php和mysql/mariadb结合
# yum install php-mysql
# rpm -ql php-mysql
/etc/php.d/mysql.ini
/etc/php.d/mysqli.ini
/etc/php.d/pdo_mysql.ini
/usr/lib64/php/modules/mysql.so
/usr/lib64/php/modules/mysqli.so
/usr/lib64/php/modules/pdo_mysql.so
# systemctl reload php-fpm
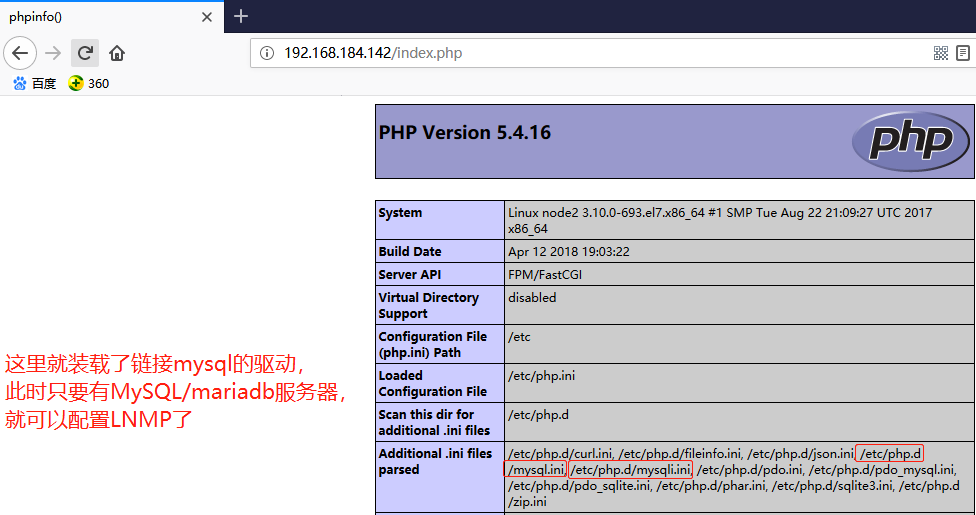
# yum install mariadb-server //安装mariadb
安装好mariadb后,验证php和mariadb是否可以结合工作
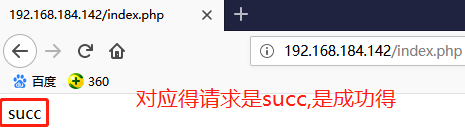
# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
<?php
$conn = mysql_connect('127.0.0.1','root','');
if ($conn)
echo succ;
else
echo fail; mysql_close();
?>
# systemctl stop mariadb //关闭mariadb后在测试
LNAMP :以nginx做代理服务器进行负载均衡,后端的服务器平台是多个LAMP,在这种场景中nginx和后端的LAMP交互时是两个web服务器之间的交互(http协议),LAMP中的php可以以 apache的模块进行工作。
动态内容和静态内容分离:php服务器和MySQL服务器与后端负载均衡的服务器不在同一个服务器上
LNMP, fastcgi_cache fastcgi协议的缓存服务器
| Syntax: |
[ |
|---|---|
| Default: | — |
| Context: | http //需要定义在http上下文 |
fastcgi_cache_path /data/nginx/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=one:10m;
以上是定义位置以及定义方法,定义完成后需要使用fastvgi_cache进行调用
| Syntax: | fastcgi_cache |
|---|---|
| Default: |
fastcgi_cache off; |
| Context: | http, server, location 使用上下文 |
示例:LNMP通过fastcgi_cahce加速响应
# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf //首先编辑nginx的主配置文件http上下文
fastcgi_cache_path /cache/fastcgi/ levels=1:1 keys_zone=fcgicache:10m inactive=3m max_size=1g;
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf //在对应的location中进行调用
location ~ \.php$ { //对应的php的location中进行调用
fastcgi_cache fcgicache;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# systemctl reload nginx
# mkdir /cache/fastcgi -pv
# ll /cache
total 0
drwx------ 2 nginx root 6 Nov 29 05:02 fastcgi
drwxr-xr-x 4 nginx nginx 24 Nov 28 23:41 nginx
#vim /usr/share/nginx/html/test.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
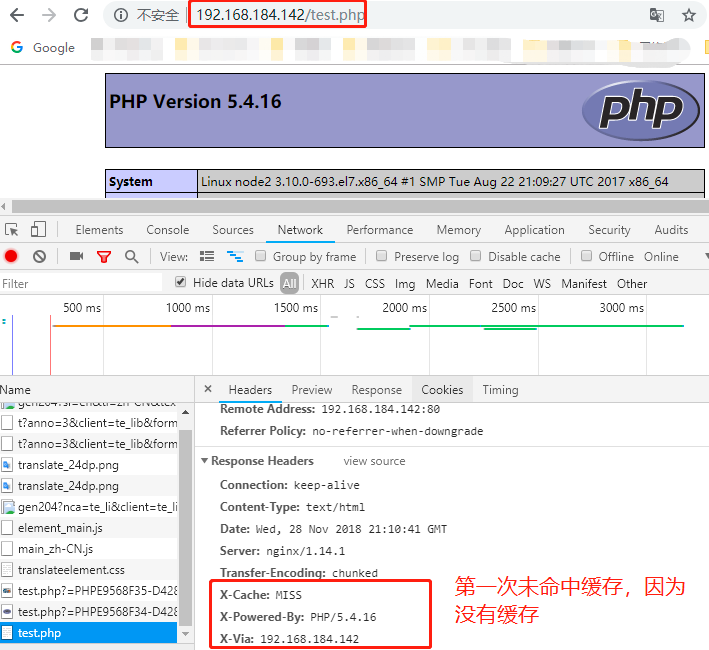
再次刷新时发现X-Cache仍然是MISS,即无法缓存
#vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf //在php配置段中指明缓存响应码,如果不指明,就不缓存
fastcgi_cache_valid 200 10m;
fastcgi_cache_valid 302 3m;
fastcgi_cache_valid any 1m;
下面利用ab命令对开启缓存和不开启缓存进行性能对比
1、首先关闭fastcgi_cache
# /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
#fastcgi_cache fcgicache;
fastcgi_cache off; //暂时关闭fastcgi_cache
# systemctl reload nginx
# yum install httpd-tools
# ab -n 10000 -c 100 http://192.168.184.142/test.php -n是请求数量,-c是并发量
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: $>
Copyright Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/ Benchmarking 192.168.184.142 (be patient)
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Finished requests Server Software: nginx/1.14.
Server Hostname: 192.168.184.142
Server Port: Document Path: /test.php
Document Length: bytes Concurrency Level:
Time taken for tests: 4.891 seconds
Complete requests:
Failed requests:
(Connect: , Receive: , Length: , Exceptions: )
Write errors:
Total transferred: bytes
HTML transferred: bytes
Requests per second: 2044.69 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 48.907 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.489 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 86863.18 [Kbytes/sec] received Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0.5
Processing: 13.7
Waiting: 13.6
Total: 13.6 Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
% (longest request)
2、开启fastcgi_cache
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
fastcgi_cache fcgicache;
#fastcgi_cache off;
#systemctl reload nginx
# ab -n 10000 -c 100 http://192.168.184.142/test.php
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: $>
Copyright Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/ Benchmarking 192.168.184.142 (be patient)
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Completed requests
Finished requests Server Software: nginx/1.14.
Server Hostname: 192.168.184.142
Server Port: Document Path: /test.php
Document Length: bytes Concurrency Level:
Time taken for tests: 0.527 seconds
Complete requests:
Failed requests:
Write errors:
Total transferred: bytes
HTML transferred: bytes
Requests per second: 18986.36 [#/sec] (mean) //与上面的对比差距是非常大的
Time per request: 5.267 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.053 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 806845.98 [Kbytes/sec] received Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0.3
Processing: 0.9
Waiting: 0.9
Total: 0.9 Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
%
% (longest request)
练习:
(1) root为同一路径;
(2) root为不同的路径;
location \.php$ {
root /web/app/wp;
}
location / {
root /web/htdocs;
}
如何解决root路径不同的问题?
(3) fpm server为另一主机;
location \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass fastcgi://192.168.184.142:9000;
}
location / {
root /web/htdocs;
}
总结:
cache:
proxy_cache
fastcgi_cache
7、nginx的upstream及fastcgi模块应用的更多相关文章
- nginx fastcgi模块ngx_http_fastcgi_module详细解析、使用手册、完整翻译
ngx_http_fastcgi_module 模块允许将请求传递给 FastCGI 服务器. 示例配置 location / { fastcgi_pass localhost:9000; fastc ...
- nginx的upstream目前支持5种方式的分配
Nginx nginx的upstream目前支持5种方式的分配 FROM: 转载 1 轮询(默认) 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器, 如果后端服务器down掉, 能自动剔除. 2 w ...
- nginx添加sticky cookie 分流模块
需要下载nginx源码和sticky,在nginx配置文件中添加sticky模块,然后重新编译nginx. #准备安装基础环境:yum install gcc openssl-devel pcre-d ...
- Nginx的几个重要模块
ngx_http_ssl_module 让Nginx可以支持HTTPS的模块,此模块下的大多数指令都应用在http,server上下文 ①ssl on | off; 是否开启ssl功能 ②ssl_ce ...
- Nginx系列1之部分模块详解
1 内核模块: 名称: daemon 语法: daemon on |off 默认值: on 功能: 决定nginx 在前台执行还是后台守护进程执行的 ================== 名称: En ...
- nginx的upstream目前支持5种方式的分配(转)
nginx的upstream目前支持5种方式的分配 1.轮询(默认) 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除. 2.weight 指定轮询几率,weight ...
- nginx会话保持之sticky模块
nginx会话保持之nginx-sticky-module模块 在使用负载均衡的时候会遇到会话保持的问题,常用的方法有:1.ip hash,根据客户端的IP,将请求分配到不同的服务器上:2.cooki ...
- Nginx的upstream的5种分配方式
转自:Nginx的upstream目前支持5种分配方式 1.轮询(默认) 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除. 2.weight指定轮询几率,weigh ...
- nginx通过upstream实现负载均衡
随着业务和用户不断增加,单台服务器无法满足业务需求,产生服务器集群的场景.为了能充分利用服务器集群,最理想的方式就是整个集群的利用率都很平均且稳定在理想值范围内. 负载均衡(Load Balance) ...
随机推荐
- 【转】Tomcat 快速入门
本文转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/jingmoxukong/p/8258837.html?utm_source=gold_browser_extension 目录 Tomca ...
- xshell中出现的绿色背景的文件夹
这种文件夹表示权限为777的文件夹 可以使用chmod 777 fileName进行权限修改 如果需要将文件夹以及其子文件夹的权限全部置为777 chmod 777 -R directoryName/ ...
- centos6.8卸载DB2 10.5
1.卸载实例 Ø 使用Root用户登陆 cd /opt/ibm/db2/V9.5/instance/ ./db2idrop db2inst1 ./dasdrop db2inst1 2.卸载db2 Ø ...
- HDU 1233 还是畅通工程 (最小生成树 )
某省调查乡村交通状况,得到的统计表中列出了任意两村庄间的距离.省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个村庄间都可以实现公路交通(但不一定有直接的公路相连,只要能间接通过公路可达即可),并要求铺设的公路 ...
- [转载]oracle函数listagg的使用说明
工作中经常遇到很多需求是这样的,根据条件汇总某些字段,比如我遇到的是,我们公司有三个投资平台,同一个客户拿手机号在三个平台都注册了,但注册过的用户名不一样,显示的时候需要根据手机号显示所有注册过的名称 ...
- NoSql Cassandra
我们为什么要使用NOSQL非关系数据库? 随着互联网web2.0网站的兴起,非关系型的数据库现在成了一个极其热门的新领域,非关系数据库产品的发展非常迅速.而传统的关系数据库在应付web2.0网站,特别 ...
- win10系统jdk安装和环境变量配置
新换电脑的原因,要重新安装jdk,完整记录一下安装过程 jdk版本用的1.7(公司默认版本) 这是jdk安装目录 更改为D:\jdk\java\jdk1.7 安装jre目录 更改为D:\jdk\ ...
- 【linux应用】将一个大文件按行拆分成小文件
例如将一个BLM.txt文件分成前缀为 BLM_ 的1000个小文件,后缀为系数形式,且后缀为4位数字形式 先利用 wc -l BLM.txt #读出BLM.txt有多少行. 再利用 split 命令 ...
- Tomcat配置Manager管理员
修改文件: D:\MyDev\Tomcat\apache-tomcat-7.0.68\conf\tomcat-users.xml 配置内容: <role rolename="mana ...
- Opencv改变图像亮度和对比度以及优化
https://blog.csdn.net/u013139259/article/details/52145377 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog.cs ...