Spring ( 四 )Spring的AOP动态代理、切面编程
个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一、AOP切面编程
1、什么是AOP
AOP是面向切面编程。全称:Aspect Oriented Programming
面向切面编程指的是:程序是运行期间,动态地将某段代码插入到原来方法代码的某些位置中。这就叫面向切面编程。
2、一个简单计算数功能加日记
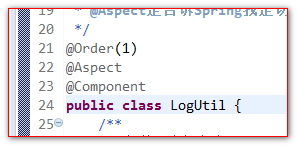
public class LogUtil {
public static void logBefore(String method, Object... args) {
System.out.println("方法是【" + method + "】,参数是:" + Arrays.asList(args));// 日记
}
public static void logAfterReturning(String method, Object result) {
System.out.println("方法是【" + method + "】,返回值是:" + result);// 日记
}
}public interface Calculate {
// 加法
public int add(int num1, int num2);
// 加法
public int add(int num1, int num2, int num3);
// 除法
public int div(int num1, int num2);
}
实现类
public class Calculator implements Calculate {
@Override
public int add(int num1, int num2) {
LogUtil.logBefore("add", num1, num2);
int result = num1 + num2;
LogUtil.logAfterReturning("add", result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int add(int num1, int num2, int num3) {
LogUtil.logBefore("add", num1, num2, num3);
int result = num1 + num2 + num3;
LogUtil.logAfterReturning("add", result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int num1, int num2) {
LogUtil.logBefore("div", num1, num2);
int result = num1 / num2;
LogUtil.logAfterReturning("div", result);
return result;
}
}测试:
//告诉junit测试,我的Spring容器配置文件在哪里
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
//使用Spring扩展的junit4运行器去运行测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class SpringTest {
@Autowired
Calculator calculate;
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
calculate.add(100, 100);
System.out.println("=================================");
calculate.div(100, 0);
}
}结果:
方法 前置通知logBefore 是【add】,参数是:[100, 100]
目标方法 add(int num1, int num2) 正在执行
方法 后置通知logAfter 是【add】,参数是:[100, 100]
方法 返回通知logAfterReturning 是【add】,返回值是:200
=================================
方法 前置通知logBefore 是【div】,参数是:[100, 0]
目标方法 div(int num1, int num2) 正在执行
方法 后置通知logAfter 是【div】,参数是:[100, 0]
方法 异常通知logAfterThrowing 是【div】,异常是:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
十月 29, 2019 8:01:20 下午 org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext doClose
信息: Closing org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext@42d3bd8b: startup date [Tue Oct 29 20:01:19 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy
实现业务原理分析:

4、使用代理实现日记
4.1、使用jdk动态代理统一日记
增强功能:
public class LogUtil {
/**
* 前置通知
*
* @param method
* @param args
*/
public static void logBefore(String method, Object... args) {
System.out.println("方法 前置通知logBefore 是【" + method + "】,参数是:" + Arrays.asList(args));// 日记
}
/**
* 后置通知
*
* @param method
* @param args
*/
public static void logAfter(String method, Object... args) {
System.out.println("方法 后置通知logAfter 是【" + method + "】,参数是:" + Arrays.asList(args));// 日记
}
/**
* 返回通知 == 记录方法的返回值
*
* @param method
* @param result
*/
public static void logAfterReturning(String method, Object result) {
System.out.println("方法 返回通知logAfterReturning 是【" + method + "】,返回值是:" + result);// 日记
}
/**
* 异常通知 == 记录方法的异常信息
*
* @param method
* @param result
*/
public static void logAfterThrowing(String method, Throwable exc) {
System.out.println("方法 异常通知logAfterThrowing 是【" + method + "】,异常是:" + exc);// 日记
}
}代理类:
public class JdkProxyFactory {
public static Object createProxy(Object target) {
// 给目标对象创建代理
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* 每次调用代理方法,就会调用invoke拦截方法,做一些增强的工作
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
try {
// 前置通知
LogUtil.logBefore(method.getName(), args);
// 调用目标方法
result = method.invoke(target, args);
} finally {
// 后置通知
LogUtil.logAfter(method.getName(), args);
}
// 返回通知
LogUtil.logAfterReturning(method.getName(), result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
ogUtil.logAfterThrowing(method.getName(), e);
throw e;
}
return result;
}
});
}
}
测试及结果:
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
// 在计算器的每个方法中都需要记录下方法的参数。和方法的返回值。
// 接下来的需求是,给所有的类似Calculator这样的对象,的每个方法都需要统一加上类似的功能。
Calculate calculate = new Calculator();
//创建代理对象
Calculate proxy = (Calculate) JdkProxyFactory.createProxy(calculate);
System.out.println(proxy.add(100, 200));// 前置,后置,返回
System.out.println("=============华丽的分隔线=================");
System.out.println(proxy.div(200, 0));// 前置 ,后置,异常
}方法 前置通知logBefore 是【add】,参数是:[100, 200]
目标方法 add(int num1, int num2) 正在执行
方法 后置通知logAfter 是【add】,参数是:[100, 200]
方法 返回通知logAfterReturning 是【add】,返回值是:300
300
=============华丽的分隔线=================
方法 前置通知logBefore 是【div】,参数是:[200, 0]
目标方法 div(int num1, int num2) 正在执行
方法 后置通知logAfter 是【div】,参数是:[200, 0]
方法 异常通知logAfterThrowing 是【div】,异常是:java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException
优点:这种方式已经解决我们前面所有日记需要的问题。非常的灵活。而且可以方便的在后期进行维护和升级。
缺点:当然使用jdk动态代理,需要有接口。如果没有接口。就无法使用jdk动态代理。

4.2、使用cglib代理
public class CglibProxyFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculate = new Calculator();
// 创建代理对象
Calculator proxy = (Calculator) createProxy(calculate);
System.out.println(proxy.add(100, 200));// 前置,后置,返回
System.out.println("=============华丽的分隔线=================");
System.out.println(proxy.div(200, 0));// 前置 ,后置,异常
}
public static Object createProxy(Object target) {
// JDK动态代理,是根据 目标对象的接口去生成一个实现类。
// Cglib增强工具类
// Cglib动态代理。是根据目标对象本身,生成一个子类。
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 设置目标对象的类型
enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());
// 设置用来拦截目标方法的接口
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
/**
* intercept方法每次调用代理对象,都会执行intercept
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args,
MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
// 当前 目标方法返回值
Object result = null;
try {
try {
// 前置通知
LogUtil.logBefore(method.getName(), args);
// 调用目标方法
result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(proxy, args);
} finally {
// 后置通知
LogUtil.logAfter(method.getName(), args);
}
// 返回通知
LogUtil.logAfterReturning(method.getName(), result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
LogUtil.logAfterThrowing(method.getName(), e);
throw e;
}
return result;
}
});
// create生成代理对象
return enhancer.create();
}
}执行结果:
方法 前置通知logBefore 是【add】,参数是:[100, 200]
目标方法 add(int num1, int num2) 正在执行
方法 后置通知logAfter 是【add】,参数是:[100, 200]
方法 返回通知logAfterReturning 是【add】,返回值是:300
300
=============华丽的分隔线=================
方法 前置通知logBefore 是【div】,参数是:[200, 0]
目标方法 div(int num1, int num2) 正在执行
方法 后置通知logAfter 是【div】,参数是:[200, 0]
方法 异常通知logAfterThrowing 是【div】,异常是:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at com.atguigu.pojo.Calculator.div(Calculator.java:23)
at com.atguigu.pojo.Calculator$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$cb948d28.CGLIB$div$2(<generated>)
at com.atguigu.pojo.Calculator$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$cb948d28$$FastClassByCGLIB$$557a5f0b.invoke(<generated>)
at net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy.invokeSuper(MethodProxy.java:215)
at com.atguigu.proxy.CglibProxyFactory$1.intercept(CglibProxyFactory.java:52)
at com.atguigu.pojo.Calculator$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$cb948d28.div(<generated>)
at com.atguigu.proxy.CglibProxyFactory.main(CglibProxyFactory.java:25)
优点:在没有接口的情况下,同样可以实现代理的效果。
缺点:同样需要自己编码实现代理全部过程。
但是为了更好的整合Spring框架使用。所以我们需要学习一下Spring 的AOP 功能。也就是学习Spring提供的AOP功能。
二、Spring框架的AOP功能
1、AOP编程的专业术语
通知(Advice)
通知就是增强的代码。比如前置增强的代码。后置增强的代码。异常增强代码。这些就叫通知
切面(Aspect)
切面就是包含有通知代码的类叫切面。
横切关注点
横切关注点,就是我们可以添加增强代码的位置。比如前置位置,后置位置,异常位置。和返回值位置。这些都叫横切关注点。
目标(Target)
目标对象就是被关注的对象。或者被代理的对象。
代理(Proxy)
为了拦截目标对象方法,而被创建出来的那个对象,就叫做代理对象。
连接点(Joinpoint)
连接点指的是横切关注点和程序代码的连接,叫连接点。
切入点(pointcut)
切入点指的是用户真正处理的连接点,叫切入点。
在Spring中切入点通过org.springframework.aop.Pointcut 接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件。
图解AOP专业术语:

2、使用Spring实现AOP简单切面编程
导包:
com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar
spring-aop-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar
spring-beans-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar
spring-test-4.3.18.RELEASE.jar切入点表达式,是告诉Spring窗口,当前这个通知对哪个方法感兴趣
前置通知怎么描述@Before
代码
@Component
public class Calculator implements Calculate {/**
* @Aspect是告诉Spring我是切面类
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogUtil {
/**
* @Before表示前置通知
* execution( public int com.atguigu.pojo.Calculator.add(int,
* int) ) 是切入点表达式
*/
@Before("execution( public int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, int) )")
public static void logBefore() {
System.out.println("方法 前置通知logBefore 是【】,参数是:" );// 日记
}配置信息:
<!--
包扫描关心的是组件注解
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.webcode"></context:component-scan>
<!--
启动自动代理,对@Aspect进行支持
关心的是AOP注解
-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>测试代码:
//告诉junit测试,我的Spring容器配置文件在哪里
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
//使用Spring扩展的junit4运行器去运行测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class SpringTest {
@Autowired
Calculate calculate;
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
calculate.add(100, 100);
System.out.println("=================================");
calculate.div(100, 100);
}
}
3、Spring切面中的代理对象
在Spring中,可以对有接口的对象和无接口的对象分别进行代理。在使用上有些细微的差别。
1) 如果被代理的对象实现了接口。在获取对象的时候,必须要以接口来接收返回的对象。

2) 如果被代理对象,如果没有实现接口。获取对象的时候使用对象类型本身

4、Spring的切入点表达式
@PointCut切入点表达式语法格式是: execution(访问权限 返回值类型 方法全限定名(参数类型列表))
execution( public int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, int) )
访问权限 public
返回值类型 int
方法全限定名 包名+类包+方法名 ===>>>>com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add
(参数类型列表) (int, int)
限定符:
*表示任意的意思:
1)匹配某全类名下,任意或多个方法。
execution( public int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.*(int, int) )
对Calculator类的全部方法都匹配(参数类型必须是两个int)
2)在Spring中只有public权限能拦截到,访问权限可以省略(访问权限不能写*)。
execution( int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.*(int,int))execution( int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.*(int,int))public 可以省略
execution( int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, int) )
3)匹配任意类型的返回值,可以使用 * 表示
execution( * com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, int) )
* 表示任意类型的返回值。
4)匹配任意一层子包。
execution( int com.webcode.*.Calculator.add(int, int) )
上面这个*表示
com.webcode.所有子包,都可以匹配
5)任意类型参数
execution( int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, *) )
上面这个*表示任意参数类型
..:可以匹配多层路径,或任意多个任意类型参数
1)任意层级的包
execution( int com.webcode..Calculator.add(int, int) )
上面的..表示 com.webcode下的所有包都匹配
2)任意个任意类型的参数
execution( int com.webcode..Calculator.add(int, ..) )
上面的..表示任意个,任意类型的参数
模糊匹配:
// 表示任意返回值,任意方法全限定符,任意参数
execution(* *(..))
// 表示任意返回值,任意包名+任意方法名,任意参数
execution(* *.*(..))
精确匹配:
execution(public int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, int) )
确定返回值必须为:int
包名必须是:com.webcode.pojo
类包必须是:Calculator
方法名必须是:add
参数类型必须是两个int (int, int)
切入点表达式连接:&& 、||
// 表示需要同时满足两个表达式
@Before("execution(public int com.webcode.aop.Calculator.add(int, int))"
+ " && "
+ "execution(public * com.webcode.aop.Calculator.add(..))")
// 表示两个条件只需要满足一个,就会被匹配到
@Before("execution(public int com.webcode.aop.Calculator.add(int, int))"
+ " || "
+ "execution(public * com.webcode.aop.Calculator.a*(int))")
后面只对Service使用。
execution(public * com.webcode.service..*Service*.*(..))
5、Spring通知的执行顺序
Spring通知的执行顺序是:
正常情况:
前置通知====>>>>目标方法====>>>>后置通知=====>>>>返回值之后
异常情况:
前置通知====>>>>目标方法====>>>>后置通知=====>>>>抛异常通知
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogUtil {
/**
* @Before表示前置通知<br/>
* execution( public int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int, int) ) 是切入点表达式
*/
@Before("execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )")
public static void logBefore() {
System.out.println("方法 前置通知logBefore 是【】,参数是:" );// 日记
}
/**
* 后置通知====@After
*
*/
@After("execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )")
public static void logAfter() {
System.out.println("方法 后置通知logAfter 是【】,参数是:" );// 日记
}
/**
* 返回通知 == @AfterReturning
*
*/
@AfterReturning("execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )")
public static void logAfterReturning() {
System.out.println("方法 返回通知logAfterReturning 是【】,返回值是:");// 日记
}
/**
* 异常通知 == 记录方法的异常信息
*/
@AfterThrowing("execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )")
public static void logAfterThrowing() {
System.out.println("方法 异常通知logAfterThrowing 是【】,异常是:");// 日记
}
}
正常情况:
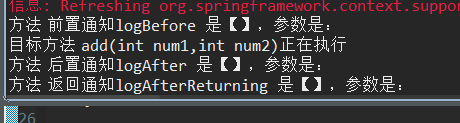
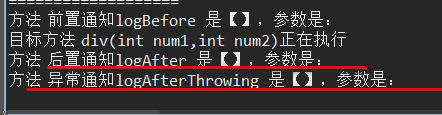
异常情况:
6、获取连接点信息
JoinPoint 是连接点的信息。
只需要在通知方法的参数中,加入一个JoinPoint参数。就可以获取到拦截方法的信息。
注意:是org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint这个类。
/**
* @Before表示前置通知<br/>
* execution( public int com.webcode.pojo.Calculator.add(int,
* int) ) 是切入点表达式
*/
@Before("execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )")
public static void logBefore(JoinPoint jp) {
// jp.getSignature().getName() 获取方法名
// jp.getArgs() 获取目标方法的参数
System.out.println("方法 前置通知logBefore 是【" + jp.getSignature().getName() + "】,参数是:"
+ Arrays.asList(jp.getArgs()));// 日记
}打印结果:
一个是正常的,一个是发生异常的
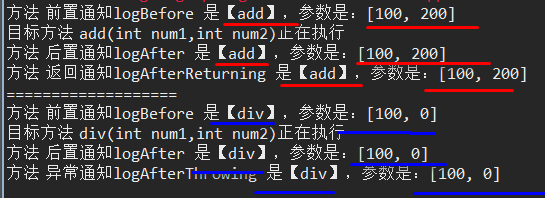
7、获取拦截方法的返回值和抛的异常信息
获取方法返回的值分为两个步骤:
1、在返回值通知的方法中,追加一个参数 Object result
2、然后在@AfterReturning注解中添加参数returning="参数名"
/**
* 返回通知 == @AfterReturning
value属性是默认属性,表示切入点表达式<br/>
* returning属性表示设置哪个参数用来接收返回值<br/>
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )", returning = "result")
public static void logAfterReturning(JoinPoint jp, Object result) {
System.out.println(
"方法 返回通知logAfterReturning 是【" + jp.getSignature().getName() + "】,返回值是:" + result);// 日记
}
获取方法抛出的异常分为两个步骤:
- 在异常通知的方法中,追加一个参数Throwable exception
- 然后在@AfterThrowing 注解中添加参数 throwing="参数名"
/**
* 异常通知 == 记录方法的异常信息
* throwing="e"表示把目标方法中抛出的异常对象用参数e来接收
*/
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )",throwing="e")
public static void logAfterThrowing(JoinPoint jp,Throwable e) {
System.out.println("方法 异常通知logAfterThrowing 是【" + jp.getSignature().getName() + "】,异常是:" + e);// 日记
}
图解方法抛异常:

8、Spring的环绕通知
- 环绕通知使用@Around注解。
- 环绕通知如果和其他通知同时执行。环绕通知会优先于其他通知之前执行。
- 环绕通知一定要有返回值(环绕如果没有返回值。后面的其他通知就无法接收到目标方法执行的结果)。
- 在环绕通知中。如果拦截异常。一定要往外抛。否则其他的异常通知是无法捕获到异常的。
/**
* 环绕通知====@Around<br/>
* 1 、环绕通知优先于普通通知先执行<br/>
* 2、在环绕通知中,一定要有返回值。否则 普通的返回通知收不到返回值<br/>
* 3、在环绕通知中,有异常一定要往外抛
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around(value = "execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )")
public static Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try {
try {
// 环绕的前置
System.out.println("环绕通知前置");
result = pjp.proceed();// 调用目标方法
} finally {
// 后置通知
System.out.println("环绕通知后置");
}
// 环绕返回
System.out.println("环绕返回通知 ,返回值:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// 环绕异常
System.out.println("环绕异常通知, 异常==>>" + e);
throw e;
}
return result;
}结果打印与分析:

9、切入点表达式的复用
- 定义一个空方法,在方法上使用@Pointcut定义切入点表达式
/**
* 定义一个切入点
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.add(int, int) )")
public static void pointcut1() {}
2、在需要使用切入点表达式的地方。使用 “方法名()” 代替 切入点表达式
@Before("pointcut1()")
public static void logBefore(JoinPoint jp) {
// jp.getSignature().getName() 获取方法名
// jp.getArgs() 获取目标方法的参数
System.out.println("方法 前置通知logBefore 是【" + jp.getSignature().getName() + "】,参数是:"
+ Arrays.asList(jp.getArgs()));// 日记
}10、多个切面的执行顺序
当我们有多个切面,多个通知的时候:
- 通知的执行顺序默认是由切面类的字母先后顺序决定。
- 在切面类上使用@Order注解决定通知执行的顺序(值越小,越先执行)
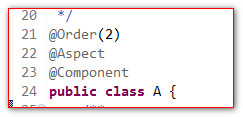
Order的值,越小越优先。
也就是上面两个切面类,LogUtil比A先执行。
执行结果

11、如何基于xml配置aop程序
1、拷贝前面注解形式的aop工程
2、去掉前面使用的所有注解
applicationContext.xml配置文件内容:
<!-- 配置目标对象 -->
<bean id="calculator" class="com.webcode.pojo.Calculator" />
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<bean id="logUtil" class="com.webcode.util.LogUtil" />
<!--
手动配置代理
-->
<aop:config>
<!--
使用哪个类做切面
-->
<aop:aspect ref="logUtil">
<!-- 定义一个可复用的切入点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.*(int, int) )"
id="pointcut1"/>
<!--
aop:before配置前置通知
method="logBefore" 哪个方法是前置通知
pointcut 给当前前置通知定义一个自己的切入点表达式
-->
<aop:before method="logBefore"
pointcut="execution(public int com.webcode..Calculator.add(int, int) )"/>
<!-- aop:after后置通知
pointcut-ref="pointcut1" 表示引用定义的切入点表达式pointcut1
-->
<aop:after method="logAfter" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<!-- 配置返回通知 -->
<aop:after-returning method="logAfterReturning"
pointcut-ref="pointcut1" returning="result"/>
<!-- 异常通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="logAfterThrowing"
pointcut-ref="pointcut1" throwing="e"
/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Spring ( 四 )Spring的AOP动态代理、切面编程的更多相关文章
- Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3)
Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3) 1.0 静态代理模式的缺点: 1.在该系统中有多少的dao就的写多少的proxy,麻烦 2.如果目标接口有方法的改动,则proxy也需要改动. Person ...
- Spring总结六:AOP(面向切面编程)
概述: AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面的编程),它是可以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加功能的一种技术.它是一种新的 ...
- Spring总结七:AOP动态代理的实现
Spring中的AOP代理可以使JDK动态代理,也可以是CGLIB代理,前者基于接口,后者基于子类. 首先我们来用代码简单演示jdk动态代理: 现在有一个商品的增删改查的操作 /** * 商品操作接口 ...
- Spring(三)--AOP【面向切面编程】、通知类型及使用、切入点表达式
1.概念:Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程 在方法的前后添加方法 2.作用:本质上来说是一种简化代码的方式 继承机制 封装方法 动 ...
- Spring AOP动态代理实现,解决Spring Boot中无法正常启用JDK动态代理的问题
Spring AOP底层的动态代理实现有两种方式:一种是JDK动态代理,另一种是CGLib动态代理. JDK动态代理 JDK 1.3版本以后提供了动态代理,允许开发者在运行期创建接口的代理实例,而且只 ...
- 04 Spring:01.Spring框架简介&&02.程序间耦合&&03.Spring的 IOC 和 DI&&08.面向切面编程 AOP&&10.Spring中事务控制
spring共四天 第一天:spring框架的概述以及spring中基于XML的IOC配置 第二天:spring中基于注解的IOC和ioc的案例 第三天:spring中的aop和基于XML以及注解的A ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:Spring AOP(面向切面编程)
面向切面编程(AOP)和面向对象编程(OOP)类似,也是一种编程模式.Spring AOP 是基于 AOP 编程模式的一个框架,它的使用有效减少了系统间的重复代码,达到了模块间的松耦合目的. AOP ...
- Spring的三大核心思想:IOC(控制反转),DI(依赖注入),AOP(面向切面编程)
Spring核心思想,IoC与DI详解(如果还不明白,放弃java吧) 1.IoC是什么? IoC(Inversion of Control)控制反转,IoC是一种新的Java编程模式,目前很多 ...
- 技术的正宗与野路子 c#, AOP动态代理实现动态权限控制(一) 探索基于.NET下实现一句话木马之asmx篇 asp.net core 系列 9 环境(Development、Staging 、Production)
黄衫女子的武功似乎与周芷若乃是一路,飘忽灵动,变幻无方,但举手抬足之间却是正而不邪,如说周芷若形似鬼魅,那黄衫女子便是态拟神仙. 这段描写出自<倚天屠龙记>第三十八回. “九阴神抓”本是& ...
随机推荐
- 记录:通过ffmpeg rtsp转 http m3u8
环境 Windows 10 大华rtsp直播 转 http请求m3u8 ffmpeg -rtsp_transport tcp -i "rtsp://账号:密码@IP:端口/cam/realm ...
- Mysql常用sql语句(八)- where 条件查询
测试必备的Mysql常用sql语句,每天敲一篇,每次敲三遍,每月一循环,全都可记住!! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1683347.html 前言 ...
- 一文搞懂HMM(隐马尔可夫模型)-转载
写在文前:原博文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/skyme/p/4651331.html 什么是熵(Entropy) 简单来说,熵是表示物质系统状态的一种度量,用它老表征系统的无 ...
- [hdu4300] next数组的应用
题意:给你一个密文和明文的对应表以及一个密文+明文的字符串,明文可能只出现前面的一部分(也就是说是原明文的前缀),求最短的明文. 思路:首先密文的长度至少占到一半,所以先把那一半解密,问题转化为找一个 ...
- HTML简单的伪装与造假
利用浏览器制止台能简单的修改内容,致使其造成伪装. 打开网页控制台后,不要管那些眼花撩乱的代码,我们直接寻找控制台顶部的 Tab 栏 找到 Console 这个 Tab,点击它,把代码 documen ...
- mysql-kettle-superset电商可视化数据分析
1.项目概述 需求 对电商业务中的用户.商品.订单的数据进行分析,观察运营的情况 架构 业务数据库:Mysql:存储最原始的数据 ETL:Kettle 数据仓库:Mysql:存储需要进行分析处理的数据 ...
- 【Jmeter学习】【第一节】【Jmeter的安装】
转载至https://www.cnblogs.com/qinlangsky/p/11941230.html 写的非常详细
- 「雕爷学编程」Arduino动手做(8)——湿度传感器模块
37款传感器和模块的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止37种的.鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器与模块,依照实践出真知(动手试试)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里准备 ...
- spark机器学习从0到1逻辑斯蒂回归之(四)
逻辑斯蒂回归 一.概念 逻辑斯蒂回归(logistic regression)是统计学习中的经典分类方法,属于对数线性模型.logistic回归的因变量可以是二分类的,也可以是多分类的.logis ...
- 贝叶斯优化(Bayesian Optimization)只需要看这一篇就够了,算法到python实现
贝叶斯优化 (BayesianOptimization) 1 问题提出 神经网咯是有许多超参数决定的,例如网络深度,学习率,正则等等.如何寻找最好的超参数组合,是一个老人靠经验,新人靠运气的任务. 穷 ...
