java8之lambda表达式入门
- class Student{
- private String name;
- private Double score;
- public Student(String name, Double score) {
- this.name = name;
- this.score = score;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public Double getScore() {
- return score;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public void setScore(Double score) {
- this.score = score;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "{"
- + "\"name\":\"" + name + "\""
- + ", \"score\":\"" + score + "\""
- + "}";
- }
- }:
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
- {
- add(new Student("stu1",100.0));
- add(new Student("stu2",97.0));
- add(new Student("stu3",96.0));
- add(new Student("stu4",95.0));
- }
- };
- Collections.sort(studentList, new Comparator<Student>() {
- @Override
- public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
- return Double.compare(o1.getScore(),o2.getScore());
- }
- });
- System.out.println(studentList);
- }
代码调用Collections.sort方法对集合进行排序,其中第二个参数是一个匿名内部类,sort方法调用内部类中的compare方法对list进行位置交换,因为java中的参数类型只能是类或者基本数据类型,所以虽然传入的是一个Comparator类,但是实际上可以理解成为了传递compare方法而不得不传递一个Comparator类 ,这种方式显得比较笨拙,而且大量使用的话代码严重冗余,这种情况在java8中通过使用lambda表达式来解决。
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface Comparator<T> {
- int compare(T o1, T o2);
- }
- public void test1_(){
- List<Student> studentList = new ArrayList<Student>(){
- {
- add(new Student("stu1",100.0));
- add(new Student("stu2",97.0));
- add(new Student("stu3",96.0));
- add(new Student("stu4",95.0));
- }
- };
- Collections.sort(studentList,(s1,s2)-> Double.compare(s1.getScore(),s2.getScore()));
- System.out.println(studentList);
- }
- public void testThread(){
- new Thread(new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- System.out.println("hello, i am thread!");
- }
- }).start();
- }
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface Runnable {
- /**
- * When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
- * to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
- * <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
- * thread.
- * <p>
- * The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
- * take any action whatsoever.
- *
- * @see java.lang.Thread#run()
- */
- public abstract void run();
- }
- public void testThread_(){
- new Thread(()-> System.out.println("hello, i am thread!")).start();
- }
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface MyFunctionalInterface {
- public void single(String msg);
- }
- /**
- * 需要单个参数
- */
- public static void testOnePar(MyFunctionalInterface myFunctionalInterface){
- myFunctionalInterface.single("msg");
- }
- /**
- * 一个参数,可以省略参数的括号
- */
- @Test
- public void testOneParameter(){
- testOnePar(x-> System.out.println(x));
- }


- /**
- * 需要单个参数
- */
- public static void testOnePar1(Consumer unaryOperator){
- unaryOperator.accept("msg");
- }
- public static void test1_() {
- List<String> strLst = new ArrayList<String>() {
- {
- add("adfkjsdkfjdskjfkds");
- add("asdfasdfafgfgf");
- add("public static void main");
- }
- };
- Collections.sort(strLst, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
- System.out.println(strLst);
- }
- class Father {
- public void greet() {
- System.out.println("Hello, i am function in father!");
- }
- }
- class Child extends Father {
- @Override
- public void greet() {
- Runnable runnable = super::greet;
- new Thread(runnable).start();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args){
- new Child().greet();
- }
- List<String> labels = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd");
- Stream<Button> buttonStream = labels.stream().map(Button::new);
- <R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);
- public class Button extends ButtonBase {
- /**
- * Creates a button with the specified text as its label.
- *
- * @param text A text string for its label.
- */
- public Button(String text) {
- super(text);
- initialize();
- }
- }
- Button[] buttons1 = buttonStream.toArray(Button[]::new);
- <A> A[] toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator);
- public class LambdaTest3 {
- @Test
- public void test1_(){
- List<Integer> list = this.asList(ArrayList::new ,1,2,3,4,5);
- list.forEach(System.out::println);
- }
- public <T> List<T> asList(MyCrator<List<T>> creator,T... a){
- List<T> list = creator.create();
- for (T t : a)
- list.add(t);
- return list;
- }
- }
- interface MyCrator<T extends List<?>>{
- T create();
- }
- public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
- return new ArrayList<>(a);
- }
- public class LambdaTest4 {
- public void doWork1(){
- Runnable runnable = ()->{
- System.out.println(this.toString());
- System.out.println("lambda express run...");
- };
- new Thread(runnable).start();
- }
- public void doWork2(){
- Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- System.out.println(this.toString());
- System.out.println("anony function run...");
- }
- };
- new Thread(runnable).start();
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- new LambdaTest4().doWork1();
- new LambdaTest4().doWork2();
- }
- }
- com.java8.lambda.LambdaTest4@74f84cf
- lambda express run...
- com.java8.lambda.LambdaTest4$1@4295c176
- anony function run...
.png)
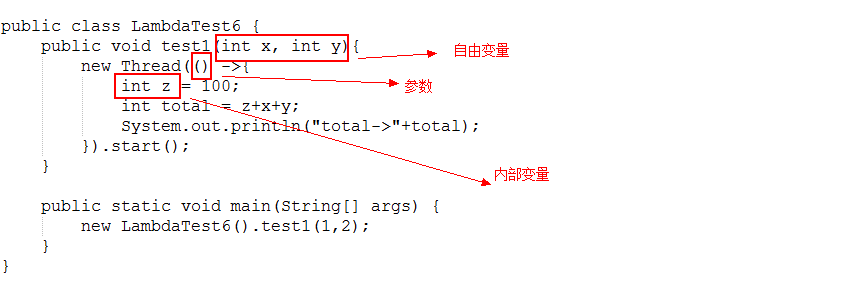
- public class Outer {
- public AnnoInner getAnnoInner(int x) {
- int y = 100;
- return new AnnoInner() {
- int z = 100;
- @Override
- public int add() {
- return x + y + z;
- }
- };
- }
- public AnnoInner AnnoInnergetAnnoInner1(List<Integer> list1) {
- List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
- return ()->{
- list2.add(123);
- int count = 0;
- Iterator<Integer> it = list1.iterator();
- while (it.hasNext()){
- count+=it.next();
- }
- Iterator<Integer> it1 = list2.iterator();
- while (it1.hasNext()){
- count+=it1.next();
- }
- return count;
- };
- }
- @Test
- public void test(){
- AnnoInner res = new Outer().AnnoInnergetAnnoInner1(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1,2,3)));
- System.out.println(res.add());
- }
- }
- interface AnnoInner {
- int add();
- }
- @FunctionalInterface
- public interface Comparator<T> {
- int compare(T o1, T o2);
- boolean equals(Object obj);
- default Comparator<T> reversed() {
- return Collections.reverseOrder(this);
- }
- default Comparator<T> thenComparing(Comparator<? super T> other) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(other);
- return (Comparator<T> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> {
- int res = compare(c1, c2);
- return (res != 0) ? res : other.compare(c1, c2);
- };
- }
- default <U> Comparator<T> thenComparing(
- Function<? super T, ? extends U> keyExtractor,
- Comparator<? super U> keyComparator)
- {
- return thenComparing(comparing(keyExtractor, keyComparator));
- }
- default <U extends Comparable<? super U>> Comparator<T> thenComparing(
- Function<? super T, ? extends U> keyExtractor)
- {
- return thenComparing(comparing(keyExtractor));
- }
- default Comparator<T> thenComparingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> keyExtractor) {
- return thenComparing(comparingInt(keyExtractor));
- }
- default Comparator<T> thenComparingLong(ToLongFunction<? super T> keyExtractor) {
- return thenComparing(comparingLong(keyExtractor));
- }
- default Comparator<T> thenComparingDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T> keyExtractor) {
- return thenComparing(comparingDouble(keyExtractor));
- }
- public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> Comparator<T> reverseOrder() {
- return Collections.reverseOrder();
- }
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> Comparator<T> naturalOrder() {
- return (Comparator<T>) Comparators.NaturalOrderComparator.INSTANCE;
- }
- public static <T> Comparator<T> nullsFirst(Comparator<? super T> comparator) {
- return new Comparators.NullComparator<>(true, comparator);
- }
- public static <T> Comparator<T> nullsLast(Comparator<? super T> comparator) {
- return new Comparators.NullComparator<>(false, comparator);
- }
- public static <T, U> Comparator<T> comparing(
- Function<? super T, ? extends U> keyExtractor,
- Comparator<? super U> keyComparator)
- {
- Objects.requireNonNull(keyExtractor);
- Objects.requireNonNull(keyComparator);
- return (Comparator<T> & Serializable)
- (c1, c2) -> keyComparator.compare(keyExtractor.apply(c1),
- keyExtractor.apply(c2));
- }
- public static <T, U extends Comparable<? super U>> Comparator<T> comparing(
- Function<? super T, ? extends U> keyExtractor)
- {
- Objects.requireNonNull(keyExtractor);
- return (Comparator<T> & Serializable)
- (c1, c2) -> keyExtractor.apply(c1).compareTo(keyExtractor.apply(c2));
- }
- public static <T> Comparator<T> comparingInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> keyExtractor) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(keyExtractor);
- return (Comparator<T> & Serializable)
- (c1, c2) -> Integer.compare(keyExtractor.applyAsInt(c1), keyExtractor.applyAsInt(c2));
- }
- public static <T> Comparator<T> comparingLong(ToLongFunction<? super T> keyExtractor) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(keyExtractor);
- return (Comparator<T> & Serializable)
- (c1, c2) -> Long.compare(keyExtractor.applyAsLong(c1), keyExtractor.applyAsLong(c2));
- }
- public static<T> Comparator<T> comparingDouble(ToDoubleFunction<? super T> keyExtractor) {
- Objects.requireNonNull(keyExtractor);
- return (Comparator<T> & Serializable)
- (c1, c2) -> Double.compare(keyExtractor.applyAsDouble(c1), keyExtractor.applyAsDouble(c2));
- }
- }
- public class LambdaTest5 implements myInterface1, myInterface2 {
- @Override
- public void getName() {
- myInterface1.super.getName();
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- new LambdaTest5().getName();
- }
- }
- interface myInterface1 {
- default void getName() {
- System.out.println("myInterface1 getName");
- }
- ;
- }
- interface myInterface2 {
- default void getName() {
- System.out.println("myInterface2 getName");
- }
- }
java8之lambda表达式入门的更多相关文章
- 函数式编程/lambda表达式入门
函数式编程/lambda表达式入门 本篇主要讲解 lambda表达式的入门,涉及为什么使用函数式编程,以及jdk8提供的函数式接口 和 接口的默认方法 等等 1.什么是命令式编程 命令式编程就是我们去 ...
- Java Lambda表达式入门
Java Lambda表达式入门 http://blog.csdn.net/renfufei/article/details/24600507 Java 8十个lambda表达式案例 http://w ...
- Java8中Lambda表达式的10个例子
Java8中Lambda表达式的10个例子 例1 用Lambda表达式实现Runnable接口 //Before Java 8: new Thread(new Runnable() { @Overri ...
- java8的lambda表达式,将List<DTO> 转为 List<DO>
将List<PhoneDTO>转为List<PhoneDO>,通过java8的lambda表达式来操作,比传统的for循环精简很多: /** * List<PhoneDT ...
- java8的lambda表达式
关于java8的lambda表达式 lambda表达式一般用于接口,因为lambda表达式是函数式编程. 1.有且仅有一个抽象方法被称为函数式接口,函数式接口可以显示的被@FunctionalInte ...
- 30分钟入门Java8之lambda表达式
前言 Google在今年发布Android N开发者预览版,一并宣布开始支持Java 8.我们终于能在Android开发中使用到Java8的一些语言特性了.目前支持: 默认方法 lambda表达式 多 ...
- 十分钟学会Java8的lambda表达式和Stream API
01:前言一直在用JDK8 ,却从未用过Stream,为了对数组或集合进行一些排序.过滤或数据处理,只会写for循环或者foreach,这就是我曾经的一个写照. 刚开始写写是打基础,但写的多了,各种乏 ...
- Java8的lambda表达式和Stream API
一直在用JDK8 ,却从未用过Stream,为了对数组或集合进行一些排序.过滤或数据处理,只会写for循环或者foreach,这就是我曾经的一个写照. 刚开始写写是打基础,但写的多了,各种乏味,非过来 ...
- Java8(一)--lambda表达式
相信作为一个Java程序员都会或多或少的了解过Java8中的lambda表达式.函数式编程等,本人也是用过lambda表达式,使用的都是比较简单 的实现 通过一个例子去都感受lambda: Compa ...
随机推荐
- 【Android Developers Training】 12. 支持不同屏幕
注:本文翻译自Google官方的Android Developers Training文档,译者技术一般,由于喜爱安卓而产生了翻译的念头,纯属个人兴趣爱好. 原文链接:http://developer ...
- html网页的兼容性和css优先级
网页不仅是在一个浏览器上显示的网页,也要多考虑其他浏览器的兼容性,火狐.谷歌.搜狗等浏览器总体来说,网页的变化不大,最主要的是还是IE浏览器. color:red\9; IE6 IE7 IE8 ...
- C#调用TSC条码打印机打印二维码
#region 调用TSC打印机打印 /// <summary> /// 调用TSC打印机打印 /// </summary> /// <param name=" ...
- gulp 运用 的理解
ugulp.task('build', function() { runSequence('clean', 'copy', ['uglify', 'sass', 'htmlmin'], 'base64 ...
- Hibernate框架 初识 ORM概念 搭建Hibernate环境 Hibernate Api
ORM概念 在学习 Hibernate 之前,我们先来了解ORM 对象关系映射 O, Object 对象 R,Realtion 关系 (关系型数据库: MySQL, Oracle…) M,Ma ...
- java 线程 理解 解析
1 线程的概述 进程:正在运行的程序,负责了这个程序的内存分配,代表了内存中的执行区域. 线程:就是在一个进程中负者一个执行路径. 多线程:就是在一个进程中多个执行路径同时执行. 假象: 电脑上的程序 ...
- jquery.jconfirm兼容IE6
因目标用户还在大量使用IE6(想吐CAO),只能做向下兼容,但之前使用的这个插件在IE6上并不支持.所以做了些处理才行. 以下为解决方法: IE6不支持position: fixed,所以需要对CSS ...
- (cljs/run-at (JSVM. :all) "Metadata就这样哦")
前言 动态类型语言,少了静态类型语言必须声明变量类型的累赘,但也缺失了编译时类型检查和编译时优化的好处.cljs虽然作为动态类型语言,但其提供Metadata让我们在必要的时候可选择地补充类型提示, ...
- ES6 新增命令
let 用来声明变量.它的用法类似于var,但是所声明的变量, 只在let命令所在的代码块内有效. 例: {var a=10; let b=20;}; console.lo ...
- Android - TabHost 与 Fragment 制作页面切换效果
Android - TabHost 与 Fragment 制作页面切换效果 Android API 19 , API 23 三个标签页置于顶端 效果图: 在文件BoardTabHost.java中定义 ...
