【SpringBoot源码分析】-Bean的加载过程
-- 以下内容均基于2.1.8.RELEASE版本
在《SpringBoot启动过程的分析》系列文章中简要的对SpringBoot整体的启动流程作了梳理,但并未针对诸多细节进行分析。前面的篇章中介绍了从SpringBoot应用程序入口开始执行,一直到上下文刷新完成。期间它加载了所有的类,但是并未直接指出它是在哪个环节加载的类,在加载的过程中如何处理的,以及我们在程序入口所使用的各种注解是如何解析的。本文将对这一疑惑进行解答。
要分析SpringBoot加载类的过程,就必须清晰的知道我们的类到底在哪个环节被加载的。也就是需要定位到加载类的入口,如何来确定这个入口呢?通过阅读spring-framework的官方文档可以得知我们可以从ApplicationContext中来通过getBean()方法来获取Bean。那么通过这个入口就能找到存放Bean的地方,找到存放Bean的地方就可以通过调试得知它在什么时候被加载进来,进而确定Bean加载的入口。
找到Bean存放位置
这里通过一个简单示例来展示如何寻找Bean存放位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(Example.class);
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = application.run(args);
// 从容器中获取一个Bean
Example2 example2 = context.getBean(Example2.class);
}
上述代码是一个非常常见的获取Bean的代码,跟踪context.getBean()方法就能找到它存放的位置。
// AbstractApplicationContext.class
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
// 从BeanFactory获取Bean
return getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType);
}
// DefaultListableBeanFactory.class
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
return getBean(requiredType, (Object[]) null);
}
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object... args) throws BeansException {
Assert.notNull(requiredType, "Required type must not be null");
// 可以看到Object对象是这里获取的
Object resolved = resolveBean(ResolvableType.forRawClass(requiredType), args, false);
if (resolved == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(requiredType);
}
return (T) resolved;
}
// ...中间省略部分代码
private String[] doGetBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
// ① Check all bean definitions.
for (String beanName : this.beanDefinitionNames) {
// ...中间省略部分代码
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
① - 一路跟踪下来,可以看到所有的Bean都是在BeanFactory的beanDefinitionNames里面存放。因此关注这个属性何时被赋值就可以找到Bean加载的入口。
确定Bean在哪个环节被加载
当得知Bean存放于BeanFactory的beanDefinitionNames属性中,在启动阶段关注这个属性值的变化即可确定它在哪个阶段被赋值,可以肯定的是,它一定是在上下文容器创建完毕之后才会加载,因为容器都没有怎么存放。下图就展示了在创建完毕之后的上下文中Bean的初始化数量。
图: 创建完毕上下文容器
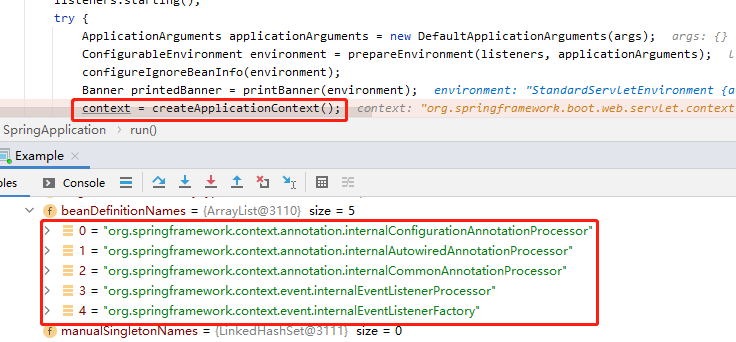
图中所展示的几个Bean是SpringBoot内置的处理器,在SpringBoot启动过程的分析-创建应用程序上下文一文中已经介绍过此处不再次解读。在创建完毕上下文之后有两个重要操作:预处理上下文、刷新上下文。那么初始化类必然就在这两个步骤中间了。首先在刷新上下文处打断点,看看在预处理上下文时是否初始化了其他的Bean。
图:预处理上下文完毕
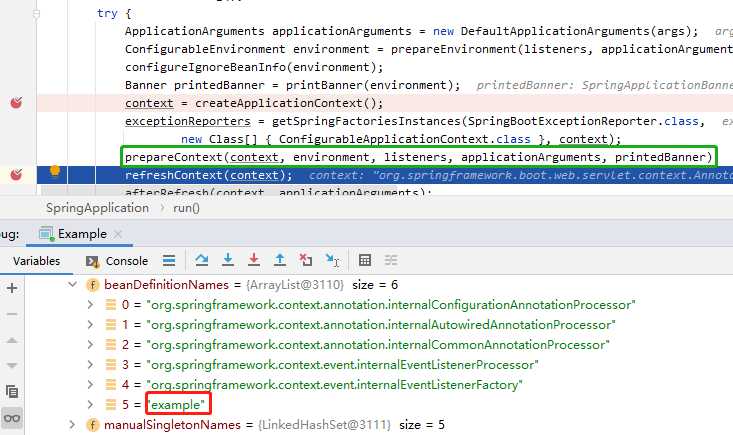
此处可以发现它多了一个"Example"的类,单并未出现其他新的类,Example类是笔者调试程序的入口,在前面文章中也已经介绍过。因此可以断定,其他的类肯定在刷新上下文容器的时候被加载。快速确定方法就是在刷新上下文容器下方打断点,查看beanDefinitionNames的内容变化。在确定了是刷新容器时加载所有类之后,进入刷新容器的代码,可以看到它也清晰的划分了多个步骤,和上面一样,以每个方法为界,观察bean的加载情况。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
//...省略部分代码
}
}
笔者在经过调试之后确定了会在invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);这个方法内部加载所有的类。至此就确定了Bean的实际加载点。
通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor加载所有的类
提示:
下文中所提到的"BeanFactoryPostProcessor",均表示类型为BeanFactoryPostProcessor的接口统称,包括了它的扩展接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor以及他们的实现类。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法是加载并调用所有的BeanFactoryProcessor,我们在前面的文章中已经详细介绍了它的执行流程和业务细节,不明白的同学可以再去回顾一下SpringBoot启动过程的分析-刷新ApplicationContext。这里再重申一下有关于BeanFactoryPostProcessor的相关概念。加强了这些概念,后续对其他代码的理解也会更容易。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor,是Spring内部诸多PostProcessor中的一种,注意它的前缀名称为BeanFactory,Bean工厂意味着它可以创建Bean,根据它的注释描述可以得知它可以修改Bean的定义,也可以修改Bean的属性值,但是它只能用于处理BeanDefinition,而不能处理Bean的实例。简单说就是,它可以在类实例化之前去修改它。另外一个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor它继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,对其进行了扩展,主要用于修改上下文中的Bean定义,加载所有常规的Bean,添加Bean。简单点理解就是它要比BeanFactoryPostProcessor更先执行。主要用于注册Bean。
在调用AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法的时候需要注意它传入的BeanFactoryPostProcessor参数,具体可以看代码:
// AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// ①
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// ...省略部分代码
}
public List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() {
return this.beanFactoryPostProcessors;
}
① - 这里需要注意传入的参数,它由getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法提供,而这个方法返回的是AbstractApplicationContext.beanFactoryPostProcessor这个属性值。这个属性内部所定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor都是在ApplicationContextInitializer的扩展中添加进来的,而创建上下文容器时添加的内部的处理器则存放在DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanDefinitionNames这个属性中。所以在处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor的时候首先处理的是ApplicationContextInitializer中的内容。
通过两处不同的BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以反推出BeanFactoryPostProcessor初始化的两种方式:
- 通过ConfigurableApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor)来添加
- 通过BeanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)来注册一个Bean
本文的重点是分析Bean加载,此处对于BeanFactoryPostProcessor的植入涉及到另外一个课题:Spring框架的扩展点。对扩展点的分析此处先占位,有兴趣可以查看SpringFramework的扩展点
实际上对于Bean加载不光包括我们自己编写的业务代码,也包括SpringBoot自己的其他组件。因为BeanFactoryPostProcessor本身也是一个类。他们在ApplicationContextInitializer接口中被添加,或是在BeanDefinitionRegistry中被注册。区别就是一个是直接添加实例,一个是注册BeanDefinition。言归正传回到Bean的加载中来;此处对于通过ApplicationContextInitializer接口中被添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor不作分析,因为代码比较简洁,他们本身也没涉及过多的操作,感兴趣的可以自己debug。这里重点分析通过BeanDefinitionRegistry注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor即DefaultListableBeanFactory.beanDefinitionNames这个属性中注册的类。内置的BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在容器创建的时候加入的,可参考之前的分析注册内定的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.DefaultEventListenerFactory
org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
经过查看这些内置的类,只有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor和类加载相关。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
主要用于对@Configuration注解进行处理。在SpringBoot应用中,往往都是从一个Main函数开始,启动类上面也必须使用@SpringBootApplication注解来标明它的身份;因此@Configuration注解也代表着应用的起点;因在BeanFactoryPostProcessor被调用的时候是按照优先级来的,首先被调用的是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,所以首先执行postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)方法。
// ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.java
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// ①
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
// ②
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
// ③
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
// ④
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
① - 获取注册ID
② - 判断当前Processor是否被执行过
③ - 添加到已处理列表
④ - 处理配置相关的BeanDefinition
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取所有已注册的BeanDefinition,寻找具有@Configuration注解的类
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
// 遍历所有的beanName
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
// 根据名称找到BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 判断当前类是Full模式还是Lite模式,就为了打印个日志?No,查看日志内容,打印的是:当前类已经被当做一个configuration类被处理过。
// 那就意味着默认情况下它是没有设置ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE 这个属性的。
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
}
}
// 判断当前处理的类是不是完整的配置类,也就是是否被@Configuration注解修饰,若被修饰则会给当前的BeanDefinition设置一个attribute(org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.configurationClass = full)
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
// 加入配置候选列表
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// 若没有被@Configuration注解的类,直接返回
// Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found
if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 根据优先级排序
// Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable
configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> {
int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition());
int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition());
return Integer.compare(i1, i2);
});
// 设置BeanNameGenerator用于生成稍后检测到的Bean的名称
// Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context
SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null;
if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) {
sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry;
if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {
BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR);
if (generator != null) {
this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator;
this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator;
}
}
}
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = new StandardEnvironment();
}
// 新建一个配置类解析器,用于解析所有@Configuration注解的类
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
// 将要被解析的配置类
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
// 已经被解析的配置类
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
// ① 开始解析配置类
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
// ② 获取解析到的配置类
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
// ③ 构建Reader对象,为加载Bean做准备 Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
// ④ 从配置类开始加载Bean
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
candidates.clear();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
// Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes
if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) {
sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) {
// Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op
// for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext.
((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache();
}
}
根据上面的void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)方法中的do-while循环可以看到,它内部是按照解析@Configuration->取出@Configuration->构建BeanDefinitionReader->从@Configuration读取BeanDefinition的流程来完成类的加载。
开始解析@Configuration类
@Configuration注解是Spring中基于Java配置容器中的一个注解,属于类级别的注解,它主要用于标明一组@Bean定义的来源。通常@Configuration和@Bean同时使用。
// ConfigurationClassParser.java
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
// 遍历所有具有@Configuration注解的类
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
// 解析AnnotatedBeanDefinition类型的配置类(可以获取类的注解元数据)
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);
}
}
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
// 包装为ConfigurationClass对象
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName));
}
// 判断是否已经执行过
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass);
if (existingClass != null) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
if (existingClass.isImported()) {
existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass);
}
// Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it.
return;
}
else {
// Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import.
// Let's remove the old one and go with the new one.
this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass);
this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals);
}
}
// 包装为SourceClass便于统一处理
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass);
do {
// 这里才开始处理配置类
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
// 真正开始处理配置的方法
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass)
throws IOException {
// 优先处理@Component注解
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) {
// 递归处理
// Recursively process any member (nested) classes first
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass);
}
// 处理@PropertySource注解
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
// 处理@ComponentScan注解
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
// 处理@Import注解
// Process any @Import annotations
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
// 处理@ImportResource注解
// Process any @ImportResource annotations
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
// 处理单个@Bean方法
// Process individual @Bean methods
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// 处理接口默认方法
// Process default methods on interfaces
processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass);
// 处理父类的方法
// Process superclass, if any
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
// No superclass -> processing is complete
return null;
}
@Configuration配置类同时也和其他注解有关联,这里说的关联是其他注解的行为会影响配置类本身的状态。例如方法中提到的@Component、@ComponentScan、@PropertySource、@Import、@Bean、@ImportResource。
处理@Component注解
@Component注解表示被修饰的类将会被识别为受Spring管理的类。将会被注册到Bean容器中。
private void processMemberClasses(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException {
// 获取成员类
Collection<SourceClass> memberClasses = sourceClass.getMemberClasses();
if (!memberClasses.isEmpty()) {
List<SourceClass> candidates = new ArrayList<>(memberClasses.size());
for (SourceClass memberClass : memberClasses) {
// 判断是否有@Configuration或者@Component注解
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate(memberClass.getMetadata()) && !memberClass.getMetadata().getC
lassName().equals(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName())) {
candidates.add(memberClass);
}
}
// 排序
OrderComparator.sort(candidates);
// 检测是否有循环导入(@Import)的问题
for (SourceClass candidate : candidates) {
if (this.importStack.contains(configClass)) {
this.problemReporter.error(new CircularImportProblem(configClass, this.importStack));
}
else {
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
// 递归调用处理
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass));
}
finally {
this.importStack.pop();
}
}
}
}
}
在该方法中,主要用于处理当前传入的configClass内部的嵌套类、成员类中是否有@Configuration、@Component注解。一般来说@Configuratio
n都是单独使用的一个类。
处理@PropertySource注解
@PropertySource注解用于加载指定的properties配置文件到Spring的Environment中
// 内部实现比较简单,自行debug即可
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class, org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) {
// 判断当前环境对象是否是可配置的
if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
处理@ComponentScan注解
@ComponentScan注解用于指明当前应用将扫描哪些包下的具有@Component注解的类。这个注解必须添加到@Configuration类中
// 根据ComponentScans配置的包路径查找带@Component注解的类
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() && !this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
// 获取所有带@Component注解的类
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
这里重点分析它是如何查找@ComponentScans注解的,跳过无用的调用链,查看真正开始查找的方法。
// AnnotationConfigUtils.java
// 需要注意的是参数:metadata代表从哪里获取,containerClassName表示包含注解(例如@ComponentScans,它本身的值可以包含多个@ComponentScan),annotationClassName是当前要获取的目标注解也就是@ComponentScan
static Set<AnnotationAttributes> attributesForRepeatable(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String containerClassName, String annotationClassName) {
Set<AnnotationAttributes> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// ①
// Direct annotation present?
addAttributesIfNotNull(result, metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(annotationClassName, false));
// ②
// Container annotation present?
Map<String, Object> container = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(containerClassName, false);
if (container != null && container.containsKey("value")) {
for (Map<String, Object> containedAttributes : (Map<String, Object>[]) container.get("value")) {
addAttributesIfNotNull(result, containedAttributes);
}
}
// Return merged result
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(result);
}
提示:
在这个方法内部分了两个操作,第一个是直接获取@ComponentScan这个注解,第二个是获取@ComponentScans注解。这两者是有区别的。
① - 此处为@ComponentScan,称之为直接注解”,即在类上面直接声明的注解。
// StandardAnnotationMetadata.class
public Map<String, Object> getAnnotationAttributes(String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString) {
return (this.annotations.length > 0 ? AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(getIntrospectedClass(), annotationName, classValuesAsString, this.nestedAnnotationsAsMap) : null);
}
// AnnotatedElementUtils.class
public static AnnotationAttributes getMergedAnnotationAttributes(AnnotatedElement element,
String annotationName, boolean classValuesAsString, boolean nestedAnnotationsAsMap) {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = searchWithGetSemantics(element, null, annotationName, new MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor(classValuesAsString, nestedAnnotationsAsMap));
AnnotationUtils.postProcessAnnotationAttributes(element, attributes, classValuesAsString, nestedAnnotationsAsMap);
return attributes;
}
// 通过一系列的重载方法,最终调用此方法
private static <T> T searchWithGetSemantics(AnnotatedElement element,
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> annotationTypes, @Nullable String annotationName,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> containerType, Processor<T> processor,
Set<AnnotatedElement> visited, int metaDepth) {
if (visited.add(element)) {
try {
// Start searching within locally declared annotations
// 获取当前元素声明的所有注解
List<Annotation> declaredAnnotations = Arrays.asList(AnnotationUtils.getDeclaredAnnotations(element));
// 获取这些注解中指定的类型
T result = searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations(element, declaredAnnotations, annotationTypes, annotationName, containerType, processor, visited, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
if (element instanceof Class) { // otherwise getAnnotations doesn't return anything new
Class<?> superclass = ((Class<?>) element).getSuperclass();
if (superclass != null && superclass != Object.class) {
List<Annotation> inheritedAnnotations = new LinkedList<>();
for (Annotation annotation : element.getAnnotations()) {
if (!declaredAnnotations.contains(annotation)) {
inheritedAnnotations.add(annotation);
}
}
// Continue searching within inherited annotations
result = searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations(element, inheritedAnnotations,
annotationTypes, annotationName, containerType, processor, visited, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
AnnotationUtils.handleIntrospectionFailure(element, ex);
}
}
return null;
}
private static <T> T searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations(@Nullable AnnotatedElement element,
List<Annotation> annotations, Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> annotationTypes,
@Nullable String annotationName, @Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> containerType,
Processor<T> processor, Set<AnnotatedElement> visited, int metaDepth) {
// 遍历所有注解
// Search in annotations
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
// 获取当前注解类型
Class<? extends Annotation> currentAnnotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (!AnnotationUtils.isInJavaLangAnnotationPackage(currentAnnotationType)) {
// 判断是否处理过、当前注解的名称是否和将要查找的一致、是否默认处理(默认为true,请debug的时候注意传入的参数)
if (annotationTypes.contains(currentAnnotationType) || currentAnnotationType.getName().equals(annotationName) || processor.alwaysProcesses()) {
// 若匹配,则查找内部的注解属性
T result = processor.process(element, annotation, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
if (processor.aggregates() && metaDepth == 0) {
processor.getAggregatedResults().add(result);
}
else {
return result;
}
}
}
// 如果没有找到
// Repeatable annotations in container?
else if (currentAnnotationType == containerType) {
for (Annotation contained : getRawAnnotationsFromContainer(element, annotation)) {
T result = processor.process(element, contained, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
// No need to post-process since repeatable annotations within a
// container cannot be composed annotations.
processor.getAggregatedResults().add(result);
}
}
}
}
}
// Recursively search in meta-annotations
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<? extends Annotation> currentAnnotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (!AnnotationUtils.hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly(currentAnnotationType)) {
T result = searchWithGetSemantics(currentAnnotationType, annotationTypes, annotationName, containerType, processor, visited, metaDepth + 1);
if (result != null) {
processor.postProcess(element, annotation, result);
if (processor.aggregates() && metaDepth == 0) {
processor.getAggregatedResults().add(result);
}
else {
return result;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
// AnnotatedElementUtils.class内部类AnnotatedElementUtils.class
public AnnotationAttributes process(@Nullable AnnotatedElement annotatedElement, Annotation annotation, int metaDepth) {
return AnnotationUtils.retrieveAnnotationAttributes(annotatedElement, annotation, this.classValuesAsString, this.nestedAnnotationsAsMap);
}
// AnnotationUtils.class
static AnnotationAttributes retrieveAnnotationAttributes(@Nullable Object annotatedElement,
Annotation annotation, boolean classValuesAsString, boolean nestedAnnotationsAsMap) {
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
AnnotationAttributes attributes = new AnnotationAttributes(annotationType);
// 遍历注解的方法,获取属性名称和属性值,填充至AnnotationAttributes对象内部(实际上就是个Map)
for (Method method : getAttributeMethods(annotationType)) {
try {
Object attributeValue = method.invoke(annotation);
Object defaultValue = method.getDefaultValue();
if (defaultValue != null && ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, defaultValue)) {
attributeValue = new DefaultValueHolder(defaultValue);
}
attributes.put(method.getName(), adaptValue(annotatedElement, attributeValue, classValuesAsString, nestedAnnotationsAsMap));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof InvocationTargetException) {
Throwable targetException = ((InvocationTargetException) ex).getTargetException();
rethrowAnnotationConfigurationException(targetException);
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not obtain annotation attribute value for " + method, ex);
}
}
return attributes;
}
② - 此处为@ComponentScans,称之为”容器注解”,它可以包含多个@ComponentScan,代码逻辑和获取直接注解@ComponentScan并没有太大差异,可自行debug
看到这里可以得出一个结论:有3种使用注解定义包扫描路径的方法
- @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.example")
- @ComponentScan(value = {"com.example"})
- @ComponentScans({@ComponentScan("com.abcd"), @ComponentScan("com.efgh")})
注意:其中1和2是可以同时存在,1和3可以同时存在,2和3不可以同时存在
1、2同时存在只取2的值
1、3同时存在取1、3的值
处理到这一步,仅仅是获取到了所有的@ComponentScan注解,接下来还需要解析注解里面配置的包路径
// ConfigurationClassParser.class 284行
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// 解析当前注解配置的包路径下的类
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions = this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// 检查返回的BeanDefinition里面是否有其他的配置类,如果需要的话会递归进行解析
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
// 若是配置类,执行配置类的解析操作
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
// 以下代码为获取BeanDefinition的具体流程
// ComponentScanAnnotationParser.class
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> parse(AnnotationAttributes componentScan, final String declaringClass) {
// 构建扫描器
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this.registry, componentScan.getBoolean("useDefaultFilters"), this.environment, this.resourceLoader);
// 构建类名生成器
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> generatorClass = componentScan.getClass("nameGenerator");
boolean useInheritedGenerator = (BeanNameGenerator.class == generatorClass);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(useInheritedGenerator ? this.beanNameGenerator : BeanUtils.instantiateClass(generatorClass));
// 获取类的作用域模型
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = componentScan.getEnum("scopedProxy");
if (scopedProxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
scanner.setScopedProxyMode(scopedProxyMode);
}
else {
Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> resolverClass = componentScan.getClass("scopeResolver");
scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(resolverClass));
}
// 获取资源模式(注解配置扫描包都是扫描class因此此处为:**/*.class)
scanner.setResourcePattern(componentScan.getString("resourcePattern"));
// 获取@ComponentScan注解里面配置的include过滤器
for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("includeFilters")) {
for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
// 获取@ComponentScan注解里面配置的exclude过滤器
for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("excludeFilters")) {
for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) {
scanner.addExcludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
// 获取@ComponentScan注解里面配置的lazyInit值
boolean lazyInit = componentScan.getBoolean("lazyInit");
if (lazyInit) {
scanner.getBeanDefinitionDefaults().setLazyInit(true);
}
// 获取需要扫描的路径集合
Set<String> basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>();
String[] basePackagesArray = componentScan.getStringArray("basePackages");
for (String pkg : basePackagesArray) {
String[] tokenized = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(pkg), ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
Collections.addAll(basePackages, tokenized);
}
for (Class<?> clazz : componentScan.getClassArray("basePackageClasses")) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
}
if (basePackages.isEmpty()) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(declaringClass));
}
scanner.addExcludeFilter(new AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter(false, false) {
@Override
protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
return declaringClass.equals(className);
}
});
// 通过扫描器扫描指定路径下的具有@Component注解的类
return scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages));
}
// ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.class
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
// 查找所有@Component注解标识的类
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
// 获取作用域元数据
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
// 生成类名
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
// 对普通的Bean 进行处理
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
// 对包含有注解的Bean进行处理,比如@Lazy、@Primary
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
// 检查当前加载的Bean名称是否有冲突
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
// ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
if (this.componentsIndex != null && indexSupportsIncludeFilters()) {
return addCandidateComponentsFromIndex(this.componentsIndex, basePackage);
}
else {
// 真正开始搜索类的方法
return scanCandidateComponents(basePackage);
}
}
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
// 获取资源的路径
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
// 获取所有资源
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 为每一个类生成BeanDefinition对象
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
// 判断是否具有@Component注解
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
至此,通过@ComponentScan注解配置扫描指定的包,到获取到具体的带有@Component注解的类已经全部获取完毕。
处理@Import注解
@Import注解主要用于引入另外一个@Configuration。和Spring XML配置文件中的标签功能一样。
// ConfigurationClassParser.class 302行
// 处理@Import注解,请注意参数内部的getImports方法
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true);
private Set<SourceClass> getImports(SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException {
Set<SourceClass> imports = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Set<SourceClass> visited = new LinkedHashSet<>();
collectImports(sourceClass, imports, visited);
return imports;
}
// 递归获取@Import注解
private void collectImports(SourceClass sourceClass, Set<SourceClass> imports, Set<SourceClass> visited) throws IOException {
// 添加已处理的避免无限递归
if (visited.add(sourceClass)) {
// 获取传入资源上的注解列表
for (SourceClass annotation : sourceClass.getAnnotations()) {
// 获取注解名称
String annName = annotation.getMetadata().getClassName();
// 若当前注解不是@Import则递归查找
if (!annName.equals(Import.class.getName())) {
collectImports(annotation, imports, visited);
}
}
// 添加已经获取的所有注解
imports.addAll(sourceClass.getAnnotationAttributes(Import.class.getName(), "value"));
}
}
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass, Collection<SourceClass> importCandidates, boolean checkForCircularImports) {
if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (checkForCircularImports && isChainedImportOnStack(configClass)) {
this.problemReporter.error(new CircularImportProblem(configClass, this.importStack));
}
else {
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
// 是否是ImportSelector的实现
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportSelector selector = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(selector, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection<SourceClass> importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames);
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, false);
}
}
// 是否是ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的实现
else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// delegate to it to register additional bean definitions
Class<?> candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar registrar = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class);
ParserStrategyUtils.invokeAwareMethods(registrar, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
}
// 都不是的话把它当做@Configuration来处理
else {
// Candidate class not an ImportSelector or ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// process it as an @Configuration class
this.importStack.registerImport(currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());
// 将其作为@Configuration处理
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass));
}
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" +
configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex);
}
finally {
this.importStack.pop();
}
}
}
processImports() 方法用于处理解析到的Import的类,分为3种类型"ImportSelector"的实现、"ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar"的实现、"本身也是一个@Configuration"的实现。
ImporSelector的实现:
主要用于导入@Configuration配置类,并且可以实现EnvironmentAware、BeanFactoryAware、BeanClassLoaderAware、ResourceLoaderAware接口,并在调用ImportSelector.selectImports方法之前调用它们。
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的实现:
用于导入导入@Configuration配置了,并可以注册BeanDefinition
@Configuration:
如果导入的是一个配置,则进入配置解析功能
处理@ImportResource注解
用于引入Spring xml配置文件,类似于Spring XML中的标签,默认使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader来解析XML中的标签。
例如:
@Configuration
@ImportResource("classpath:/com/acme/properties-config.xml")
public class AppConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
return new DriverManagerDataSource(url, username, password);
}
}
源码解析:
AnnotationAttributes importResource = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class);
if (importResource != null) {
// ①
String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations");
// ②
Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader");
for (String resource : resources) {
// ③
String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource);
// ④
configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass);
}
}
① - 获取@ImportResource注解的value值
② - 获取BeanDefinitionReader
③ - 处理资源路径下的占位符
④ - 将资源和对应的解析器存放至当前配置类的importedResources属性中,它是一个LinkedHashMap
处理@Bean注解
此处处理的是在配置类中具有@Bean注解的方法
// ①
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
// ②
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
// ④
private void processInterfaces(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException {
for (SourceClass ifc : sourceClass.getInterfaces()) {
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(ifc);
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
if (!methodMetadata.isAbstract()) {
// A default method or other concrete method on a Java 8+ interface...
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
}
processInterfaces(configClass, ifc);
}
}
// ⑤
if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) {
String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName();
if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") &&
!this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) {
this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass);
// Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse
return sourceClass.getSuperClass();
}
}
① - 获取所有具有@Bean注解的方法
② - 将获取到的方法包装为BeanMethod对象(表示一个具有@Bean注解的@Configuration类的方法)保存到当前配置类的beanMethods属性中
④ - 处理接口中具有@Bean注解的方法
⑤ - 处理父类中具有@Bean注解的方法
取出@Configuration
直接从Parser中取出之前解析时缓存的配置类,因为这段代码在do-while循环中,因此首先移除已处理的。
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed);
构建BeanDefinitionReader
若Reader为空,则创建,用于读取配置中的BeanDefinition
if (this.reader == null) {
this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader(
registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment,
this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry());
}
@Configuration读取BeanDefinition
前面对各种注解的的解析最终并没有处理解析的结果,而是将其放在了ConfigurationClass对象的属性当中存储,在这里将通过Reader来处理这
些不同来源的BeanDefinition。
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Set<ConfigurationClass> configurationModel) {
TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator = new TrackedConditionEvaluator();
// ①
for (ConfigurationClass configClass : configurationModel) {
// ②
loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(configClass, trackedConditionEvaluator);
}
}
① - 遍历所有的@Configuration
② - 从@Configuration读取BeanDefinition
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) {
// ①
if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) {
String beanName = configClass.getBeanName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
this.registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
this.importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
return;
}
// ②
if (configClass.isImported()) {
registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass);
}
// ③
for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);
}
// ④
loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources());
// ⑤
loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars());
}
① - 是否需要跳过
② - 当前配置类本身是否通过@Import导入,若有则将自身注册为BeanDefinition
③ - 当前配置类中是否有@Bean注解修饰的方法,若有则处理
④ - 加载从@ImportResource导入的XML文件中定义的Bean
⑤ - 加载从@Import导入的BeanDefinition
合并已处理的BeanDefinition
// ①
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) {
// ②
String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
// ③
Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames));
// ④
Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>();
// ⑤
for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) {
alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
}
// ⑥
for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) {
// ⑦
if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) {
// ⑧
BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) &&
!alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName));
}
}
}
// ⑨
candidateNames = newCandidateNames;
}
① - candidateNames 在方法的一开始就从registry中获取已经处理过的BeanDefinition名称
② - newCandidateNames 表示本次从配置类的解析中加载完毕BeanDefinition之后的BeanDefinition名称列表,它包含第一步里面的名称
③ - 将第一步的名称列表转换为Set集合
④ - 声明已解析的集合,此处用Set因为它可以保证元素不重复
⑤ - 遍历本次已经处理的所有类集合,将其加入第四步声明的Set集合内
⑥ - 遍历registry中现有的列表
⑦ - 当前的BeanDefinition必须是本次代码执行时加入的才进行处理
⑧ - 获取当前处理的类,判断是否为Configuration,并设置FULL模式和LITE模式
⑨ - 获取全部已经处理的类赋值给candidateNames
总结
SpringBoot中对于框架外的类加载从容器刷新阶段中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)方法开始。用于调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor,位于org.springframework.context.annotation包下的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class实现了这个接口。
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类并未直接实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor,而是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor。所以需要搞清楚他们各自方法的执行顺序。
在加载BeanDefinition之前,先获取所有的@Configuration,按照它的优先级排序。接着循环解析这些配置类,在解析的过程中又根据不同的注解来加载不同的内容。从而完成整个应用内部的BeanDefinition获取。
【SpringBoot源码分析】-Bean的加载过程的更多相关文章
- 从SpringBoot源码分析 配置文件的加载原理和优先级
本文从SpringBoot源码分析 配置文件的加载原理和配置文件的优先级 跟入源码之前,先提一个问题: SpringBoot 既可以加载指定目录下的配置文件获取配置项,也可以通过启动参数( ...
- Dubbo源码分析之ExtensionLoader加载过程解析
ExtensionLoader加载机制阅读: Dubbo的类加载机制是模仿jdk的spi加载机制: Jdk的SPI扩展加载机制:约定是当服务的提供者每增加一个接口的实现类时,需要在jar包的META ...
- 【MyBatis源码分析】Configuration加载(下篇)
元素设置 继续MyBatis的Configuration加载源码分析: private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { Properties s ...
- Android 7.0 Gallery图库源码分析3 - 数据加载及显示流程
前面分析Gallery启动流程时,说了传给DataManager的data的key是AlbumSetPage.KEY_MEDIA_PATH,value值,是”/combo/{/local/all,/p ...
- Tomcat8源码笔记(三)Catalina加载过程
之前介绍过 Catalina加载过程是Bootstrap的load调用的 Tomcat8源码笔记(二)Bootstrap启动 按照Catalina的load过程,大致如下: 接下来一步步分析加载过程 ...
- 【Spring源码分析系列】加载Bean
/** * Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream, * which must be parsable using DOM. * ...
- 【MyBatis源码分析】Configuration加载(上篇)
config.xml解析为org.w3c.dom.Document 本文首先来简单看一下MyBatis中将config.xml解析为org.w3c.dom.Document的流程,代码为上文的这部分: ...
- ZuulServlet源码分析及ZuulFilter加载
参考https://yq.aliyun.com/wenji/2...https://blog.csdn.net/lds2227... 1.声明ZuulServlet @Configuration @E ...
- [ipsec][strongswan] strongswan源码分析--(四)plugin加载优先级原理
前言 如前所述, 我们知道,strongswan以插件功能来提供各种各样的功能.插件之间彼此相互提供功能,同时也有可能提供重复的功能. 这个时候,便需要一个优先级关系,来保证先后加载顺序. 方法 在配 ...
- ViewPager部分源码分析一:加载数据
onMeasure()调用populate(),完成首次数据初始化. populate()维护ViewPager的page,包括mItems和mAdapter. populate(): if (cur ...
随机推荐
- Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
接口简介 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口是 Spring 初始化 BeanFactory 时对外暴露的扩展点,Spring IoC 容器允许 BeanFactoryPostPr ...
- oracle 查看 FK constraint referenced_table及columns
select uc.table_name, uc.r_constraint_name, ucc.table_name, listagg(ucc.column_name, ',') within gro ...
- Java开发不懂Docker,学尽Java也枉然,阿里P8架构师手把手带你玩转Docker实战
转: Java开发不懂Docker,学尽Java也枉然,阿里P8架构师手把手带你玩转Docker实战 Docker简介 Docker 是一个开源的应用容器引擎,让开发者可以打包他们的应用以及依赖包到一 ...
- 【Arduino学习笔记03】面包板基础知识
终端带 这里有一块面包板,它后面的黏贴纸被撕去了.你可以看到很多在底部的平行金属条. 金属条的结构:金属条的顶部有一个小夹子.这些夹子能将一条导线或某个部件的引脚固定在塑料洞上,使它们放置在适当的位置 ...
- python中函数与方法的区别
在python中,其实函数和方法的区别取决于其调用者,在普通的函数定义中就叫做函数 例如: def func(): print('这是一个函数') 而在一个类中定义时,就将其分为两种情况 第一种:被称 ...
- 爬虫必知必会(6)_提升scrapy框架爬取数据的效率之配置篇
如何提升scrapy爬取数据的效率:只需要将如下五个步骤配置在配置文件中即可 增加并发:默认scrapy开启的并发线程为32个,可以适当进行增加.在settings配置文件中修改CONCURRENT_ ...
- (数据科学学习手札112)Python+Dash快速web应用开发——表单控件篇(上)
本文示例代码已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 1 简介 这是我的系列教程Python+Dash快速web ...
- CRC校验原理和verilog实现方法(一)
1.CRC简介 CRC全称循环冗余校验(Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC),是通信领域数据传输技术中常用的检错方法,用于保证数据传输的可靠性.网上有关这方面的博客和资料很多,本 ...
- 【linux】驱动-2-内核模块
目录 前言 2. 内核模块 2.1 内核模块概念 2.1.1 内核 2.1.2 内核模块机制的引入 2.2 内核模块 2.2.1 内核模块参考例程 2.2.2 内核模块命令 2.2.3 系统自动加载模 ...
- 学习笔记-git 上传
0.git add * (如果你需要修改源码需要在 1 之前使用,然后再回到 1) 1.git commit -m '提交文字描述' 2.git push -u origin master (上传到主 ...
