HDU 1011 Starship Troopers【树形DP/有依赖的01背包】
To kill all the bugs is always easier than to capture their brains. A map is drawn for you, with all the rooms marked by the amount of bugs inside, and the possibility of containing a brain. The cavern's structure is like a tree in such a way that there is one unique path leading to each room from the entrance. To finish the battle as soon as possible, you do not want to wait for the troopers to clear a room before advancing to the next one, instead you have to leave some troopers at each room passed to fight all the bugs inside. The troopers never re-enter a room where they have visited before.
A starship trooper can fight against 20 bugs. Since you do not have enough troopers, you can only take some of the rooms and let the nerve gas do the rest of the job. At the mean time, you should maximize the possibility of capturing a brain. To simplify the problem, just maximize the sum of all the possibilities of containing brains for the taken rooms. Making such a plan is a difficult job. You need the help of a computer.
InputThe input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains two integers N (0 < N <= 100) and M (0 <= M <= 100), which are the number of rooms in the cavern and the number of starship troopers you have, respectively. The following N lines give the description of the rooms. Each line contains two non-negative integers -- the amount of bugs inside and the possibility of containing a brain, respectively. The next N - 1 lines give the description of tunnels. Each tunnel is described by two integers, which are the indices of the two rooms it connects. Rooms are numbered from 1 and room 1 is the entrance to the cavern.
The last test case is followed by two -1's.
OutputFor each test case, print on a single line the maximum sum of all the possibilities of containing brains for the taken rooms.
Sample Input
5 10
50 10
40 10
40 20
65 30
70 30
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
1 1
20 7
-1 -1
Sample Output
50
7
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<cctype>
#include<stack>
#include<sstream>
#include<list>
#include<assert.h>
#include<bitset>
#include<numeric>
#define debug() puts("++++")
#define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sqr(x) ((x)*(x))
#define ms(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define sz size()
#define be begin()
#define pu push_up
#define pd push_down
#define cl clear()
#define lowbit(x) -x&x
#define all 1,n,1
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=(x); i<=(n); i++)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef pair<int,int> P;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL LNF = 1e18;
const int maxm = 1e6 + ;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double eps = 1e-;
const int dx[] = {-,,,,,,-,-};
const int dy[] = {,,,-,,-,,-};
int dir[][] = {{,},{,-},{-,},{,}};
const int mon[] = {, , , , , , , , , , , , };
const int monn[] = {, , , , , , , , , , , , };
const int mod = ;
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define ll long long
const int maxn = 1e4+;
int t,n,m,x,y;
int dp[maxn][],p[maxn],b[maxn];
int cost[maxn];
struct node
{
int u,v,nxt;
}e[maxn*];
int head[maxn];
int tot=;
void init()
{
ms(head,-);
ms(dp,);
}
void add(int u,int v)
{
e[tot].v=v;
e[tot].nxt=head[u];
head[u]=tot++;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
for(int i=cost[u];i<=m;i++)
dp[u][i]=p[u]; //小于cost的无法获得经验 - dp[i][1]=val;
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-; i=e[i].nxt) //相当于背包种类
{
int v=e[i].v;
if(v==fa) continue;
dfs(v,u);
for(int j=m; j>=cost[u]; j--) //祖先的人力范围
{
for(int k=; k<=j-cost[u]; k++) //子树的人力范围
{
dp[u][j]=max(dp[u][j],dp[u][j-k] + dp[v][k]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
if(n==-&&m==-) break;
init();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&b[i],&p[i]);
cost[i]=(b[i]+)/; //花费人力
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&x, &y);
add(x,y);
add(y,x);
}
if(!m)
{
printf("0\n");continue;
}
dfs(,-);
printf("%d\n",dp[][m]);
}
}
/* 【题意】
给你n和m代表n个点,m个士兵,要到下一个房间必须攻破上一个房间,每个士兵最多消灭20个BUG,就算不足20个BUG也要安排一个士兵
以1点为源点,向相邻的点移动,每个点有一个代价(值/20)和价值。
求花费m的士兵得到的最大价值是多少。 就是:给定一棵树,从1号顶点进入树中,每次可以分配人到其他可达的顶点去,杀死所有的bugs可以获取brain值,求出m个人最多能获取多少brain值。
【类型】
树形DP 【分析】
一看到价值和代价同时出现,马上想到背包,而且是有限的物品(结点),那么是01背包。
看出这是一棵树,那么就是树形01背包,对于树形DP自有一套应对方法。
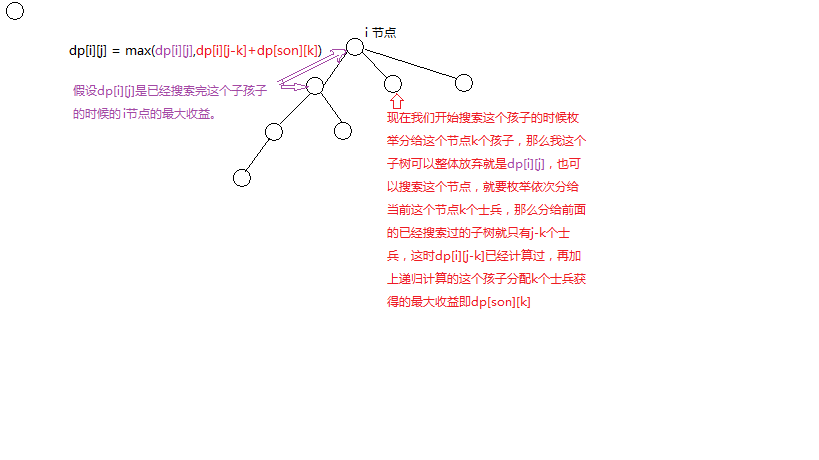
设dp[i][j]:以i为根的子树有j个士兵的时候最多获得的价值。
转移方程:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i][j-k] + dp[son(i)][k]); 【时间复杂度&&优化】 【trick】
分析的时候自顶向下,实现自底向上,这也是dfs的思想,树形dp一般都是在dfs过程中实现的 【数据】 */
HDU 1011 Starship Troopers【树形DP/有依赖的01背包】的更多相关文章
- hdu 1011 Starship Troopers(树形DP入门)
Starship Troopers Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU 1011 Starship Troopers 树形DP 有坑点
本来是一道很水的树形DP题 设dp[i][j]表示,带着j个人去攻打以节点i为根的子树的最大收益 结果wa了一整晚 原因: 坑点1: 即使这个节点里面没有守卫,你如果想获得这个节点的收益,你还是必须派 ...
- [HDU 1011] Starship Troopers (树形dp)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1011 dp[u][i]为以u为根节点的,花了不超过i元钱能够得到的最大价值 因为题目里说要访问子节点必 ...
- hdu 1011 Starship Troopers 树形背包dp
Starship Troopers Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- hdu 1011 Starship Troopers(树形背包)
Starship Troopers Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU 1011 Starship Troopers 树形+背包dp
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1011 题意:每个节点有两个值bug和brain,当清扫该节点的所有bug时就得到brain值,只有当父节点被 ...
- HDU 1011 Starship Troopers (树dp)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1011 题意: 题目大意是有n个房间组成一棵树,你有m个士兵,从1号房间开始让士兵向相邻的房间出发,每个 ...
- HDU 1561 The more, The Better【树形DP/有依赖的分组背包】
ACboy很喜欢玩一种战略游戏,在一个地图上,有N座城堡,每座城堡都有一定的宝物,在每次游戏中ACboy允许攻克M个城堡并获得里面的宝物.但由于地理位置原因,有些城堡不能直接攻克,要攻克这些城堡必须先 ...
- hdu 1011 Starship Troopers 经典的树形DP ****
Starship Troopers Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Other ...
随机推荐
- JS日期对象扩展-日期格式化
日期对象扩展(日期格式化)yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss.S Date.prototype.format = function(fmt) { var o = { "M+" ...
- MySql 利用函数 查询所有子节点
前提:mysql 函数 find_in_set(str,strlist), cast(value as type) 一.find_in_set(str,strlist):如果字符串str是在的 ...
- mvc BundleConfig实现对Css、Js压缩打包加载
Bundle不是.net Framework框架中的一员,使用Bundle首先要先添加引用,如下: nuget包管理--程序包管理控制台--Install-Package Microsoft.AspN ...
- 【hdu5381】维护区间内所有子区间的gcd之和-线段树
题意:给定n个数,m个询问,每次询问一个区间内所有连续子区间的gcd的和.n,m<=10^5 题解: 这题和之前比赛的一题很像.我们从小到大枚举r,固定右端点枚举左端点,维护的区间最多只有log ...
- 【Contest Hunter【弱省胡策】Round #0-Flower Dance】组合数学+DP
题目链接: http://ch.ezoj.tk/contest/%E3%80%90%E5%BC%B1%E7%9C%81%E8%83%A1%E7%AD%96%E3%80%91Round%20%230/F ...
- 【洛谷 P4934】 礼物 (位运算+DP)
题目链接 位运算+\(DP\)=状压\(DP\)?(雾 \(a\&b>=min(a,b)\)在集合的意义上就是\(a\subseteq b\) 所以对每个数的子集向子集连一条边,然后答案 ...
- Pythone3 sys模块
1.sys.argv 可以实现从程序外部向程序传递参数2.sys.exit() 程序中间退出,exit(0)正常退出,其他为异常退出3.sys.getdefaultencoding() 获取系统编码方 ...
- 在linux程序里面,知道一个函数地址,改函数是属于某个动态库的,怎么样得到这个动态库的全【转】
转自:http://www.360doc.com/content/17/1012/11/48326749_694292472.shtml 另外dl_iterate_phdr可以查到当前进程所装在的所有 ...
- linux===给新手的 10 个有用 Linux 命令行技巧(转)
本文转自:http://www.codeceo.com/article/10-linux-useful-command.html?ref=myread 仅用作学习交流使用.如有侵权,立删 我记得我第一 ...
- delphi2006语言新特性:Record类型高级用法
delphi语言在传统的Records类型的基础上增加了许多像类一样的高级功能,如:Records可以有属性和方法(包括构造constructors),类属性,类方法,类静态字段和内嵌类型.下面这个示 ...
