Spring Bean 生命周期2
一、BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor的区别
BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor都是spring初始化bean的扩展点。两个接口非常相似。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以对bean的定义(配置元数据)进行处理。也就是说,Spring IoC容器允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实际实例化任何其它的bean之前读取配置元数据,并有可能修改它。如果你愿意,你可以配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor。你还能通过设置'order'属性来控制BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。
注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实例,需要重载void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
通过beanFactory可以获取bean的示例或定义等。同时可以修改bean的属性,这是和BeanPostProcessor最大的区别。
例如:
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("xxBean");
MutablePropertyValues mpv = bd.getPropertyValues();
if(pv.contains("xxName")) {
pv.addPropertyValue("xxName", "icoder");
}
注册BeanPostProcessor的实例,需要重载
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
和
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
还有一点区别就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的回调比BeanPostProcessor要早。
二、BeanPostProcessors
1、bean生成过程
首先回顾下bean的生命周期如下图:
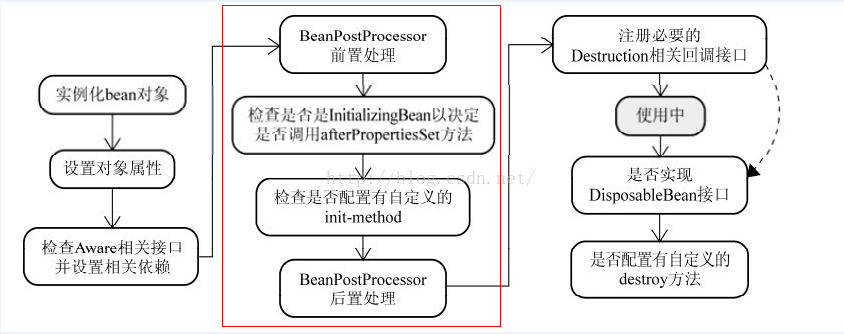
2、BeanPostProcessors接口
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
*/
//实例化、依赖注入完毕,在调用显示的初始化之前完成一些定制的初始化任务
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
*/
//实例化、依赖注入、初始化完毕时执行
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
如果这个接口的某个实现类被注册到某个容器,那么该容器的每个受管Bean在调用初始化方法的前后,都会获得该接口实现类的一个回调。容器调用接口定义的方法时会将该受管Bean的实例和名字通过参数传入方法,进过处理后通过方法的返回值返回给容器。
要使用BeanPostProcessor回调,就必须先在容器中注册实现该接口的类,那么如何注册呢?BeanFactory和ApplicationContext容器的注册方式不大一样:
- 若使用BeanFactory,则必须要显示的调用其addBeanPostProcessor()方法进行注册,参数为BeanPostProcessor实现类的实例;
- 如果是使用ApplicationContext,那么容器会在配置文件在中自动寻找实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的Bean,然后自动注册,我们要做的只是配置一个BeanPostProcessor实现类的Bean就可以了。
假如我们使用了多个的BeanPostProcessor的实现类,那么如何确定处理顺序呢?其实只要实现Ordered接口,设置order属性就可以很轻松的确定不同实现类的处理顺序了。
3、示例
3.1 applicationContext.xml
3.2 自己的业务bean
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class User {
@Value("老名字")
private String name;
@Value("50")
private Integer id; public Integer getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
3.3 postProcessor bean
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class UserPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
if(o instanceof User){
User user = (User)o;
user.setName("新名字");
user.setId(100);
return user;
}
return o;
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
return o;
}
}
3.4 测试方法
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = (User) cxt.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user.toString());
}
}
3.5 执行结果
如果没有<bean id="userPostProcessor" class="com.meituan.hyt.test1.UserPostProcessor"/>
User{name='老名字', id=50}
添加<bean id="userPostProcessor" class="com.meituan.hyt.test1.UserPostProcessor"/>
User{name='新名字', id=100}
4、InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的子接口

三、与BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的区别
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:允许自定义对ApplicationContext的 bean definitions 进行修饰,扩展功能。
1、实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,会被Application contexts自动发现
2、BeanFactoryPostProcessor 仅仅对 bean definitions 发生关系,不能对bean instances 交互,对bean instances 的交互,由BeanPostProcessor的实现来处理
3、PropertyResourceConfigurer 是一个典型的实现 (PropertyResourceConfigurer是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的一个实现)
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口实现类可以在当前BeanFactory初始化后,bean实例化之前对BeanFactory做一些处理。BeanFactoryPostProcessor是针对于bean容器的,在调用它时,BeanFactory只加载了bean的定义,还没有对它们进行实例化,所以我们可以通过对BeanFactory的处理来达到影响之后实例化bean的效果。跟BeanPostProcessor一样,ApplicationContext也能自动检测和调用容器中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
示例1:
package com.meituan.hyt.test1; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; public class UserBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor doing");
}
}
applicationContext.xml中添加bean配置
<bean id="userBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.meituan.hyt.test1.UserBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/>
重新运行,结果
BeanFactoryPostProcessor doing
User{name='新名字', id=100}
示例2:
<bean id="user" class="com.gym.UserServiceImpl" >
<property name="username" value="${username_}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password_}"/>
</bean>
spring支持系统对username_进行占位符的配置为properties文件配置,试想如果我们有个配置中心,我们希望spring启动的时候,从远程配置中心取数据,而非本地文件,这里就需要我们自定义一个实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor的PropertyResourceConfigurer 实例。
看下面的例子:
bean.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"
default-autowire="byName"> <bean id="user" class="com.gym.UserServiceImpl" >
<property name="username" value="${username_}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password_}"/>
</bean> <bean id="myFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.gym.MyFilePlaceHolderBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
模拟从远程取文件:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderUtils; /**
* @author xinchun.wang
*/
public class MyFilePlaceHolderBeanFactoryPostProcessor
extends PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer implements InitializingBean{ public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
List<Properties> list = new ArrayList<Properties>();
Properties p = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("config.properties");
list.add(p);
//这里是关键,这就设置了我们远程取得的List<Properties>列表
setPropertiesArray(list.toArray(new Properties[list.size()]));
} }
javaBean配置:
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService{
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
public UserServiceImpl(){
logger.info("UserServiceImpl 构造函数 ");
}
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
logger.info("UserServiceImpl setUsername {}",username);
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
logger.info("UserServiceImpl setPassword {}",password);
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserServiceImpl [username=" + username + ", password="
+ password + "]";
}
}
测试:
public class TestApplicationContext {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml");
IUserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(IUserService.class);
String password = userService.getPassword();
applicationContext.destroy();
System.out.println(password);
}
}
Spring Bean 生命周期2的更多相关文章
- spring bean 生命周期和 ? 作用域? spirng bean 相互依赖? jvm oom ? jvm 监控工具? ThreadLocal 原理
1. spring bean 生命周期 1. 实例化一个bean ,即new 2. 初始化bean 的属性 3. 如果实现接口 BeanNameAware ,调用 setBeanName 4. Bea ...
- Spring点滴四:Spring Bean生命周期
Spring Bean 生命周期示意图: 了解Spring的生命周期非常重要,我们可以利用Spring机制来定制Bean的实例化过程. -------------------------------- ...
- Spring Bean 生命周期之destroy——终极信仰
上一篇文章 Spring Bean 生命周期之我从哪里来 说明了我是谁? 和 我从哪里来? 的两大哲学问题,今天我们要讨论一下终极哲学我要到哪里去? 初始化 Spring Bean 有三种方式: @P ...
- 常见问题:Web/Servlet生命周期与Spring Bean生命周期
Servlet生命周期 init()初始化阶段 Servlet容器加载Servlet(web.xml中有load-on-startup=1;Servlet容器启动后用户首次向Servlet发请求;Se ...
- 大厂高频面试题Spring Bean生命周期最详解
Spring作为当前Java最流行.最强大的轻量级框架.Spring Bean的生命周期也是面试高频题,了解Spring Bean周期也能更好地帮助我们解决日常开发中的问题.程序员应该都知道Sprin ...
- Spring Bean生命周期,好像人的一生。。
大家好,我是老三,上节我们手撸了一个简单的IOC容器五分钟,手撸一个Spring容器!,这节我们来看一看Spring中Bean的生命周期,我发现,和人的一生真的很像. 简单说说IoC和Bean IoC ...
- 睡前聊一聊"spring bean 生命周期"
spring bean 生命周期=实属初销+2个常见接口+3个Aware型接口+2个生命周期接口 实属初销:spring bean生命周期只有四个阶段,即实例化->属性赋值->初始化-&g ...
- Spring bean 生命周期验证
一.从源码注释看bean生命周期 从JDK源码上看,BeanFactory实现类需要支持Bean的完整生命周期,完整的初始化方法及其标准顺序(格式:接口 方法)为: 1.BeanNameAware s ...
- 【不懂】spring bean生命周期
完整的生命周期(牢记): 1.spring容器准备 2.实例化bean 3.注入依赖关系 4.初始化bean 5.使用bean 6.销毁bean Bean的完整生命週期可以認為是從容器建立初始化Bea ...
随机推荐
- bufferedReader 乱码问题
public static void main(String arsg[]) throws Exception{ BufferedReader bufferedReader = new Buffere ...
- 动态链接库中函数的地址确定---PLT和GOT [转]
前面写过动态链接库 延迟绑定的一篇博文,那篇文章我非常喜欢,但是当时刚搞清楚,自己写的比较凌乱,我最近学习了Ulrich Drepper的How to write share library,学习了几 ...
- PHP-mysqllib和mysqlnd
1.什么是mysqlnd驱动? PHP手册上的描述:MySQL Native Driver is a replacement for the MySQL Client Library (libmysq ...
- Oracle 12c RAC 搭建手册
1 共享设备配置 1.1 设备划分说明 冗余策略 卷划分及大小说明 OCRVOTING Ocrvoting01 8G Ocrvoting02 8G Ocrvoting03 8G ...
- android屏幕亮度
/** * 获得当前屏幕亮度的模式 * SCREEN_BRIGHTNESS_MODE_AUTOMATIC=1 为自动调节屏幕亮度 * SCREEN_BRIGHTNESS_MODE_MANUAL=0 为 ...
- 苹果MAC中安装并搭建Android开发环境的详细步骤
Android的开发平台搭建主要需要的工具有:Java虚拟机JDK.Eclipse.Eclipse插件ADT(Android Developer Tool)和Android开发包SDK,以下是具体的安 ...
- Zend 安装 OpenExplorer插件
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/binyao02123202/article/details/8954249 OpenExplorer是一款打开导进来的项目文件或文件夹所在磁盘的位置的 ...
- PHP5.3以上版本没有libmysql.dll,以及由此带来的困扰
有朋友下载了PHP5.3,PHP5.4版本想加载mysql支持的时候发现没有libmysql.dll文件,无法完成mysql配置,其实PHP5.3版本开始,使用mysqlnd库,不再使用libmysq ...
- python file operation
file.open(name[,mode[,buffering]]) 模式的类型有: r 默认只读 w 以写方式打开,如果文件不存在则会先创建,如果文件存在则先把文件内容清空(truncate ...
- 学习Python遇到的那些坑
1. 初始化一个类,这个方法名必须为”__init__(object)“.顺便提一下,两边的下划线是均是2个 2. 每个程序块都要使用冒号!!!! 3. 如果程序中使用了非英文字符,需要在Python ...
