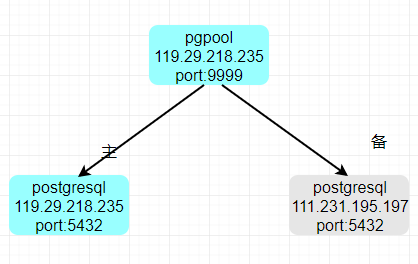
centos7 pgpool+postgresql
安装postgresql
安装pgpool
- rpm -ivh http://www.pgpool.net/yum/rpms/3.7/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgpool-II-release-3.7-1.noarch.rpm
- yum -y install pgpool-II-pg95
- yum -y install pgpool-II-pg95-debuginfo
- yum -y install pgpool-II-pg95-devel
- yum -y install pgpool-II-pg95-extensions
- 开机启动
- systemctl enable pgpool
添加Pgpool-II运行用户
- [root@im110 pgpool-II]# useradd pgpool
- [root@im110 pgpool-II]# passwd pgpool
- Changing password for user pgpool.
- New password:
- Retype new password:
- passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
- [root@im110 pgpool-II]# chown -R pgpool.pgpool /etc/pgpool-II
- [root@im110 pgpool-II]# mkdir -p /var/run/pgpool/
- [root@im110 pgpool-II]# chown pgpool.pgpool /var/run/pgpool/
修改配置文件
先备份所有配置文件
vi pgpool.conf修改后如下
- # ----------------------------
- # pgPool-II configuration file
- # ----------------------------
- #
- # This file consists of lines of the form:
- #
- # name = value
- #
- # Whitespace may be used. Comments are introduced with "#" anywhere on a line.
- # The complete list of parameter names and allowed values can be found in the
- # pgPool-II documentation.
- #
- # This file is read on server startup and when the server receives a SIGHUP
- # signal. If you edit the file on a running system, you have to SIGHUP the
- # server for the changes to take effect, or use "pgpool reload". Some
- # parameters, which are marked below, require a server shutdown and restart to
- # take effect.
- #
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # CONNECTIONS
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # - pgpool Connection Settings -
- listen_addresses = '*'
- # Host name or IP address to listen on:
- # '*' for all, '' for no TCP/IP connections
- # (change requires restart)
- port =
- # Port number
- # (change requires restart)
- socket_dir = '/var/run/postgresql'
- # Unix domain socket path
- # The Debian package defaults to
- # /var/run/postgresql
- # (change requires restart)
- listen_backlog_multiplier =
- # Set the backlog parameter of listen() to
- # num_init_children * listen_backlog_multiplier.
- # (change requires restart)
- serialize_accept = off
- # whether to serialize accept() call to avoid thundering herd problem
- # (change requires restart)
- # - pgpool Communication Manager Connection Settings -
- pcp_listen_addresses = '*'
- # Host name or IP address for pcp process to listen on:
- # '*' for all, '' for no TCP/IP connections
- # (change requires restart)
- pcp_port =
- # Port number for pcp
- # (change requires restart)
- pcp_socket_dir = '/var/run/postgresql'
- # Unix domain socket path for pcp
- # The Debian package defaults to
- # /var/run/postgresql
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Backend Connection Settings -
- backend_hostname0 = '119.29.218.235'
- # Host name or IP address to connect to for backend
- backend_port0 =
- # Port number for backend
- backend_weight0 =
- # Weight for backend (only in load balancing mode)
- backend_data_directory0 = '/var/lib/pgsql/data'
- # Data directory for backend
- backend_flag0 = 'ALLOW_TO_FAILOVER'
- # Controls various backend behavior
- # ALLOW_TO_FAILOVER, DISALLOW_TO_FAILOVER
- # or ALWAYS_MASTER
- backend_hostname1 = '111.231.195.197'
- backend_port1 =
- backend_weight1 =
- backend_data_directory1 = '/var/lib/pgsql/data'
- backend_flag1 = 'ALLOW_TO_FAILOVER'
- # - Authentication -
- enable_pool_hba = on
- # Use pool_hba.conf for client authentication
- pool_passwd = 'pool_passwd'
- # File name of pool_passwd for md5 authentication.
- # "" disables pool_passwd.
- # (change requires restart)
- authentication_timeout =
- # Delay in seconds to complete client authentication
- # means no timeout.
- # - SSL Connections -
- ssl = off
- # Enable SSL support
- # (change requires restart)
- #ssl_key = './server.key'
- # Path to the SSL private key file
- # (change requires restart)
- #ssl_cert = './server.cert'
- # Path to the SSL public certificate file
- # (change requires restart)
- #ssl_ca_cert = ''
- # Path to a single PEM format file
- # containing CA root certificate(s)
- # (change requires restart)
- #ssl_ca_cert_dir = ''
- # Directory containing CA root certificate(s)
- # (change requires restart)
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # POOLS
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # - Concurrent session and pool size -
- num_init_children =
- # Number of concurrent sessions allowed
- # (change requires restart)
- max_pool =
- # Number of connection pool caches per connection
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Life time -
- child_life_time =
- # Pool exits after being idle for this many seconds
- child_max_connections =
- # Pool exits after receiving that many connections
- # means no exit
- connection_life_time =
- # Connection to backend closes after being idle for this many seconds
- # means no close
- client_idle_limit =
- # Client is disconnected after being idle for that many seconds
- # (even inside an explicit transactions!)
- # means no disconnection
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # LOGS
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # - Where to log -
- log_destination = 'stderr'
- # Where to log
- # Valid values are combinations of stderr,
- # and syslog. Default to stderr.
- # - What to log -
- log_line_prefix = '%t: pid %p: ' # printf-style string to output at beginning of each log line.
- log_connections = off
- # Log connections
- log_hostname = off
- # Hostname will be shown in ps status
- # and in logs if connections are logged
- log_statement = off
- # Log all statements
- log_per_node_statement = off
- # Log all statements
- # with node and backend informations
- log_standby_delay = 'none'
- # Log standby delay
- # Valid values are combinations of always,
- # if_over_threshold, none
- # - Syslog specific -
- syslog_facility = 'LOCAL0'
- # Syslog local facility. Default to LOCAL0
- syslog_ident = 'pgpool'
- # Syslog program identification string
- # Default to 'pgpool'
- # - Debug -
- #log_error_verbosity = default # terse, default, or verbose messages
- #client_min_messages = notice # values in order of decreasing detail:
- # debug5
- # debug4
- # debug3
- # debug2
- # debug1
- # log
- # notice
- # warning
- # error
- #log_min_messages = warning # values in order of decreasing detail:
- # debug5
- # debug4
- # debug3
- # debug2
- # debug1
- # info
- # notice
- # warning
- # error
- # log
- # fatal
- # panic
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # FILE LOCATIONS
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- pid_file_name = '/var/run/pgpool/pgpool.pid'
- # PID file name
- # Can be specified as relative to the"
- # location of pgpool.conf file or
- # as an absolute path
- # (change requires restart)
- logdir = '/var/log/pgpool'
- # Directory of pgPool status file
- # (change requires restart)
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # CONNECTION POOLING
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- connection_cache = on
- # Activate connection pools
- # (change requires restart)
- # Semicolon separated list of queries
- # to be issued at the end of a session
- # The default is for 8.3 and later
- reset_query_list = 'ABORT; DISCARD ALL'
- # The following one is for 8.2 and before
- #reset_query_list = 'ABORT; RESET ALL; SET SESSION AUTHORIZATION DEFAULT'
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # REPLICATION MODE
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- replication_mode = off
- # Activate replication mode
- # (change requires restart)
- replicate_select = off
- # Replicate SELECT statements
- # when in replication mode
- # replicate_select is higher priority than
- # load_balance_mode.
- insert_lock = on
- # Automatically locks a dummy row or a table
- # with INSERT statements to keep SERIAL data
- # consistency
- # Without SERIAL, no lock will be issued
- lobj_lock_table = ''
- # When rewriting lo_creat command in
- # replication mode, specify table name to
- # lock
- # - Degenerate handling -
- replication_stop_on_mismatch = off
- # On disagreement with the packet kind
- # sent from backend, degenerate the node
- # which is most likely "minority"
- # If off, just force to exit this session
- failover_if_affected_tuples_mismatch = off
- # On disagreement with the number of affected
- # tuples in UPDATE/DELETE queries, then
- # degenerate the node which is most likely
- # "minority".
- # If off, just abort the transaction to
- # keep the consistency
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # LOAD BALANCING MODE
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- load_balance_mode = off
- # Activate load balancing mode
- # (change requires restart)
- ignore_leading_white_space = on
- # Ignore leading white spaces of each query
- white_function_list = ''
- # Comma separated list of function names
- # that don't write to database
- # Regexp are accepted
- black_function_list = 'nextval,setval,nextval,setval'
- # Comma separated list of function names
- # that write to database
- # Regexp are accepted
- database_redirect_preference_list = ''
- # comma separated list of pairs of database and node id.
- # example: postgres:primary,mydb[-]:,mydb[-]:'
- # valid for streaming replicaton mode only.
- app_name_redirect_preference_list = ''
- # comma separated list of pairs of app name and node id.
- # example: 'psql:primary,myapp[0-4]:1,myapp[5-9]:standby'
- # valid for streaming replicaton mode only.
- allow_sql_comments = off
- # if on, ignore SQL comments when judging if load balance or
- # query cache is possible.
- # If off, SQL comments effectively prevent the judgment
- # (pre 3.4 behavior).
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # MASTER/SLAVE MODE
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- master_slave_mode = off
- # Activate master/slave mode
- # (change requires restart)
- master_slave_sub_mode = 'stream'
- # Master/slave sub mode
- # Valid values are combinations stream, slony
- # or logical. Default is stream.
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Streaming -
- sr_check_period =
- # Streaming replication check period
- # Disabled () by default
- sr_check_user = 'postgres'
- # Streaming replication check user
- # This is necessary even if you disable
- # streaming replication delay check with
- # sr_check_period =
- sr_check_password = 'your pass word'
- # Password for streaming replication check user
- sr_check_database = 'postgres'
- # Database name for streaming replication check
- delay_threshold =
- # Threshold before not dispatching query to standby node
- # Unit is in bytes
- # Disabled () by default
- # - Special commands -
- follow_master_command = ''
- # Executes this command after master failover
- # Special values:
- # %d = node id
- # %h = host name
- # %p = port number
- # %D = database cluster path
- # %m = new master node id
- # %H = hostname of the new master node
- # %M = old master node id
- # %P = old primary node id
- # %r = new master port number
- # %R = new master database cluster path
- # %% = '%' character
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # HEALTH CHECK GLOBAL PARAMETERS
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- health_check_period =
- # Health check period
- # Disabled () by default
- health_check_timeout =
- # Health check timeout
- # means no timeout
- health_check_user = 'nobody'
- # Health check user
- health_check_password = ''
- # Password for health check user
- health_check_database = ''
- # Database name for health check. If '', tries 'postgres' frist, then 'template1'
- health_check_max_retries =
- # Maximum number of times to retry a failed health check before giving up.
- health_check_retry_delay =
- # Amount of time to wait (in seconds) between retries.
- connect_timeout =
- # Timeout value in milliseconds before giving up to connect to backend.
- # Default is ms ( second). Flaky network user may want to increase
- # the value. means no timeout.
- # Note that this value is not only used for health check,
- # but also for ordinary conection to backend.
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # HEALTH CHECK PER NODE PARAMETERS (OPTIONAL)
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- #health_check_period0 =
- #health_check_timeout0 =
- #health_check_user0 = 'nobody'
- #health_check_password0 = ''
- #health_check_database0 = ''
- #health_check_max_retries0 =
- #health_check_retry_delay0 =
- #connect_timeout0 =
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # FAILOVER AND FAILBACK
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- failover_command = '/usr/local/bin/failover_stream.sh %d %H /tmp/trigger_file0'
- # Executes this command at failover
- # Special values:
- # %d = node id
- # %h = host name
- # %p = port number
- # %D = database cluster path
- # %m = new master node id
- # %H = hostname of the new master node
- # %M = old master node id
- # %P = old primary node id
- # %r = new master port number
- # %R = new master database cluster path
- # %% = '%' character
- failback_command = ''
- # Executes this command at failback.
- # Special values:
- # %d = node id
- # %h = host name
- # %p = port number
- # %D = database cluster path
- # %m = new master node id
- # %H = hostname of the new master node
- # %M = old master node id
- # %P = old primary node id
- # %r = new master port number
- # %R = new master database cluster path
- # %% = '%' character
- fail_over_on_backend_error = on
- # Initiates failover when reading/writing to the
- # backend communication socket fails
- # If set to off, pgpool will report an
- # error and disconnect the session.
- search_primary_node_timeout =
- # Timeout in seconds to search for the
- # primary node when a failover occurs.
- # means no timeout, keep searching
- # for a primary node forever.
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # ONLINE RECOVERY
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- recovery_user = 'nobody'
- # Online recovery user
- recovery_password = ''
- # Online recovery password
- recovery_1st_stage_command = ''
- # Executes a command in first stage
- recovery_2nd_stage_command = ''
- # Executes a command in second stage
- recovery_timeout =
- # Timeout in seconds to wait for the
- # recovering node's postmaster to start up
- # means no wait
- client_idle_limit_in_recovery =
- # Client is disconnected after being idle
- # for that many seconds in the second stage
- # of online recovery
- # means no disconnection
- # - means immediate disconnection
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # WATCHDOG
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # - Enabling -
- use_watchdog = off
- # Activates watchdog
- # (change requires restart)
- # -Connection to up stream servers -
- trusted_servers = ''
- # trusted server list which are used
- # to confirm network connection
- # (hostA,hostB,hostC,...)
- # (change requires restart)
- ping_path = '/bin'
- # ping command path
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Watchdog communication Settings -
- wd_hostname = ''
- # Host name or IP address of this watchdog
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_port =
- # port number for watchdog service
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_priority =
- # priority of this watchdog in leader election
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_authkey = ''
- # Authentication key for watchdog communication
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_ipc_socket_dir = '/var/run/postgresql'
- # Unix domain socket path for watchdog IPC socket
- # The Debian package defaults to
- # /var/run/postgresql
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Virtual IP control Setting -
- delegate_IP = ''
- # delegate IP address
- # If this is empty, virtual IP never bring up.
- # (change requires restart)
- if_cmd_path = '/sbin'
- # path to the directory where if_up/down_cmd exists
- # (change requires restart)
- if_up_cmd = 'ip addr add $_IP_$/24 dev eth0 label eth0:0'
- # startup delegate IP command
- # (change requires restart)
- if_down_cmd = 'ip addr del $_IP_$/24 dev eth0'
- # shutdown delegate IP command
- # (change requires restart)
- arping_path = '/usr/sbin'
- # arping command path
- # (change requires restart)
- arping_cmd = 'arping -U $_IP_$ -w 1'
- # arping command
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Behaivor on escalation Setting -
- clear_memqcache_on_escalation = on
- # Clear all the query cache on shared memory
- # when standby pgpool escalate to active pgpool
- # (= virtual IP holder).
- # This should be off if client connects to pgpool
- # not using virtual IP.
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_escalation_command = ''
- # Executes this command at escalation on new active pgpool.
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_de_escalation_command = ''
- # Executes this command when master pgpool resigns from being master.
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Watchdog consensus settings for failover -
- failover_when_quorum_exists = on
- # Only perform backend node failover
- # when the watchdog cluster holds the quorum
- # (change requires restart)
- failover_require_consensus = on
- # Perform failover when majority of Pgpool-II nodes
- # aggrees on the backend node status change
- # (change requires restart)
- allow_multiple_failover_requests_from_node = off
- # A Pgpool-II node can cast multiple votes
- # for building the consensus on failover
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Lifecheck Setting -
- # -- common --
- wd_monitoring_interfaces_list = '' # Comma separated list of interfaces names to monitor.
- # if any interface from the list is active the watchdog will
- # consider the network is fine
- # 'any' to enable monitoring on all interfaces except loopback
- # '' to disable monitoring
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_lifecheck_method = 'heartbeat'
- # Method of watchdog lifecheck ('heartbeat' or 'query' or 'external')
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_interval =
- # lifecheck interval (sec) >
- # (change requires restart)
- # -- heartbeat mode --
- wd_heartbeat_port =
- # Port number for receiving heartbeat signal
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_heartbeat_keepalive =
- # Interval time of sending heartbeat signal (sec)
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_heartbeat_deadtime =
- # Deadtime interval for heartbeat signal (sec)
- # (change requires restart)
- heartbeat_destination0 = 'host0_ip1'
- # Host name or IP address of destination
- # for sending heartbeat signal.
- # (change requires restart)
- heartbeat_destination_port0 =
- # Port number of destination for sending
- # heartbeat signal. Usually this is the
- # same as wd_heartbeat_port.
- # (change requires restart)
- heartbeat_device0 = ''
- # Name of NIC device (such like 'eth0')
- # used for sending/receiving heartbeat
- # signal to/from destination .
- # This works only when this is not empty
- # and pgpool has root privilege.
- # (change requires restart)
- #heartbeat_destination1 = 'host0_ip2'
- #heartbeat_destination_port1 =
- #heartbeat_device1 = ''
- # -- query mode --
- wd_life_point =
- # lifecheck retry times
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_lifecheck_query = 'SELECT 1'
- # lifecheck query to pgpool from watchdog
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_lifecheck_dbname = 'template1'
- # Database name connected for lifecheck
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_lifecheck_user = 'nobody'
- # watchdog user monitoring pgpools in lifecheck
- # (change requires restart)
- wd_lifecheck_password = ''
- # Password for watchdog user in lifecheck
- # (change requires restart)
- # - Other pgpool Connection Settings -
- #other_pgpool_hostname0 = 'host0'
- # Host name or IP address to connect to for other pgpool
- # (change requires restart)
- #other_pgpool_port0 =
- # Port number for other pgpool
- # (change requires restart)
- #other_wd_port0 =
- # Port number for other watchdog
- # (change requires restart)
- #other_pgpool_hostname1 = 'host1'
- #other_pgpool_port1 =
- #other_wd_port1 =
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # OTHERS
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- relcache_expire =
- # Life time of relation cache in seconds.
- # means no cache expiration(the default).
- # The relation cache is used for cache the
- # query result against PostgreSQL system
- # catalog to obtain various information
- # including table structures or if it's a
- # temporary table or not. The cache is
- # maintained in a pgpool child local memory
- # and being kept as long as it survives.
- # If someone modify the table by using
- # ALTER TABLE or some such, the relcache is
- # not consistent anymore.
- # For this purpose, cache_expiration
- # controls the life time of the cache.
- relcache_size =
- # Number of relation cache
- # entry. If you see frequently:
- # "pool_search_relcache: cache replacement happend"
- # in the pgpool log, you might want to increate this number.
- check_temp_table = on
- # If on, enable temporary table check in SELECT statements.
- # This initiates queries against system catalog of primary/master
- # thus increases load of master.
- # If you are absolutely sure that your system never uses temporary tables
- # and you want to save access to primary/master, you could turn this off.
- # Default is on.
- check_unlogged_table = on
- # If on, enable unlogged table check in SELECT statements.
- # This initiates queries against system catalog of primary/master
- # thus increases load of master.
- # If you are absolutely sure that your system never uses unlogged tables
- # and you want to save access to primary/master, you could turn this off.
- # Default is on.
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- # IN MEMORY QUERY MEMORY CACHE
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- memory_cache_enabled = off
- # If on, use the memory cache functionality, off by default
- memqcache_method = 'shmem'
- # Cache storage method. either 'shmem'(shared memory) or
- # 'memcached'. 'shmem' by default
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_memcached_host = 'localhost'
- # Memcached host name or IP address. Mandatory if
- # memqcache_method = 'memcached'.
- # Defaults to localhost.
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_memcached_port =
- # Memcached port number. Mondatory if memqcache_method = 'memcached'.
- # Defaults to .
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_total_size =
- # Total memory size in bytes for storing memory cache.
- # Mandatory if memqcache_method = 'shmem'.
- # Defaults to 64MB.
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_max_num_cache =
- # Total number of cache entries. Mandatory
- # if memqcache_method = 'shmem'.
- # Each cache entry consumes bytes on shared memory.
- # Defaults to ,,(.8MB).
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_expire =
- # Memory cache entry life time specified in seconds.
- # means infinite life time. by default.
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_auto_cache_invalidation = on
- # If on, invalidation of query cache is triggered by corresponding
- # DDL/DML/DCL(and memqcache_expire). If off, it is only triggered
- # by memqcache_expire. on by default.
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_maxcache =
- # Maximum SELECT result size in bytes.
- # Must be smaller than memqcache_cache_block_size. Defaults to 400KB.
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_cache_block_size =
- # Cache block size in bytes. Mandatory if memqcache_method = 'shmem'.
- # Defaults to 1MB.
- # (change requires restart)
- memqcache_oiddir = '/var/log/pgpool/oiddir'
- # Temporary work directory to record table oids
- # (change requires restart)
- white_memqcache_table_list = ''
- # Comma separated list of table names to memcache
- # that don't write to database
- # Regexp are accepted
- black_memqcache_table_list = ''
- # Comma separated list of table names not to memcache
- # that don't write to database
- # Regexp are accepted
vi pool_hba.conf修改后如下
- # pgpool Client Authentication Configuration File
- # ===============================================
- #
- # The format rule in this file follows the rules in the PostgreSQL
- # Administrator's Guide. Refer to chapter "Client Authentication" for a
- # complete description. A short synopsis follows.
- #
- # This file controls: which hosts are allowed to connect, how clients
- # are authenticated, which user names they can use, which databases they
- # can access. Records take one of these forms:
- #
- # local DATABASE USER METHOD [OPTION]
- # host DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD [OPTION]
- #
- # (The uppercase items must be replaced by actual values.)
- #
- # The first field is the connection type: "local" is a Unix-domain
- # socket, "host" is either a plain or SSL-encrypted TCP/IP socket.
- #
- # DATABASE can be "all", "sameuser", a database name, or a comma-separated
- # list thereof. Note that "samegroup" like in PostgreSQL's pg_hba.conf
- # file is not supported, since pgpool does not know which group a user
- # belongs to. Also note that the database specified here may not exist in
- # the backend PostgreSQL. pgpool will authenticate based on the database's
- # name, not based on whether it exists or not.
- #
- # USER can be "all", a user name, or a comma-separated list thereof. In
- # both the DATABASE and USER fields you can also write a file name prefixed
- # with "@" to include names from a separate file. Note that a group name
- # prefixed with "+" like in PostgreSQL's pg_hba.conf file is not supported
- # because of the same reason as "samegroup" token. Also note that a user
- # name specified here may not exist in the backend PostgreSQL. pgpool will
- # authenticate based on the user's name, not based on whether he/she exists.
- #
- # CIDR-ADDRESS specifies the set of hosts the record matches.
- # It is made up of an IP address and a CIDR mask that is an integer
- # (between and (IPv4) that specifies the number of significant bits in
- # the mask. Alternatively, you can write an IP address and netmask in
- # separate columns to specify the set of hosts.
- #
- # METHOD can be "trust", "reject", "md5" or "pam". Note that "pam" sends passwords
- # in clear text.
- #
- # OPTION is the name of the PAM service. Default service name is "pgpool"
- #
- # Database and user names containing spaces, commas, quotes and other special
- # characters must be quoted. Quoting one of the keywords "all" or "sameuser"
- # makes the name lose its special character, and just match a database or
- # username with that name.
- #
- # This file is read on pgpool startup. If you edit the file on a running
- # system, you have to restart the pgpool for the changes to take effect.
- # Put your actual configuration here
- # ----------------------------------
- #
- # If you want to allow non-local connections, you need to add more
- # "host" records. In that case you will also need to make pgpool listen
- # on a non-local interface via the listen_addresses configuration parameter.
- #
- # TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD
- # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
- local all all trust
- # IPv4 local connections:
- host all all 0.0.0.0/ md5
- #host all all 127.0.0.1/ trust
- host all all ::/ trust
启用配置文件pool_passwd
- [root@pgpool etc]# pg_md5 -m -p -u postgres pool_passwd
- password:
创建主从切换脚本
- [root@pgpool bin]# vi /usr/local/bin/failover_stream.sh
- # Failover command for streaming replication.
- # This script assumes that DB node is primary, and is standby.
- #
- # If standby goes down, do nothing. If primary goes down, create a
- # trigger file so that standby takes over primary node.
- #
- # Arguments: $: failed node id. $: new master hostname. $: path to
- # trigger file.
- failed_node=$
- new_master=$
- trigger_file=$
- # Do nothing if standby goes down.
- if [ $failed_node = ]; then
- exit ;
- fi
- # Create the trigger file.
- /usr/bin/ssh -T $new_master /bin/touch $trigger_file
- exit ;
- [root@pgpool bin]# chmod failover_stream.sh
启动pgpool
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# pgpool -n -d > /tmp/pgpool.log >& &
- []
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# ps -aux|grep pgpool
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : su pgpool
- pgpool 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : bash
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S+ : : vi /var/log/pgpool/pgpool_status
- root 0.0 0.1 pts/ S : : pgpool -n -d
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: PCP: wait for connection request
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: worker process
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S : : pgpool: health check process()
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ R+ : : grep --color=auto pgpool
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]#
启动两台服务器数据库
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# systemctl start postgresql
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# ps -aux|grep postgresql
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S+ : : grep --color=auto postgresql
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# ps -aux|grep postgres
- postgres 0.0 0.2 ? S : : /usr/bin/postgres -D /var/lib/pgsql/data -p
- postgres 0.0 0.0 ? Ss : : postgres: logger process
- postgres 0.0 0.0 ? Ss : : postgres: checkpointer process
- postgres 0.0 0.0 ? Ss : : postgres: writer process
- postgres 0.0 0.0 ? Ss : : postgres: wal writer process
- postgres 0.0 0.0 ? Ss : : postgres: autovacuum launcher process
- postgres 0.0 0.0 ? Ss : : postgres: stats collector process
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ S+ : : grep --color=auto postgres
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]#
连接测试
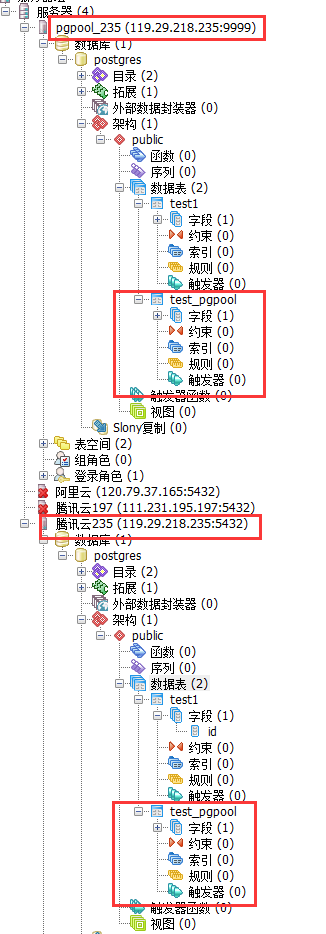
1.连接pgpool,能看到235的数据

2.在pgpool新建test_pgpool表,235的数据库也可以看到表,但备机197上似乎没有看到test_pgpool

3.修改配置文件
- vi pgpool.conf
- 改下面两个属性
- replication_mode = true
- load_balance_mode = true
- 然后关闭客户端的连接
- 235上停止pgpool: pgpool stop
- 235上启动pgpool: pgpool

4.通过主节点建表test_pgpool2,可以看到主、备节点均有test_pgpool2
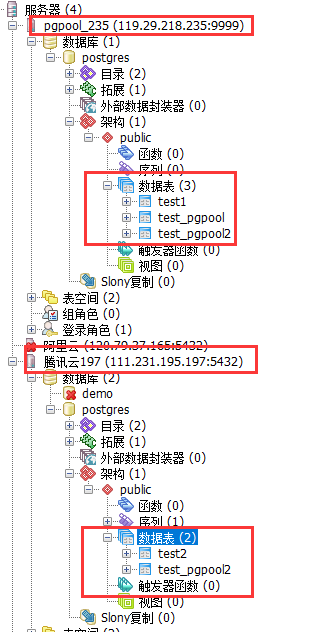
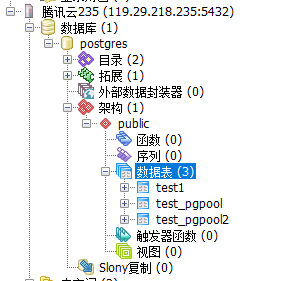
5.关掉235上的postgresql,看看能否切换到197
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# systemctl stop postgresql
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]# ps -aux|grep postgres
- root 0.0 0.0 ? S : : pgpool: postgres postgres 113.116.51.86() idle
- root 0.0 0.0 pts/ R+ : : grep --color=auto postgres
- [root@VM_176_134_centos pgpool-II]#
可以看到已经切换到197了,表明在运行中,如果235挂掉了,还有197可用。
但是发现再启动235后的数据库后,pgpool不会自动切回来,可能切换脚本有问题,这个不弄了,等专业的来

参考
官方文档:pgpool-II 入门教程
centos7 pgpool+postgresql的更多相关文章
- 19.CentOS7下PostgreSQL安装过程
CentOS7下PostgreSQL安装过程 装包 sudo yum install postgresql-server postgresql-contrib 说明: 这种方式直接明了,其他方法也可以 ...
- centos7部署postgresql集群高可用 patroni + etcd 之patroni篇
实验环境:centos7.4纯净版 postgres版本: 9.6.15 etcd版本:3.3.11 patroni版本:1.6.0 patroni介绍可参考:https://github.com/z ...
- centos7下postgresql数据库安装及配置
1.安装 #yum install -y postgresql-server 2.postgresql数据库初始化 #service postgresql initdb 3.启动postgresql服 ...
- pgpool postgresql集群、中间件
pgpool-II是一个工作于PostgreSQL服务器端和PostgreSQL客户端之间的中间件,它提供了如下的功能: 1.连接池 pgpool-II中保存了到PostgreSQL服务器的连接,然后 ...
- CentOS7安装Postgresql
执行命令 Yum install postgresql-server Yum install postgresql-contrib 安装完成后,检查postgresql的服务状态 Systemctl ...
- 阿里云ecs centos7安装 postgresql 9.4
rpm -Uvh http://yum.postgresql.org/9.4/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-centos94-9.4-3.noarch.rpm yum insta ...
- Centos7安装 PostgreSQL步骤
1. 安装服务器即可. Yum install postgresql-server Yum install postgresql-contrib 2. 验证是否安装成功: rpm -aq| grep ...
- centos7 安装 PostgreSql
确定你是管理员,然后运行命令: yum -y install postgresql-server postgresql-contrib 初始化数据库 postgresql-setup initdb 启 ...
- CentOS7 安装Postgresql 11+ 源码编译安装Postgis-2.5.2
####安装Postgresql-11yum install zlib-devel gcc makegroupadd postgresuseradd -g postgres postgrespassw ...
随机推荐
- vuex的数据交互
methods:{ ...mapMutations({aaa:hs}) //将mutations的方法暴露出来,进行调用 aaa是他的名字 ...mapActions(['hs']) //将actio ...
- scipy优化器optimizer
#optimazer优化器 from scipy.optimize import minimize def rosem(x): return sum(100.0*(x[1:]-x[:-1])**2.0 ...
- VS2017+WIN10自动生成类、接口的说明(修改类模板的方法)
微软发布VS2017的时候,我第一时间离线一份专业版,安装到了自己的电脑上,开始体验,但是问题来了,在开发中建立类和接口的时候,说 明注释总要自己写一次,烦!~~于是还是像以前一样改IDE默认的类和接 ...
- arctan
ArcTanWhen the ArcTan functional configuration is selected, the input vector (X_IN,Y_IN) is rotated( ...
- face parsing
主页:https://www.sifeiliu.net/project 基于CNN face parsing: https://www.sifeiliu.net/face-parsing codes: ...
- Flask-sqlacodegen
ORM操作有两种方式. 1.模型迁移到数据库中生成表,codefirst:使用flask-migrate: 需要flask-script: from flask_script import Manag ...
- Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2) B. Vladik and Complicated Book
B. Vladik and Complicated Book time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- 25 行 Python 代码实现人脸识别——OpenCV 技术教程
OpenCV OpenCV 是最流行的计算机视觉库,原本用 C 和 C++ 开发,现在也支持 Python. 它使用机器学习算法在图像中搜索人的面部.对于人脸这么复杂的东西,并没有一个简单的检测能对是 ...
- 【BZOJ2111】[ZJOI2010]排列计数(组合数学)
[BZOJ2111][ZJOI2010]排列计数(组合数学) 题面 BZOJ 洛谷 题解 就是今年九省联考\(D1T2\)的弱化版? 直接递归组合数算就好了. 注意一下模数可以小于\(n\),所以要存 ...
- volatile的实现原理与应用
Java代码在编译后会变成Java字节码,字节码被类加载器加载到JVM里,JVM执行字节码,最终需要转化为汇编指令在CPU上执行,Java中所使用的并发机制依赖于JVM的实现和CPU的指令. vola ...