[模拟] Codeforces - 1191C - Tokitsukaze and Discard Items
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently, Tokitsukaze found an interesting game. Tokitsukaze had nn items at the beginning of this game. However, she thought there were too many items, so now she wants to discard mm (1≤m≤n1≤m≤n) special items of them.
These nn items are marked with indices from 11 to nn. In the beginning, the item with index ii is placed on the ii-th position. Items are divided into several pages orderly, such that each page contains exactly kk positions and the last positions on the last page may be left empty.
Tokitsukaze would do the following operation: focus on the first special page that contains at least one special item, and at one time, Tokitsukaze would discard all special items on this page. After an item is discarded or moved, its old position would be empty, and then the item below it, if exists, would move up to this empty position. The movement may bring many items forward and even into previous pages, so Tokitsukaze would keep waiting until all the items stop moving, and then do the operation (i.e. check the special page and discard the special items) repeatedly until there is no item need to be discarded.
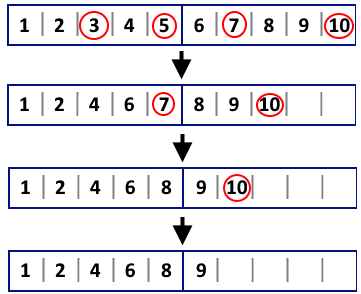 Consider the first example from the statement: n=10n=10, m=4m=4, k=5k=5, p=[3,5,7,10]p=[3,5,7,10]. The are two pages. Initially, the first page is special (since it is the first page containing a special item). So Tokitsukaze discards the special items with indices 33 and 55. After, the first page remains to be special. It contains [1,2,4,6,7][1,2,4,6,7], Tokitsukaze discards the special item with index 77. After, the second page is special (since it is the first page containing a special item). It contains [9,10][9,10], Tokitsukaze discards the special item with index 1010.
Consider the first example from the statement: n=10n=10, m=4m=4, k=5k=5, p=[3,5,7,10]p=[3,5,7,10]. The are two pages. Initially, the first page is special (since it is the first page containing a special item). So Tokitsukaze discards the special items with indices 33 and 55. After, the first page remains to be special. It contains [1,2,4,6,7][1,2,4,6,7], Tokitsukaze discards the special item with index 77. After, the second page is special (since it is the first page containing a special item). It contains [9,10][9,10], Tokitsukaze discards the special item with index 1010.
Tokitsukaze wants to know the number of operations she would do in total.
The first line contains three integers nn, mm and kk (1≤n≤10181≤n≤1018, 1≤m≤1051≤m≤105, 1≤m,k≤n1≤m,k≤n) — the number of items, the number of special items to be discarded and the number of positions in each page.
The second line contains mm distinct integers p1,p2,…,pmp1,p2,…,pm (1≤p1<p2<…<pm≤n1≤p1<p2<…<pm≤n) — the indices of special items which should be discarded.
Print a single integer — the number of operations that Tokitsukaze would do in total.
10 4 5
3 5 7 10
3
13 4 5
7 8 9 10
1
For the first example:
- In the first operation, Tokitsukaze would focus on the first page [1,2,3,4,5][1,2,3,4,5] and discard items with indices 33 and 55;
- In the second operation, Tokitsukaze would focus on the first page [1,2,4,6,7][1,2,4,6,7] and discard item with index 77;
- In the third operation, Tokitsukaze would focus on the second page [9,10][9,10] and discard item with index 1010.
For the second example, Tokitsukaze would focus on the second page [6,7,8,9,10][6,7,8,9,10] and discard all special items at once.
题意:
一开始有n个数,这些数从1到n编号,每k个数为一组,现在给出m个要删去的特殊数,有一种操作,从第一个包含特殊数的组开始删,一次可以把一组里所有特殊数删掉,删掉数后会有空位,这些空位会被后面的数依次补上,并形成新的组,问最少需要操作多少次
思路:
考虑当前最多可以删到那个数,并求出那个数的坐标,就要知道最大可以到哪个坐标,现在定义一个最大容纳量,
最大容纳量=页数*页容量+删掉的数,页数=1+要再翻多少页(从第1页开始),
要再翻多少页=(当前坐标-已经删掉的个数-1)/页容量(-1是减去它本身)
一直删到不能再删(已经删的个数要小于等于m且最大坐标要小于等于最大容纳量)
每次统计操作次数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int amn=1e5+;
ll n,m,k,sp[amn];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
cin>>sp[i];
ll tp=,ans=,jg;
while(tp<=m){
jg=((sp[tp]-tp-)/k+)*k+tp; ///最大容纳量=页数*页容量+删掉的数,页数=1+要再翻多少页(从第1页开始),要再翻多少页=(当前坐标-已经删掉的个数-1)/页容量(-1是减去它本身)
while(tp<=m&&sp[tp]<=jg)tp++; ///一直删到不能再删(已经删的个数要小于等于m且最大坐标要小于等于最大容纳量)
ans++;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
/***
一开始有n个数,这些数从1到n编号,每k个数为一组,现在给出m个要删去的特殊数,有一种操作,从第一个包含特殊数的组开始删,一次可以把一组里所有特殊数删掉,删掉数后会有空位,这些空位会被后面的数依次补上,并形成新的组,问最少需要操作多少次
考虑当前最多可以删到那个数,并求出那个数的坐标,就要知道最大可以到哪个坐标,现在定义一个最大容纳量,
最大容纳量=页数*页容量+删掉的数,页数=1+要再翻多少页(从第1页开始),
要再翻多少页=(当前坐标-已经删掉的个数-1)/页容量(-1是减去它本身)
一直删到不能再删(已经删的个数要小于等于m且最大坐标要小于等于最大容纳量)
每次统计操作次数
***/
[模拟] Codeforces - 1191C - Tokitsukaze and Discard Items的更多相关文章
- Codeforces - 1191C - Tokitsukaze and Discard Items - 模拟
https://codeforces.com/contest/1191/problem/C 一开始想象了一下,既然每次删除都是往前面靠,那么好像就是页数*页容量+空位数=最多容纳到的坐标. 至于为什么 ...
- Codeforces 1190A. Tokitsukaze and Discard Items
传送门 显然从左到右考虑每个要删除的数 维护一个 $cnt$ 表示之前已经删除了 $cnt$ 个数,那么当前所有要删除数的实际位置就要减去 $cnt$ 直接暴力枚举哪些数在最左边一个块然后一起删除 每 ...
- [Codeforces 1191D] Tokitsukaze, CSL and Stone Game(博弈论)
[Codeforces 1191D] Tokitsukaze, CSL and Stone Game(博弈论) 题面 有n堆石子,两个人轮流取石子,一次只能从某堆里取一颗.如果某个人取的时候已经没有石 ...
- Codeforces - 1191B - Tokitsukaze and Mahjong - 模拟
https://codeforces.com/contest/1191/problem/B 小心坎张听的情况. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespac ...
- 贪心+模拟 Codeforces Round #288 (Div. 2) C. Anya and Ghosts
题目传送门 /* 贪心 + 模拟:首先,如果蜡烛的燃烧时间小于最少需要点燃的蜡烛数一定是-1(蜡烛是1秒点一支), num[g[i]]记录每个鬼访问时已点燃的蜡烛数,若不够,tmp为还需要的蜡烛数, ...
- 模拟 Codeforces Round #203 (Div. 2) C. Bombs
题目地址:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/350/C /* 题意:机器人上下左右走路,把其他的机器人都干掉要几步,好吧我其实没读懂题目, 看着样例猜出 ...
- 模拟 Codeforces Round #249 (Div. 2) C. Cardiogram
题目地址:http://codeforces.com/contest/435/problem/C /* 题意:给一组公式,一组数据,计算得到一系列的坐标点,画出折线图:) 模拟题:蛮恶心的,不过也简单 ...
- 模拟 Codeforces Round #297 (Div. 2) A. Vitaliy and Pie
题目传送门 /* 模拟:这就是一道模拟水题,看到标签是贪心,还以为错了呢 题目倒是很长:) */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> ...
- queue+模拟 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) C. Soldier and Cards
题目传送门 /* 题意:两堆牌,每次拿出上面的牌做比较,大的一方收走两张牌,直到一方没有牌 queue容器:模拟上述过程,当次数达到最大值时判断为-1 */ #include <cstdio&g ...
随机推荐
- ARTS 第 1 周
每周一道算法.点评一篇英文技术文章.学习一个技术技巧.分享一个技术观点和思路 Algorithm 题目:两数和 给定一个整数数组,返回这两个数字的索引,使它们相加为一个指定的数. 因为是返回两个数字的 ...
- 94-datetmie模块
目录 datetmie模块 1 返回当前时间 2 当前时间+3天 3 当前时间-3天 4 当前时间-3小时 5 当前时间+30分钟 6 时间替换 datetmie模块 datetime模块可以看成是时 ...
- MVC03
1.添加model model 的作用是什么? 处理项目的数据模型,与数据库交互 .net推荐的处理数据的方式:使用 idd framework 1)新建model 右键models文件夹,选择添加, ...
- 那是我夕阳下的奔跑,电商网站PC端详情页图片放大效果实现
在详情页浏览时商品大图还是不能完全看清楚商品的细节,该特效实现鼠标悬停在商品大图上时,在商品大图右侧出现放大镜效果并根据鼠标的位置来改变右侧大图的显示内容,放大镜中的内容和鼠标悬停位置的内容相同.该特 ...
- CSS单位计算总结
CSS单位总结 公共部分css body { background-color: #000; color: skyblue; margin: 0; padding: 0; } body>div& ...
- text-decoration与color属性
text-decoration属性值 如果指定某个标签的text-decoration属性时,希望为其添加多个样式(比如:上划线.下划线.删除线),那么需要把所有的值合并到一个规则中才会生效 p{ t ...
- 容器内init进程方案
背景 进程标识符 (PID) 是Linux 内核为每个进程提供的唯一标识符.熟悉docker的同学都知道, 所有的进程 PID都属于某一个PID namespaces, 也就是说容器具有一组自己的 P ...
- Unity C# Scoket Thread
关于 Scoket和Thread 也没什么要说的,网上有很多资料.但是需要注意的是 Scoket和Thread 都需要创建和杀死.不然一定会造成程序假死.好了上代码 服务器: using System ...
- js原型继承题目
var F = function(){}; Object.prototype.a = function(){}; Function.prototype.b = function(){}; var f ...
- django 知识点小结
以下内容为用django写blog中的一些知识点,权当复习. 一.定义view 1.get_object_or_404()是用get()查询数据,如果不存在就直接返回404 参数: get_objec ...
