MySQL 8.0 Server层最新架构详解
简介: 本文基于MySQL 8.0.25源码进行分析和总结。这里MySQL Server层指的是MySQL的优化器、执行器部分。我们对MySQL的理解还建立在5.6和5.7版本的理解之上,更多的是对比PostgreSQL或者传统数据库。然而从MySQL 8.0开始,持续每三个月的迭代和重构工作,使得MySQL Server层的整体架构有了质的飞越。下面来看下MySQL最新的架构。

作者 | 道客
来源 | 阿里技术公众号
一 背景和架构
本文基于MySQL 8.0.25源码进行分析和总结。这里MySQL Server层指的是MySQL的优化器、执行器部分。我们对MySQL的理解还建立在5.6和5.7版本的理解之上,更多的是对比PostgreSQL或者传统数据库。然而从MySQL 8.0开始,持续每三个月的迭代和重构工作,使得MySQL Server层的整体架构有了质的飞越。下面来看下MySQL最新的架构。
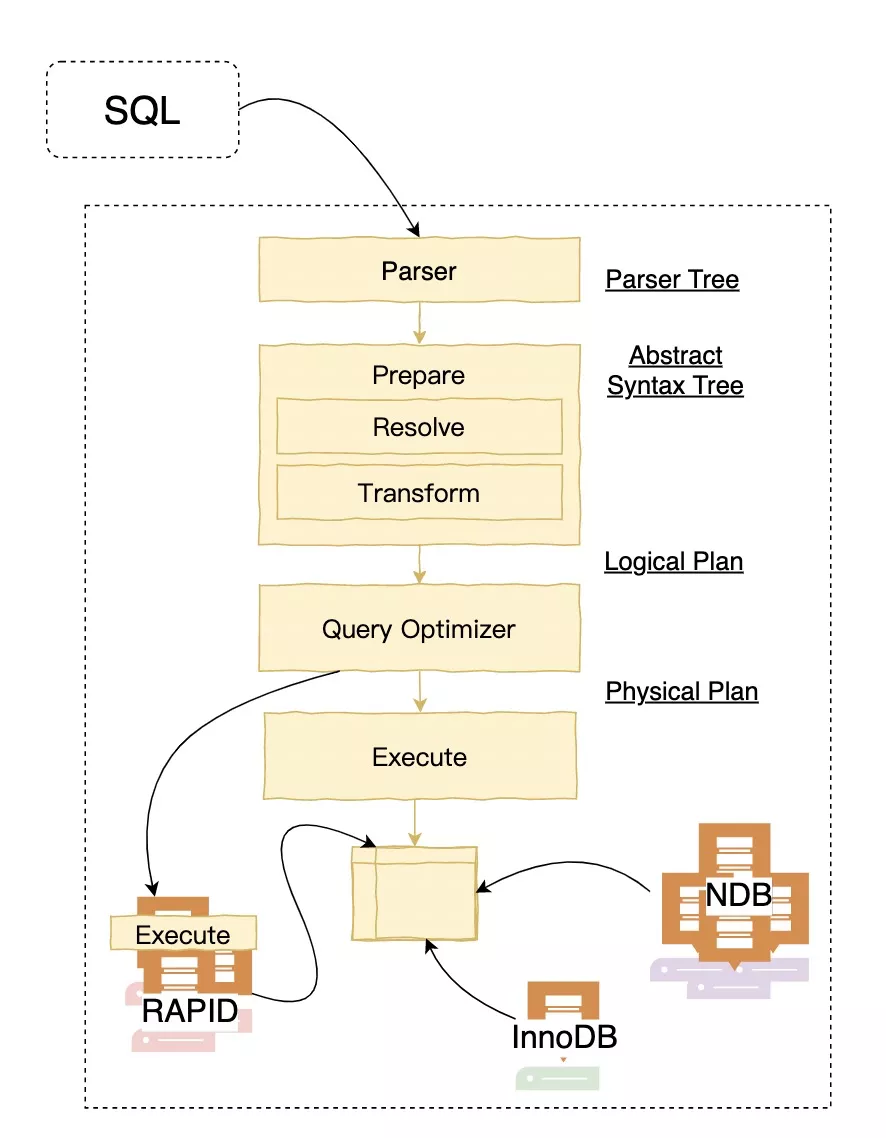
我们可以看到最新的MySQL的分层架构和其他数据库并没有太大的区别,另外值得一提的是从图中可以看出MySQL现在更多的加强InnoDB、NDB集群和RAPID(HeatWave clusters)内存集群架构的演进。下面我们就看下具体细节,我们这次不随着官方的Feature实现和重构顺序进行理解,本文更偏向于从优化器、执行器的流程角度来演进。
二 MySQL 解析器Parser
首先从Parser开始,官方MySQL 8.0使用Bison进行了重写,生成Parser Tree,同时Parser Tree会contextualize生成MySQL抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree)。
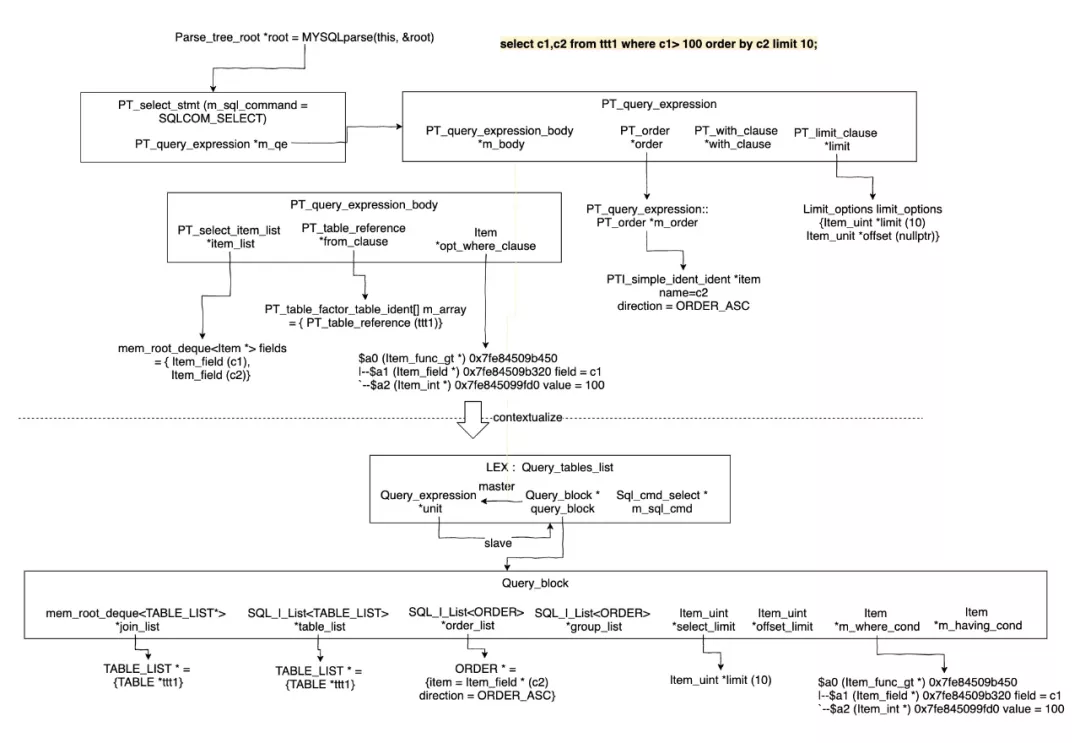
MySQL抽象语法树和其他数据库有些不同,是由比较让人拗口的SELECT_LEX_UNIT/SELECT_LEX类交替构成的,然而这两个结构在最新的版本中已经重命名成标准的SELECT_LEX -> Query_block和SELECT_LEX_UNIT -> Query_expression。Query_block是代表查询块,而Query_expression是包含多个查询块的查询表达式,包括UNION AND/OR的查询块(如SELECT FROM t1 union SELECT FROM t2)或者有多Level的ORDER BY/LIMIT (如SELECT * FROM t1 ORDER BY a LIMIT 10) ORDER BY b LIMIT 5。
例如,来看一个复杂的嵌套查询:
(SELECT *
FROM ttt1)
UNION ALL
(SELECT *
FROM
(SELECT *
FROM ttt2) AS a,
(SELECT *
FROM ttt3
UNION ALL SELECT *
FROM ttt4) AS b)在MySQL中就可以用下面方式表达:
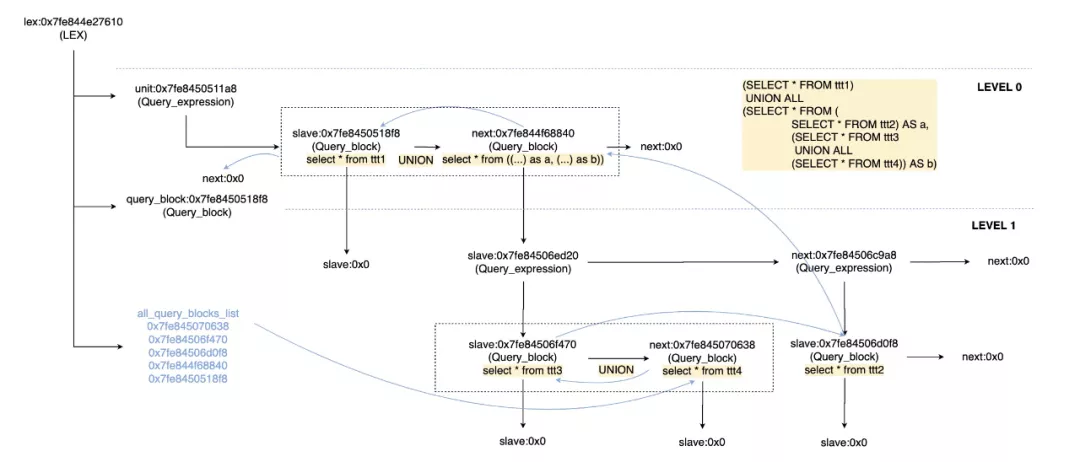
经过解析和转换后的语法树仍然建立在Query_block和Query_expression的框架下,只不过有些LEVEL的query block被消除或者合并了,这里不再详细展开。
三 MySQL prepare/rewrite阶段
接下来我们要经过resolve和transformation过程Query_expression::prepare->Query_block::prepare,这个过程包括(按功能分而非完全按照执行顺序):
1 Setup and Fix
- setup_tables:Set up table leaves in the query block based on list of tables.
- resolve_placeholder_tables/merge_derived/setup_table_function/setup_materialized_derived:Resolve derived table, view or table function references in query block.
- setup_natural_join_row_types:Compute and store the row types of the top-most NATURAL/USING joins.
- setup_wild:Expand all '*' in list of expressions with the matching column references.
- setup_base_ref_items:Set query_block's base_ref_items.
- setup_fields:Check that all given fields exists and fill struct with current data.
- setup_conds:Resolve WHERE condition and join conditions.
- setup_group:Resolve and set up the GROUP BY list.
- m_having_cond->fix_fields:Setup the HAVING clause.
- resolve_rollup:Resolve items in SELECT list and ORDER BY list for rollup processing.
- resolve_rollup_item:Resolve an item (and its tree) for rollup processing by replacing items matching grouped expressions with Item_rollup_group_items and updating properties (m_nullable, PROP_ROLLUP_FIELD). Also check any GROUPING function for incorrect column.
- setup_order:Set up the ORDER BY clause.
- resolve_limits:Resolve OFFSET and LIMIT clauses.
- Window::setup_windows1:Set up windows after setup_order() and before setup_order_final().
- setup_order_final:Do final setup of ORDER BY clause, after the query block is fully resolved.
- setup_ftfuncs:Setup full-text functions after resolving HAVING.
- resolve_rollup_wfs : Replace group by field references inside window functions with references in the presence of ROLLUP.
2 Transformation
- remove_redundant_subquery_clause : Permanently remove redundant parts from the query if 1) This is a subquery 2) Not normalizing a view. Removal should take place when a query involving a view is optimized, not when the view is created.
- remove_base_options:Remove SELECT_DISTINCT options from a query block if can skip distinct.
resolve_subquery : Resolve predicate involving subquery, perform early unconditional subquery transformations.
- Convert subquery predicate into semi-join, or
- Mark the subquery for execution using materialization, or
- Perform IN->EXISTS transformation, or
- Perform more/less ALL/ANY -> MIN/MAX rewrite
- Substitute trivial scalar-context subquery with its value
- transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived:Transform eligible scalar subqueries to derived tables.
- flatten_subqueries:Convert semi-join subquery predicates into semi-join join nests. Convert candidate subquery predicates into semi-join join nests. This transformation is performed once in query lifetime and is irreversible.
apply_local_transforms :
- delete_unused_merged_columns : If query block contains one or more merged derived tables/views, walk through lists of columns in select lists and remove unused columns.
- simplify_joins:Convert all outer joins to inner joins if possible
- prune_partitions:Perform partition pruning for a given table and condition.
- push_conditions_to_derived_tables:Pushing conditions down to derived tables must be done after validity checks of grouped queries done by apply_local_transforms();
- Window::eliminate_unused_objects:Eliminate unused window definitions, redundant sorts etc.
这里,节省篇幅,我们只举例关注下和top_join_list相关的simple_joins这个函数的作用,对于Query_block中嵌套join的简化过程。
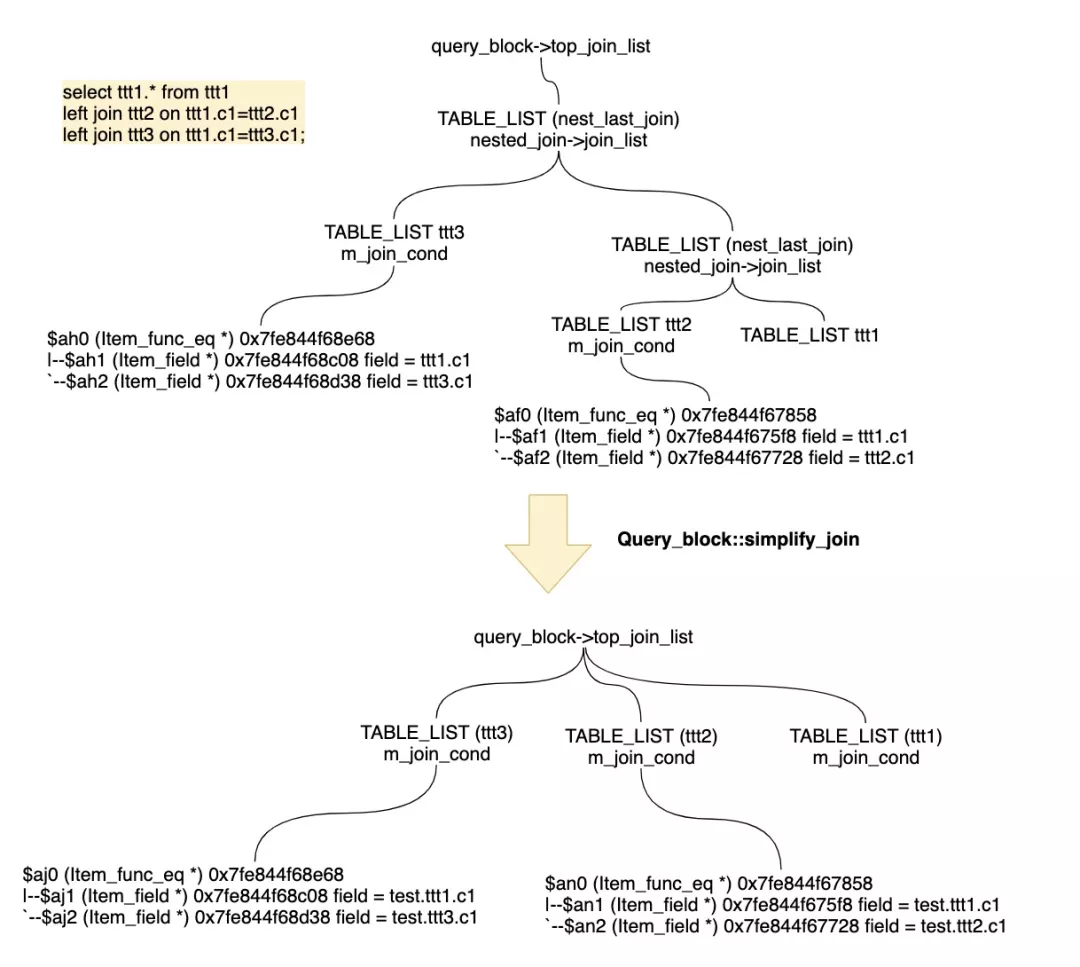
3 对比PostgreSQL
为了更清晰的理解标准数据库的做法,我们这里引用了PostgreSQL的这三个过程:
Parser
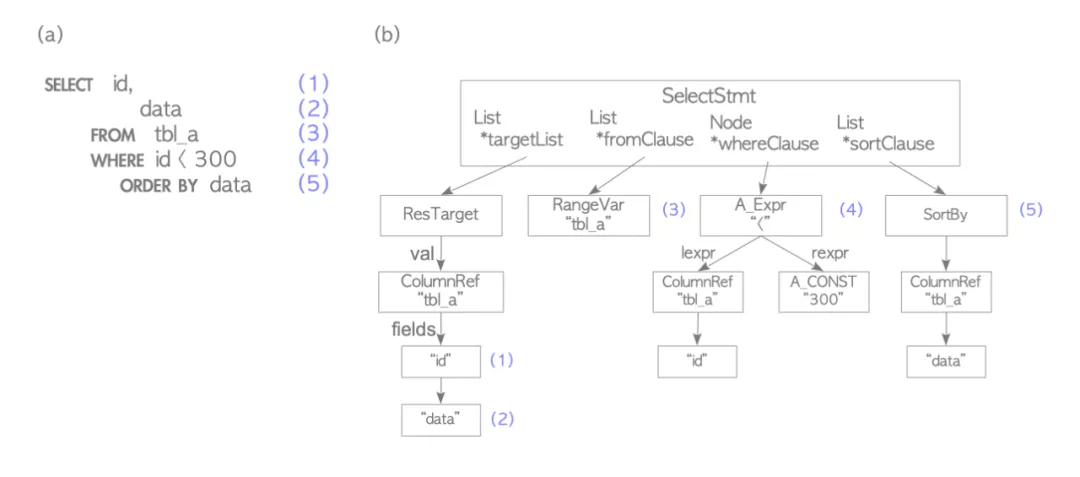
下图首先Parser把SQL语句生成parse tree。
testdb=# SELECT id, data FROM tbl_a WHERE id < 300 ORDER BY data;
Analyzer/Analyser
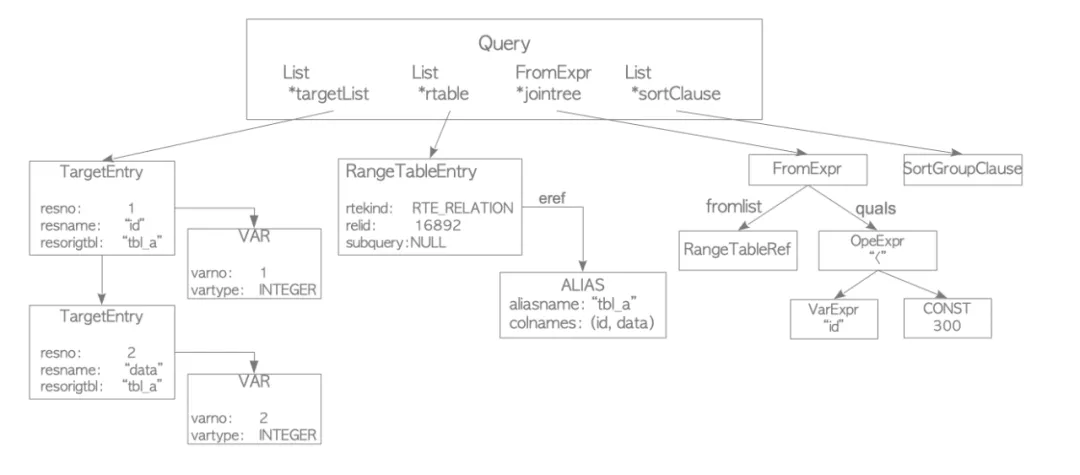
下图展示了PostgreSQL的analyzer/analyser如何将parse tree通过语义分析后生成query tree。
Rewriter
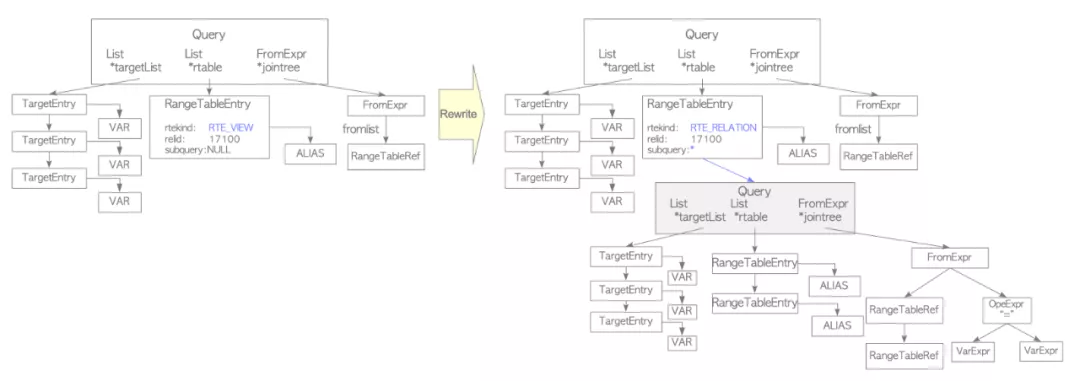
Rewriter会根据规则系统中的规则把query tree进行转换改写。
sampledb=# CREATE VIEW employees_list
sampledb-# AS SELECT e.id, e.name, d.name AS department
sampledb-# FROM employees AS e, departments AS d WHERE e.department_id = d.id;
下图的例子就是一个包含view的query tree如何展开成新的query tree。
sampledb=# SELECT * FROM employees_list;
四 MySQL Optimize和Planning阶段
接下来我们进入了逻辑计划生成物理计划的过程,本文还是注重于结构的解析,而不去介绍生成的细节,MySQL过去在8.0.22之前,主要依赖的结构就是JOIN和QEP_TAB。JOIN是与之对应的每个Query_block,而QEP_TAB对应的每个Query_block涉及到的具体“表”的顺序、方法和执行计划。然而在8.0.22之后,新的基于Hypergraph的优化器算法成功的抛弃了QEP_TAB结构来表达左深树的执行计划,而直接使用HyperNode/HyperEdge的图来表示执行计划。
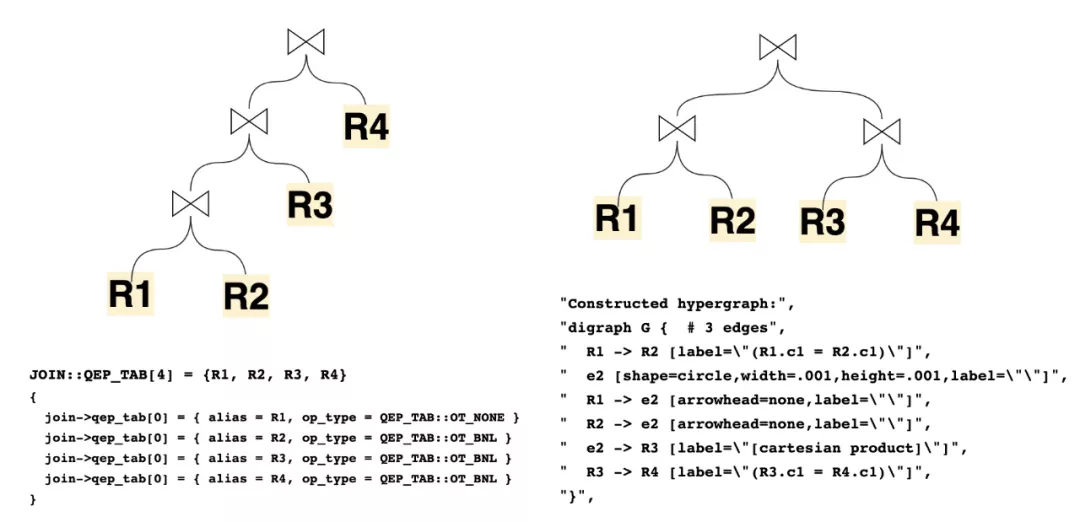
举例可以看到数据结构表达的left deep tree和超图结构表达的bushy tree对应的不同计划展现:
| -> Inner hash join (no condition) (cost=1.40 rows=1)
-> Table scan on R4 (cost=0.35 rows=1)
-> Hash
-> Inner hash join (no condition) (cost=1.05 rows=1)
-> Table scan on R3 (cost=0.35 rows=1)
-> Hash
-> Inner hash join (no condition) (cost=0.70 rows=1)
-> Table scan on R2 (cost=0.35 rows=1)
-> Hash
-> Table scan on R1 (cost=0.35 rows=1)
| -> Nested loop inner join (cost=0.55..0.55 rows=0)
-> Nested loop inner join (cost=0.50..0.50 rows=0)
-> Table scan on R4 (cost=0.25..0.25 rows=1)
-> Filter: (R4.c1 = R3.c1) (cost=0.35..0.35 rows=0)
-> Table scan on R3 (cost=0.25..0.25 rows=1)
-> Nested loop inner join (cost=0.50..0.50 rows=0)
-> Table scan on R2 (cost=0.25..0.25 rows=1)
-> Filter: (R2.c1 = R1.c1) (cost=0.35..0.35 rows=0)
-> Table scan on R1 (cost=0.25..0.25 rows=1)MySQL8.0.2x为了更好的兼容两种优化器,引入了新的类AccessPath,可以认为这是MySQL为了解耦执行器和不同优化器抽象出来的Plan Tree。
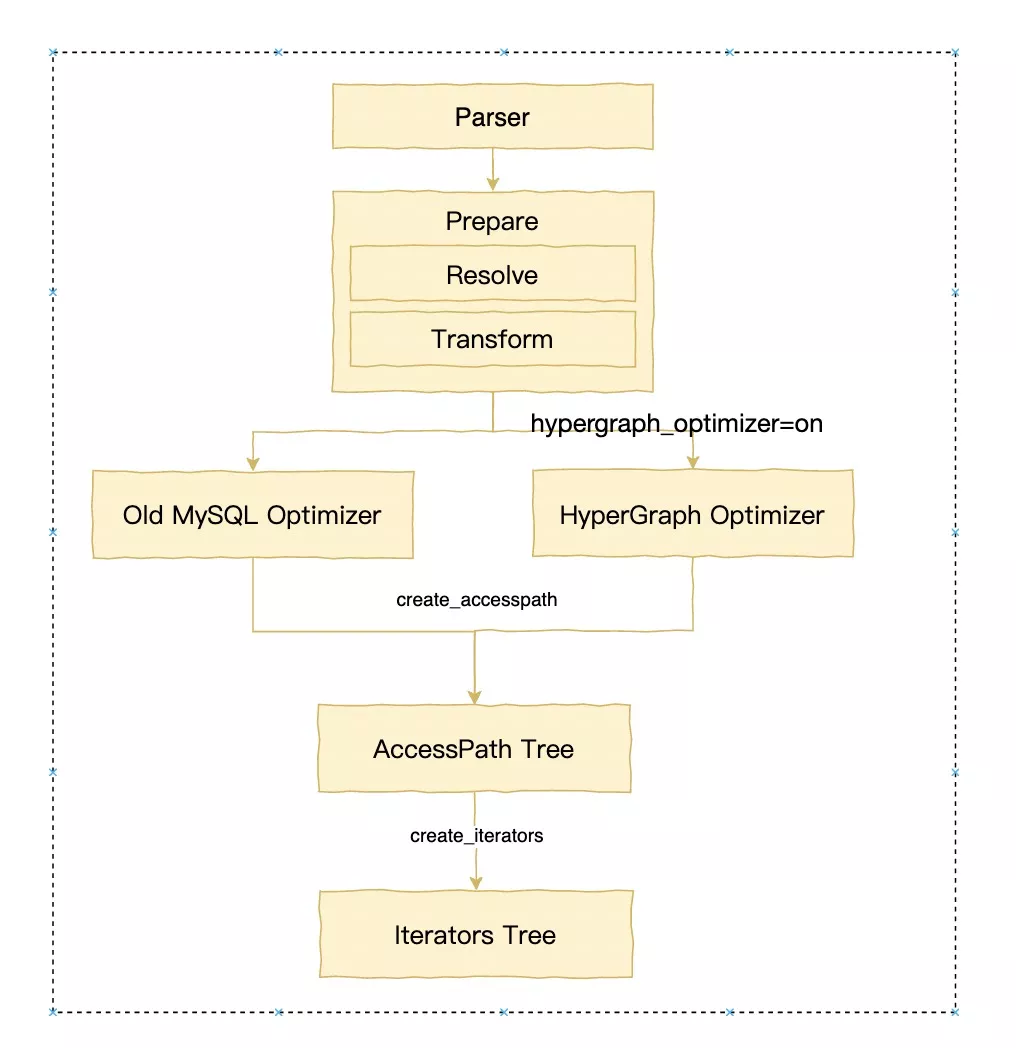
1 老优化器的入口
老优化器仍然走JOIN::optimize来把query block转换成query execution plan (QEP)。
这个阶段仍然做一些逻辑的重写工作,这个阶段的转换可以理解为基于cost-based优化前做准备,详细步骤如下:
Logical transformations
- optimize_derived : Optimize the query expression representing a derived table/view.
- optimize_cond : Equality/constant propagation.
- prune_table_partitions : Partition pruning.
- optimize_aggregated_query : COUNT(*), MIN(), MAX() constant substitution in case of implicit grouping.
- substitute_gc : ORDER BY optimization, substitute all expressions in the WHERE condition and ORDER/GROUP lists that match generated columns (GC) expressions with GC fields, if any.
Perform cost-based optimization of table order and access path selection.
- JOIN::make_join_plan() : Set up join order and initial access paths.
Post-join order optimization
- substitute_for_best_equal_field : Create optimal table conditions from the where clause and the join conditions.
- make_join_query_block : Inject outer-join guarding conditions.
- Adjust data access methods after determining table condition (several times).
- optimize_distinct_group_order : Optimize ORDER BY/DISTINCT.
- optimize_fts_query : Perform FULLTEXT search before all regular searches.
- remove_eq_conds : Removes const and eq items. Returns the new item, or nullptr if no condition.
- replace_index_subquery/create_access_paths_for_index_subquery : See if this subquery can be evaluated with subselect_indexsubquery_engine.
- setup_join_buffering : Check whether join cache could be used.
Code generation
- alloc_qep(tables) : Create QEP_TAB array.
- test_skip_sort : Try to optimize away sorting/distinct.
- make_join_readinfo : Plan refinement stage: do various setup things for the executor.
- make_tmp_tables_info : Setup temporary table usage for grouping and/or sorting.
- push_to_engines : Push (parts of) the query execution down to the storage engines if they can provide faster execution of the query, or part of it.
- create_access_paths : generated ACCESS_PATH.
2 新优化器的入口
新优化器默认不打开,必须通过set optimizer_switch="hypergraph_optimizer=on"; 来打开。主要通过FindBestQueryPlan函数来实现,逻辑如下:
- 先判断是否属于新优化器可以支持的Query语法(CheckSupportedQuery),不支持的直接返回错误ER_HYPERGRAPH_NOT_SUPPORTED_YET。
- 转化top_join_list变成JoinHypergraph结构。由于Hypergraph是比较独立的算法层面的实现,JoinHypergraph结构用来更好的把数据库的结构包装到Hypergraph的edges和nodes的概念上的。
- 通过EnumerateAllConnectedPartitions实现论文中的DPhyp算法。
- CostingReceiver类包含了过去JOIN planning的主要逻辑,包括根据cost选择相应的访问路径,根据DPhyp生成的子计划进行评估,保留cost最小的子计划。
- 得到root_path后,接下来处理group/agg/having/sort/limit的。对于Group by操作,目前Hypergraph使用sorting first + streaming aggregation的方式。
举例看下Plan(AccessPath)和SQL的关系:
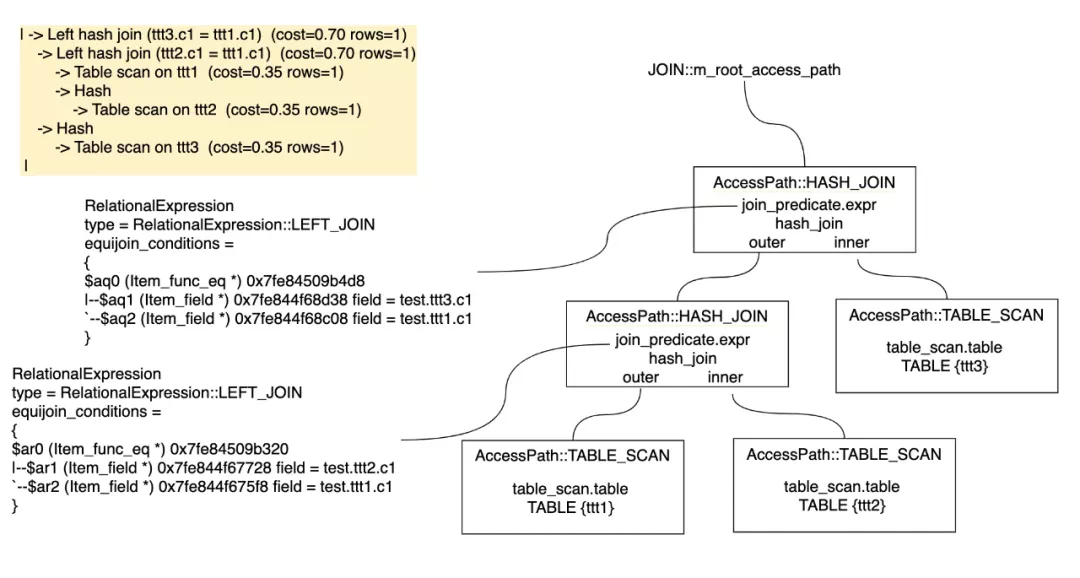
最后生成Iterator执行器框架需要的Iterator执行载体,AccessPath和Iterator是一对一的关系(Access paths are a query planning structure that correspond 1:1 to iterators)。
Query_expression::m_root_iterator = CreateIteratorFromAccessPath(......)
unique_ptr_destroy_only<RowIterator> CreateIteratorFromAccessPath(
THD *thd, AccessPath *path, JOIN *join, bool eligible_for_batch_mode) {
......
switch (path->type) {
case AccessPath::TABLE_SCAN: {
const auto ¶m = path->table_scan();
iterator = NewIterator<TableScanIterator>(
thd, param.table, path->num_output_rows, examined_rows);
break;
}
case AccessPath::INDEX_SCAN: {
const auto ¶m = path->index_scan();
if (param.reverse) {
iterator = NewIterator<IndexScanIterator<true>>(
thd, param.table, param.idx, param.use_order, path->num_output_rows,
examined_rows);
} else {
iterator = NewIterator<IndexScanIterator<false>>(
thd, param.table, param.idx, param.use_order, path->num_output_rows,
examined_rows);
}
break;
}
case AccessPath::REF: {
......
}3 对比PostgreSQL
testdb=# EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM tbl_a WHERE id < 300 ORDER BY data;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------
Sort (cost=182.34..183.09 rows=300 width=8)
Sort Key: data
-> Seq Scan on tbl_a (cost=0.00..170.00 rows=300 width=8)
Filter: (id < 300)
(4 rows)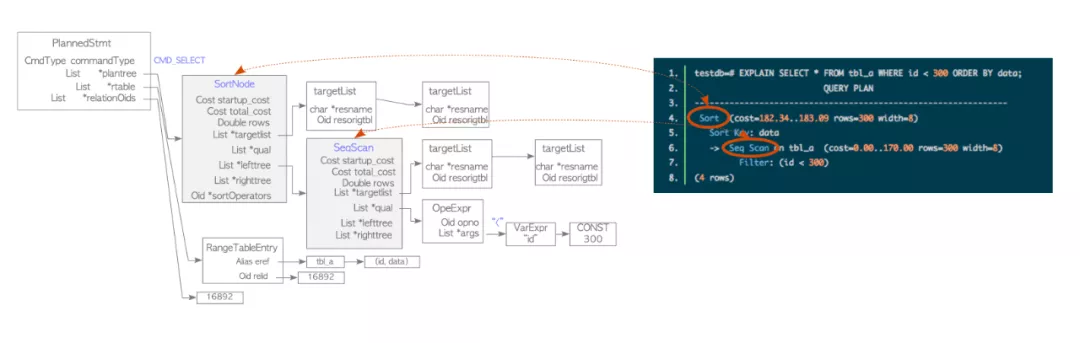
五 总结
本文主要focus在MySQL最新版本官方的源码上,重点分析了官方的重构在多阶段和各阶段结构上的变化和联系,更多的是为了让大家了解一个全新的MySQL的发展。
本文为阿里云原创内容,未经允许不得转载。
MySQL 8.0 Server层最新架构详解的更多相关文章
- MySQL 8.0.20 安装教程图文详解(windows 64位)
MySQL 8.0.20 安装教程图文详解(windows 64位) 更新时间:2020年05月09日 15:09:04 转载 作者:瘦肉粥不加糖 这篇文章主要介绍了MySQL 8.0. ...
- MySQL 8.0的关系数据库新特性详解
前言 MySQL 8.0 当前的最新版本是 8.0.4 rc,估计正式版本出来也快了.本文介绍几个 8.0 在关系数据库方面的主要新特性. 你可能已经知道 MySQL 从版本 5.7 开始提供了 No ...
- 支撑5亿用户、1.5亿活跃用户的Twitter最新架构详解及相关实现
如果你对项目管理.系统架构有兴趣,请加微信订阅号"softjg",加入这个PM.架构师的大家庭 摘要:Twitter出道之初只是个奋斗在RoR上的小站点,而如今已拥有1.5亿的活跃 ...
- NopCommerce源码架构详解--初识高性能的开源商城系统cms
很多人都说通过阅读.学习大神们高质量的代码是提高自己技术能力最快的方式之一.我觉得通过阅读NopCommerce的源码,可以从中学习很多企业系统.软件开发的规范和一些新的技术.技巧,可以快速地提高我们 ...
- NopCommerce源码架构详解
NopCommerce源码架构详解--初识高性能的开源商城系统cms 很多人都说通过阅读.学习大神们高质量的代码是提高自己技术能力最快的方式之一.我觉得通过阅读NopCommerce的源码,可以从 ...
- Spark2.1.0——内置Web框架详解
Spark2.1.0——内置Web框架详解 任何系统都需要提供监控功能,否则在运行期间发生一些异常时,我们将会束手无策.也许有人说,可以增加日志来解决这个问题.日志只能解决你的程序逻辑在运行期的监控, ...
- Zookeeper系列二:分布式架构详解、分布式技术详解、分布式事务
一.分布式架构详解 1.分布式发展历程 1.1 单点集中式 特点:App.DB.FileServer都部署在一台机器上.并且访问请求量较少 1.2 应用服务和数据服务拆分 特点:App.DB.Fi ...
- Spark2.1.0——内置RPC框架详解
Spark2.1.0——内置RPC框架详解 在Spark中很多地方都涉及网络通信,比如Spark各个组件间的消息互通.用户文件与Jar包的上传.节点间的Shuffle过程.Block数据的复制与备份等 ...
- MYSQL服务器my.cnf配置文档详解
MYSQL服务器my.cnf配置文档详解 硬件:内存16G [client] port = 3306 socket = /data/3306/mysql.sock [mysql] no-auto-re ...
- 领域驱动设计(Domain Driven Design)参考架构详解
摘要 本文将介绍领域驱动设计(Domain Driven Design)的官方参考架构,该架构分成了Interfaces.Applications和Domain三层以及包含各类基础设施的Infrast ...
随机推荐
- 5G+实时云渲染,让元宇宙应用触手可及
从2021年初被称为"元宇宙第一股"的罗布乐思(Roblox)正式在纽交所上市,到2021年10月Facebook更名为"Meta"宣布进军元宇宙,再到如今各大 ...
- drf(Book序列化练习、user表练习)
一. APIView版本 1. models.py from django.db import models # Create your models here. class CommonField( ...
- 【福利】JetBrains 全家桶永久免费使用
Jetbrains系列的IDE公认是最好的集成开发工具,但是收费且挺贵.我们以PhpStorm为例,新用户第一年需要199$,注意是$,还不是人民币,这个价格一上来肯定筛选掉一大批用户.确实好用,所以 ...
- Linux服务器下启动和关闭node
首先将node工程的代码和node_modules目录上传到服务器的某一个目录下 1.用forever 进行管理 前提:linux下已经安装了node npm install -g forever / ...
- 16 JavaScript逗号运算符
16 JavaScript逗号运算符 Python 逗号运算符一般用于组合多个表达式,其返回值是最后一个表达式的值,例如: function s(){ console.log(1), console. ...
- #Tarjan,贪心#LOJ 3684 「COCI 2022.3」Usmjeravanje
题目传送门 分析 可以发现题目实际上求的是最小强连通分量个数. 并且每个强连通分量必然是由最多两段区间 \(a_l\sim a_r,b_L\sim b_R\) 组成的 只要存在一条路 \(b_R-&g ...
- K8s技术全景:架构、应用与优化
本文深入探讨了Kubernetes(K8s)的关键方面,包括其架构.容器编排.网络与存储管理.安全与合规.高可用性.灾难恢复以及监控与日志系统. 关注[TechLeadCloud],分享互联网架构.云 ...
- Python 布尔类型
布尔值表示两个值之一:True(真)或False(假). 布尔值 在编程中,您经常需要知道一个表达式是否为True或False. 您可以在Python中评估任何表达式,并获得两个答案之一:True或F ...
- SAST-数据流分析方法-理论
引言 众所周知,数据流分析是实现污点分析的一种常用技术 数据流分析分为过程内的数据流分析与过程间的数据流分析.前者是对一个方法体内的数据流分析,主要是基于CFG分析,不涉及方法调用:后者是基于不同方法 ...
- centos部署Django二:项目上传及测试
1. 上传项目 用 ftp 或者 sftp 上传项目到服务器. *:如果上传时,报各种错误,可以考虑下是不是服务器中文件夹权限的问题.如果是权限的问题,可以使用命令修改文件夹权限后在上传:chmod ...
