Spring(四)Spring JdbcTemplate&声明式事务
JdbcTemplate基本使用
01-JdbcTemplate基本使用-概述(了解)
JdbcTemplate是spring框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始繁琐的Jdbc API对象的简单封装。spring框架为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。例如:操作关系型数据的JdbcTemplate和HibernateTemplate,操作nosql数据库的RedisTemplate,操作消息队列的JmsTemplate等等。
02-JdbcTemplate基本使用-开发步骤(理解)
①导入spring-jdbc和spring-tx坐标
tx是事务也需要导入
②创建数据库表和实体
③创建JdbcTemplate对象
④执行数据库操作
03-JdbcTemplate基本使用-快速入门代码实现(应用)
导入spring-jdbc和spring-tx坐标
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>itheima_spring_jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>itheima_spring_jdbc Maven Webapp</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.32</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>创建数据库表和实体
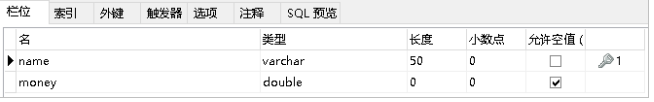
package com.itheima.domain;
public class Account {
private String name;
private double money;
public String getNa me() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}创建JdbcTemplate对象
执行数据库操作
package com.itheima.test;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
@Test
//测试JdbcTemplate开发步骤
public void test1() throws PropertyVetoException {
//创建数据源对象
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setUser("root");
dataSource.setPassword("123456");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//设置数据源对象 知道数据库在哪
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
//执行操作
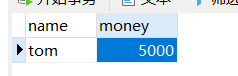
int row = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(?,?)", "tom", 5000);
System.out.println(row);
}
}

04-JdbcTemplate基本使用-spring产生模板对象分析(理解)
我们可以将JdbcTemplate的创建权交给Spring,将数据源DataSource的创建权也交给Spring,在Spring容器内部将数据源DataSource注入到JdbcTemplate模版对象中,然后通过Spring容器获得JdbcTemplate对象来执行操作
05-JdbcTemplate基本使用-spring产生模板对象代码实现(应用)
配置如下:
<!--数据源对象-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!--jdbc模板对象-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>测试代码
@Test
//测试Spring产生jdbcTemplate对象
public void test2() throws PropertyVetoException {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = app.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
int row = jdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(?,?)", "lisi", 5000);
System.out.println(row);
}06-JdbcTemplate基本使用-spring产生模板对象代码实现(抽取jdbc.properties)(应用)
将数据库的连接信息抽取到外部配置文件中,和spring的配置文件分离开,有利于后期维护
properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456配置文件修改为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--加载jdbc.properties-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--数据源对象-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--jdbc模板对象-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>07-JdbcTemplate基本使用-常用操作-更新操作(应用)
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JdbcTemplateCRUDTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//修改更新
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=? where name=?",10000,"tom");
}
//删除
@Test
public void testDelete(){
jdbcTemplate.update("delete from account where name=?","tom");
}
}08-JdbcTemplate基本使用-常用操作-查询操作(应用)
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Account;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JdbcTemplateCRUDTest {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//聚合查询
@Test
public void testQueryCount(){
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from account", Long.class);
System.out.println(count);
}
//查询一个
@Test
public void testQueryOne(){
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from account where name=?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), "tom");
System.out.println(account);
}
//查询所有
@Test
public void testQueryAll(){
List<Account> accountList = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class));
System.out.println(accountList);
}
}09-JdbcTemplate基本使用-知识要点(理解,记忆)
①导入spring-jdbc和spring-tx坐标
②创建数据库表和实体
③创建JdbcTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = newJdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);④执行数据库操作
//更新操作:
jdbcTemplate.update (sql,params)
//查询操作:
jdbcTemplate.query (sql,Mapper,params)
jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Mapper,params)声明式事务控制
1. 编程式事务控制相关对象(基础)
1.1 PlatformTransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager 接口是 spring 的事务管理器,它里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法。
注意:
PlatformTransactionManager 是接口类型,不同的 Dao 层技术则有不同的实现类,例如:Dao 层技术是jdbc 或 mybatis 时:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager实现类
Dao 层技术是hibernate时:org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager
1.2 TransactionDefinition
TransactionDefinition 是事务的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法:

1. 事务隔离级别
设置隔离级别,可以解决事务并发产生的问题,如脏读、不可重复读和虚读(幻读)。
ISOLATION_DEFAULT 默认
ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED 不能解决
ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED 解决脏读
ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ 解决不可重复读
ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE 都可以,但性能低
2. 事务传播行为
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常
REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作
超时时间:默认值是-1,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置
是否只读:建议查询时设置为只读
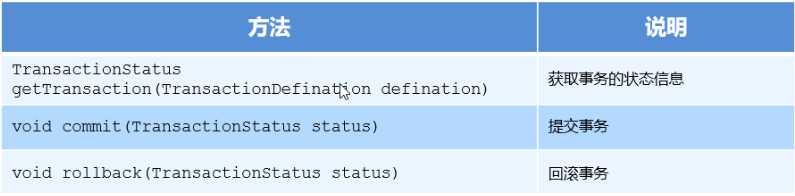
1.3 TransactionStatus
TransactionStatus 接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态,方法介绍如下。

1.4 知识要点
TransactionStatus=PlatformTransactionManager + TransactionDefinition
编程式事务控制三大对象
PlatformTransactionManager
TransactionDefinition
TransactionStatus
2 基于 XML 的声明式事务控制
2.1 什么是声明式事务控制
Spring 的声明式事务顾名思义就是采用声明的方式来处理事务。这里所说的声明,就是指在配置文件中声明,用在 Spring 配置文件中声明式的处理事务来代替代码式的处理事务。
声明式事务处理的作用
事务管理不侵入开发的组件。具体来说,业务逻辑对象就不会意识到正在事务管理之中,事实上也应该如此,因为事务管理是属于系统层面的服务,而不是业务逻辑的一部分,如果想要改变事务管理策划的话,也只需要在定义文件中重新配置即可
在不需要事务管理的时候,只要在设定文件上修改一下,即可移去事务管理服务,无需改变代码重新编译,这样维护起来极其方便
注意:Spring 声明式事务控制底层就是AOP。
2.2 声明式事务控制的实现
声明式事务控制明确事项:
谁是切点?业务方法
谁是通知?增强,就是事务通知
配置切面?AOP配置
①引入tx命名空间
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
②配置事务增强
③配置事务 AOP 织入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
">
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"/>
</bean>
<!--目标对象 内部的方法就是切点-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
</bean>
<!--配置平台事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--通知 事务的增强-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--设置事务的属性信息的-->
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="save" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="findAll" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置事务的aop织入-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointcut" expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
④测试事务控制转账业务代码
@Override
public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) {
accountDao.out(outMan,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.in(inMan,money);
}2.3 切点方法的事务参数的配置
<!--事务增强配置-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
//设置事务的属性信息
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>其中,tx:method 代表切点方法的事务参数的配置,例如:
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="-1" read-only="false"/>name:切点方法名称
isolation:事务的隔离级别
propogation:事务的传播行为
timeout:超时时间
read-only:是否只读
2.4 知识要点
声明式事务控制的配置要点
平台事务管理器配置
事务通知的配置

事务aop织入的配置


3 基于注解的声明式事务控制
3.1 使用注解配置声明式事务控制
1.编写 AccoutDao
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void out(String outMan, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money-? where name=?",money,outMan);
}
public void in(String inMan, double money) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money=money+? where name=?",money,inMan);
}
}2.编写 AccoutService
@Service("accountService")
@Transactional
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void transfer(String outMan, String inMan, double money) {
accountDao.out(outMan,money);
int i = 1/0;
accountDao.in(inMan,money);
}
}3.编写 applicationContext.xml 配置文件
一定要加上注解驱动
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<!--组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="user" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--事物的注解驱动-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>3.2 注解配置声明式事务控制解析
①使用 @Transactional 在需要进行事务控制的类或是方法上修饰,注解可用的属性同 xml 配置方式,例如隔离级别、传播行为等。
②注解使用在类上,那么该类下的所有方法都使用同一套注解参数配置。
③使用在方法上,不同的方法可以采用不同的事务参数配置。
④Xml配置文件中要开启事务的注解驱动<tx:annotation-driven />
3.3 知识要点
注解声明式事务控制的配置要点
平台事务管理器配置(xml方式)
事务通知的配置(@Transactional注解配置)
事务注解驱动的配置 <tx:annotation-driven/>
Spring(四)Spring JdbcTemplate&声明式事务的更多相关文章
- 八、Spring之深入理解声明式事务
Spring之深入理解声明式事务 何为事务? 事务就是把一系列的动作当成一个独立的工作单元,这些动作要么全部完成,要么全部不起作用. 事务的四个属性: 1.原子性(atomicity) 事务是原子性操 ...
- spring基于xml的声明式事务控制配置步骤
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.sp ...
- spring学习08(声明式事务)
11.声明式事务 11.1 回顾事务 事务在项目开发过程非常重要,涉及到数据的一致性的问题,不容马虎! 事务管理是企业级应用程序开发中必备技术,用来确保数据的完整性和一致性. 事务就是把一系列的动作当 ...
- spring boot中的声明式事务管理及编程式事务管理
这几天在做一个功能,具体的情况是这样的: 项目中原有的几个功能模块中有数据上报的功能,现在需要在这几个功能模块的上报之后生成一条消息记录,然后入库,在写个接口供前台来拉取消息记录. 看到这个需求,首先 ...
- Spring注解驱动开发(四)-----aop、声明式事务
AOP 概念 指在程序运行期间动态的将某段代码切入到指定方法指定位置进行运行的编程方式:-----基于动态代理 一个aop示例 1.导入aop模块:Spring AOP:(spring-aspects ...
- Spring学习笔记:声明式事务管理增删改查业务
一.关于是事务 以方法为单位,进行事务控制:抛出异常,事务回滚. 最小的执行单位为方法.决定执行成败是通过是否抛出异常来判断的,抛出异常即执行失败 二.声明式事务: 声明式事务(declarative ...
- spring基于XML的声明式事务控制
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?><beans xmlns="http://www.sp ...
- spring基于注解的声明式事务控制
package com.hope.service.impl;import com.hope.dao.IAccountDao;import com.hope.domain.Account;import ...
- spring事物配置,声明式事务管理和基于@Transactional注解的使用
http://blog.csdn.net/bao19901210/article/details/41724355 http://www.cnblogs.com/leiOOlei/p/3725911. ...
随机推荐
- Mila Fletcher :其实高度自律的人生并没有那么难养成
在日常生活中,我们经常会发现,不论是学习,考证,工作,都需要坚持付出.但是很多人都没有办法在枯燥的学习过程中持续下去,这通常是因为不够自律导致的.但是尽管大家都知道自律是多么重要,却没有几个人可以真正 ...
- Content type 'application/json;charset=UTF-8' not supported异常的解决过程
首先说一下当时的场景,其实就是一个很简单的添加操作,后台传递的值是json格式的,如下图 ,后台对应的实体类, @Data @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false) ...
- Vue学习笔记-Windows系统Git安装(按装vue-element-admin报错)
一 使用环境: windows 7 64位操作系统 二 Windows系统Git安装(Git是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,可以有效.高速的处理从很小到非常大的项目版本管理,是目前使用范围最广的版 ...
- 解决 DatePickerDialog 在 Android7.0 API24 上使用 AlertDialog.THEME_TRADITIONAL、AlertDialog.THEME_HOLO_DARK、AlertDialog.THEME_HOLO_LIGHT等样式时无法显示为 Spinner 样式的问题
DatePickerDemoForAndroid24 解决 DatePickerDialog 在 Android7.0 API24 上使用AlertDialog.THEME_TRADITIONAL.A ...
- Java练习——String类练习
需求: 给定一个字符串String str=" Hello World",返回长度,返回o第一次出现的索引,返回最后一个o的索引,把所有的l都替换为m,并把字符串str按空格分割为 ...
- Java 集合框架 03
集合框架·HashSet 和 TreeSet HashSet存储字符串并遍历 * A:Set集合概述及特点 * 通过API查看即可 * 无索引,不可以重复,无序 * B:案例演示 * HashSet存 ...
- Java 基础加强 01
基础加强·网络编程 和 GUI 网络编程概述 * A:计算机网络 * 是指将地理位置不同的具有独立功能的多台计算机及外部设备,通过通信连接起来 在网路操作系统,网络管理软件和网络通信协议的管理下,实现 ...
- 如何在 ASP.Net Core 中使用 MiniProfiler
web应用程序的性能相信是大家普遍关心的一个问题,也相信大家有很多工具可用来分析应用程序的性能并能够找到其中的瓶颈,MiniProfiler 就是这个领域中的一款产品,它是一款简单的,功能强大的web ...
- 关于主机不能访问虚拟机的web服务解决
centos7默认并没有开启80端口,我们只有开启就行 [root@localhost sysconfig]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3032/tcp ...
- 选择 FreeBSD 而不是 Linux 的技术性原因3
选择 FreeBSD 而不是 Linux 的技术性原因3 jail FreeBSD Jails 系统是另一个惊人的工程壮举. 在 2000 年 3 月 14 日的 4.0 版本中,FreeBSD 引入 ...
