iOS Mobile Development: Using Xcode Targets to Reuse the Code 使用xcode targets来实现代码复用
In the context of iOS mobile app development, a clone is simply an app that is based off another mobile app. A clone usually has more or less the same code base with probably a slightly different functionality. It’s quite common for this app to have new images, even though most of the UI is the same as the original app.
There are different ways to handle the development of clones. Probably the most common or the one that will first come to mind is using branches.
However, I’m going to talk about a different approach in the form of targets.
1. Targets versus branching
Using branches is not a bad approach by all means. However, there are some serious drawbacks when using them.
Firstly, you may need to go back to your first app to solve bugs the users may have found. Once you’ve fixed those bugs, you will want to merge those fixes in your new branch just to see that you’ll have a bunch of conflicts.
By the time you’ve successfully made the merge, you’ll notice that you’ve spend more time here than doing actual work on the new app.
Fortunately there is a better way that does not require branching. Most IDE’s have some sort of target support (in Android they are called Flavors).
Targets work more like configuration files. You use the same code for all your targets, but each target is configured differently, whether it’s a new app icon or a slight change in logic.
The setup can be tricky but it’s far more powerful than using branches. Let me show you.
2. Adding a new target
We'll be using Xcode 5 for this article and we’ll be using a project that I called MultiTarget.
The first thing you want to do is select the project item in Xcode’s project window which may look a little bit like this: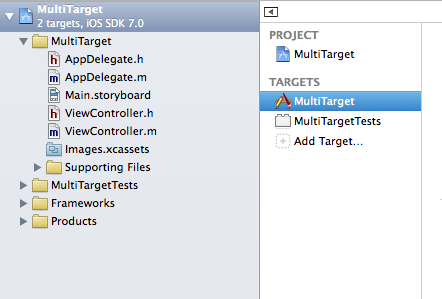
iOS App Development Xcode Adding a new Target
The first step is to duplicate the target like this:
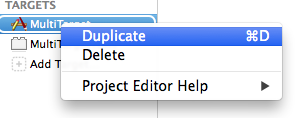
Duplicate target xcode
Change the name of the copy to whatever you want and keep it selected as we need to configure a few things.
Since this is a new app, you probably want a different bundle id for each target. You can do this manually by changing the value Bundle identifier in the Info section of the target, or you can be a bit more flexible by adding a new user defined setting.
This also allows you to have a different bundle id for an app built for Debug or Release.
To do this, select the Build Settings section and go to the Editor menu and select Add User-Defined Setting like this:
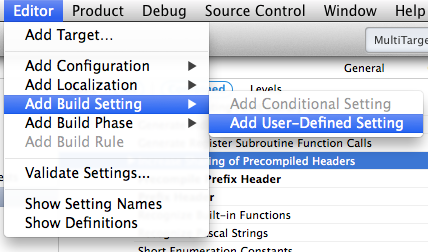
iOS App Development Xcode Using Targets
Give the new user setting a name like APP_BUNDLE_ID and give it a value:

describe the image
And finally tell the Info.plist about this setting and in the Info section change the value of the Bundle identifier to ${APP_BUNDLE_ID}:

bundle identifier xcode
Of course you can add more user settings but remember that to use this setting, you need to use the following syntax: ${YOUR_USER_SETTING}
Note: if your user setting contains spaces you will need to quote it like so: ${“YOUR_USER_SETTING”}
This is useful if your user setting is a path or some string that may contain spaces.
Now if you go to the General section of the target you will see your change reflected:

describe the image
The value here comes from the newly defined user setting and if you’ve defined a different bundle identifier for debug or release, the Bundle identifier here will change too. "Automagically!"
Pretty sweet :) Moving on…
3. Using asset catalogues 使用asset catalogues来添加不同的app icon和launch image
New in Xcode 5 are asset catalogues which are treated as special files in Xcode but are in fact, folders on your hard disk with images inside them.
Not only are asset catalogues great for organizing your image files, but they also tell you if you are missing @2x versions of your images etc…
If you used to previous versions of Xcode, you probably have a resources folder with all your images inside them. Also there are probably some other images outside this folder for your icons and launch images.
So what you need to do is make sure that you are using the asset catalogues first. This is done in the General section of the target. Above the App Icon sub section you have a button that reads: Use Assets Catalogue. Click on it and you’ll have something like this:
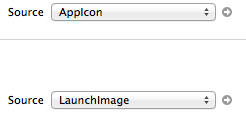
Assets Catalogue
In your files list on the left of the project window you’ll also have a file called “Images.xcassets”. Select it and you’ll see that it opens as a kind of an image organizer:
describe the image
注:点击这个xcassets文件然后进入这个文件,可以看到有appicon和launchimage两个文件,单击任何一个就会现实当前的图片资源。选择添加新的appicon后,可以重新命名,
然后单击项目名称可以浏览当前所有的targets,选择需要配置的target然后在general中查找appicon选项选择不同的文件就可以了。
1,这个必须首先全部都加载上图片资源,否则编译会报错找不到合适的资源
2,这个必须提供尺寸合适的图片资源,如果不合适虽然可以浏览但是编译一样会报上面的错误
3,具体的尺寸可以查看相关文档,
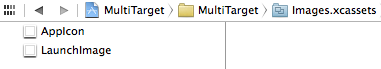
The images you see here are from your first app. So you probably want to add the icons and launch images from the new app.
Select the + button at the bottom and select New App Icon. Repeat to make a New Launch Image.
![]()
new app icon xcode
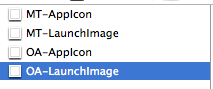
You will want to rename the App Icon and LaunchImage to match the new app name. I did it by adding a prefix to the file name:
launch image
That way you can pick which icons and launch image you want to use for each target. Select them in the General section of the target, as shown here:
![]()
select icons xcode
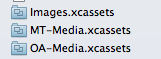
Finally, you will want to use separate asset catalogues for all the images of your app. In my example project I’m using 3 asset catalogues:
- one used by both targets for the app icon and launch image (the Images.xcassets file)
- one used by the MultiTarget target
- one used by the OtherApp target (ie the second app)
separate asset
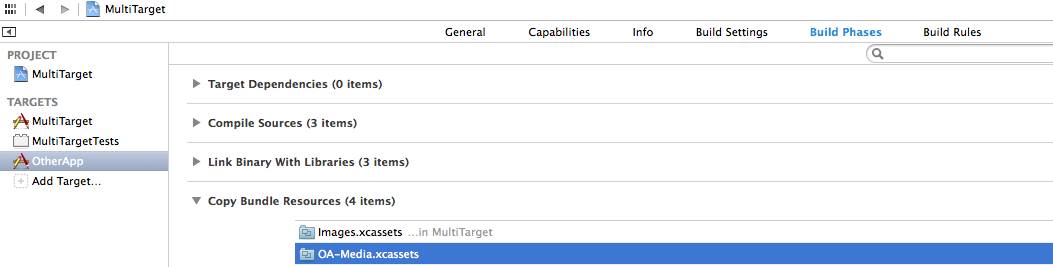
The only thing you need to do is tell each target which asset catalogue you want to use.
You do this in the Build Phases section of the target, under the Copy Bundle Resources subsection:
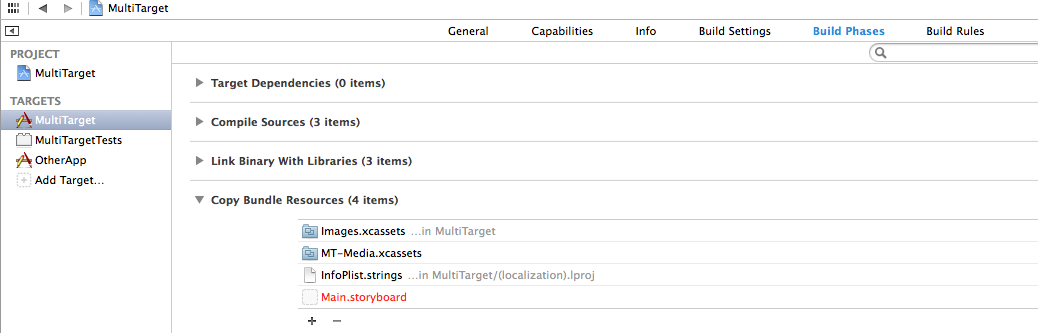
build phase 1 xcode
describe the image
As you can see from the images above, both targets use the same Images.xcassets file (which holds the app icon and launch images). But the MultiTarget target uses the MT-Media.xcassets and the OtherApp target uses the OA-Media.xcassets.
At this point you’ve successfully separated image assets and some configuration settings while using the same code base.
However, just adding a new skin to the new app is probably not the only change you wanted to make. So let’s talk about changing the logic of the app.
4. The same but different
可以设置预编译宏来区分不同的target来在代码中做不同的处理,在target的build settings中选择Apple LLVM 5.1-Preprocessing 然后填写预编译宏名称 然后代码中只要如下:
#ifdef T2
NSLog(@"TestTarget2-Info.plist");
#elif T1
NSLog(@"TestTarget-Info.plist");
#endif
If we had used branches instead of targets, we would probably have to solve merge conflicts at some point. Even in a world with no conflicts at all, maintaining 2 code bases is not an easy task, even if they are similar.
When using targets we can also organize our code in such a way that it would look as if we had 2 similar code bases and still maintain one big code base at the same time.
However, purists might not consider it to be very elegant.
Enter the world of preprocessor macros. Most C-based languages and its compilers support this feature which allows you to use one part of your code depending on the condition that you supply.
For example, suppose you have this method:
- (void)greet {
NSLog@“Welcome to MultiTarget”);
}
No matter which target you select, the method will always show the same text in the log. This is not what you want of course.
So how can we change this method to be different depending on the selected target? You guessed it, with preprocessor macros.
In Xcode you add preprocessor macros in the Build Settings section of the target. Double click on the right of the text “Preprocessor Macros” and a pop up will show up with a list of all your macros. Add a new macro for each target. For instance for MultiTarget, I added the macro MT and for OtherApp I added the macro OA:
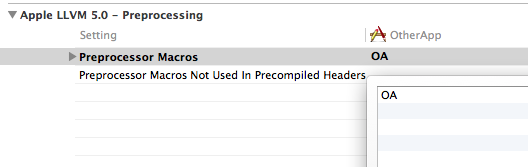
Preprocessor Macros
Now to use these macros, you’ll need to change the code above like this:
- (void)greet {
#ifdef MT
NSLog@“Welcome to MultiTarget”);
#elif OA
NSLog@“Welcome to OtherApp”);
#endif
}
#ifdef simply means “if defined”. In human terms it comes to asking the compiler if the MT or OA macro is available. Since each target has a different macro, one of the 2 macros will always be set (depending on the selected target you used to build the app).
It should be noted that preprocessor macros don’t need to be words alone, they can be something like: DEBUG=1
However, they are used a little differently. In this format you usually are more interested in the value of the macro rather than knowing if the macro is available at all.
So instead of using #ifdef you simply use #if like this:
#if DEBUG == 1
// do something for DEBUG mode
#endif
Please refer to the documentation of the C language for more information on how to use these statements.
5. No more conflicts…
As you can see, the target solution is not that hard to implement and is definitely less messy than if you’d use branches. The process of merging branches specially can be quite hard and could even lead to data loss.
By just separating your assets and adding some statements to select code depending on the target you are able to maintain multiple apps at the same time, so to speak.
And if you use user defined settings and preprocessor macros, you’ll find that this approach is far more flexible than branches.
I hope you can find good use of this tutorial and if you have any questions post them below.
Until next time!
Jesus De Meyer has a Bachelor's degree in Multimedia and Communication Technology from the PIH University in Kortrijk, Belgium. He has 15 years of experience developing software applications for Mac and more than 5 years in iOS mobile app development. He currently works at iTexico as an iOS 7 Mobile App Developer and in his spare time he works on his own mobile apps.
iOS Mobile Development: Using Xcode Targets to Reuse the Code 使用xcode targets来实现代码复用的更多相关文章
- 翻译Beginning iOS 7 Development中文版
不会iOS开发好像真的说只是去,来本中文版的Beginning iOS 7 Development吧. 看了Beginning iOS 7 Development这本书,感觉蛮不错的.全英文的,没有中 ...
- 【转】Xcode概览(Xcode 6版):循序渐进认识Xcode
该系列文章翻译自苹果的Xcode Overview文档,对大部分开发者来说,已经非常熟悉Xcode的功能和特性,不过伴随着iOS 8 SDK的发布,Xcode 6中也有些许调整,所以对该文档进行了翻译 ...
- [iOS] 使用xib做为应用程序入口 with Code
[iOS] 使用xib做为应用程序入口 with Code 前言 开发iOS APP的时候,使用storyboard能够快速并且直觉的建立用户界面.但在多人团队开发的情景中,因为storyboard是 ...
- iOS 个人账号 iOS APP Development 灰色不可选
如图,现在的开发者账号是有几个人共用的,已经 生成了一个Development 的证书,我想再申请一个,出现了这样的情况.网上有说的是申请证书个数到了上限,需要删除已经生成的.因为生成的证书其他人需要 ...
- Launch Google Map in Android / IOS Mobile
<!--This only works in android mobile phone--><a href="geo:0,0?q=myaddress+encode)__&q ...
- iOS开发之--png图片编译时报错 (Command /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/usr/bin/copypng failed with exit code 1 )
编译或者运行APP的时候,老是报这个错误:Command /Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/usr/bin/copypng failed with ...
- 【 Beginning iOS 7 Development《精通iOS7开发》】05 Autorotation and Autosizing
一.旋转后相对位置不变 watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvZ29nbGVy/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0 ...
- iOS 学习笔记 七 (2015.03.29)code snippet操作
1.code snippet 备份路径:~/Library/Developer/Xcode/UserData/CodeSnippets/
- 加快XCode编译链接速度(200%+)—XCode编译慢液
最近在一个大型项目的开发的时候遇到一个很头疼的问题,由于该项目的代码更,每次建立联系1纪要.浪费时间调试.因此,一些研究如何提高编译链接速度,这里给大家分享. 为了提高编译和链接的是以下三种方式的速度 ...
随机推荐
- Linux学习-核心与核心模块
谈完了整个开机的流程,您应该会知道,在整个开机的过程当中,是否能够成功的驱动我们主机的硬 件配备, 是核心 (kernel) 的工作!而核心一般都是压缩文件,因此在使用核心之前,就得要将他解 压缩后, ...
- session工作原理
什么是Sesson? 这个是状态保持三大对象之一! 原意是会话,会议的意思! 就是你打开浏览器到关闭浏览器 这期间称为一个会话,也就是一个session, 它是保存在服务器端的. 每当客户端请求页面时 ...
- Makefile基础(三)
第一章:C语言之Makefile基础(一) 第二章:C语言之Makefile基础(二) 再来看一个简单的例子: [root@localhost linux_c]# cat Makefile foo = ...
- WCF服务编程——数据契约快速入门
WCF序列化流程 序列化 默认用户自定义类型(类和结构)并不支持序列化,因为.NET无法判断对象状态是否需要反射到流. 用户自定义类的实例支持序列化 需要添加[Serialazable].若要允许可序 ...
- python+selenium面试题
selenium中如何判断元素是否存在? selenium中没有提供原生的方法判断元素是否存在,一般我们可以通过定位元素+异常捕获的方式判断. # 判断元素是否存在 try: dr.find_elem ...
- [uiautomator篇][8] 增加应用读取内置存储卡的权限
1 要在androidmainfest.xml增加权限(这样之后,在设备上的权限才可以点击,不然是灰色) <uses-permission android:name="android. ...
- Jupyter Notebook与Jupyterhub的安装与配置
Jupyter Notebook是一个很好用的交互环境,Jupyterhub则在此基础上实现了多用户的管理.最近配置这个环境的时候也遇到了一些坑,想想自己疯狂百度的过程,在此把自己的完整安装配置流程记 ...
- C#拆箱和装箱成本
从原理上可以看出,装箱时,生成的是全新的引用对象,这会有时间损耗,也就是造成效率降低. 文章:.Net常见面试题整理(2)——装箱和拆箱 装箱,产生新的引用对象,并且赋值,然后引用. 拆箱,往往跟随着 ...
- 【转】hibernate映射(单向双向的一对多、多对一以及一对一、多对一)
多对一关联映射:在多的一端加入一个外键指向一的一端,它维护的关系是多指向一 一对多关联映射:在多的一端加入一个外键指向一的一端,它维护的关系是一指向多 也就是说一对多和多对一的映射策略是一样的,只是站 ...
- 基于2.9.6vue-cli初始化webpack工程
前天做了组内的分享 讲了些webpack的东西 整个流程以及build文件夹内webpack相关的一些js所有的代码 每行代码什么意思 有什么作用 都做了很详细的标明. webpack是3.6的 今天 ...
