3 TFRecord样例程序实战
将图片数据写入Record文件
# 定义函数转化变量类型。
def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value])) # 读取mnist数据。
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("F:/data_of_zengjie/a_minist",dtype=tf.uint8, one_hot=True)
images = mnist.train.images
labels = mnist.train.labels
pixels = images.shape[1]
num_examples = mnist.train.num_examples # 输出TFRecord文件的地址。
filename = "./TFRecord_Output/output.tfrecords"
if not os.path.exists('./TFRecord_Output/'):
os.makedirs('./TFRecord_Output/')
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(filename)
print (num_examples)
#for index in range(num_examples):
#for index in range(9):
for index in range(101):
#for index in range(54999):
image_raw = images[index].tostring() example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'pixels': _int64_feature(pixels),
'label': _int64_feature(np.argmax(labels[index])),
'image_raw': _bytes_feature(image_raw)
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
print ("TFRecord文件已保存。")
在上面的代码中:通过for index in range(101):
可以控制写入文件的Example数量。
一次读取一个样例
# 读取文件。
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["./TFRecord_Output/output.tfrecords"])
# 每次读取一个
_,serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue) features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64)
}) images = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'],tf.uint8)
labels = tf.cast(features['label'],tf.int32)
pixels = tf.cast(features['pixels'],tf.int32) sess = tf.Session() # 启动多线程处理输入数据。
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(10):
image, label, pixel = sess.run([images, labels, pixels])
print (image.shape,label,pixel) #image是长度为784的数组

一次读取多个样例,
使用read_up_to(注意当前代码所在的方格不要和前面的程序都放在jupyter notebook中运行。否则前面的定义会影响下一个方格代码的执行。最好刷新一下kernel,重新选择某个方格运行。)
注意:从
_,serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# 解析读取的样例。
features = tf.parse_single_example(
改为
_,serialized_example = reader.read_up_to(filename_queue,10)
# 解析读取的样例。
features = tf.parse_example(
# 读取文件。
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["./TFRecord_Output/output.tfrecords"]) # 每次读取多个
_,serialized_example = reader.read_up_to(filename_queue,10)
# 解析读取的样例。
features = tf.parse_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64)
}) images = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'],tf.uint8)
labels = tf.cast(features['label'],tf.int32)
pixels = tf.cast(features['pixels'],tf.int32)
print(images.get_shape()) #通过输出,发现是(?,?)也就是无法确定shape。 sess = tf.Session()
# 启动多线程处理输入数据。
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(100):
image, label, pixel = sess.run([images, labels, pixels])
print(image.shape)
print(label.shape)
 、
、
但是有一个问题就是:
第一:假设在一开始写入TFreord的时候,使用的是for index in range(101):
即写入的是101个example,而这里一次读取10个,那么总是会出现某一次为(1,784)的情况。即read_up_to没有为了单次达标10个而循环读取的功能。当文件读到最后的时候,它不会从文件的开头再重新读取,而是直接读1个作为那次read_up_to(10)的结果。但是,还保留了一点比较好的地方就是,这里for i in range(100):100次读取,每次读取10个example(不考虑那种只读1个的情况),明显超出了文件的101个example。但是,read_up_to为了满足全部读取次数,此时会循环读取。也就是说,read_up_to不会为了单次达标多少个example而循环读取,但是会为了读取次数达标,而循环读取。
读取TFRecord文件,每次读取多个,使用的是batch
# 读取文件。
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["./TFRecord_Output/output.tfrecords"]) # 每次读取多个
_,serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# 解析读取的样例。
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64)
}) images = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'],tf.uint8)
labels = tf.cast(features['label'],tf.int32)
pixels = tf.cast(features['pixels'],tf.int32)
print(images.get_shape()) #通过输出,发现是(?,?)也就是无法确定shape。 batch_size = 10
capacity = 1000 + 3 * batch_size #images.set_shape(784,)
images.set_shape([784])
labels.set_shape([])
pixels.set_shape([])
image_batch, label_batch, pixel_batch = tf.train.batch(
[images, labels, pixels], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=capacity) sess = tf.Session()
# 启动多线程处理输入数据。
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(100): image, label, pixel = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch, pixel_batch ])
print(image.shape)
print(label.shape)
注意:首先,使用batch必须做到一点:
即用set_shape对tensor等进行指定shape否则会
ValueError: All shapes must be fully defined: [TensorShape([Dimension(None)]), TensorShape([]), TensorShape([])]
其次,batch不同于read_up_to,不仅仅会不断的在文件中循环读取,而且一定会为了凑出batch个数目,而循环。所以,不会像使用read_up_to那样出现(1,784)的那种情况。而是全部是(10,784)的情形。
此外,batch还有一个好处是:
会建立一个最大容量为capacity的队列,即如下图所示:
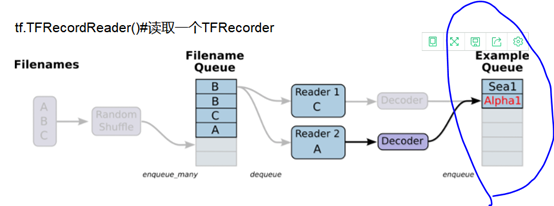
即最后一部分标出的batch。所以,训练神经网络从Example Queue中取batch的时候,另外一个进程可以同步向队列中添加batch。这样的话,就可以避免IO瓶颈。而如果使用read_up_to,则不能像tf.train.batch一样能够构建一个队列,并且支持训练进程和数据处理进程并行化。()
同时使用batch和read_up_to
# 读取文件。
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["./TFRecord_Output/output.tfrecords"]) # 每次读取多个
_,serialized_example = reader.read_up_to(filename_queue,10)
# 解析读取的样例。
features = tf.parse_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([],tf.int64)
}) images = tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'],tf.uint8)
labels = tf.cast(features['label'],tf.int32)
pixels = tf.cast(features['pixels'],tf.int32)
print(images.get_shape()) #通过输出,发现是(?,?)也就是无法确定shape。 batch_size = 10
capacity = 1000 + 3 * batch_size #images.set_shape(784,) images.set_shape([10,784])
labels.set_shape([10])
pixels.set_shape([10])
image_batch, label_batch, pixel_batch = tf.train.batch(
[images, labels, pixels], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=capacity)
sess = tf.Session()
# 启动多线程处理输入数据。
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,coord=coord) for i in range(100): #image, label, pixel = sess.run([images, labels, pixels])
image, label, pixel = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch, pixel_batch ])
print(image.shape)
print(label.shape)
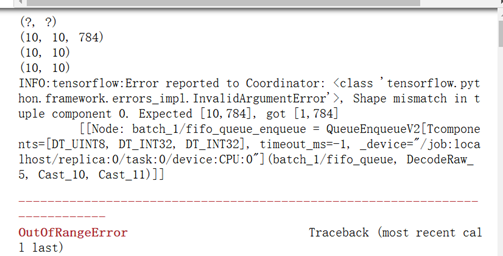
可以看出101个example。
一个batch是10次,1次又是read_up_to(10),所以,一个batch就读了100个。
接着下一个batch的时候,又调用read_up_to时,只剩下1个了,因此报出expected[10,784],got [1,784]的错误。
但是,我们试探性的直接将read_up_to改为102.也就是一次read_UP_to就超出整个文件包含的example,发现:

所以,read_up_to是文件剩多少,就读多少,然后再一直循环下去。不会说为了凑够102.改为100.输出是:

那么上述报错的原因究竟是什么???
正是因为read_up_to是文件剩余多少,就读多少。但是同时使用batch的情况下,需要set_shape。
此时,文件中101个example,一次batch以后读出10*10个example。下一次batch时,调用read_up_to(10),但是只剩下一个了。于是得到的是[1,784]和set的[10,784]有矛盾。故而报错。
3 TFRecord样例程序实战的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow TFRecord样例程序
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dat ...
- 在Ubuntu下构建Bullet以及执行Bullet的样例程序
在Ubuntu下构建Bullet以及执行Bullet的样例程序 1.找到Bullet的下载页,地址是:https://code.google.com/p/bullet/downloads/list 2 ...
- SNF快速开发平台MVC-各种级联绑定方式,演示样例程序(包含表单和表格控件)
做了这么多项目,经常会使用到级联.联动的情况. 如:省.市.县.区.一级分类.二级分类.三级分类.仓库.货位. 方式:有表单需要做级联的,还是表格行上需要做级联操作的. 实现:实现方法也有很多种方式. ...
- Tuxedo安装、配置、以及演示样例程序 (学习网址)
Tuxedo安装.配置.以及演示样例程序 (学习网址): 1.http://liu9403.iteye.com/blog/1415684 2.http://www.cnblogs.com/fnng/a ...
- Java读取Excel文件(包括xls和xlsx)的样例程序
样例程序如下所示,其中: parseXls()函数依赖于jxl,只能读取xls格式文件: parseExcel()函数依赖于apache poi,能够读取xls和xlsx两种格式的文件. jxl的依赖 ...
- Python Socket 编程——聊天室演示样例程序
上一篇 我们学习了简单的 Python TCP Socket 编程,通过分别写服务端和client的代码了解主要的 Python Socket 编程模型.本文再通过一个样例来加强一下对 Socket ...
- 80、tensorflow最佳实践样例程序
''' Created on Apr 21, 2017 @author: P0079482 ''' #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- import tensorflow as tf #定义神 ...
- Java 连接 Hive的样例程序及解析
以后编程基于这个样例可节省查阅API的时间. private static String driverName = "org.apache.hadoop.hive.jdbc.HiveDriv ...
- Direct3D 9 入门样例程序 圆锥体
介绍 Directx3D 9 什么是DirectX,非常好说了,Win32 C++ API.主要是多媒体编程方面的,长处体如今高性能了,如今我知道的版本号最高是D3D11,可是我是学习入门的,从D3D ...
随机推荐
- 博客主题皮肤探索-GitHub和jsdelivr的使用
有个前言 本萌并不会前端相关的知识,一切都是自己慢慢摸索出来的,如果存在代码方面的不足,请尽快告诉我~~~ 使用一个主题 目前我博客使用是 https://www.cnblogs.com/bndong ...
- Locust源码目录结构及模块作用
Locust源码目录结构及模块作用如下: 参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/biheyu828/article/details/84031942
- my.工坊_ZZ
1.查了下,可以将 考古升上去,但是 还是使用 2级的考古技能,这样比较赚,高级的反而不赚.但是看到有人说 考古升到 3/4 不能再用 洛阳铲 了. 于是有了两种情况,我暂定的做法:先将 考古升到2级 ...
- ORACLE MERGE INTO UPDATE DELETE 用法
ORACLE MERGE INTO UPDATE DELETE 用法 使用该MERGE语句从一个或多个源中选择行以进行更新或插入表或视图.您可以指定条件以确定是更新还是插入目标表或视图. 此语句是组合 ...
- es与hive整合
在hive classpath中添加elasticsearch-hadoop.jar,以下方法任一种均可: 1.启动hiveserver2 前,在hive-site.xml文件中更改hive.aux. ...
- (转)Cobbler自动化部署最佳实践
原文:http://www.xuliangwei.com/xubusi/446.html 运维自动化在生产环境中占据着举足轻重的地位,尤其是面对几百台,几千台甚至几万台的服务器时,仅仅是安装操作系统, ...
- Java学习之路(四):面向对象
Java中的面向对象 概念:面向对象的原本的意思是“”万物皆对象“” 面向对象思想的特点: 是一种更符合我们思想习惯的思想,将复杂的事情简单化 使我们角色发生了转换,将我们从执行者变成了指挥者 面向对 ...
- 在VM虚拟机中彻底删除Linux系统
前言:很久之前安装了Linux虚拟系统,然后用户名忘记了,想着重新安装个Ubuntu系统,就想着删除以前的系统. 删除方法如下: 1.点击打开该Linux系统. 2. 点击虚拟机的左上方“虚拟机”-& ...
- Git学习系列之为什么选择Git?
为什么选择Git? 流行的软件版本开源管理软件,有CVS.SVN.GIT版本管理工具,Git的优势在哪里呢? Git 和 CVS.SVN不同,是一个分布式的源代码管理工具,它很强,也很快,Linux内 ...
- 【Css】一个简单的图片库
今天做一个简单的图片库! 其实这个在w3school教程里介绍得很好了,不过看到什么,自己动手做一次,记得也深刻不是. 我们分几步来走: 第一步:先写一个坯子. <html> <he ...
