MIT课程
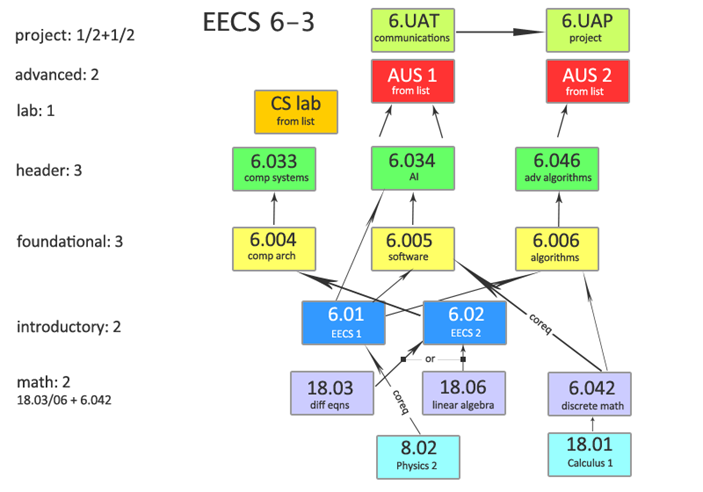
8.02 Physics II (电磁学基础)
Introduction to electromagnetism and electrostatics: electric charge, Coulomb's law, electric structure of matter; conductors and dielectrics. Concepts of electrostatic field and potential, electrostatic energy. Electric currents, magnetic fields and Ampere's law. Magnetic materials. Time-varying fields and Faraday's law of induction. Basic electric circuits. Electromagnetic waves and Maxwell's equations. Subject taught using the TEAL (Technology Enabled Active Learning) studio format which utilizes small group interaction and current technology to help students develop intuition about, and conceptual models of, physical phenomena.
Fall: R. Redwine, J. Conrad
Spring: Staff
课本: Sen-Ben Liao, "Introduction to Electricity and Magnetism (Custom)", Person Custom, 2004
网址: http://mit.edu/8.02t/www/
18.01 Calculus I (微积分基础,相当于高等数学上册内容)
Differentiation and integration of functions of one variable, with applications. Informal treatment of limits and continuity. Differentiation: definition, rules, application to graphing, rates, approximations, and extremum problems. Indefinite integration; separable first-order differential equations. Definite integral; fundamental theorem of calculus. Applications of integration to geometry and science. Elementary functions. Techniques of integration. Polar coordinates. L'Hôpital's rule. Improper integrals. Infinite series: geometric, p-harmonic, simple comparison tests, power series for some elementary functions.
Fall: P. Seidel
Spring: Information: D. Vogan
课本: George Simmons, “Calculus with Analytic Geometry”, McGraw-Hill, 2nd Edition, 1996
网址: http://math.mit.edu/classes/18.01/
18.03 Differential Equations(微分方程)
Study of ordinary differential equations (ODEs), including modeling physical systems. Solution of first-order ODEs by analytical, graphical, and numerical methods. Linear ODEs, primarily second order with constant coefficients. Complex numbers and exponentials. Inhomogeneous equations: polynomial, sinusoidal, and exponential inputs. Oscillations, damping, resonance. Fourier series inputs; resonant terms. Laplace transform methods; convolution and delta function. Matrix methods for first order linear systems: eigenvalues and eigenvectors, matrix exponentials, variation of parameters. Nonlinear autonomous systems: critical point analysis, phase plane diagrams, applications to modeling.
Fall: B. Brubaker
Spring: H. Miller
课本: Edwards, C. Henry; Penney, David E. "Elementary Differential Equations with Boundary Value Problems", Prentice Hall PTR, 6th edition, 2007
网址: http://math.mit.edu/classes/18.03/
18.06 Linear Algebra(线性代数)
Basic subject on matrix theory and linear algebra, emphasizing topics useful in other disciplines, including systems of equations, vector spaces, determinants, eigenvalues, singular value decomposition, and positive definite matrices. Applications to least-squares approximations, stability of differential equations, networks, Fourier transforms, and Markov processes. Uses MATLAB. Compared with 18.700, more emphasis on matrix algorithms and many applications.
Fall: A. Edelman
Spring: G. Strang
课本:Strang, Gilbert "Introduction to Linear Algebra" Wellesley-Cambridge Press, 4th edition, 2009
网址: http://web.mit.edu/18.06/www/
6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science(基础离散数学)
Elementary discrete mathematics for computer science and engineering. Emphasis on mathematical definitions and proofs as well as on applicable methods. Topics: formal logic notation, proof methods; induction, well-ordering; sets, relations; elementary graph theory; integer congruences; asymptotic notation and growth of functions; permutations and combinations, counting principles; discrete probability. Further selected topics such as: recursive definition and structural induction; state machines and invariants; recurrences; generating functions.
A. R. Meyer, T. Leighton
No textbook information available
网址: http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.042/spring12/
6.01 EECS介绍1
An integrated introduction to electrical engineering and computer science, taught using substantial laboratory experiments with mobile robots. Key issues in the design of engineered artifacts operating in the natural world: measuring and modeling system behaviors; assessing errors in sensors and effectors; specifying tasks; designing solutions based on analytical and computational models; planning, executing, and evaluating experimental tests of performance; refining models and designs. Issues addressed in the context of computer programs, control systems, probabilistic inference problems, circuits and transducers, which all play important roles in achieving robust operation of a large variety of engineered systems. 6 Engineering Design Points.
D. M. Freeman, L. P. Kaelbling, T. Lozano-Perez
No required or recommended textbooks
网址: http://mit.edu/6.01/mercurial/spring12/www/index.html
6.02 EECS介绍2
Explores communication signals, systems and networks. Substantial laboratory experiments illustrate the role of abstraction and modularity in engineering design. Students gain practical experience in building reliable systems using imperfect components; selecting appropriate design metrics; choosing effective representations for information; and evaluating tradeoffs in complex systems. Topics include physical characterization and modeling of transmission systems in the time and frequency domains; analog and digital signaling; coding; detecting and correcting errors; relating information transmission rate to signal power, bandwidth and noise; and engineering of packet-switched networks. 6 Engineering Design Points.
C. J. Terman, H. Balakrishnan, J. K. White
No textbook information available
6..004 Computtation Structures(计算机体系结构)
Introduces architecture of digital systems, emphasizing structural principles common to a wide range of technologies. Multilevel implementation strategies; definition of new primitives (e.g., gates, instructions, procedures, and processes) and their mechanization using lower-level elements. Analysis of potential concurrency; precedence constraints and performance measures; pipelined and multidimensional systems. Instruction set design issues; architectural support for contemporary software structures. 4 Engineering Design Points.
S. A. Ward, C. J. Terman
No textbook information available
6.005 Elements of Software Construction(软件构建基础)
Introduction to the fundamental principles and techniques of software development that have greatest impact on practice. Topics include capturing the essence of a problem by recognizing and inventing suitable abstractions; key paradigms, including state machines, functional programming, and object-oriented programming; use of design patterns to bridge gap between models and code; the role of interfaces and specification in achieving modularity and decoupling; reasoning about code using invariants; testing, test-case generation and coverage; essentials of programming with objects, functions, and abstract types. Includes exercises in modeling, design, implementation and reasoning. 12 Engineering Design Points.
D. N. Jackson, R. C. Miller
No textbook information available
6.006 Introduction to Algoithms(算法导论)
Introduction to mathematical modeling of computational problems, as well as common algorithms, algorithmic paradigms, and data structures used to solve these problems. Emphasizes the relationship between algorithms and programming, and introduces basic performance measures and analysis techniques for these problems.
R. L. Rivest, S. Devadas
课本: Thomas H.Cormen, Charles E.Leiserson, Ronald L.Rivest, and Clifford Stein, "Introduction to Algorithms", MIT Press, second edition, 2001
6.033 Computer System Engineering(计算机系统工程)
Topics on the engineering of computer software and hardware systems: techniques for controlling complexity; strong modularity using client-server design, operating systems; performance, networks; naming; security and privacy; fault-tolerant systems, atomicity and coordination of concurrent activities, and recovery; impact of computer systems on society. Case studies of working systems and readings from the current literature provide comparisons and contrasts. Two design projects. Students engage in extensive written communication exercises. Enrollment may be limited. 4 Engineering Design Points.
M. F. Kaashoek, H. Balakrishnan
课本: Sltzer, Jerome H., Kaashoek, and M.Frans, "Principles of Computer System Design: An Introduction", Elsevier Science & Technology Books, 2009
课本(国内引进): 大学计算机教育国外著名教材系列:计算机系统设计原理(影印版)
6.034 Artificial Intelligence(人工智能)
Introduces representations, techniques, and architectures used to build applied systems and to account for intelligence from a computational point of view. Applications of rule chaining, heuristic search, constraint propagation, constrained search, inheritance, and other problem-solving paradigms. Applications of identification trees, neural nets, genetic algorithms, and other learning paradigms. Speculations on the contributions of human vision and language systems to human intelligence. 4 Engineering Design Points.
Fall: P. H. Winston
Spring: R. A. Barzilay
课本: Stuart Russell, Peter Norvig, "Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach", Prentice Hall, 3rd edition, 2009
网址: http://ai6034.mit.edu/fall10/index.php?title=Main_Page
6.046J Design and Analysis of Algorithms(算法设计分析)
Techniques for the design and analysis of efficient algorithms, emphasizing methods useful in practice. Topics include sorting; search trees, heaps, and hashing; divide-and-conquer; dynamic programming; greedy algorithms; amortized analysis; graph algorithms; and shortest paths. Advanced topics may include network flow; computational geometry; number-theoretic algorithms; polynomial and matrix calculations; caching; and parallel computing.
C. E. Leiserson, M. Goemans
课本: Thomas H.Cormen, Charles E.Leiserson, Ronald L.Rivest, and Clifford Stein, "Introduction to Algorithms", MIT Press, second edition, 2001
网址: http://theory.lcs.mit.edu/classes/6.046/
AUS - Advanced Undergraduate Subjects (高级课程,选择两门)
Advanced Undergraduate Subjects (AUS's) build on the foundation and header subjects to provide an introduction to broadly-recognized areas of specialization in EECS. The AUS's provide an opportunity for integration of earlier learning and may include design- or project-oriented capstone experience.
Undergraduate students are required to take two AUS's, and should choose these subjects based on their interest in the associated areas of specialization. The AUS's also provide a basis for more advanced subjects for students in the MEng program (where they can be used as part of the required concentration).
Subjects used to satisfy the AUS requirement may not also be used to satisfy other requirements, such as the Department lab requirement.
6.022J Quantitative Systems Physiology
6.023J Fields, Forces and Flows in Biological Systems
6.035 Computer Language Engineering
6.045J Automata, Computability and Complexity
6.047 Computational Biology: Genomes, Networks, Evolution
6.049 Evolutionary Biology
6.061 Introduction to Electric Power Systems
6.077 Semiconductor Device Physics (Spring 2011 only)
6.111 Introductory Digital Systems Laboratory
6.115 Microcomputer Project Laboratory
6.131 Power Electronics Laboratory
6.141J Robotics: Science and Systems I
6.142J Robotics Science and Systems II
6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems
6.173 Multicore Systems Laboratory
6.207 Networks
6.301 Solid-State Circuits
6.302 Feedback Systems
6.336J Introduction to Numerical Simulation
6.341 Discrete-Time Signal Processing
6.434J Statistics for Engineers and Scientists
6.502J Introduction to Molecular Simulations
6.503 Foundations of Algorithms and Computational Techniques in Systems Biology
6.602 Fundamentals of Photonics
6.608 Introduction to Particle Accelerators
6.641 Electromagnetic Fields, Forces, and Motion
6.701 Introduction to Nanoelectronics
6.717 Design and Fabrication of Microelectromechanical Systems
6.801 Machine Vision
6.802 Computational Systems Biology
6.803 The Human Intelligence Enterprise
6.804J Computational Cognitive Science
6.805 Ethics and the Law on the Electronic Frontier
6.813 User Interface Design and Implementation
6.814 Database Systems
6.815 Digital and Computational Photography
6.825 Techniques in Artificial Intelligence
6.837 Computer Graphics
6.840J Theory of Computation
6.854J Advanced Algorithms
6.857 Network and Computer Security
6.858 Computer Systems Security
6.863J Natural Language and the Computer Representation of Knowledge
6.867 Machine Learning
网址: http://student.mit.edu/catalog/m6c.html
UAT - Preparation for Undergraduate Advanced Project
Instruction in aspects of effective technical oral presentations through exposure to different workplace communication skills. As preparation for the advanced undergraduate project (UAP), students develop research topics, identify a research supervisor, and prepare a short research proposal for an oral presentation.
T. L. Eng
No textbook information available
UAP - Undergraduate Advanced Project (相当于毕业设计之类)
Research project for those students completing the SB degree, to be arranged by the student and an appropriate MIT faculty member. Students who register for this subject must consult the department undergraduate office. Students engage in extensive written communications exercises.
C. J. Terman
No textbook information available
网址: http://www.eecs.mit.edu/ug/uap.html
Communication Requirement(沟通课程)
All undergraduates are required to complete a multi-phase communication requirement which requires that four classes be completed, usually one in each academic year. The first two years' classes (CI-H) are taken from among designated classes within the HASS requirement. The third and fourth classes (CI-M) are taken from among designated CI-M classes within the student's major program or department. The CI-M classes taken satisfy the major program requirements as well as CI-M and their units count as units beyond the GIRs.
MIT课程的更多相关文章
- mit课程ocw-mathematics
https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/find-by-topic/#cat=mathematics Course # Course Title Level 1.010 Uncerta ...
- mit课程ocw-business
https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/find-by-topic/#cat=business Course # Course Title Level 1.011 Project Ev ...
- MIT JOS学习笔记01:环境配置、Boot Loader(2016.10.22)
未经许可谢绝以任何形式对本文内容进行转载! 一.环境配置 关于MIT课程中使用的JOS的配置教程网上已经有很多了,在这里就不做介绍,个人使用的是Ubuntu 16.04 + qemu.另注,本文章中贴 ...
- 线性代数导论 | Linear Algebra 课程
搞统计的线性代数和概率论必须精通,最好要能锻炼出直觉,再学机器学习才会事半功倍. 线性代数只推荐Prof. Gilbert Strang的MIT课程,有视频,有教材,有习题,有考试,一套学下来基本就入 ...
- 我的“MIT Challenge”
前言 在学习之余看到了一个有趣的挑战,名叫"MIT Challenge",这个挑战的目标是在一年365天之内学习 MIT 计算机系本科本科学生四年的课程.自己大二学习算法时也曾学习 ...
- 世界名校网络课程大盘点,美国大学CS专业十三大研究方向,世界50所知名大学提供开放课程
世界名校网络课程大盘点 加州大学伯克利分校http://webcast.berkeley.edu/ 加州大学伯克利分校与斯坦福大学. 麻省理工学院等一同被誉为美国工程科技界的学术 领袖,其常年位居 ...
- Raft论文学习笔记
先附上论文链接 https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.824/papers/raft-extended.pdf 最近在自学MIT的6.824分布式课程,找到两个比较好的githu ...
- 解决持久化数据太大,单个节点的硬盘无法存储的问题;解决运算量太大,单个节点的内存、CPU无法处理的问题
需要学习的技术很多,要自学新知识也不是一件容易的事,选择一个自己比较感兴趣的会是一个比较好的开端,于是,打算学一学分布式系统. 带着问题,有目的的学习,先了解整体架构,在深入感兴趣的细节,这是我的计划 ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册00 - 翻译起因
从上一次学习MIT的操作系统课程又过去了一年.上次学习并没有坚持下去.想来虽有种种原因,其还在自身无法坚持罢了.故此次再鼓起勇气重新学习,发现课程都已由2014改版为2016了.但大部分内容并没有改变 ...
随机推荐
- Mysql安装 ----> 基于源码包安装
1)基于源码包安装MySQL [root@localhost ~]# rpm -q mysql mysql-server mariadb mairadb-server //检查有没 ...
- Verilog状态机
以1011为例 代码如下: //1011(Meay型) module state1(clk,in,rst_n,out); input clk; input rst_n; input in; outpu ...
- Android的界面组件使用之ImageButton和ImageView,ImageSwitcher和GridView
(一)ImageButton和ImageView ImageButton与Button的功能完全相同,只是ImageButton上显示的是图像,并且每个ImageButton组件都必须指定一个id,以 ...
- selenium webdriver 操作select
@Test public void test() { WebDriver driver=ExplorerBase.IESetting(); driver.get("http://unique ...
- selenium webdriver 定位元素 第一部分
static final WebDriver driver = ExplorerBase.IESetting(); // 实例化一个浏览器对象 @Test //@Ignore public void ...
- Vue日常报错
报错信息: Error: Cannot find module 'webpack/bin/config-yargs' at Function.Module._resolveFilename (inte ...
- requests库 cookie和session
cookie 如果一个相应中包含了cookie,那么可以利用cookie属性拿到这个返回的cookie值: res = requests.get('http://www.baidu.com') pri ...
- R语言 一个向量的值分派给另一个向量
group = sample(seq(1,10),size = 20,replace = T) #这20个组分别属于1,...,10 v = rnorm(length(unique(group)),0 ...
- VMware 设置共享文件夹
1. 打开: 虚拟机 -> 设置 -> 选项 2. 选择 “总是启用” ,然后点 “添加” 选择你要共享的本地文件夹,最后点确定. 3. Linux下在 /mnt/hgfs 文件夹下就可以 ...
- Spring MVC中的ResponseEntity和ResponseBody的区别
1.ResponseEntity的优先级高于@ResponseBody. 在不是ResponseEntity的情况下才去检查有没有@ResponseBody注解. 如果响应类型是ResponseEnt ...
