python实现逻辑回归
首先得明确逻辑回归与线性回归不同,它是一种分类模型。而且是一种二分类模型。
首先我们需要知道sigmoid函数,其公式表达如下:
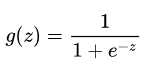
其函数曲线如下:
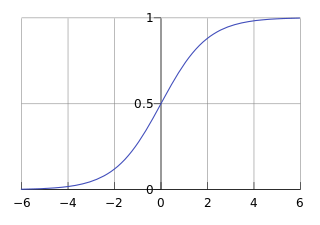
sigmoid函数有什么性质呢?
1、关于(0,0.5) 对称
2、值域范围在(0,1)之间
3、单调递增
4、光滑
5、中间较陡,两侧较平缓
6、其导数为g(z)(1-g(z)),即可以用原函数直接计算
于是逻辑回归的函数形式可以用以下公式表示:

其中θ表示权重参数,x表示输入。θTx为决策边界,就是该决策边界将不同类数据区分开来。
为什么使用sigmoid函数呢?
1、sigmoid函数本身的性质
2、推导而来
我们知道伯努利分布:
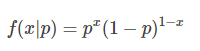
当x=1时,f(1|p) =p,当x=0时,f(0|p)=1-p
首先要明确伯努利分布也是指数族,指数族的一般表达式为:

由于:
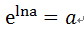
则有:

所以:
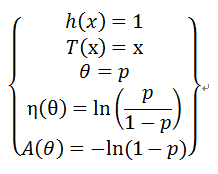
因为:
 则有:
则有:
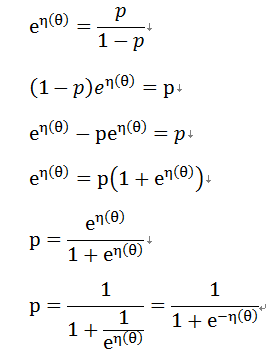
逻辑回归代价函数:

为什么这么定义呢?
以单个样本为例:

上面式子等价于:
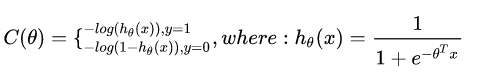
当y=1时,其图像如下:
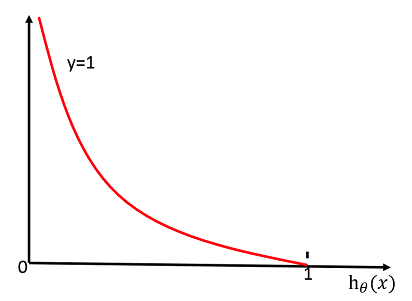
也就是说当hθ(x)的值越接近1,C(θ) 的值就越小。
同理当y=0时,其图像如下:
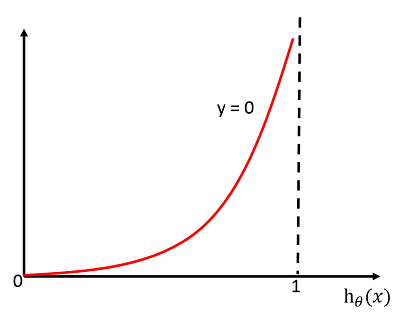
也就是说当hθ(x)的值越接近0,C(θ) 的值就越小。
这样就可以将不同类区分开来。
代价函数的倒数如下:
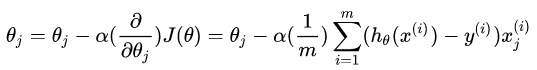
推导过程如下:
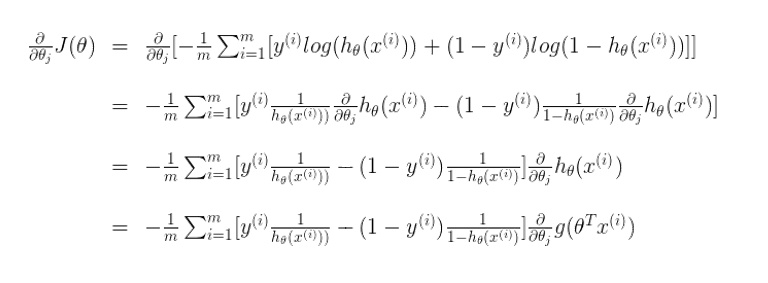
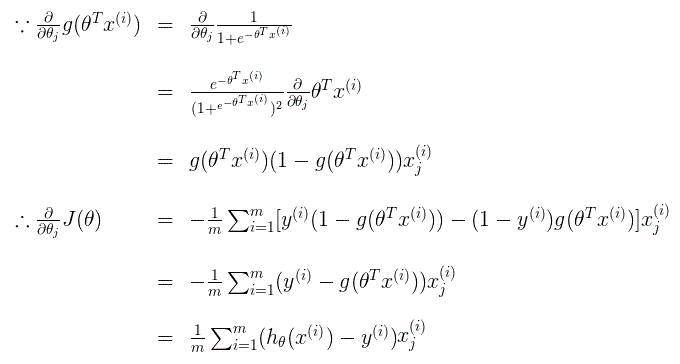
上面参考了:
https://blog.csdn.net/sun_wangdong/article/details/80780368
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28415991
接下来就是代码实现了,代码来源: https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch
from __future__ import print_function, division
import numpy as np
import math
from mlfromscratch.utils import make_diagonal, Plot
from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.activation_functions import Sigmoid class LogisticRegression():
""" Logistic Regression classifier.
Parameters:
-----------
learning_rate: float
The step length that will be taken when following the negative gradient during
training.
gradient_descent: boolean
True or false depending if gradient descent should be used when training. If
false then we use batch optimization by least squares.
"""
def __init__(self, learning_rate=.1, gradient_descent=True):
self.param = None
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.gradient_descent = gradient_descent
self.sigmoid = Sigmoid() def _initialize_parameters(self, X):
n_features = np.shape(X)[1]
# Initialize parameters between [-1/sqrt(N), 1/sqrt(N)]
limit = 1 / math.sqrt(n_features)
self.param = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, (n_features,)) def fit(self, X, y, n_iterations=4000):
self._initialize_parameters(X)
# Tune parameters for n iterations
for i in range(n_iterations):
# Make a new prediction
y_pred = self.sigmoid(X.dot(self.param))
if self.gradient_descent:
# Move against the gradient of the loss function with
# respect to the parameters to minimize the loss
self.param -= self.learning_rate * -(y - y_pred).dot(X)
else:
# Make a diagonal matrix of the sigmoid gradient column vector
diag_gradient = make_diagonal(self.sigmoid.gradient(X.dot(self.param)))
# Batch opt:
self.param = np.linalg.pinv(X.T.dot(diag_gradient).dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(diag_gradient.dot(X).dot(self.param) + y - y_pred) def predict(self, X):
y_pred = np.round(self.sigmoid(X.dot(self.param))).astype(int)
return y_pred
说明:np.linalg.pinv()用于计算矩阵的pseudo-inverse(伪逆)。第一种方法求解使用随机梯度下降。
其中make_diagonal()函数如下:用于将向量转换为对角矩阵
def make_diagonal(x):
""" Converts a vector into an diagonal matrix """
m = np.zeros((len(x), len(x)))
for i in range(len(m[0])):
m[i, i] = x[i]
return m
其中Sigmoid代码如下:
class Sigmoid():
def __call__(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) def gradient(self, x):
return self.__call__(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
最后是主函数运行代码:
from __future__ import print_function
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Import helper functions
import sys
sys.path.append("/content/drive/My Drive/learn/ML-From-Scratch/")
from mlfromscratch.utils import make_diagonal, normalize, train_test_split, accuracy_score
from mlfromscratch.deep_learning.activation_functions import Sigmoid
from mlfromscratch.utils import Plot
from mlfromscratch.supervised_learning import LogisticRegression def main():
# Load dataset
data = datasets.load_iris()
X = normalize(data.data[data.target != 0])
y = data.target[data.target != 0]
y[y == 1] = 0
y[y == 2] = 1 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33, seed=1) clf = LogisticRegression(gradient_descent=True)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test) accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print ("Accuracy:", accuracy) # Reduce dimension to two using PCA and plot the results
Plot().plot_in_2d(X_test, y_pred, title="Logistic Regression", accuracy=accuracy) if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
结果:
Accuracy: 0.9393939393939394

python实现逻辑回归的更多相关文章
- 机器学习_线性回归和逻辑回归_案例实战:Python实现逻辑回归与梯度下降策略_项目实战:使用逻辑回归判断信用卡欺诈检测
线性回归: 注:为偏置项,这一项的x的值假设为[1,1,1,1,1....] 注:为使似然函数越大,则需要最小二乘法函数越小越好 线性回归中为什么选用平方和作为误差函数?假设模型结果与测量值 误差满足 ...
- 机器学习之使用Python完成逻辑回归
一.任务基础 我们将建立一个逻辑回归模型来预测一个学生是否被大学录取.假设你是一个大学系的管理员,你想根据两次考试的结果来决定每个申请人的录取机会.你有以前的申请人的历史数据,你可以用它作为逻辑回归的 ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——逻辑回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- Python之逻辑回归模型来预测
建立一个逻辑回归模型来预测一个学生是否被录取. import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt impor ...
- python机器学习-逻辑回归
1.逻辑函数 假设数据集有n个独立的特征,x1到xn为样本的n个特征.常规的回归算法的目标是拟合出一个多项式函数,使得预测值与真实值的误差最小: 而我们希望这样的f(x)能够具有很好的逻辑判断性质,最 ...
- python机器学习——逻辑回归
我们知道感知器算法对于不能完全线性分割的数据是无能为力的,在这一篇将会介绍另一种非常有效的二分类模型--逻辑回归.在分类任务中,它被广泛使用 逻辑回归是一个分类模型,在实现之前我们先介绍几个概念: 几 ...
- Python使用逻辑回归估算OR值
第一种是统计学方法,需要用到 statsmodels包 statsmodels是统计和计量经济学的package,包含了用于参数评估和统计测试的实用工具 第二种是机器学习,需要使用sklearn中的L ...
- 用python实现逻辑回归
机器学习课程的一个实验,整理出来共享. 原理很简单,优化方法是用的梯度下降.后面有测试结果. # coding=utf-8 from math import exp import matplotlib ...
- Python之逻辑回归
代码: import numpy as np from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegress ...
随机推荐
- 逃生 HDU 4857(反向建图 + 拓扑排序)
逃生 链接 Problem Description 糟糕的事情发生啦,现在大家都忙着逃命.但是逃命的通道很窄,大家只能排成一行. 现在有n个人,从1标号到n.同时有一些奇怪的约束条件,每个都形如:a必 ...
- 实际开发中 dao、entity的代码怎样自动生成?一款工具送给你
01 关注"一猿小讲"朋友,都知道以往的文章一直倡导拒绝 CRUD,那到底什么是 CRUD?今天咱们就聊聊 Java 妹子小猿与数据库老头交互的事儿. 产品小汪铿锵有力的说:小猿同 ...
- 使用git上传代码到GitHub
1.安装git git在Windows上安装很简单,在官网下载git的安装包后打开,然后一路next就好.安装完git之后,在文件夹中右击鼠标,出现Git Bash Here就表示安装完成了. 选择G ...
- Light of future-冲刺Day 2
目录 归属班级 →2019秋福大软件工程实践Z班 作业要求 →团队作业第五次-项目冲刺 团队名称 未来之光 这个作业的目标 第二天的冲刺总结 作业正文 →Light of future-冲刺Day 2 ...
- DALI 48V驱动
DALI-CC-30W-48V技术手册 产品名称:DALI-CC-30W-48V 支持协议:IEC 62386-101:2018,IEC 62386-102:2018,IEC 62386-207:20 ...
- Java第十二天,权限修饰符
Java当中权限修饰符共有四种.分别是public.protected.(default).private. 注:YSE代表可访问,NO代表不可访问. 同一个类 同一个包,非继承 不同的包,有继承 ...
- "被删除的文本"组件:<del> —— 快应用组件库H-UI
 <import name="del" src="../Common/ui/h-ui/text/c_tag_del"></import> ...
- HTML5实现刷脸支付
最近刷脸支付很火,老板们当然要追赶时代潮流,于是就有了刷脸支付这个项目.前端实现关键的技术是摄像头录像,拍照和人脸比对,本文来探讨一下如何在html5环境中如何实现刷脸支付以及开发过程中遇到的问题. ...
- qt creator源码全方面分析(4-0)
Qt系统 Qt Creator源码是在Qt对象和框架基础下写的,因此,阅读Qt Creator源码,你首先对Qt得有一定的了解. Qt Core Qt Core特征: The Meta-Object ...
- linux中操作k8s的基本命令-更新中
linux中操作k8s的基本命令 最近工作中使用到了k8s,那么就来总结下平时使用到的基本的命令 获取某个namespace下的pod 获取某个namespace下的pod,展示出ip和pod信息 查 ...
