IO代码记忆
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("hello.txt"); String s = "hello world"; fw.write(s,0,s.length()); fw.flush(); OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("hello2.txt")); osw.write(s,0,s.length()); osw.flush(); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("hello3.txt")),true); pw.println(s);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("hello.txt");
String s = "hello world";
fw.write(s,0,s.length());
fw.flush();
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("hello2.txt"));
osw.write(s,0,s.length());
osw.flush();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("hello3.txt")),true);
pw.println(s);
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.io.Reader;
public class ReadFromFile {
/**
* 以字节为单位读取文件,常用于读二进制文件,如图片、声音、影像等文件。
* @param fileName 文件的名
*/
public static void readFileByBytes(String fileName){
File file = new File(fileName);
InputStream in = null;
try {
System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读一个字节:");
// 一次读一个字节
in = new FileInputStream(file);
int tempbyte;
while((tempbyte=in.read()) != -1){
System.out.write(tempbyte);
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
System.out.println("以字节为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:");
//一次读多个字节
byte[] tempbytes = new byte[100];
int byteread = 0;
in = new FileInputStream(fileName);
ReadFromFile.showAvailableBytes(in);
//读入多个字节到字节数组中,byteread为一次读入的字节数
while ((byteread = in.read(tempbytes)) != -1){
System.out.write(tempbytes, 0, byteread);
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null){
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 以字符为单位读取文件,常用于读文本,数字等类型的文件
* @param fileName 文件名
*/
public static void readFileByChars(String fileName){
File file = new File(fileName);
Reader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读一个字节:");
// 一次读一个字符
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));
int tempchar;
while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1){
//对于windows下,rn这两个字符在一起时,表示一个换行。
//但如果这两个字符分开显示时,会换两次行。
//因此,屏蔽掉r,或者屏蔽n。否则,将会多出很多空行。
if (((char)tempchar) != 'r'){
System.out.print((char)tempchar);
}
}
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
System.out.println("以字符为单位读取文件内容,一次读多个字节:");
//一次读多个字符
char[] tempchars = new char[30];
int charread = 0;
reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName));
//读入多个字符到字符数组中,charread为一次读取字符数
while ((charread = reader.read(tempchars))!=-1){
//同样屏蔽掉r不显示
if ((charread == tempchars.length)&&(tempchars[tempchars.length-1] != 'r')){
System.out.print(tempchars);
}else{
for (int i=0; i<charread; i++){
if(tempchars[i] == 'r'){
continue;
}else{
System.out.print(tempchars[i]);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (reader != null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 以行为单位读取文件,常用于读面向行的格式化文件
* @param fileName 文件名
*/
public static void readFileByLines(String fileName){
File file = new File(fileName);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以行为单位读取文件内容,一次读一整行:");
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
int line = 1;
//一次读入一行,直到读入null为文件结束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null){
//显示行号
System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + tempString);
line++;
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 随机读取文件内容
* @param fileName 文件名
*/
public static void readFileByRandomAccess(String fileName){
RandomAccessFile randomFile = null;
try {
System.out.println("随机读取一段文件内容:");
// 打开一个随机访问文件流,按只读方式
randomFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r");
// 文件长度,字节数
long fileLength = randomFile.length();
// 读文件的起始位置
int beginIndex = (fileLength > 4) ? 4 : 0;
//将读文件的开始位置移到beginIndex位置。
randomFile.seek(beginIndex);
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
int byteread = 0;
//一次读10个字节,如果文件内容不足10个字节,则读剩下的字节。
//将一次读取的字节数赋给byteread
while ((byteread = randomFile.read(bytes)) != -1){
System.out.write(bytes, 0, byteread);
}
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (randomFile != null){
try {
randomFile.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
/**
* 显示输入流中还剩的字节数
* @param in
*/
private static void showAvailableBytes(InputStream in){
try {
System.out.println("当前字节输入流中的字节数为:" + in.available());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName = "C:/temp/newTemp.txt";
ReadFromFile.readFileByBytes(fileName);
ReadFromFile.readFileByChars(fileName);
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
ReadFromFile.readFileByRandomAccess(fileName);
}
}
二、将内容追加到文件尾部
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
/**
* 将内容追加到文件尾部
*/
public class AppendToFile {
/**
* A方法追加文件:使用RandomAccessFile
* @param fileName 文件名
* @param content 追加的内容
*/
public static void appendMethodA(String fileName,
String content){
try {
// 打开一个随机访问文件流,按读写方式
RandomAccessFile randomFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "rw");
// 文件长度,字节数
long fileLength = randomFile.length();
//将写文件指针移到文件尾。
randomFile.seek(fileLength);
randomFile.writeBytes(content);
randomFile.close();
} catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* B方法追加文件:使用FileWriter
* @param fileName
* @param content
*/
public static void appendMethodB(String fileName, String content){
try {
//打开一个写文件器,构造函数中的第二个参数true表示以追加形式写文件
FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(fileName, true);
writer.write(content);
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fileName = "C:/temp/newTemp.txt";
String content = "new append!";
//按方法A追加文件
AppendToFile.appendMethodA(fileName, content);
AppendToFile.appendMethodA(fileName, "append end. n");
//显示文件内容
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
//按方法B追加文件
AppendToFile.appendMethodB(fileName, content);
AppendToFile.appendMethodB(fileName, "append end. n");
//显示文件内容
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
}
}
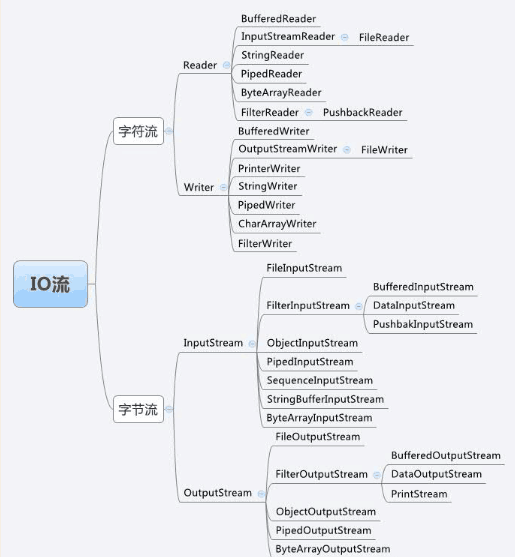
IO代码记忆的更多相关文章
- IO—代码—基础及其用例
字节流:文件.图片.歌曲 使用字节流的应用场景:如果是读写的数据都不需要转换成字符的时候,则使用字节流. 字节流处理单元为1个字节, 操作字节和字节数组.不能直接处理Unicode字符 字节流可用于任 ...
- Java Socket, DatagramSocket, ServerSocketChannel io代码跟踪
Java Socket, DatagramSocket, ServerSocketChannel这三个分别对应了,TCP, udp, NIO通信API封装.JDK封装了,想跟下代码,看下具体最后是怎么 ...
- 为了记忆和方便翻阅 vue构建后的结构目录说明
一. ├── build // 项目构建(webpack)相关代码 记忆:(够贱) 9个 │ ├── build.js // 生产环 ...
- socket.io简单入门(一.实现简单的图表推送)
引子:随着nodejs蓬勃发展,虽然主要业务系统因为架构健壮性不会选择nodejs座位应用服务器.但是大量的内部系统却可以使用nodejs试水,大量的前端开发人员转入全堆开发也是一个因素. 研究本例主 ...
- socket.io稳定性及事件测试
socket.io测试报告 1.socekt.io能坚持多久 将服务器上的socekt.io代码从早上9:30分开始运行到晚上18点,每100毫秒发送一条数据,数据大概15个字符,同时开启5个连接 结 ...
- 并发式IO的解决方案:多路非阻塞式IO、多路复用、异步IO
在Linux应用编程中的并发式IO的三种解决方案是: (1) 多路非阻塞式IO (2) 多路复用 (3) 异步IO 以下代码将以操作鼠标和键盘为实例来演示. 1. 多路非阻塞式IO 多路非阻塞式IO访 ...
- Koa,React和socket.io
安装 socket.io/socket.io-client 基本用法 首先koa和socket.io代码片段 const server = require('http'). const server ...
- python学习之路-第八天-文件IO、储存器模块
文件IO.储存器模块 文件IO 代码示例: # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #! /usr/bin/python # filename:using_file.py poem = '''\ ...
- File IO(NIO.2):路径类 和 路径操作
路径类 Java SE 7版本中引入的Path类是java.nio.file包的主要入口点之一.如果您的应用程序使用文件I / O,您将需要了解此类的强大功能. 版本注意:如果您有使用java.io. ...
随机推荐
- JMeter参数化实现
参数化:指对每次发起的请求,参数名称相同,参数值进行替换,如登录三次系统,每次用不同的用户名和密码. 1.1.1. 从csv文件读取(CSV Data Set Config) 步骤: 1)新建一个文 ...
- 记录python学习过程中的一些小心得
1.python中一切皆对象,内置数据结构也是对象.处理一个对象就是利用它带有的方法和属性,对该对象进行处理,一步步达到我们想要的结果. 2.编程时,先构思好我们处理的对象是什么,具有哪些属性和方法, ...
- eclipse 更换 JDK 版本后报错
在实际开发过程中,可能由于项目的需要,我们需要更换 JDK 的版本.但是更换后会报错,如下: Java compiler level does not match the version of the ...
- 对DataTable(或者DataSet)修改后,提交修改到数据库
http://blog.csdn.net/nidexuanzhe/article/details/8228832 说明:通常我们在做数据库交互时,并不一定要使用特定的SQL语句来更新数据,.NET F ...
- php一篇入门
<?php header("Content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8");//设置编码也可以通过html中的 head中的 <met ...
- HyperV下安装Centos 7全屏显示方法
Hyper-v一般模式的分辨率很小,所以我们在电脑上显示的时候往往不能全屏,即使全屏了也只是轮廓全部工作区并没有全屏显示.导致这个问题的原因是:我们在装系统时,没有选择合适的屏幕分辨率,所以这里只要在 ...
- 树上操作[HAOI 2015]
树链剖分裸题: 树剖点这里:传送门 代码: #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define sight(c) ('0'<=c&&c<='9') ...
- R语言命令行参数
批量画图任务中,需要在R中传入若干参数,之前对做法是在perl中每一个任务建立一个Rscript,这种方式超级不cool,在群里学习到R的@ARGV调用方式,差不多能够达到批量任务的要求: a ...
- 微信小程序开发之picker
一.绑定简单数组 通过bindChange控制index,使得当前选择值发生改变 示例1 data: { Data: ['A','B'], Index: 0, }, <picker class= ...
- js设置元素class方法小结及classList相关
给DOM元素设置class是我们在项目中非常容易遇到的,网上的资料和总结也比较多,下面比较全面的整理一下,希望给到大家一些帮助!并引用两种成熟的classList的兼容方法 一.el.setA ...
